d04ae39ade99c3be46f1bba18daed6a7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33

土壤重金属污染修复空间与主要污染元素的识别 汇报人:张静 时间: 2014 -4 -20

Contents 1 Geo. Detector 原理 2 Geo. Detector 应用 3 Geo. Detector 操作 4 Geo. Detector 实验
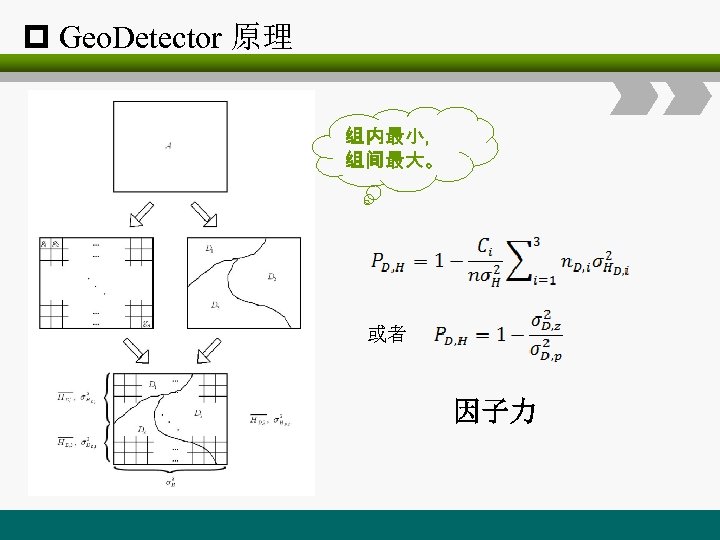
p Geo. Detector 原理 组内最小, 组间最大。 或者 因子力
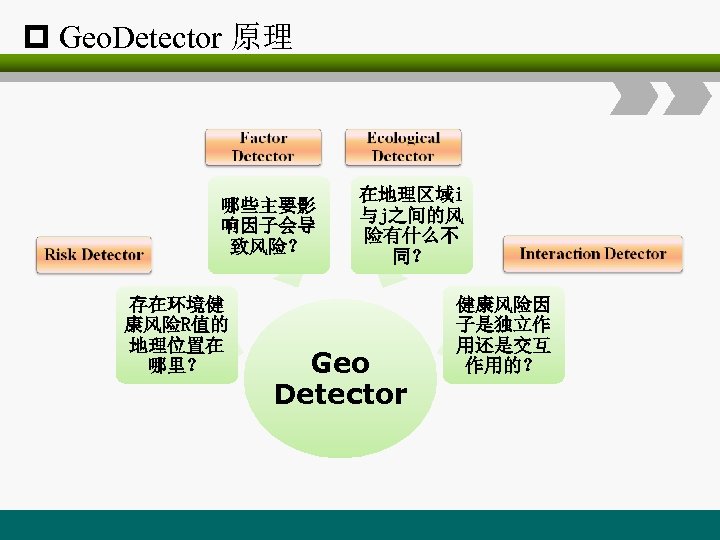
p Geo. Detector 原理 哪些主要影 响因子会导 致风险? 存在环境健 康风险R值的 地理位置在 哪里? 在地理区域i 与j之间的风 险有什么不 同? Geo Detector 健康风险因 子是独立作 用还是交互 作用的?
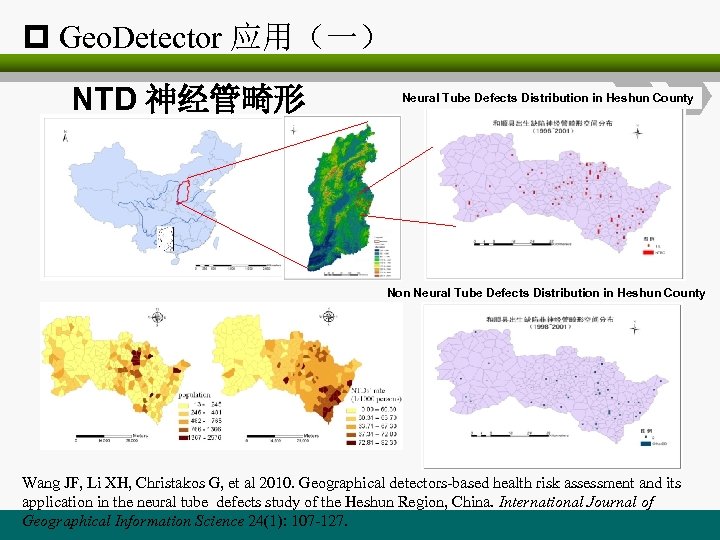
p Geo. Detector 应用(一) NTD 神经管畸形 Neural Tube Defects Distribution in Heshun County Non Neural Tube Defects Distribution in Heshun County Wang JF, Li XH, Christakos G, et al 2010. Geographical detectors-based health risk assessment and its application in the neural tube defects study of the Heshun Region, China. International Journal of Geographical Information Science 24(1): 107 -127.
