78850fa5ac13690c329e12e8132dd2bc.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27

ทนทางปญญา Intellectual Capital KM 743 ผศ. ดร. ปตพงษ ยอดมงคล Asst. Prof. Dr. Pitipong Yodmongkol วทยาลยศลปะ สอ และเทคโนโลย มหาวทยาลยเชยงใหม College of Arts Media and Technology, Chiang Mai University

IC INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL
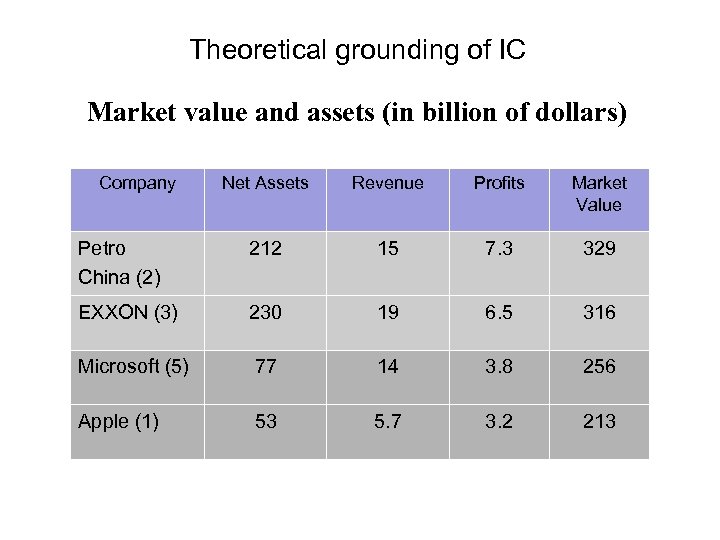
Theoretical grounding of IC Market value and assets (in billion of dollars) Company Net Assets Revenue Profits Market Value Petro China (2) 212 15 7. 3 329 EXXON (3) 230 19 6. 5 316 Microsoft (5) 77 14 3. 8 256 Apple (1) 53 5. 7 3. 2 213
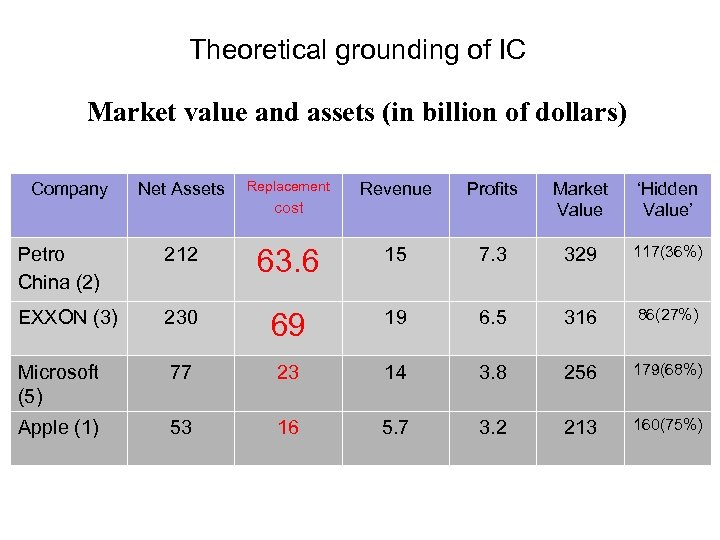
Theoretical grounding of IC Market value and assets (in billion of dollars) Company Net Assets Replacement Revenue Profits Market Value ‘Hidden Value’ 7. 3 329 117(36%) cost Petro China (2) 212 63. 6 15 EXXON (3) 230 69 19 6. 5 316 86(27%) Microsoft (5) 77 23 14 3. 8 256 179(68%) Apple (1) 53 16 5. 7 3. 2 213 160(75%)

The new business world • Microsoft which was the 172 nd place on Fortune 500 list of 1996, became the most valuable company in the world with a very lower number of tangible assets. • In 1999, Microsoft was the most successful shareholder value creating company of any in the US with a MVA (enterprise value less capital employed) of $629. 5 billion. • Apple has became the most valuable company in the world in 2011 with a very lower number of tangible assets (58, XXX MLD) (Fortune Magazine, 1999, Steward, 1997)

