日本の明治時代 –女のへんせん Japan’s Meiji Era – A Woman’s


日本の明治時代 –女のへんせん Japan’s Meiji Era – A Woman’s Change

Meiji Era The 45 year period where the Meiji Emperor reigned (Oct. 23rd 1868 – July 30th 1912) Meiji Jidai 「明治時代」means Enlightened Rule which references new advances in technology and culture after years of isolation from outside and foreign influences It’s the period of Japan’s major modernization and rising influence/world power The Meiji Era is……
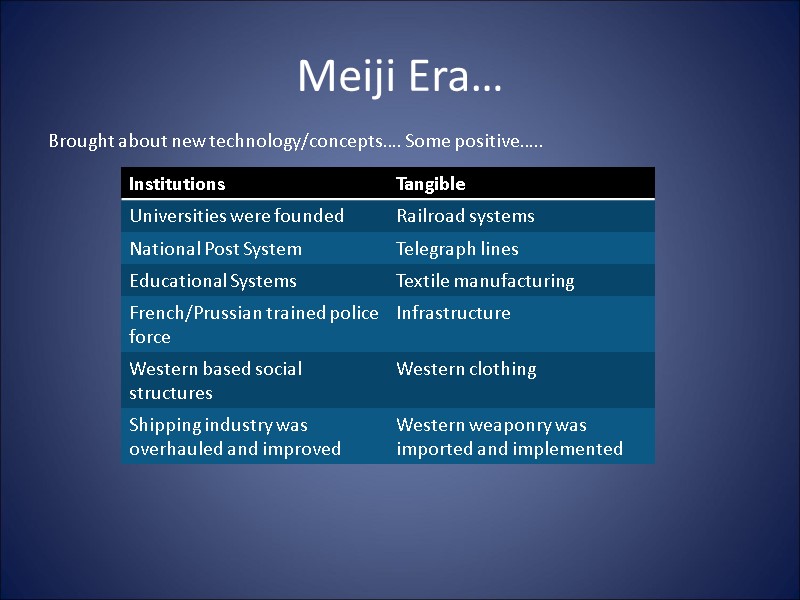
Meiji Era… Brought about new technology/concepts…. Some positive…..

…..And some negative. Meiji Policies Produced some of these: Taxes on farmers increased due to the need for urban development which caused confusion and anger. The bloody tax which demanded mandatory military service Harsh working conditions for lower class citizens General mistrust of Western culture and influences Gender roles were stratified even further

This led to…. In 1871, the Meiji Emperor ordered that Western clothing must be worn by high officials during business hours Women would also follow this trend and wear Western clothing

Japanese Women Would wear Western clothing in public and changing into traditional clothing at home Discovered that Western clothing was not suitable to Japanese living style Dresses were impractical for sitting on tatami flooring Western shoes were hard to use when following the custom of removing shoes in a building And their clothing

Kimono Japanese women would still wear kimono Material would vary in weight, type, and design according to the seasons The cloth was cut into eight pieces The colors and design would describe a complex message system Bright colors: reserved for youth Subtle colors: reserved for more mature

Hair In 1872, the Emperor cut off the topknot and started to grow Western style facial hair Women would often wear Victorian hair styles with traditional kimono or a Western dress

Examples of Meiji Era clothing:
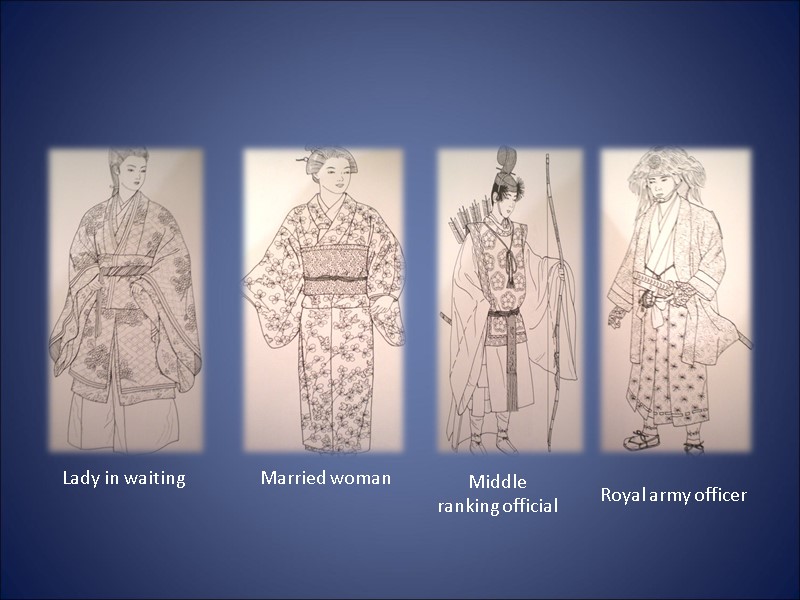
Lady in waiting Married woman Middle ranking official Royal army officer
Gender Roles During the Meiji Era, gender roles were redefined following more Western standards Many were outlined in the Imperial Constitution and other legal documents Women would face harder segregation compared to the Tokugawa Era

