f6a5e1b5956885e13c285e6d7a88cb71.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42
 WHO and its activities in quality assurance of medicines Sabine Kopp, Ph. D Quality Assurance and Safety: Medicines Essential Drugs and Medicines Policy World Health Organization
WHO and its activities in quality assurance of medicines Sabine Kopp, Ph. D Quality Assurance and Safety: Medicines Essential Drugs and Medicines Policy World Health Organization
 n 1. What is WHO? n 2. How does WHO work and for whom? n 3. Details on WHO activities in the areas of quality assurance, including: ä ä ä n 4. Summary SK 2003 2 - INN - Int. Ph. -GMP -Stability -pre-qualification project. . . WHO - EDM
n 1. What is WHO? n 2. How does WHO work and for whom? n 3. Details on WHO activities in the areas of quality assurance, including: ä ä ä n 4. Summary SK 2003 2 - INN - Int. Ph. -GMP -Stability -pre-qualification project. . . WHO - EDM
 1. What is WHO? Some basic facts n 192 Member States Two governing bodies: n WHO Secretariat: n SK 2003 3 - World Health Assembly - Executive Board - HQ - six Regional Offices - WHO Expert Panels (e. g. . . on the International Pharmacopoeia and Pharmaceutical Preparations) Constitution 1946, in force since 7 April 1948 (World Health Day) WHO - EDM
1. What is WHO? Some basic facts n 192 Member States Two governing bodies: n WHO Secretariat: n SK 2003 3 - World Health Assembly - Executive Board - HQ - six Regional Offices - WHO Expert Panels (e. g. . . on the International Pharmacopoeia and Pharmaceutical Preparations) Constitution 1946, in force since 7 April 1948 (World Health Day) WHO - EDM
 2. How does WHO work and for whom? n WHO’s main functions: n - To act as the directing and coordinating authority on international health work n - To encourage technical cooperation for health with Member States SK 2003 4 inter alia WHO - EDM
2. How does WHO work and for whom? n WHO’s main functions: n - To act as the directing and coordinating authority on international health work n - To encourage technical cooperation for health with Member States SK 2003 4 inter alia WHO - EDM
 --> WHO responsibilities (inter alia) n To assist governments, upon request, in strengthening health services n To provide information, counsel and assist in the field of health To stimulate eradication of epidemics, endemics and other diseases To promote cooperation among scientific and professional groups which contribute to the enhancement of health To promote international conventions and agreements in health matters To promote and conduct research in the field of health To develop, establish and promote international standards for food, biological and pharmaceutical products. . . . n n n SK 2003 5 WHO - EDM
--> WHO responsibilities (inter alia) n To assist governments, upon request, in strengthening health services n To provide information, counsel and assist in the field of health To stimulate eradication of epidemics, endemics and other diseases To promote cooperation among scientific and professional groups which contribute to the enhancement of health To promote international conventions and agreements in health matters To promote and conduct research in the field of health To develop, establish and promote international standards for food, biological and pharmaceutical products. . . . n n n SK 2003 5 WHO - EDM
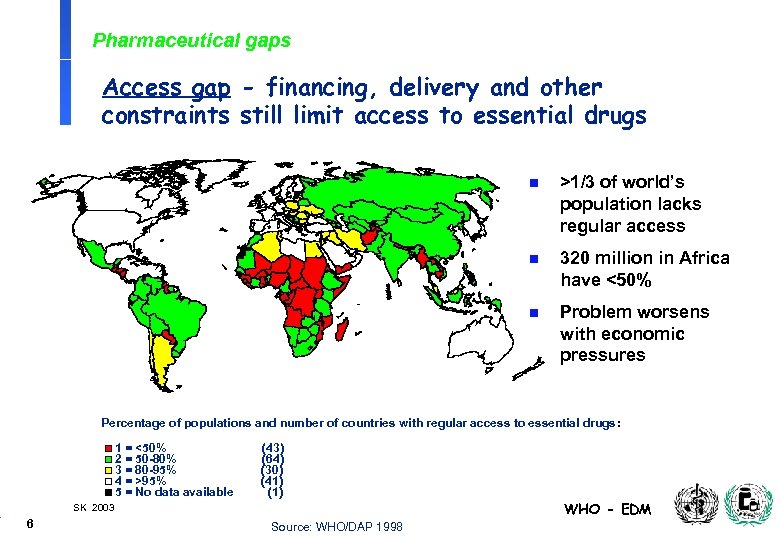 Pharmaceutical gaps Access gap - financing, delivery and other constraints still limit access to essential drugs n >1/3 of world’s population lacks regular access n 320 million in Africa have <50% n Problem worsens with economic pressures Percentage of populations and number of countries with regular access to essential drugs: 1 = <50% 2 = 50 -80% 3 = 80 -95% 4 = >95% 5 = No data available (43) (64) (30) (41) (1) WHO - EDM SK 2003 6 Source: WHO/DAP 1998