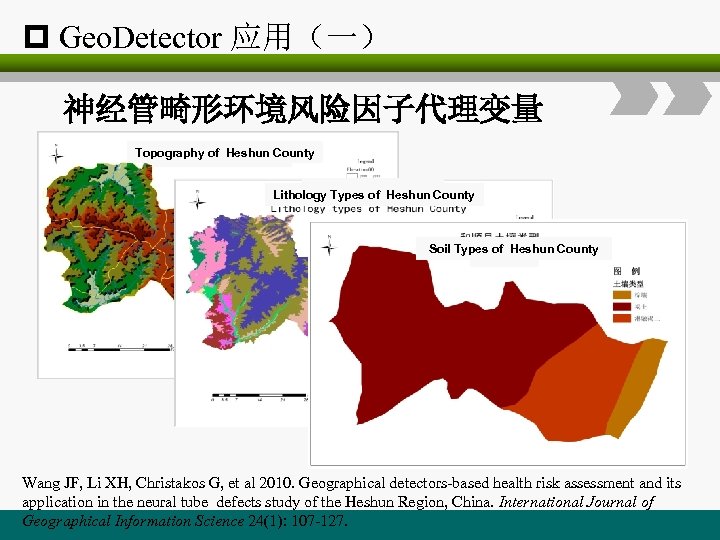
p Geo. Detector 应用(一) 神经管畸形环境风险因子代理变量 Topography of Heshun County Lithology Types of Heshun County Soil Types of Heshun County Wang JF, Li XH, Christakos G, et al 2010. Geographical detectors-based health risk assessment and its application in the neural tube defects study of the Heshun Region, China. International Journal of Geographical Information Science 24(1): 107 -127.
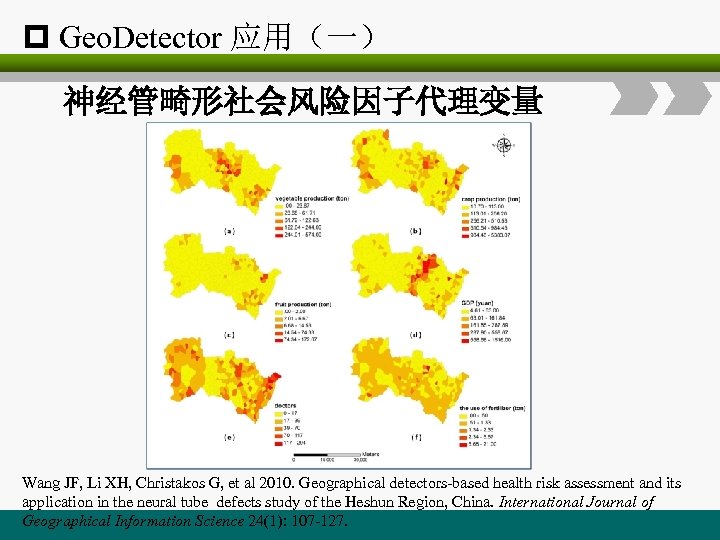
p Geo. Detector 应用(一) 神经管畸形社会风险因子代理变量 Wang JF, Li XH, Christakos G, et al 2010. Geographical detectors-based health risk assessment and its application in the neural tube defects study of the Heshun Region, China. International Journal of Geographical Information Science 24(1): 107 -127.
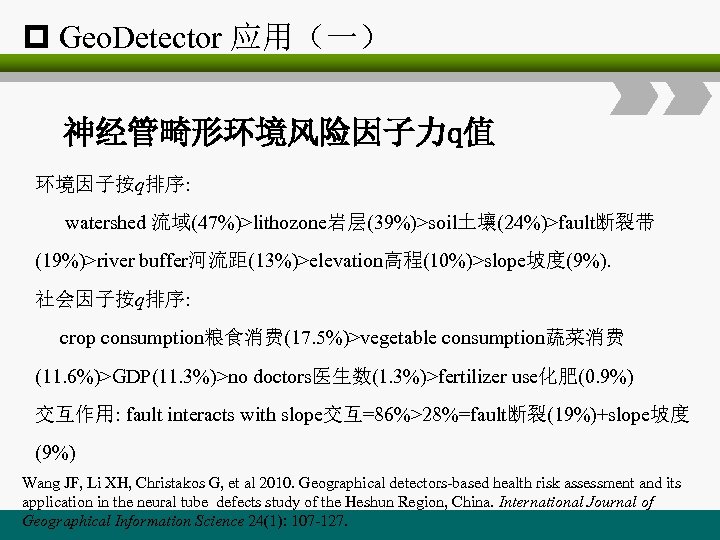
p Geo. Detector 应用(一) 神经管畸形环境风险因子力q值 环境因子按q排序: watershed 流域(47%)>lithozone岩层(39%)>soil土壤(24%)>fault断裂带 (19%)>river buffer河流距(13%)>elevation高程(10%)>slope坡度(9%). 社会因子按q排序: crop consumption粮食消费(17. 5%)>vegetable consumption蔬菜消费 (11. 6%)>GDP(11. 3%)>no doctors医生数(1. 3%)>fertilizer use化肥(0. 9%) 交互作用: fault interacts with slope交互=86%>28%=fault断裂(19%)+slope坡度 (9%) Wang JF, Li XH, Christakos G, et al 2010. Geographical detectors-based health risk assessment and its application in the neural tube defects study of the Heshun Region, China. International Journal of Geographical Information Science 24(1): 107 -127.

p Geo. Detector 应用(一) 神经管畸形结论 u Primary environment 原生环境 (watershed水系, lithozone岩层, and soil土壤) strongly controls the NTD occurrence 强烈地控制了神经管畸形的发生. u Basic nutrition (food) is more important than artificial environment (fertilizer) in controlling the spatial pattern of NTDs. 营养比人为污染(化肥)对NTD影响更大 u Ancient materials released from faults then spreading along slopes dramatically increase the risk of NTDs. 古物质溢出断层与坡度复合增加病险 u These findings have implications in the disease intervene specific in the pilot area 以上发现为研究区神经管畸形防控策略制定提供了科学依据 Wang JF, Li XH, Christakos G, et al 2010. Geographical detectors-based health risk assessment and its application in the neural tube defects study of the Heshun Region, China. International Journal of Geographical Information Science 24(1): 107 -127.

