Wages and salaries of employees of an enterprise





















lecture_8_ee.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 Wages and salaries of employees of an enterprise Lecture 8
Wages and salaries of employees of an enterprise Lecture 8
 Wage or Salary? Difference? Wages are generally paid per hour (daily or weekly basis) Usually not include paid vacations or paid sick days. Wage earners often have to give up pay for leaving early, coming in late, missing a day, or taking a vacation. Salary refers to how much you get paid every year. Salary earners get paid for performance rather than by the hour. Salaried workers are much more likely to have paid sick days and paid vacations Medical insurance Education Read more: Difference Between Wage and Salary | Difference Between | Wage vs Salary http://www.differencebetween.net/business/difference-between-wage-and-salary/#ixzz29wpBhXCE
Wage or Salary? Difference? Wages are generally paid per hour (daily or weekly basis) Usually not include paid vacations or paid sick days. Wage earners often have to give up pay for leaving early, coming in late, missing a day, or taking a vacation. Salary refers to how much you get paid every year. Salary earners get paid for performance rather than by the hour. Salaried workers are much more likely to have paid sick days and paid vacations Medical insurance Education Read more: Difference Between Wage and Salary | Difference Between | Wage vs Salary http://www.differencebetween.net/business/difference-between-wage-and-salary/#ixzz29wpBhXCE
 Wage or Salary? Difference? Summary 1. Wage earners are paid by the hour. 2. Salary earners are paid by the year. 3. Salary earners usually receive paid time when they are not working. 4. Wage earners often have to give up pay for time off. 5. Salaries are often calculated as packages. 6. Wage earners get paid more for working more than 40 hours per week. 7. Salary workers are rarely offered overtime pay. 8. Salaries can contain all kinds of benefits and perks. Read more: Difference Between Wage and Salary | Difference Between | Wage vs Salary http://www.differencebetween.net/business/difference-between-wage-and-salary/#ixzz29wpBhXCE
Wage or Salary? Difference? Summary 1. Wage earners are paid by the hour. 2. Salary earners are paid by the year. 3. Salary earners usually receive paid time when they are not working. 4. Wage earners often have to give up pay for time off. 5. Salaries are often calculated as packages. 6. Wage earners get paid more for working more than 40 hours per week. 7. Salary workers are rarely offered overtime pay. 8. Salaries can contain all kinds of benefits and perks. Read more: Difference Between Wage and Salary | Difference Between | Wage vs Salary http://www.differencebetween.net/business/difference-between-wage-and-salary/#ixzz29wpBhXCE
 WAGES AND INCENTIVES Wage payment is a matter of great importance to workers. It determines their standard of living, their attitude towards the company influences their motivation to work
WAGES AND INCENTIVES Wage payment is a matter of great importance to workers. It determines their standard of living, their attitude towards the company influences their motivation to work
 Characteristics of Wage system Simple & Equitable Guaranteed minimum wage Incentive-oriented Cost-effective Certainty
Characteristics of Wage system Simple & Equitable Guaranteed minimum wage Incentive-oriented Cost-effective Certainty
 Forms of payment Monetary (main) Nonmonetary (rare) wrong monetary circulation hyperinflation and unstable economic situation (crisis)
Forms of payment Monetary (main) Nonmonetary (rare) wrong monetary circulation hyperinflation and unstable economic situation (crisis)