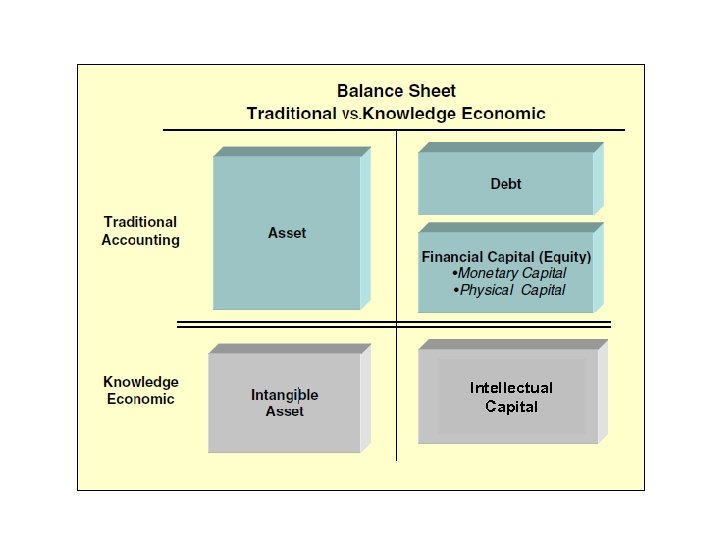
The New Business World • Knowledge Companies – Independent to / MAN / Machine / Money /Material – asset-lite (in the conventional accounting balance sheet sense) – Focus on intellectual asset • The phenomena in new economy meant that managing for shareholder value was much more about managing capital that was not represented as “assets” on the traditional balance sheet; in other words, managing what we now call “intellectual capital”.
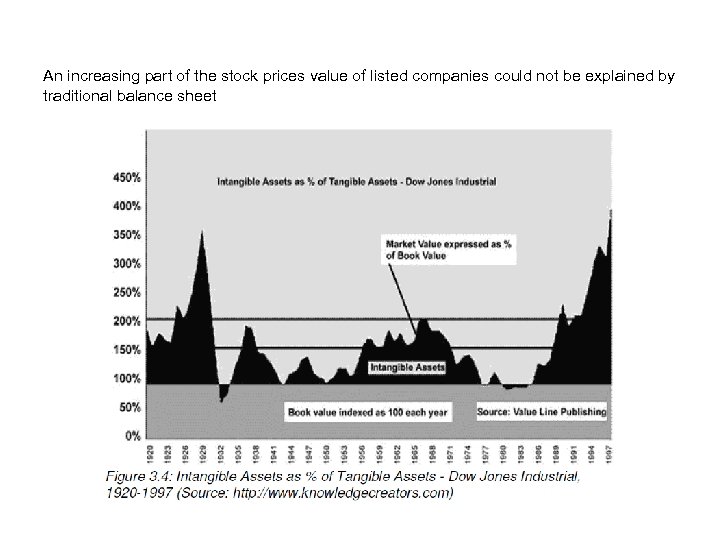
An increasing part of the stock prices value of listed companies could not be explained by traditional balance sheet

The phenomena • The management needs a new framework and tools to assist in identifying, quantifying, managing and reporting on all the capital forms [tangible & intangible] and value creating activities that are causally connected to creating value for stakeholders.

INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL • Intellectual Capital: IC : is a new management concept to the New Economy • Why? – Financial indicators can give misleading signals about knowledge -intensive companies • The maintenance of intangibles can not be treated as investments. • Profitability, or return on capital, is misleading. – The difference of market value - book value – Increasing need for transparency in business report – ICT-infrastructure can be seen as an intelligent way to manage intangible Knowledge, information, data, skill, experience, relation, process etc. , can be managed to create competitive advantages
Intellectual Capital

DEFINING IC

IC • IC belief that the main resources for building competitive advantage are intangible resources the systematic and standardized reporting about intangibles [both internal & external] will lead to better Org. performance

Intellectual Capital • IC is a concept of identifying, measuring and managing intangible assets. Remark: The field is still in its’ embryonic stage - the important of value creation - the important of value extraction - the important of knowledge - the important of IP

Core agreement of IC • IC is about intangibles • IC is the make the difference • IC give structure to Organizational resources – A theory that puts intangibles into the center of wealth creating process [communicate, interpret & control] • IC is about human & non-human resources – Representing a holistic view of the firm [human & non-human] • IC is about interaction between resources – the product of interaction between the different classes of intangibles