p Geo. Detector 应用(二) Quake Death 地震死亡 Hu Y, Wang JF, Li XH, Zhu J. 2011. Geographical detectors-based risk assessment of the under-five mortality in the 2008 Wenchuan Earthquake, China. PLo. S ONE 6(6): e 21427.

p Geo. Detector 应用(二) Quake Death 地震死亡 地貌 DEM 5岁以下儿童死亡自 然因子 坡度 断层 烈度
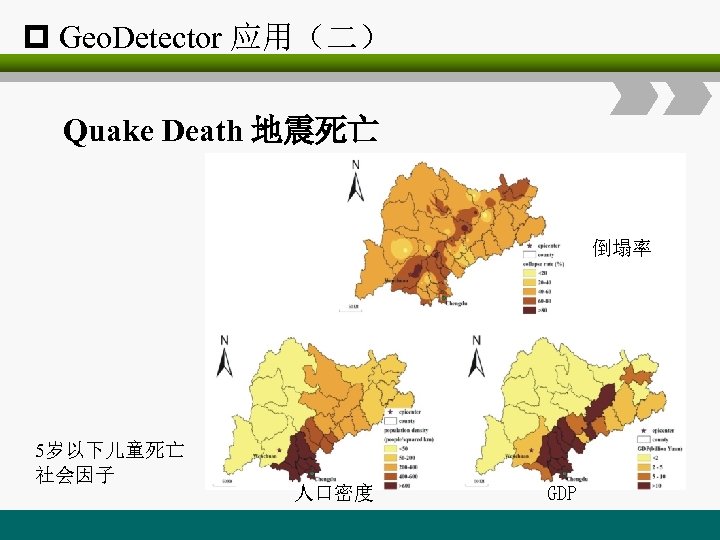
p Geo. Detector 应用(二) Quake Death 地震死亡 倒塌率 5岁以下儿童死亡 社会因子 人口密度 GDP
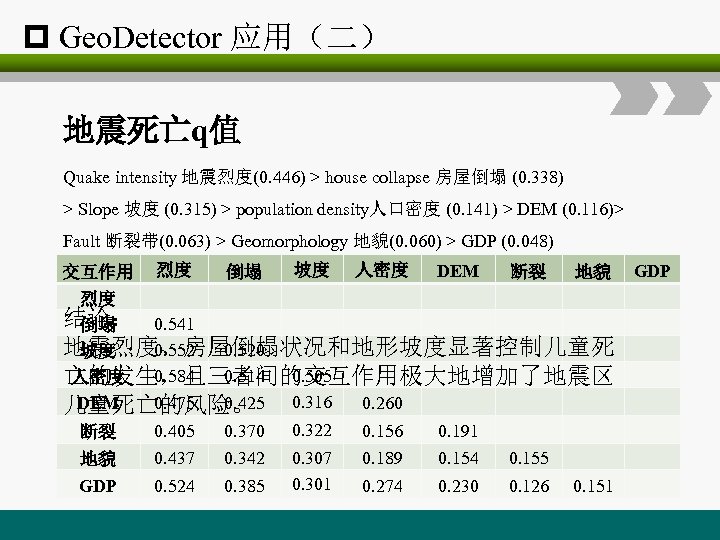
p Geo. Detector 应用(二) 地震死亡q值 Quake intensity 地震烈度(0. 446) > house collapse 房屋倒塌 (0. 338) > Slope 坡度 (0. 315) > population density人口密度 (0. 141) > DEM (0. 116)> Fault 断裂带(0. 063) > Geomorphology 地貌(0. 060) > GDP (0. 048) 交互作用 烈度 倒塌 坡度 人密度 DEM 断裂 地貌 烈度 结论: 0. 541 倒塌 地震烈度、房屋倒塌状况和地形坡度显著控制儿童死 0. 552 0. 520 坡度 0. 584 0. 514 0. 505 人密度 亡的发生,且三者间的交互作用极大地增加了地震区 0. 