 Methods of Wage Payment - Time Wage System - Piece Rate System
Methods of Wage Payment - Time Wage System - Piece Rate System
 Time Wage System In this system, the worker is paid on the basis of time spent on the work irrespective of the amount of work done. The basis of this time may be hour, day, week or month. It is widely employed in those organizations where: quality of work is more important that the volume; production involves delay and interruption due to uncontrollable factors; where the work requires a high degree of skills; where work is of such nature that efficiency can only be measured by close supervision
Time Wage System In this system, the worker is paid on the basis of time spent on the work irrespective of the amount of work done. The basis of this time may be hour, day, week or month. It is widely employed in those organizations where: quality of work is more important that the volume; production involves delay and interruption due to uncontrollable factors; where the work requires a high degree of skills; where work is of such nature that efficiency can only be measured by close supervision
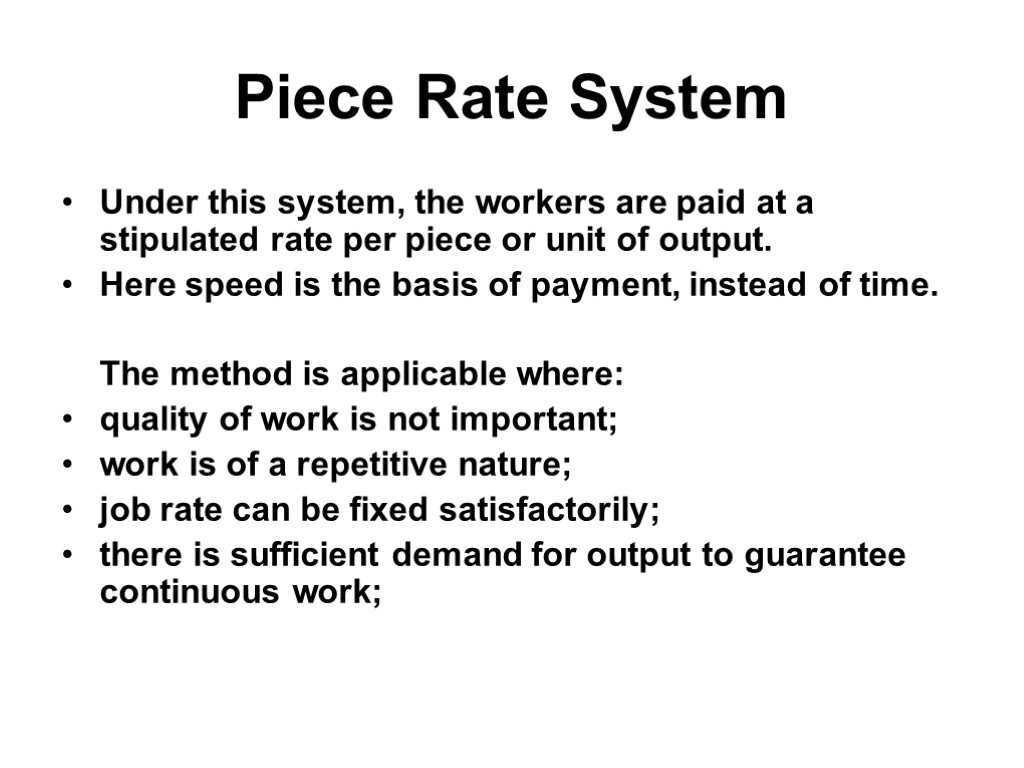
 Piece Rate System Under this system, the workers are paid at a stipulated rate per piece or unit of output. Here speed is the basis of payment, instead of time. The method is applicable where: quality of work is not important; work is of a repetitive nature; job rate can be fixed satisfactorily; there is sufficient demand for output to guarantee continuous work;
Piece Rate System Under this system, the workers are paid at a stipulated rate per piece or unit of output. Here speed is the basis of payment, instead of time. The method is applicable where: quality of work is not important; work is of a repetitive nature; job rate can be fixed satisfactorily; there is sufficient demand for output to guarantee continuous work;
 Incentive Incentives are variable rewards or extra payment granted to employees according to variations in their performance. The other name for incentives is payment by results Incentive plans foresee a basic rate usually on time basis applicable to all workers and incentive rates payable to the more efficient among them as extra compensation for their meritorious performance in terms of time, costs and quality
Incentive Incentives are variable rewards or extra payment granted to employees according to variations in their performance. The other name for incentives is payment by results Incentive plans foresee a basic rate usually on time basis applicable to all workers and incentive rates payable to the more efficient among them as extra compensation for their meritorious performance in terms of time, costs and quality
 Features of Incentive Plans Minimum wages are guaranteed to all workers. Incentives by way of bonus, etc., are offered to efficient workers for the time saved. A standard time is fixed and the worker is expected to perform the given work within the standard time
Features of Incentive Plans Minimum wages are guaranteed to all workers. Incentives by way of bonus, etc., are offered to efficient workers for the time saved. A standard time is fixed and the worker is expected to perform the given work within the standard time
 Basic Factors in Determining Pay Rates
Basic Factors in Determining Pay Rates
 Corporate Policies, Competitive Strategy, and Compensation Aligned Reward Strategy The employer’s basic task: To create a bundle of rewards—a total reward package—that specifically elicits the employee behaviors that the firm needs to support and achieve its competitive strategy. The HR or compensation manager along with top management creates pay policies that are consistent with the firm’s strategic aims.