Pharmaceutical gaps Access gap - financing, delivery and other constraints still limit access to essential drugs n >1/3 of world’s population lacks regular access n 320 million in Africa have <50% n Problem worsens with economic pressures Percentage of populations and number of countries with regular access to essential drugs: 1 = <50% 2 = 50 -80% 3 = 80 -95% 4 = >95% 5 = No data available (43) (64) (30) (41) (1) WHO - EDM SK 2003 6 Source: WHO/DAP 1998
 WHO medicine strategy What are the priorities for WHO’s medicines strategy? n Access to essential drugs ä ä n Quality and safety of all medicines ä ä n ä ä 7 by health professionals by households National drug policies ä SK 2003 creating and maintaining global guidelines and standards supporting effective drug regulation & quality assurance Rational use of medicines ä n for priority health problems (malaria, TB, childhood, HIV/AIDS) for poor and vulnerable populations integrated in national health policies and systems emphasis on implementation and monitoring WHO - EDM
WHO medicine strategy What are the priorities for WHO’s medicines strategy? n Access to essential drugs ä ä n Quality and safety of all medicines ä ä n ä ä 7 by health professionals by households National drug policies ä SK 2003 creating and maintaining global guidelines and standards supporting effective drug regulation & quality assurance Rational use of medicines ä n for priority health problems (malaria, TB, childhood, HIV/AIDS) for poor and vulnerable populations integrated in national health policies and systems emphasis on implementation and monitoring WHO - EDM
 WHO medicine strategy What guides and anchors WHO’s work in drugs and medicines policy? n Global norms, standards, guidelines, nomenclature ä ä n Essential drugs and national drug policies ä ä n 1975 resolution introducing essential drugs concept Revised drug strategy (1986) and subsequent WHA resolutions WHO medicines work today ä ä ä SK 2003 8 Expert Committees and Expert Panels WHO Collaborating Centres Governing bodies - Assembly, Executive Board, Regional Committees Meeting of Interested Parties - MIP --> changes as from 21 July 2003 WHO - EDM
WHO medicine strategy What guides and anchors WHO’s work in drugs and medicines policy? n Global norms, standards, guidelines, nomenclature ä ä n Essential drugs and national drug policies ä ä n 1975 resolution introducing essential drugs concept Revised drug strategy (1986) and subsequent WHA resolutions WHO medicines work today ä ä ä SK 2003 8 Expert Committees and Expert Panels WHO Collaborating Centres Governing bodies - Assembly, Executive Board, Regional Committees Meeting of Interested Parties - MIP --> changes as from 21 July 2003 WHO - EDM
 Challenges: past and present… n Past: ä Manufacture direct from API -> finished product ä Manufacture of API in sites close to or same as product ä Experience and long-standing knowledge of production, product and manufacture of parties involved ä Few intermediates in sales chain ä Usually stable trade and sales connections SK 2003 9 WHO - EDM
Challenges: past and present… n Past: ä Manufacture direct from API -> finished product ä Manufacture of API in sites close to or same as product ä Experience and long-standing knowledge of production, product and manufacture of parties involved ä Few intermediates in sales chain ä Usually stable trade and sales connections SK 2003 9 WHO - EDM
 Challenges: past and present… n Present: ä Rationalization of drug production ä Contracting-out of many steps in manufacture ä Many intermediates in trade and sales chain ä Trade, shipping, long distances involved ä Increase of risks… ä Increase of requirements and documentation ä Increase of national control mechanisms SK 2003 10 WHO - EDM
Challenges: past and present… n Present: ä Rationalization of drug production ä Contracting-out of many steps in manufacture ä Many intermediates in trade and sales chain ä Trade, shipping, long distances involved ä Increase of risks… ä Increase of requirements and documentation ä Increase of national control mechanisms SK 2003 10 WHO - EDM