316 DEM 0. 475 0. 425 0. 260 儿童死亡的风险。 断裂 0. 405 0. 370 0. 322 0. 156 0. 191 地貌 GDP 0. 437 0. 342 0. 189 0. 154 0. 524 0. 385 0. 307 0. 301 0. 155 0. 274 0. 230 0. 126 GDP 0. 151

p Geo. Detector 应用 作者 摘要 结论 王劲峰等 提出“因子力”概念和地理探测器 (Geo. Detector)方法,并采用 空间差异分析方法和地理探测器 对中国和顺区儿童神经管缺陷疾 病与潜在影响因子进行分析 在和顺地区(中国)主要的物理环境(流域, lithozone和土壤)强烈控制神经管缺陷( NTD ) 的发生。在空间NTD模式的控制中基本营养(食物) 比人为污染(化肥)更为重要。从地质断层释放出 古物质,随后沿着坡度使得NTD风险急剧增加。 采用空间差异分析方法和地理探 测器对汶川地震中 5岁以下儿童死 亡率与潜在风险因子之间的关系 进行评估 对汶川地震中 5岁以下儿童死亡率与潜在风险因子 之间的关系进行评估,发现:地震强度,坍塌房屋, 人口密度以及坡度为主要影响因素,且两两因素之 间具有相互作用,交互影响儿童死亡率。 利用时空分析方法和地理探测器 对云南省红塔区伤寒副伤寒流行 率进行分析 降雨季节波动与医院污水通过城市排水与排污合流 渠道发生时空耦合;经济水平与医疗资源的空间分 布发生了显著地交互作用,影响疾病空间分布。 在网格采样的基础上,运用地理 探测器对寿光蔬菜区土壤中抗生 素残留的影响因素进行探测 蔬菜种类的种植决定粪肥的使用量,在很大程度上 影响抗生素的空间分布;据此划分出了高风险污染 区,并提出通过种植区划调整(辅助影响因素调整) 来实现限控的策略。 王劲峰等 李学文等