Corporate Policies, Competitive Strategy, and Compensation Aligned Reward Strategy The employer’s basic task: To create a bundle of rewards—a total reward package—that specifically elicits the employee behaviors that the firm needs to support and achieve its competitive strategy. The HR or compensation manager along with top management creates pay policies that are consistent with the firm’s strategic aims.
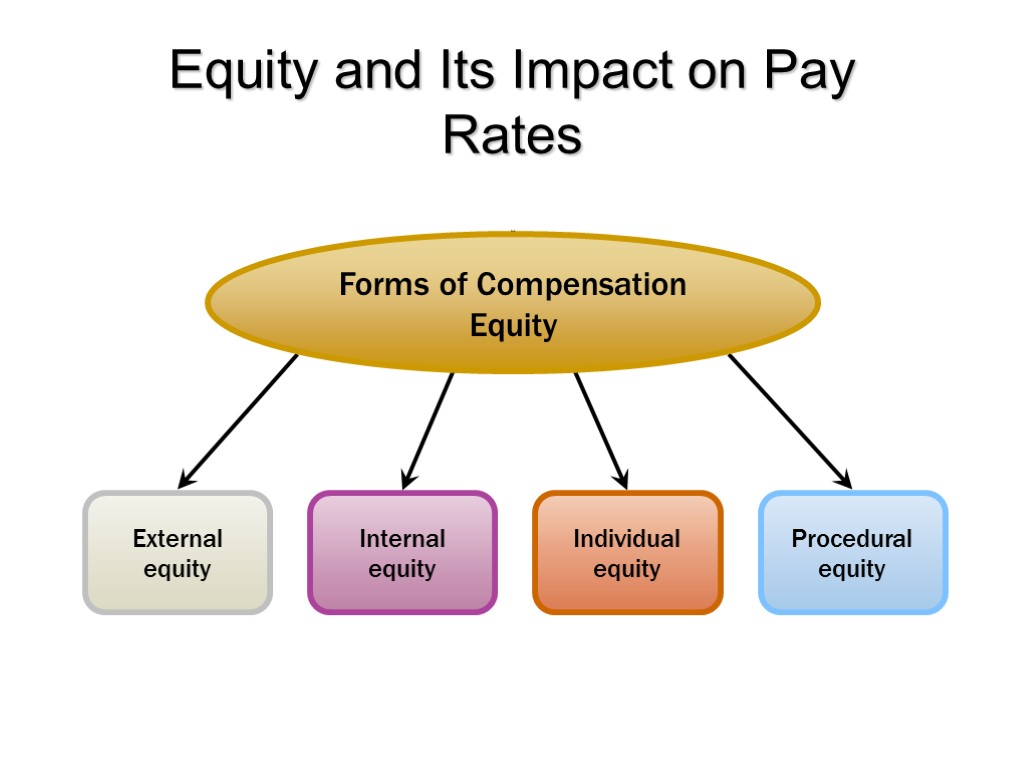
 Equity and Its Impact on Pay Rates
Equity and Its Impact on Pay Rates
