Word-formation: morphological structure and its analysis Lecture 7.










41298-lecture_5._word-formation.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 11
 Word-formation: morphological structure and its analysis Lecture 7.
Word-formation: morphological structure and its analysis Lecture 7.
 § 1. The grammar of lexicon When a word first comes into existence it is built out according to the existing patterns of the elements available in the language. Word-formation is that branch of lexicology that studies the derivative structure of existing words and the patterns on which a language builds new words. Words can be divided into smaller sense units which are generally referred to as morphemes (Greek morphe 'form' + -erne ‘the smallest distinctive unit').
§ 1. The grammar of lexicon When a word first comes into existence it is built out according to the existing patterns of the elements available in the language. Word-formation is that branch of lexicology that studies the derivative structure of existing words and the patterns on which a language builds new words. Words can be divided into smaller sense units which are generally referred to as morphemes (Greek morphe 'form' + -erne ‘the smallest distinctive unit').
 § 2. Morpheme, allomorph Morphemes are the smallest indivisible two-facet language units not independent (used as parts of words) minimum meaningful language unit (indivisible into smaller meaningful units) abstract meaning Allomorphs (from Greek altos 'other') is a positional variant of that or this morpheme occurring in a specific environment. Ex. im- occurs before bilabials (impossible), ir- before r (irregular), il- before I (illegal), in- before all other consonants and vowels (indirect, inability) Ex. [iz] in dishes, [z] in dreams and [s] in books
§ 2. Morpheme, allomorph Morphemes are the smallest indivisible two-facet language units not independent (used as parts of words) minimum meaningful language unit (indivisible into smaller meaningful units) abstract meaning Allomorphs (from Greek altos 'other') is a positional variant of that or this morpheme occurring in a specific environment. Ex. im- occurs before bilabials (impossible), ir- before r (irregular), il- before I (illegal), in- before all other consonants and vowels (indirect, inability) Ex. [iz] in dishes, [z] in dreams and [s] in books
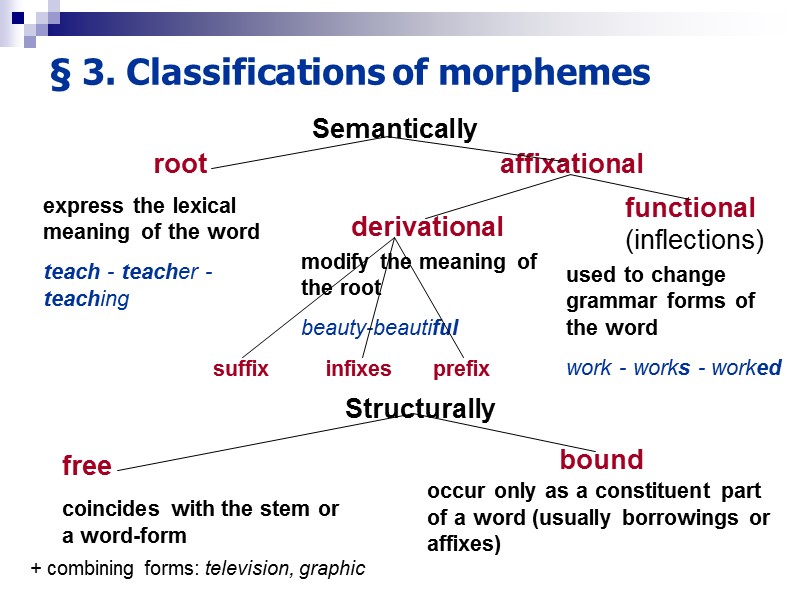
 § 3. Classifications of morphemes Semantically root affixational express the lexical meaning of the word teach - teacher - teaching derivational functional (inflections) modify the meaning of the root beauty-beautiful used to change grammar forms of the word work - works - worked Structurally free coincides with the stem or a word-form bound occur only as a constituent part of a word (usually borrowings or affixes) suffix prefix infixes + combining forms: television, graphic
§ 3. Classifications of morphemes Semantically root affixational express the lexical meaning of the word teach - teacher - teaching derivational functional (inflections) modify the meaning of the root beauty-beautiful used to change grammar forms of the word work - works - worked Structurally free coincides with the stem or a word-form bound occur only as a constituent part of a word (usually borrowings or affixes) suffix prefix infixes + combining forms: television, graphic
 § 4. Morphological types of words simple (root) words - one root morpheme and an inflexion (boy, warm, law, tables, tenth); derived words - one root morpheme, one or several affixes and an inflexion (unmanageable, lawful); compound words - two or more root morphemes and an inflexion (boyfriend, outlaw); compound-derivatives and derivative compounds - two or more root morphemes, one or more affixes and an inflexion (left-handed, warm-hearted, blue-eyed).
§ 4. Morphological types of words simple (root) words - one root morpheme and an inflexion (boy, warm, law, tables, tenth); derived words - one root morpheme, one or several affixes and an inflexion (unmanageable, lawful); compound words - two or more root morphemes and an inflexion (boyfriend, outlaw); compound-derivatives and derivative compounds - two or more root morphemes, one or more affixes and an inflexion (left-handed, warm-hearted, blue-eyed).