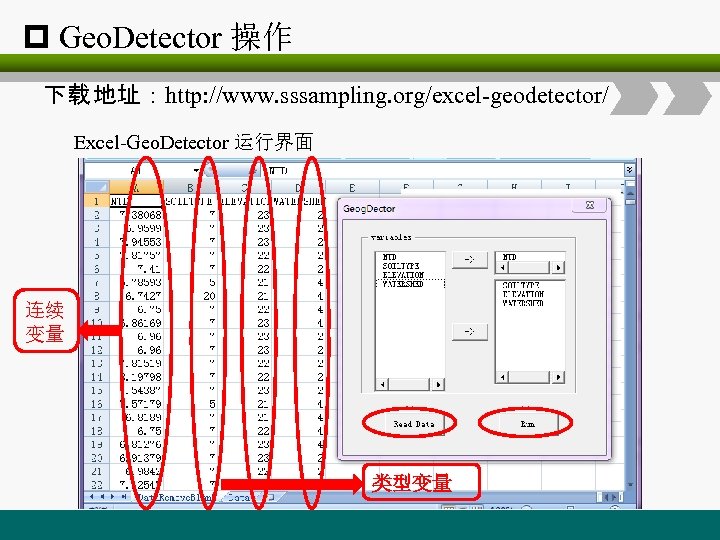
p Geo. Detector 操作 下载 地址:http: //www. sssampling. org/excel-geodetector/ Excel-Geo. Detector 运行界面 连续 变量 类型变量
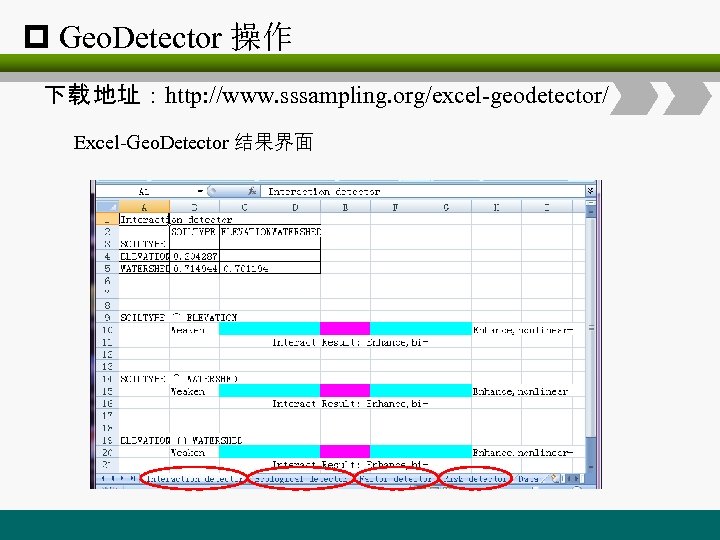
p Geo. Detector 操作 下载 地址:http: //www. sssampling. org/excel-geodetector/ Excel-Geo. Detector 结果界面
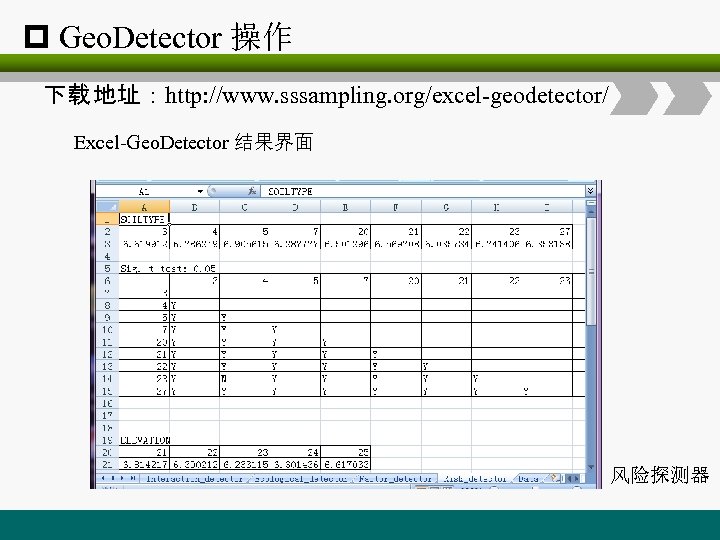
p Geo. Detector 操作 下载 地址:http: //www. sssampling. org/excel-geodetector/ Excel-Geo. Detector 结果界面 风险探测器
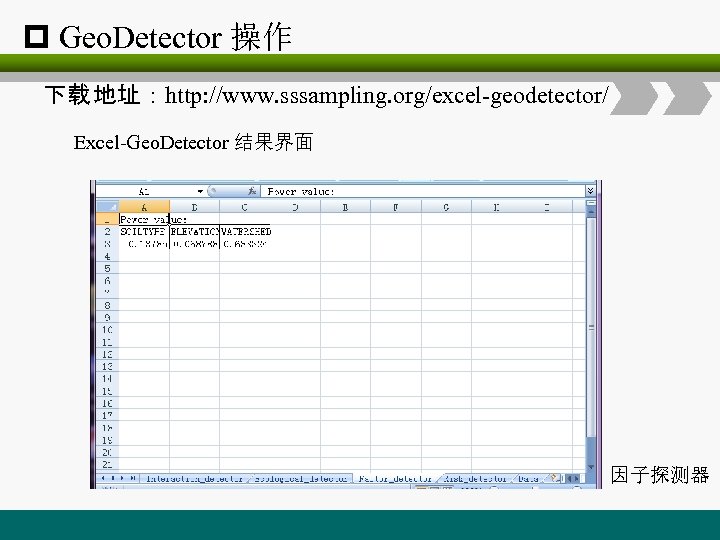
p Geo. Detector 操作 下载 地址:http: //www. sssampling. org/excel-geodetector/ Excel-Geo. Detector 结果界面 因子探测器
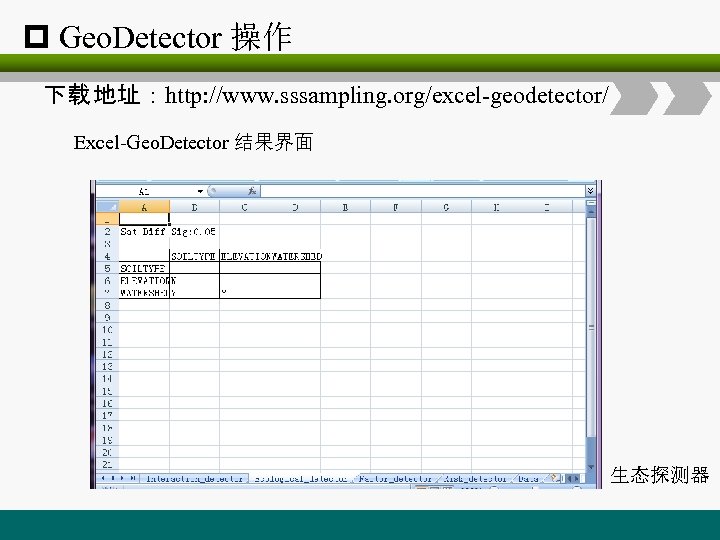
p Geo. Detector 操作 下载 地址:http: //www. sssampling. org/excel-geodetector/ Excel-Geo. Detector 结果界面 生态探测器
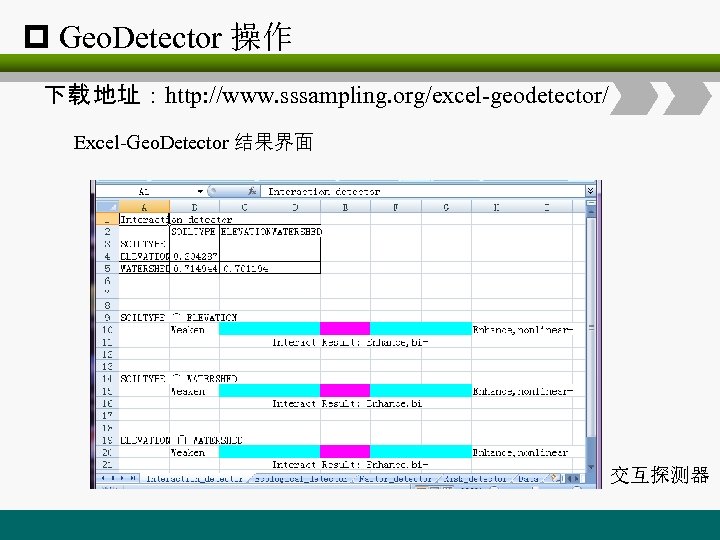