 Global challenges … n National vs international requirements Number of requirements n Application and interpretation of requirements n Import vs export control on national level Quality assurance systems applied Knowledge of product by parties involved in manufacture n n Cross-border promotion and sale n Free trade zones SK 2003 11 WHO - EDM
Global challenges … n National vs international requirements Number of requirements n Application and interpretation of requirements n Import vs export control on national level Quality assurance systems applied Knowledge of product by parties involved in manufacture n n Cross-border promotion and sale n Free trade zones SK 2003 11 WHO - EDM
 Global challenges… n Number of national and international inspections by same party Number of inspections in same site by different parties Applicability of new technologies in different settings Contracts, agreements, MRAs…. . Risks of mistakes, accidents, human errors etc n Counterfeit drugs n …. . . n n SK 2003 12 WHO - EDM
Global challenges… n Number of national and international inspections by same party Number of inspections in same site by different parties Applicability of new technologies in different settings Contracts, agreements, MRAs…. . Risks of mistakes, accidents, human errors etc n Counterfeit drugs n …. . . n n SK 2003 12 WHO - EDM
 National regulatory and inspection systems ä n In developed countries ä ä ä n well organized, controlling national market dossiers evaluation and inspections different approaches used, few MRA In developing countries ä ä SK 2003 13 --> approx. 1/3 of WHO Member States have well developed regulatory systems, approx. . 1/3 have none often difficulties of resources capacity? application of national and international guidelines… --> or non-existent …. WHO - EDM
National regulatory and inspection systems ä n In developed countries ä ä ä n well organized, controlling national market dossiers evaluation and inspections different approaches used, few MRA In developing countries ä ä SK 2003 13 --> approx. 1/3 of WHO Member States have well developed regulatory systems, approx. . 1/3 have none often difficulties of resources capacity? application of national and international guidelines… --> or non-existent …. WHO - EDM
 Experience from WHO's pre-qualification project example ARVs ä ä SK 2003 14 Inspections and dossiers evaluation can differ from country to country Small percentage of products and manufacturers participating in the project comply internationally Time needed from some manufacturers to get into compliance l data to be generated l GMP upgrade Quality Assurance at a price! WHO - EDM
Experience from WHO's pre-qualification project example ARVs ä ä SK 2003 14 Inspections and dossiers evaluation can differ from country to country Small percentage of products and manufacturers participating in the project comply internationally Time needed from some manufacturers to get into compliance l data to be generated l GMP upgrade Quality Assurance at a price! WHO - EDM
 WHO’s global guidelines and strategies n n n Requirements for drug registration and model legislation Networking among and with regulatory authorities International alerts Counterfeit network Global norms and standards in production, inspection, quality control, good storage practices and nomenclature (INN) …. . SK 2003 15 WHO - EDM
WHO’s global guidelines and strategies n n n Requirements for drug registration and model legislation Networking among and with regulatory authorities International alerts Counterfeit network Global norms and standards in production, inspection, quality control, good storage practices and nomenclature (INN) …. . SK 2003 15 WHO - EDM
 WHO has a constitutional mandate to n n "develop, establish and promote international standards with respect to biological, pharmaceutical and similar products” (Article 2(u) of WHO's Constitution) --> Good Manufacturing Practices, stability guidelines, …… INN Programme ……. SK 2003 16 WHO - EDM