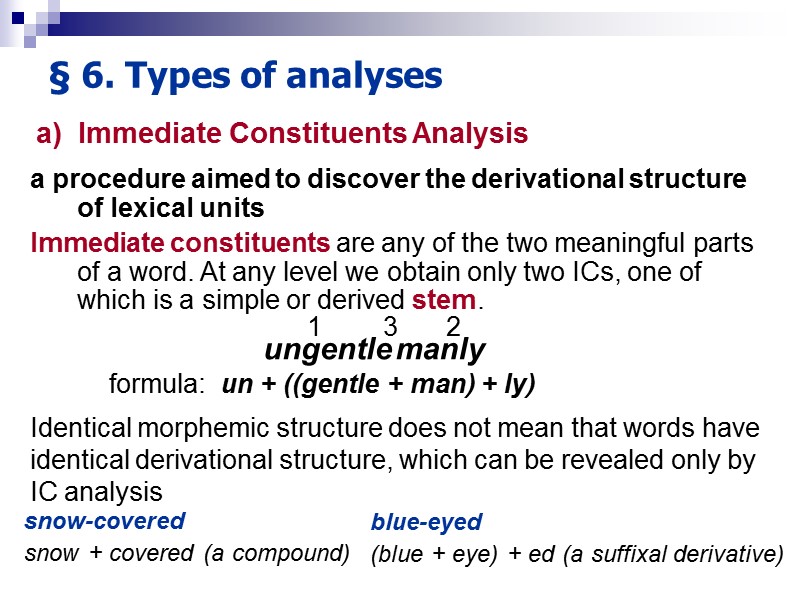
 § 6. Types of analyses a procedure aimed to discover the derivational structure of lexical units Immediate constituents are any of the two meaningful parts of a word. At any level we obtain only two ICs, one of which is a simple or derived stem. formula: un + ((gentle + man) + ly) 2 3 un gentle man ly Identical morphemic structure does not mean that words have identical derivational structure, which can be revealed only by IC analysis snow-covered snow + covered (a compound) blue-eyed (blue + eye) + ed (a suffixal derivative) a) Immediate Constituents Analysis 1
§ 6. Types of analyses a procedure aimed to discover the derivational structure of lexical units Immediate constituents are any of the two meaningful parts of a word. At any level we obtain only two ICs, one of which is a simple or derived stem. formula: un + ((gentle + man) + ly) 2 3 un gentle man ly Identical morphemic structure does not mean that words have identical derivational structure, which can be revealed only by IC analysis snow-covered snow + covered (a compound) blue-eyed (blue + eye) + ed (a suffixal derivative) a) Immediate Constituents Analysis 1
 b) Structural Word-formation Analysis studies the structural correlation with other words, the structural patterns or rules on which words are built girl :: girlish = child :: childish = spinster :: spinsterish c) Mоrphemiс Analysis states the number and type of morphemes that make up the word
b) Structural Word-formation Analysis studies the structural correlation with other words, the structural patterns or rules on which words are built girl :: girlish = child :: childish = spinster :: spinsterish c) Mоrphemiс Analysis states the number and type of morphemes that make up the word
 He gave me the heartiest welcome ever Simple, free, nominal stem coinciding with the root Functional morpheme with the meaning of superlative degree of comparison An allomorph of the morpheme –y, which is a denominal, adjective-forming, bound, derivational morpheme He greeted me cordially Derived, free, adjectival stem De-adjectival, adverb-forming, bound, derivational morpheme Simple, bound, nominal stem = root morpheme De-nominal, adjective-forming, bound, derivational morpheme
He gave me the heartiest welcome ever Simple, free, nominal stem coinciding with the root Functional morpheme with the meaning of superlative degree of comparison An allomorph of the morpheme –y, which is a denominal, adjective-forming, bound, derivational morpheme He greeted me cordially Derived, free, adjectival stem De-adjectival, adverb-forming, bound, derivational morpheme Simple, bound, nominal stem = root morpheme De-nominal, adjective-forming, bound, derivational morpheme
 § 5. Types of word-formation Main types Derivation Composition Conversion Minor types Shortening Abbreviation, acronymy Blending Sound interchange Sound imitation Distinctive stress Back-formation
§ 5. Types of word-formation Main types Derivation Composition Conversion Minor types Shortening Abbreviation, acronymy Blending Sound interchange Sound imitation Distinctive stress Back-formation
 Practical task # 5 1. What term describes the morphemes highlighted in each pair of words: assistance, reference unbearable, audible Homonyms Allomorphs Synonyms
Practical task # 5 1. What term describes the morphemes highlighted in each pair of words: assistance, reference unbearable, audible Homonyms Allomorphs Synonyms
 2. Give a TRUE or FALSE answer: Functional morphemes are used to modify lexical meaning of words. Immediate constituents analysis shows how the word was formed. Stems always coincide with foot morphemes.
2. Give a TRUE or FALSE answer: Functional morphemes are used to modify lexical meaning of words. Immediate constituents analysis shows how the word was formed. Stems always coincide with foot morphemes.