p Geo. Detector 操作 下载 地址:http: //www. sssampling. org/excel-geodetector/ Excel-Geo. Detector 结果界面 交互探测器
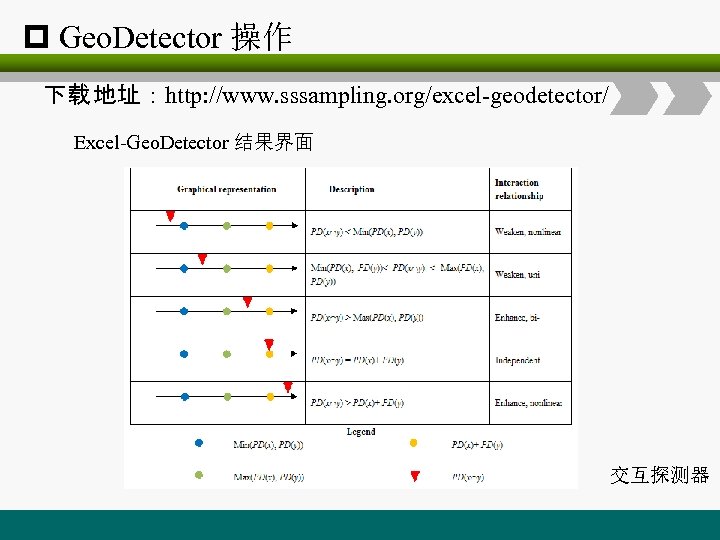
p Geo. Detector 操作 下载 地址:http: //www. sssampling. org/excel-geodetector/ Excel-Geo. Detector 结果界面 交互探测器

p Geo. Detector 操作 下载 地址:http: //www. sssampling. org/excel-geodetector/ Excel-Geo. Detector 结果界面 Enhance 加强 : PD(x y)>PD(x) or PD(x) Enhance, bi- 双加强 : PD(x y)>Max{PD(x), PD(y)} Enhance, nonlinear-非线性加强 : PD(x y)>PD(x) + q(y) Weaken 拮抗 : PD(x y)<PD(x) or q(y) Weaken, uni- 单拮抗 : Min{x, y}<PD(x y)< Max{PD(x), PD(y)} Weaken, nonlinear- 非线性拮抗 : PD(x y)<Min{PD(x), PD(y)} Independent 独立 : PD(x y)=PD(x) + PD(y) 交互探测器
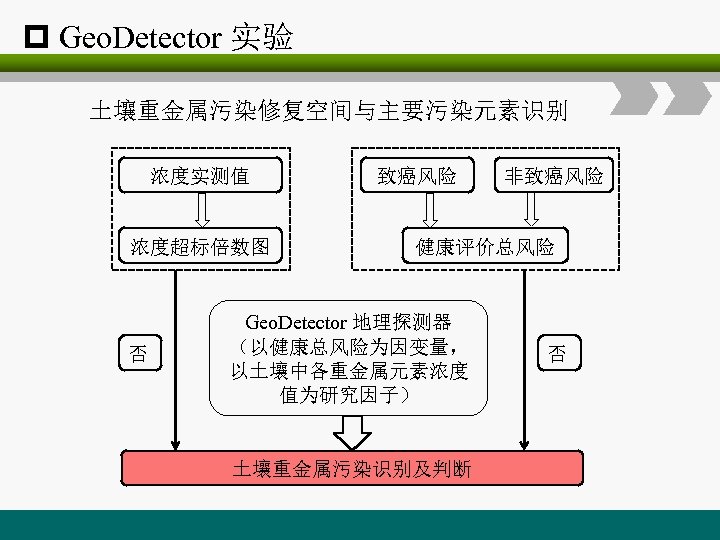
p Geo. Detector 实验 土壤重金属污染修复空间与主要污染元素识别 浓度实测值 浓度超标倍数图 否 致癌风险 非致癌风险 健康评价总风险 Geo. Detector 地理探测器 (以健康总风险为因变量, 以土壤中各重金属元素浓度 值为研究因子) 土壤重金属污染识别及判断 否