WHO has a constitutional mandate to n n "develop, establish and promote international standards with respect to biological, pharmaceutical and similar products” (Article 2(u) of WHO's Constitution) --> Good Manufacturing Practices, stability guidelines, …… INN Programme ……. SK 2003 16 WHO - EDM
 WHO Procedure for the preparation of guidelines n n n n Preliminary consultation and drafting Draft guidelines Circulation for comments Revision process. . WHO Expert Committee WHO Governing bodies Recommendation to governments for implementation --> publication in Technical Reports SK 2003 17 WHO - EDM
WHO Procedure for the preparation of guidelines n n n n Preliminary consultation and drafting Draft guidelines Circulation for comments Revision process. . WHO Expert Committee WHO Governing bodies Recommendation to governments for implementation --> publication in Technical Reports SK 2003 17 WHO - EDM
 WHO’s global guidelines and strategies - quality control ä ä SK 2003 18 International specifications (Int. Ph. , screening tests. . ) WHO Model Certificate of Analysis (COA) for use in trade and procurement Considerations for requesting analysis of drug samples Quality control laboratories v good practices for national control labs v list of equipment v External qc assessment scheme for labs WHO - EDM
WHO’s global guidelines and strategies - quality control ä ä SK 2003 18 International specifications (Int. Ph. , screening tests. . ) WHO Model Certificate of Analysis (COA) for use in trade and procurement Considerations for requesting analysis of drug samples Quality control laboratories v good practices for national control labs v list of equipment v External qc assessment scheme for labs WHO - EDM
 International Pharmacopoeia Historical overview ® ® 1874 Discussion on Unification of terminology and composition of drugs 1902 First Conference organized by Belgian Government 1906 Agreement on Unification of the Formulae of Potent Drugs ratified by 19 states 1925 Brussels agreement (signed 1929) League of Nations: “international pharmacopoeia” ® SK 2003 19 WHO - EDM
International Pharmacopoeia Historical overview ® ® 1874 Discussion on Unification of terminology and composition of drugs 1902 First Conference organized by Belgian Government 1906 Agreement on Unification of the Formulae of Potent Drugs ratified by 19 states 1925 Brussels agreement (signed 1929) League of Nations: “international pharmacopoeia” ® SK 2003 19 WHO - EDM
 International Pharmacopoeia Historical overview - 2 ® 1937 First meeting (experts from B, DK, F, NL, CH, UK, USA) League of Nations ® 1947 Interim Commission of WHO takes up health related work of League of Nations ® 1948 First World Health Assembly established Expert Committee on Unification of Pharmacopoeia SK 2003 20 WHO - EDM
International Pharmacopoeia Historical overview - 2 ® 1937 First meeting (experts from B, DK, F, NL, CH, UK, USA) League of Nations ® 1947 Interim Commission of WHO takes up health related work of League of Nations ® 1948 First World Health Assembly established Expert Committee on Unification of Pharmacopoeia SK 2003 20 WHO - EDM
 International Pharmacopoeia Historical overview - 3 ® 1950 WHA approved publication of Pharmacopoeia Internationalis ® 1951 named: Expert Committee on International Pharmacopoeia 1959 named: Expert Committee on International Pharmacopoeia and Pharmaceutical Preparations --> to date ® SK 2003 21 WHO - EDM
International Pharmacopoeia Historical overview - 3 ® 1950 WHA approved publication of Pharmacopoeia Internationalis ® 1951 named: Expert Committee on International Pharmacopoeia 1959 named: Expert Committee on International Pharmacopoeia and Pharmaceutical Preparations --> to date ® SK 2003 21 WHO - EDM
 International Pharmacopoeia ® current: Third edition ® implementation: “ready for use” by Member States ® Scope since 1975: ® ® SK 2003 22 Model List of Essential Drugs and Drugs recommended by WHO Specific disease programmes, e. g. Malaria, TB, HIV/AIDS WHO - EDM
International Pharmacopoeia ® current: Third edition ® implementation: “ready for use” by Member States ® Scope since 1975: ® ® SK 2003 22 Model List of Essential Drugs and Drugs recommended by WHO Specific disease programmes, e. g. Malaria, TB, HIV/AIDS WHO - EDM