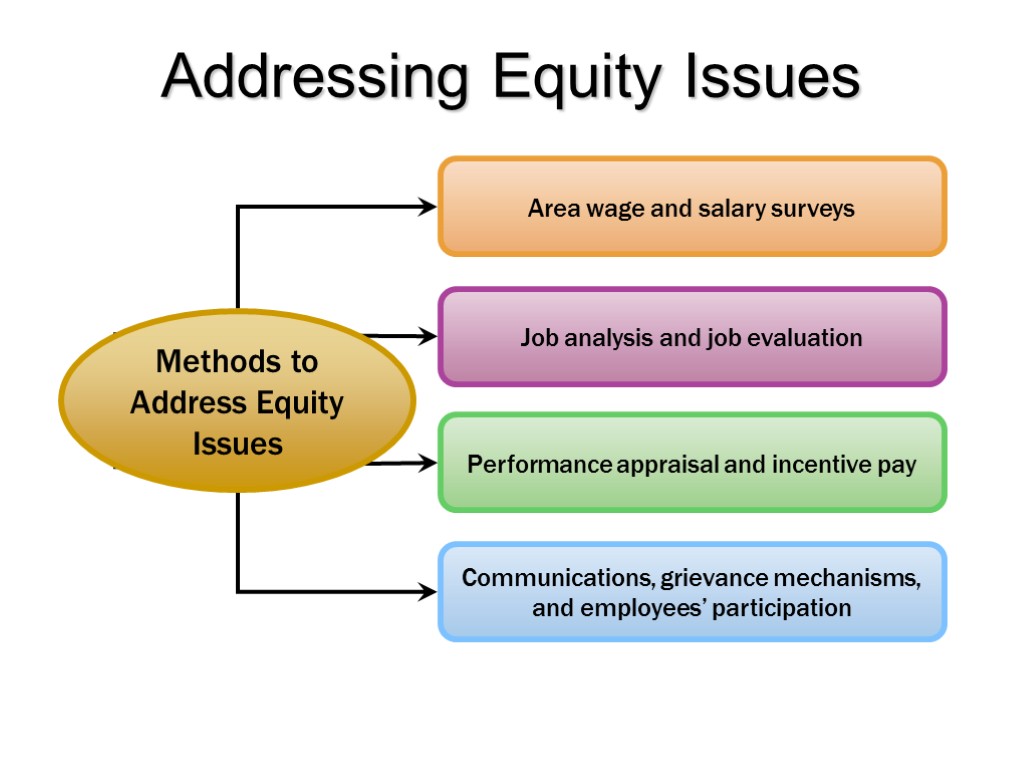
 Addressing Equity Issues
Addressing Equity Issues
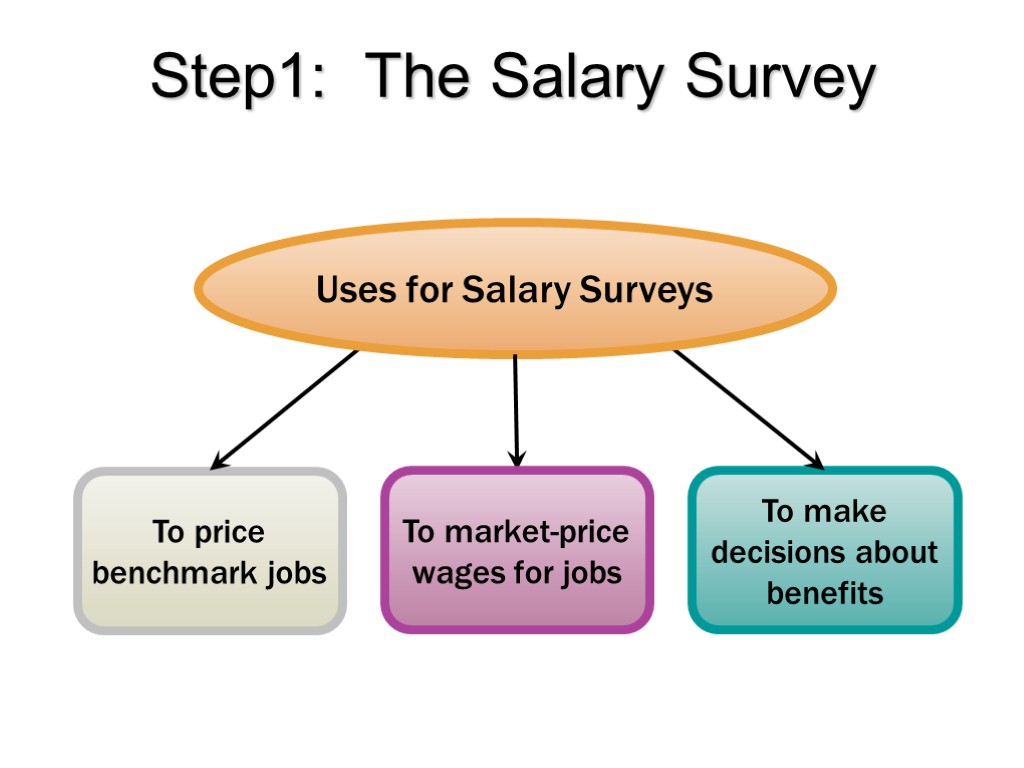
 Step1: The Salary Survey
Step1: The Salary Survey
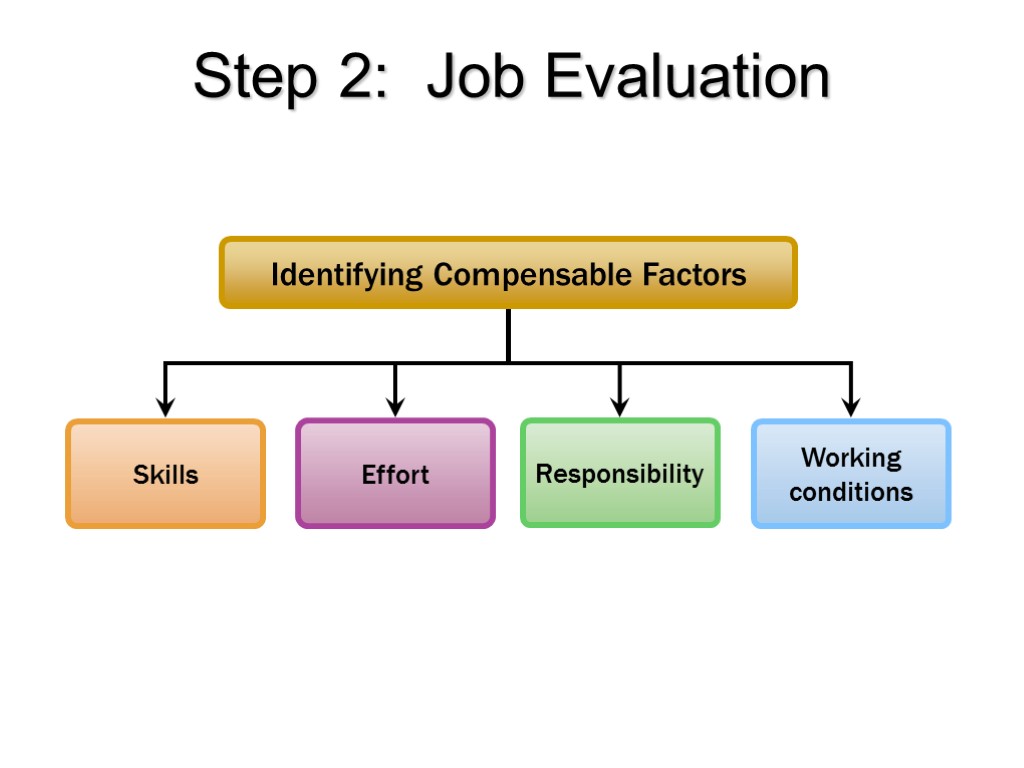
 Step 2: Job Evaluation
Step 2: Job Evaluation
 The Job Evaluation Process Performing the actual evaluation Getting the cooperation of employees Preparing for the Job Evaluation Identifying the need for the job evaluation Choosing an evaluation committee