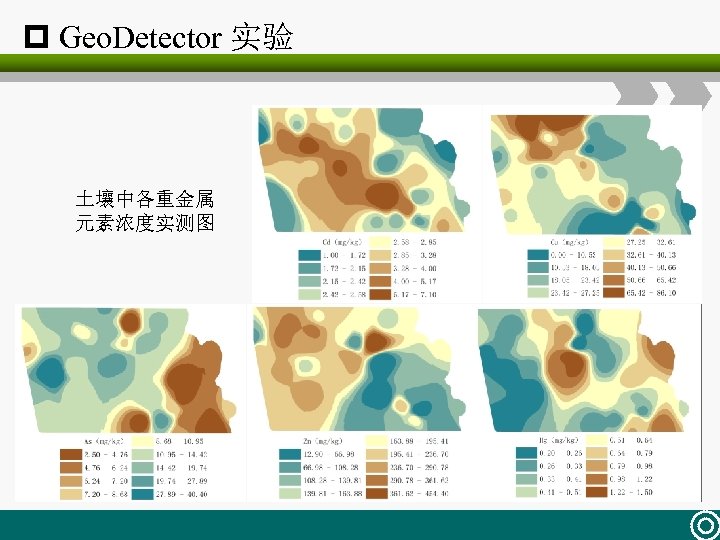
p Geo. Detector 实验 土壤中各重金属 元素浓度实测图
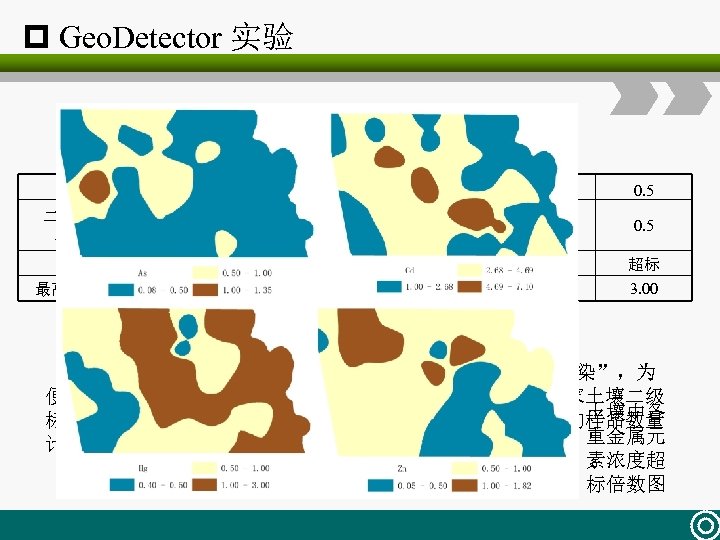
p Geo. Detector 实验 国家土壤二级标准 33 43 2. 5 20. 0 86. 1 218. 4 0. 5 二级标准( mg/kg) 300 0. 3 30 100 250 0. 5 评价 超标 超标 超标 未超标 超标 超标 最高超标倍数 1. 35 23. 67 1. 35 —— 1. 82 3. 00 注: 土壤中重金属元素总量超过二级标准就称为“土壤污染”,为 便于统一比较,以下判定土壤重金属元素是否超标均采用国家土壤二级 土壤中各 标准(农业用地标准)。需要特别说明的是超标率仅以采集的样品数量 重金属元 计算,而不是计算超标面积。 素浓度超 标倍数图
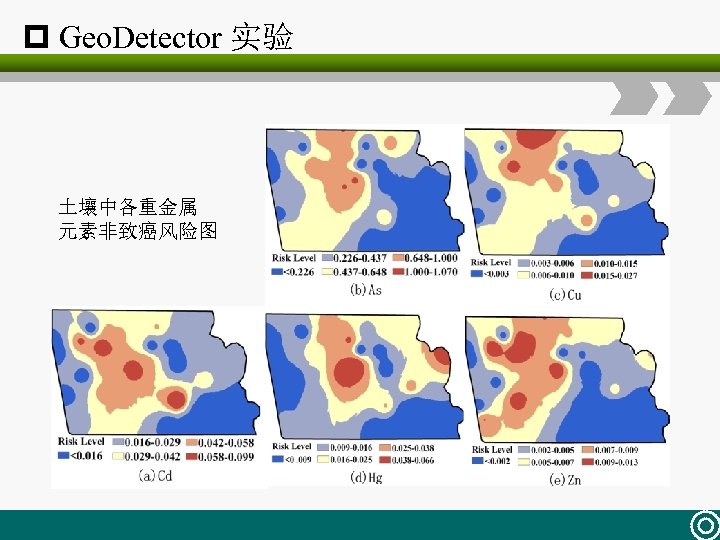
p Geo. Detector 实验 土壤中各重金属 元素非致癌风险图
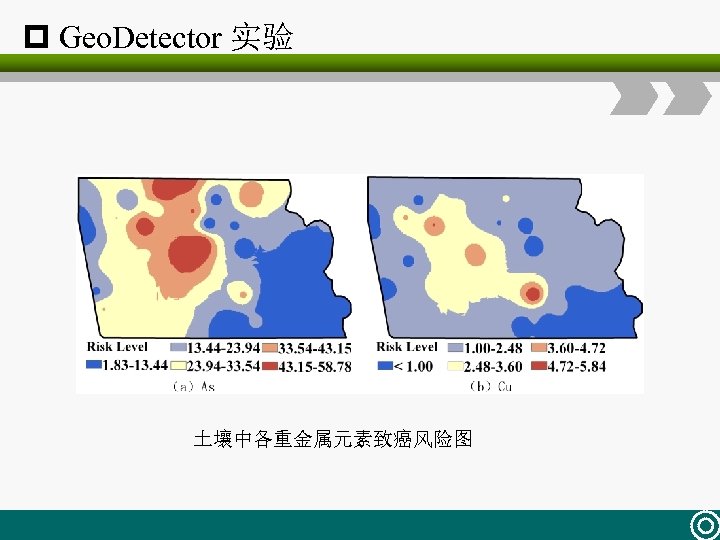
p Geo. Detector 实验 土壤中各重金属元素致癌风险图
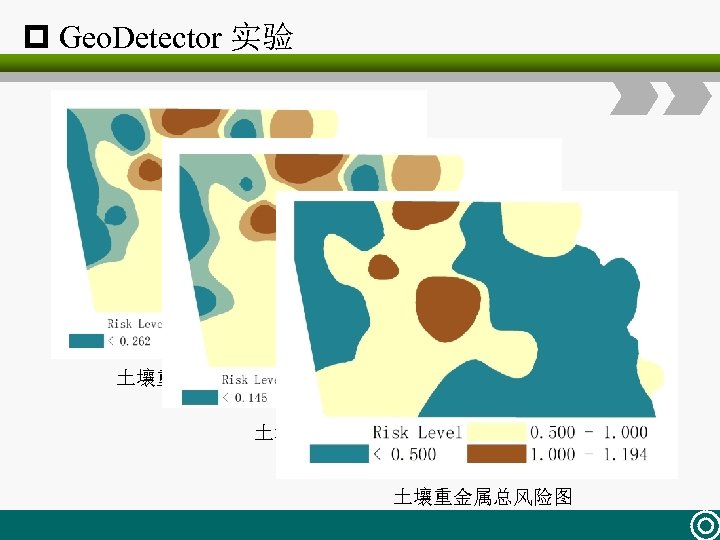
p Geo. Detector 实验 土壤重金属总非致癌风险图 土壤重金属总风险图
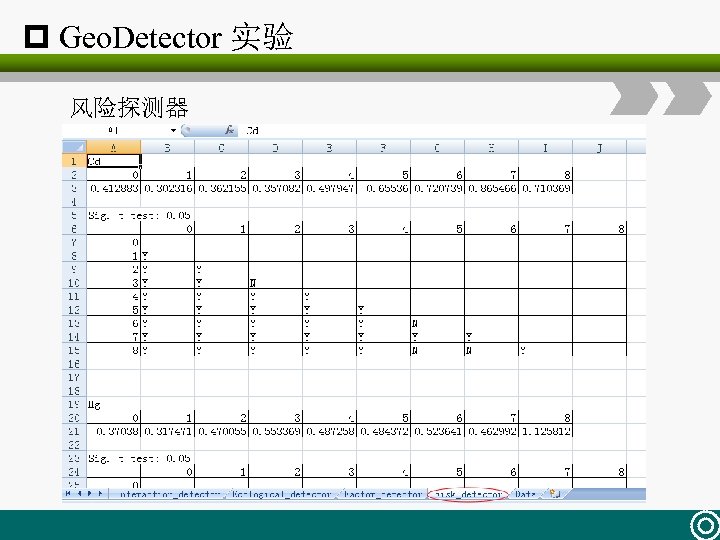
p Geo. Detector 实验 风险探测器
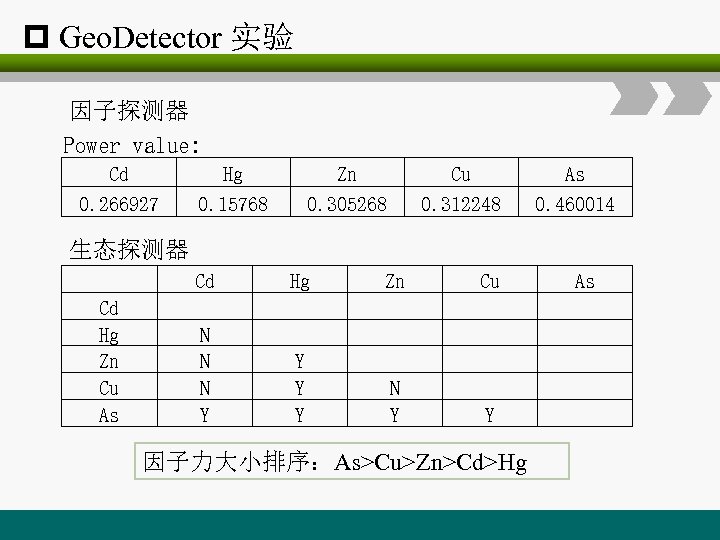