 WHO’s strategy for quality control ® Step-wise approach: l l SK 2003 23 - Basic tests (identification) - Screening tests (TLC) - International Pharmacopoeia + International reference materials (ICRS and IR reference spectra) WHO - EDM
WHO’s strategy for quality control ® Step-wise approach: l l SK 2003 23 - Basic tests (identification) - Screening tests (TLC) - International Pharmacopoeia + International reference materials (ICRS and IR reference spectra) WHO - EDM
 Int. Ph and links to other WHO activities ® Establishment of monographs for antiretrovirals, HIV medicines l l l SK 2003 24 - collaboration with other pharmacopoeias, including PDG, Ph. Eur. USP, JP, IP - collaboration with manufacturers - link with project on pre-qualification of suppliers for HIV drugs WHO - EDM
Int. Ph and links to other WHO activities ® Establishment of monographs for antiretrovirals, HIV medicines l l l SK 2003 24 - collaboration with other pharmacopoeias, including PDG, Ph. Eur. USP, JP, IP - collaboration with manufacturers - link with project on pre-qualification of suppliers for HIV drugs WHO - EDM
 Type of monographs ®Drug substances ®Excipients ®Finished ®General dosage forms methods and requirements: ® ® SK 2003 25 oral sold dosage forms dissolution testing… WHO - EDM
Type of monographs ®Drug substances ®Excipients ®Finished ®General dosage forms methods and requirements: ® ® SK 2003 25 oral sold dosage forms dissolution testing… WHO - EDM
 INNs SK 2003 26 WHO - EDM
INNs SK 2003 26 WHO - EDM
 WHO’s global guidelines and strategies distribution v WHO Certification Scheme for Products Moving in International Commerce v new scheme for pharmaceutical starting materials: v - WHO model GMP certificate, when inspected v - WHO model for self-assessment for manufacture of pharmaceutical starting materials n Good Distribution and Trading Practices for pharmaceutical starting materials Good Storage Practices n Good Distribution Practices (in preparation) n SK 2003 27 WHO - EDM
WHO’s global guidelines and strategies distribution v WHO Certification Scheme for Products Moving in International Commerce v new scheme for pharmaceutical starting materials: v - WHO model GMP certificate, when inspected v - WHO model for self-assessment for manufacture of pharmaceutical starting materials n Good Distribution and Trading Practices for pharmaceutical starting materials Good Storage Practices n Good Distribution Practices (in preparation) n SK 2003 27 WHO - EDM
 WHO’s global guidelines and strategies production n Good Manufacturing Practices …. . 1. Main principles for pharmaceutical products n 2. … for starting materials, including n ä ä n 3. … for specific pharmaceutical products: ä ä ä SK 2003 28 active pharmaceutical ingredients pharmaceutical excipients Sterile pharmaceutical products Biological products Investigational pharmaceutical products for clinical trials in humans Herbal medicines Radiopharmaceuticals WHO - EDM
WHO’s global guidelines and strategies production n Good Manufacturing Practices …. . 1. Main principles for pharmaceutical products n 2. … for starting materials, including n ä ä n 3. … for specific pharmaceutical products: ä ä ä SK 2003 28 active pharmaceutical ingredients pharmaceutical excipients Sterile pharmaceutical products Biological products Investigational pharmaceutical products for clinical trials in humans Herbal medicines Radiopharmaceuticals WHO - EDM
 WHO’s global guidelines and strategies inspection n Inspection of…. . n pharmaceutical manufacturers ä drug distribution channels (products) Guidelines for pre-approval inspection Quality systems requirements for national GMP inspectorates ä n n n Model GMP certificate Model report for inspections SK 2003 29 WHO - EDM