Core-elements of Intellectual capital • • • IC is about intangibles. An intangible is something which is “hidden or not-material”, which is “difficult to understand” and which “cannot be known by the senses”, although “it is known to be real” (Longman Dictionary). IC is the make the difference Intellectual capital is a further specification of the resource-based view of the firm. The starting point of this intangible-based view of the firm is that intangibles are the main source of value creation and competitive advantage (Edvinsson & Malone, 1997; Stewart, 1997; Sveiby, 1997). IC gives structure to organizational resources. Recognizing the importance of intangibles is one thing, but translating it into a theory is another. Drucker (1993) “we need a theory that puts knowledge (intangibles) into the centre of the wealth creating process. Intellectual capital makes it possible to communicate, interpret and control intangibles”.
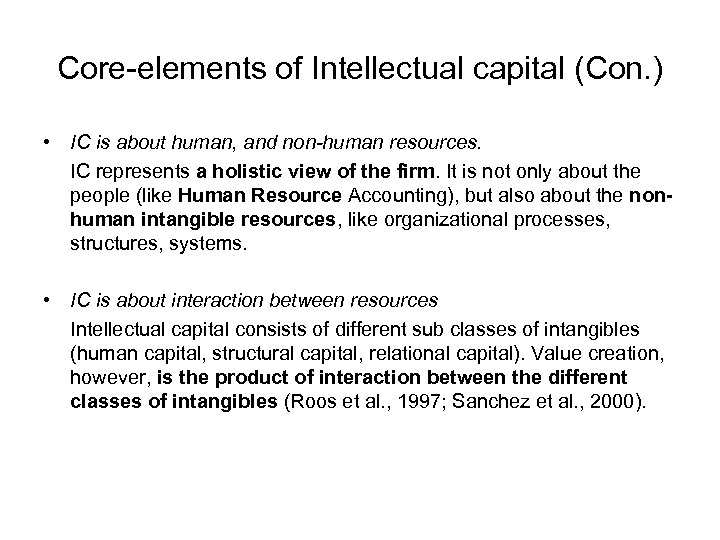
Core-elements of Intellectual capital (Con. ) • IC is about human, and non-human resources. IC represents a holistic view of the firm. It is not only about the people (like Human Resource Accounting), but also about the nonhuman intangible resources, like organizational processes, structures, systems. • IC is about interaction between resources Intellectual capital consists of different sub classes of intangibles (human capital, structural capital, relational capital). Value creation, however, is the product of interaction between the different classes of intangibles (Roos et al. , 1997; Sanchez et al. , 2000).

IC • Intellectual => Human mild – people, knowledge, skill, process, relationship, system …. . • Capital => Financial wealth – Intangible assets owns by Org in monetary terms Intellectual goes beyond the brain and capital goes beyond finance.

IC: the main qualifying characteristic • whether the resource is available or not • Does the company have access to it in order to realize its strategic goals? • IC is about strategic intangible resources [to manage IC, Org. must has strategy: contribute to the creation of Org. value and the achievement of Org goals]

The system of managing IC must be rooted in the strategy or mission of the company Intellectual capital refers to intangibles that are of strategic value to the company Intellectual capital: all intangible resources that are available to an organization, that give a relative advantage, and which in combination are able to produce future benefits.
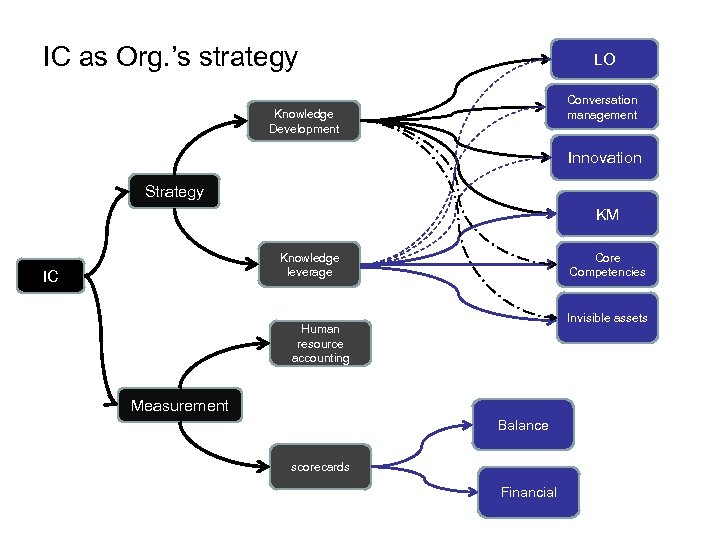
IC as Org. ’s strategy LO Conversation management Knowledge Development Innovation Strategy KM Knowledge leverage IC Core Competencies Invisible assets Human resource accounting Measurement Balance scorecards Financial
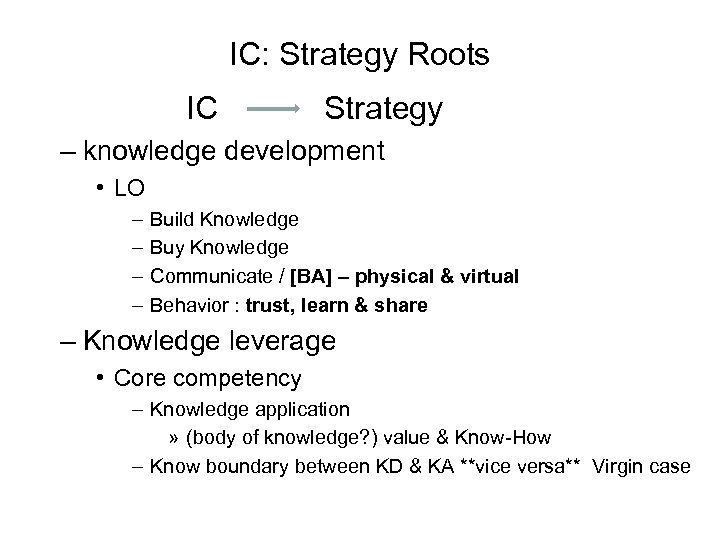
IC: Strategy Roots IC Strategy – knowledge development • LO – – Build Knowledge Buy Knowledge Communicate / [BA] – physical & virtual Behavior : trust, learn & share – Knowledge leverage • Core competency – Knowledge application » (body of knowledge? ) value & Know-How – Know boundary between KD & KA **vice versa** Virgin case