p Geo. Detector 实验 因子探测器 Power value: Cd 0. 266927 Hg 0. 15768 Zn 0. 305268 Cu 0. 312248 As 0. 460014 生态探测器 Cd Hg Zn Cu As Cd N N N Y Hg Y Y Y Zn N Y Cu Y 因子力大小排序:As>Cu>Zn>Cd>Hg As
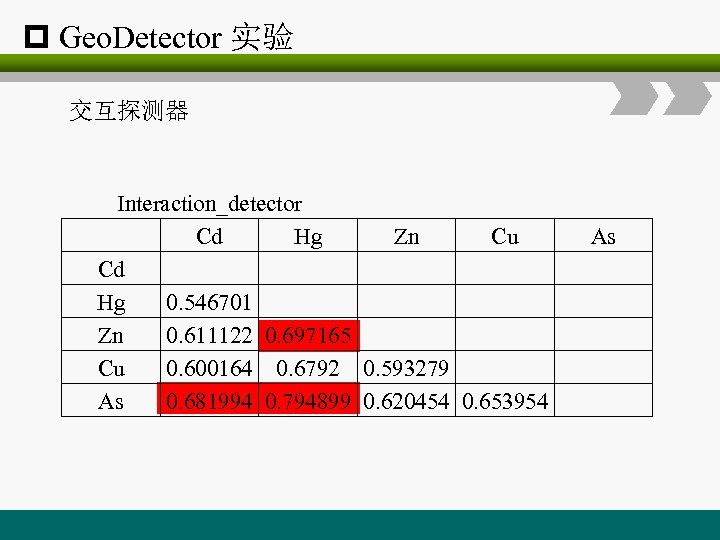
p Geo. Detector 实验 交互探测器 Interaction_detector Cd Hg Zn Cu Cd Hg 0. 546701 Zn 0. 611122 0. 697165 Cu 0. 600164 0. 6792 0. 593279 As 0. 681994 0. 794899 0. 620454 0. 653954 As
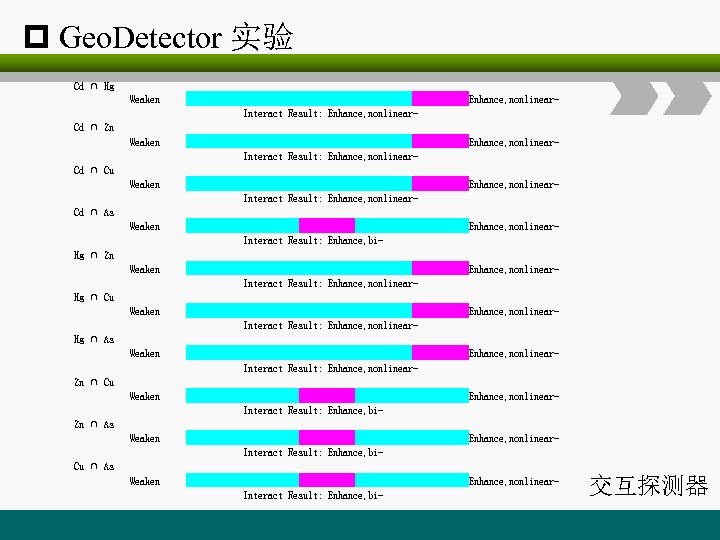
p Geo. Detector 实验 Cd ∩ Hg Weaken Interact Result: Enhance, nonlinear- Enhance, nonlinear- Weaken Interact Result: Enhance, nonlinear- Weaken Interact Result: Enhance, bi- Enhance, nonlinear- Cd ∩ Zn Cd ∩ Cu Cd ∩ As Hg ∩ Zn Hg ∩ Cu Hg ∩ As Zn ∩ Cu Zn ∩ As Cu ∩ As 交互探测器

Thank you! 汇报人:张静 时间: 2014 -4 -20
d04ae39ade99c3be46f1bba18daed6a7.ppt