WHO’s global guidelines and strategies inspection n Inspection of…. . n pharmaceutical manufacturers ä drug distribution channels (products) Guidelines for pre-approval inspection Quality systems requirements for national GMP inspectorates ä n n n Model GMP certificate Model report for inspections SK 2003 29 WHO - EDM
 WHO’s global guidelines and strategies risk analysis n Application of risk analysis to production of pharmaceuticals, adopted in 2001 SK 2003 30 WHO - EDM
WHO’s global guidelines and strategies risk analysis n Application of risk analysis to production of pharmaceuticals, adopted in 2001 SK 2003 30 WHO - EDM
 WHO stability guidelines n Title: “guidelines for stability testing of pharmaceutical products containing well established drug substances in conventional dosage forms” n n -> stability testing of final drug products -> well established (e. g. generics) -> in conventional dosage forms (e. g. tablets) SK 2003 31 WHO - EDM
WHO stability guidelines n Title: “guidelines for stability testing of pharmaceutical products containing well established drug substances in conventional dosage forms” n n -> stability testing of final drug products -> well established (e. g. generics) -> in conventional dosage forms (e. g. tablets) SK 2003 31 WHO - EDM
 Developments in 2001: new alternative being discussed to modify both ICH and WHO guidelines n for zone IV to: --> 30°C and 65% RH (then: 70%) Consultative procedure: mailing of request to experts and discussion during informal consultation Discussion and adoption during WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical Preparations held 22 -26 October 2001 in Geneva n n SK 2003 32 WHO - EDM
Developments in 2001: new alternative being discussed to modify both ICH and WHO guidelines n for zone IV to: --> 30°C and 65% RH (then: 70%) Consultative procedure: mailing of request to experts and discussion during informal consultation Discussion and adoption during WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical Preparations held 22 -26 October 2001 in Geneva n n SK 2003 32 WHO - EDM
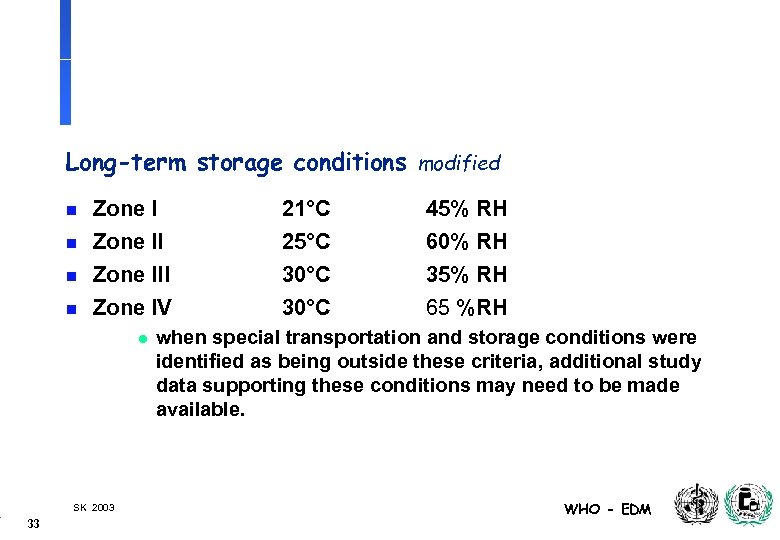 Long-term storage conditions modified n n Zone III Zone IV l SK 2003 33 21°C 25°C 30°C 45% RH 60% RH 35% RH 65 %RH when special transportation and storage conditions were identified as being outside these criteria, additional study data supporting these conditions may need to be made available. WHO - EDM
Long-term storage conditions modified n n Zone III Zone IV l SK 2003 33 21°C 25°C 30°C 45% RH 60% RH 35% RH 65 %RH when special transportation and storage conditions were identified as being outside these criteria, additional study data supporting these conditions may need to be made available. WHO - EDM
 Developments in 2002 -…. n n n February 2002: ICH Data package for registration in climatic zones II and IV --> signed off by all 6 ICH partners as step 2 document Consultative process in all three ICH regions by regulatory agencies Comments and new drafts circulated in ICH Working Group Discussed at ICH meeting February 2003 now ICH document step 4 SK 2003 34 WHO - EDM
Developments in 2002 -…. n n n February 2002: ICH Data package for registration in climatic zones II and IV --> signed off by all 6 ICH partners as step 2 document Consultative process in all three ICH regions by regulatory agencies Comments and new drafts circulated in ICH Working Group Discussed at ICH meeting February 2003 now ICH document step 4 SK 2003 34 WHO - EDM
 Access to HIV/AIDS Drugs and Diagnostics of Assured Quality - pilot procurement project n Partners: ä WHO UNICEF UNAIDS UNFPA The World Bank (support) ä --> now expanded to anti-TB and antimalarial medicines SK 2003 WHO - EDM ä ä 35
Access to HIV/AIDS Drugs and Diagnostics of Assured Quality - pilot procurement project n Partners: ä WHO UNICEF UNAIDS UNFPA The World Bank (support) ä --> now expanded to anti-TB and antimalarial medicines SK 2003 WHO - EDM ä ä 35