The Job Evaluation Process Performing the actual evaluation Getting the cooperation of employees Preparing for the Job Evaluation Identifying the need for the job evaluation Choosing an evaluation committee
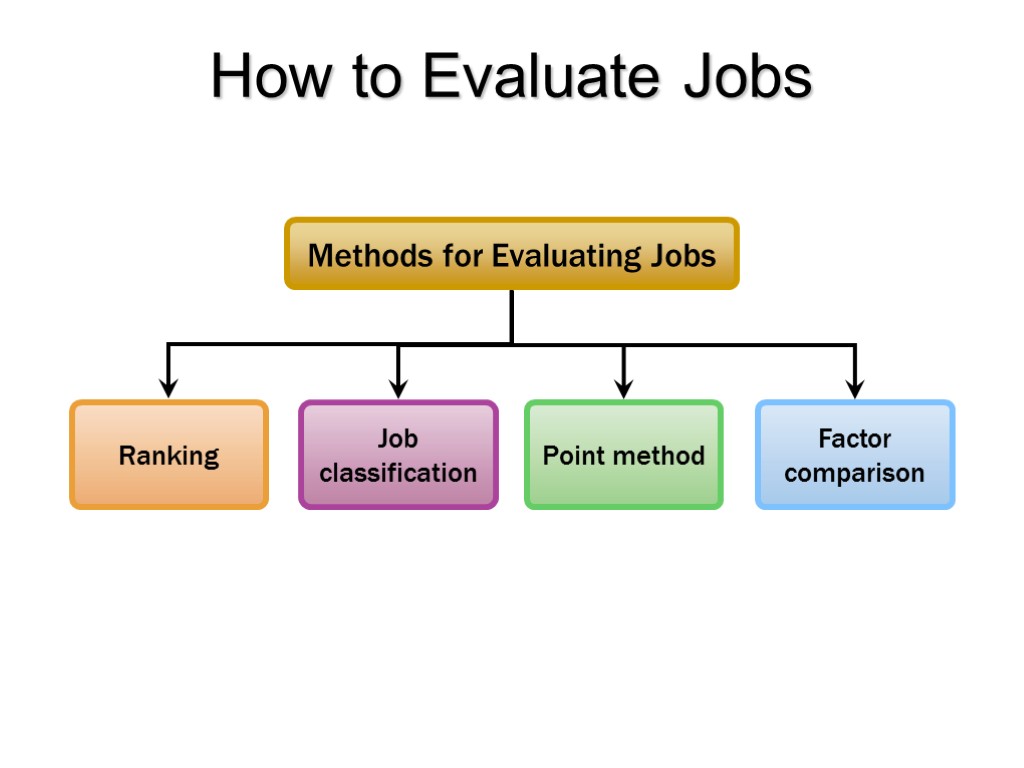
 How to Evaluate Jobs
How to Evaluate Jobs
 Job Evaluation Methods: Ranking Ranking each job relative to all other jobs, usually based on some overall factor. Steps in job ranking: Obtain job information. Select and group jobs. Select compensable factors. Rank jobs. Combine ratings.
Job Evaluation Methods: Ranking Ranking each job relative to all other jobs, usually based on some overall factor. Steps in job ranking: Obtain job information. Select and group jobs. Select compensable factors. Rank jobs. Combine ratings.
 Job Evaluation Methods: Job Classification Raters categorize jobs into groups or classes of jobs that are of roughly the same value for pay purposes. Classes contain similar jobs. Administrative assistants Grades are jobs similar in difficulty but otherwise different. Mechanics, electricians, and machinists Jobs are classed by the amount or level of compensable factors they contain.