Intellectual Capital • Intellectual Capital (IC) includes of intangible resources that contribute to the creation of value for the organization. – – – knowledge, competence and skills of people, processes and work systems, the culture that supports the people, the image in the market place (brand, trademark) relationships with customers, alliance partners and suppliers – IP
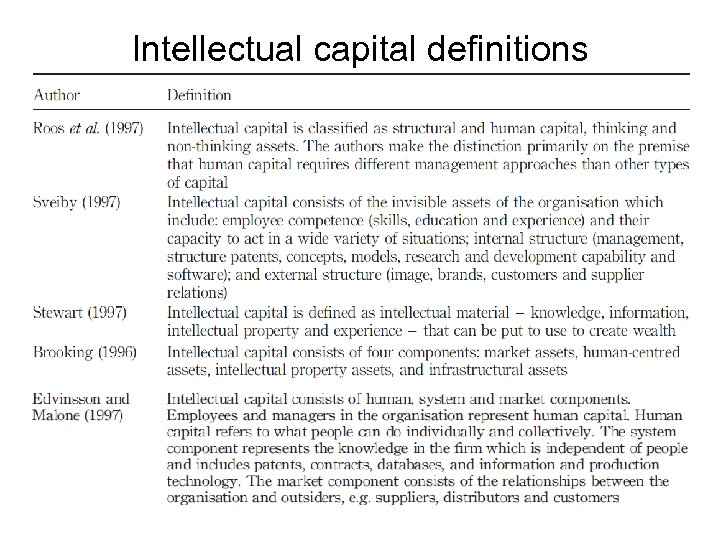
Intellectual capital definitions
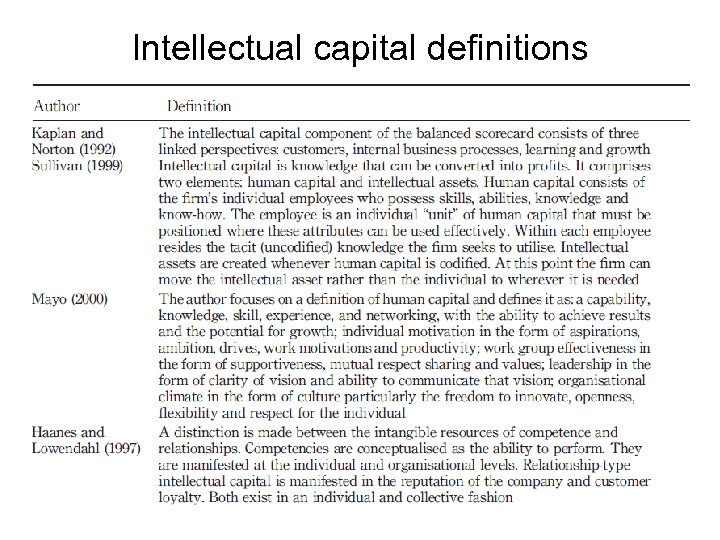
Intellectual capital definitions

Intellectual capital definitions
78850fa5ac13690c329e12e8132dd2bc.ppt