 Pilot Procurement, Quality and Sourcing Project Access to HIV/AIDS Drugs and Diagnostics of Assured Quality n Problems and deficiencies identified: ä SK 2003 36 General Problems identified with ARVs l Several substances and products not in pharmacopoeia l unacceptable chiral activity, stereo-isomerism l unacceptable impurities l lack of reference standards l no analytical methods and method validation l Regulatory authorities not following WHO recommendations for registration of products l Regulatory approval not based on thorough evaluation WHO - EDM
Pilot Procurement, Quality and Sourcing Project Access to HIV/AIDS Drugs and Diagnostics of Assured Quality n Problems and deficiencies identified: ä SK 2003 36 General Problems identified with ARVs l Several substances and products not in pharmacopoeia l unacceptable chiral activity, stereo-isomerism l unacceptable impurities l lack of reference standards l no analytical methods and method validation l Regulatory authorities not following WHO recommendations for registration of products l Regulatory approval not based on thorough evaluation WHO - EDM
 Pilot Procurement, Quality and Sourcing Project Access to HIV/AIDS Drugs and Diagnostics of Assured Quality n GMP deficiencies: ä ä ä SK 2003 37 Hormones, cytotoxics and ARVs in same area Qualification and validation lacking (premises, systems, equipment, processes) Cleaning validation No verification of air classification of areas for sterile product manufacturing Sampling and testing of APIs Loss in traceability of materials used in production WHO - EDM
Pilot Procurement, Quality and Sourcing Project Access to HIV/AIDS Drugs and Diagnostics of Assured Quality n GMP deficiencies: ä ä ä SK 2003 37 Hormones, cytotoxics and ARVs in same area Qualification and validation lacking (premises, systems, equipment, processes) Cleaning validation No verification of air classification of areas for sterile product manufacturing Sampling and testing of APIs Loss in traceability of materials used in production WHO - EDM
 WHO’s operational strategies n n Assist countries to strengthen or establish national drug regulation Study alternative ways of improving control and safe trade of starting materials and products Promote the use of WHO norms and standards Promote cooperation and harmonization among countries SK 2003 38 WHO - EDM
WHO’s operational strategies n n Assist countries to strengthen or establish national drug regulation Study alternative ways of improving control and safe trade of starting materials and products Promote the use of WHO norms and standards Promote cooperation and harmonization among countries SK 2003 38 WHO - EDM
 WHO’s operational strategies -2 v v Work with interested parties and countries to combat counterfeit and substandard drugs Establishing national and regional quality control laboratories Training of drug regulatory staff Development of “how to” manuals and tools SK 2003 39 WHO - EDM
WHO’s operational strategies -2 v v Work with interested parties and countries to combat counterfeit and substandard drugs Establishing national and regional quality control laboratories Training of drug regulatory staff Development of “how to” manuals and tools SK 2003 39 WHO - EDM
 Summary n WHO assists Member States in health related matters n WHO has inter alia a constitutional mandate to develop, establish and promote international standards WHO issued a number of guidelines and norms in the area of quality assurance Continuous dialogue and collaboration with WHO Member States, regional and international harmonization efforts in drug regulation n n SK 2003 40 WHO - EDM
Summary n WHO assists Member States in health related matters n WHO has inter alia a constitutional mandate to develop, establish and promote international standards WHO issued a number of guidelines and norms in the area of quality assurance Continuous dialogue and collaboration with WHO Member States, regional and international harmonization efforts in drug regulation n n SK 2003 40 WHO - EDM
 http: //www. who. int/medicines/ Further questions ? ? ? SK 2003 41 WHO - EDM
http: //www. who. int/medicines/ Further questions ? ? ? SK 2003 41 WHO - EDM
 http: //who. int/medicines
http: //who. int/medicines