Meiji Constitution In 1889, the Imperial Constitution provided the definition of a “family” with father as head of household Polygamy was allowed: one husband, many wives, and all children were considered a single family unit Women, men, and children were segregated into “rigid roles” in the traditional family
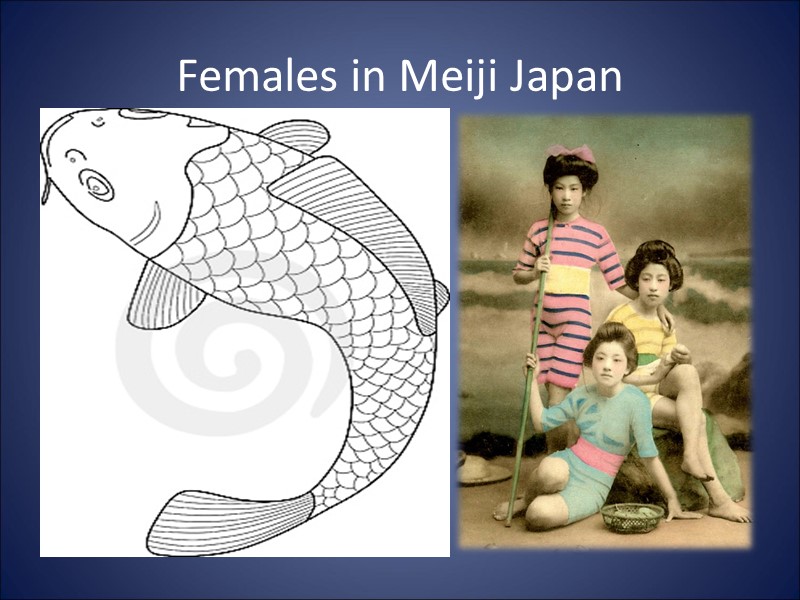
Females in Meiji Japan The Meiji Renovation removed females from government roles and reaffirmed the power of the men Government provided programs educating women on how to be good wives In 1889, females were denied voting rights Women could not join political parties under the Law of Assembly and Political Assembly

An additional problem…. “The role of Japanese women also suffered an image problem of a different kind. Westerners fell in love with the stereotype of a docile, selfless, beautiful, charming and obedient sex, which failed to address the inner lives of Japanese women or their own views on the role they played in society. This kind of willful misunderstanding later followed Japanese immigrants to America and plagued relations between the two countries for a very long period of time.”

Just for fun… Meiji in modern times The Meiji era was the set for the popular manga, Rurouni Kenshin るろうに剣心 Ironically, most of the female cast did not follow the traditional female character and persona that the Meiji government encouraged. There is a shrine in Shibuya, Tokyo that is called the “Meiji Shrine” This was a shrine dedicated to the death of the Emperor Meiji and his wife and they were enshrined in 1920.

And the most well known…. The Last Samurai Took place during the Meiji era in the year 1876 Actor Shichinosuke is credited as playing the Meiji Emperor The movie depicts the similar desire and eagerness of the emperor to import as many Western technologies and practices in order to modernize Japan

In conclusion… Meiji era lead to new technologies and institutions that helped paved a new road for Japan Meiji policy also helped re-shift gender roles and define new boundaries for men and women Legal documentation told a woman what should could do, what she could not do, and what her exact duties were Western influences helped make Japan a more modern country in the Eastern part of Asia Clothing was one major example of a mixture between East and West and reflected in daily behavior and routine
22956-meiji_era._woman's_clothings.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17