Job Evaluation Methods: Job Classification Raters categorize jobs into groups or classes of jobs that are of roughly the same value for pay purposes. Classes contain similar jobs. Administrative assistants Grades are jobs similar in difficulty but otherwise different. Mechanics, electricians, and machinists Jobs are classed by the amount or level of compensable factors they contain.
 Job Evaluation Methods: Point Method A quantitative technique that involves: Identifying the degree to which each compensable factor is present in the job. Awarding points for each degree of each factor. Calculating a total point value for the job by adding up the corresponding points for each factor.
Job Evaluation Methods: Point Method A quantitative technique that involves: Identifying the degree to which each compensable factor is present in the job. Awarding points for each degree of each factor. Calculating a total point value for the job by adding up the corresponding points for each factor.
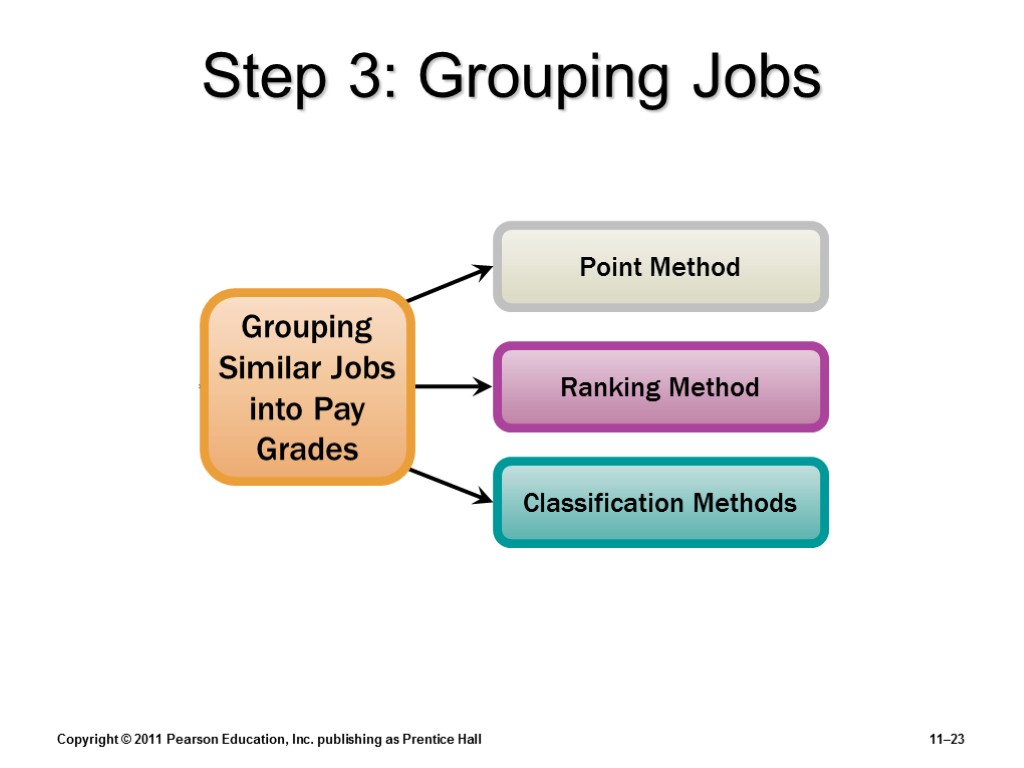
 Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 11–23 Step 3: Grouping Jobs
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 11–23 Step 3: Grouping Jobs
 Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 11–24 Step 4: Price Each Pay Grade The Wage Curve Shows the pay rates paid for jobs in each pay grade, relative to the points or rankings assigned to each job or grade by the job evaluation. Shows the relationships between the value of the job as determined by one of the job evaluation methods and the current average pay rates for your grades.
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 11–24 Step 4: Price Each Pay Grade The Wage Curve Shows the pay rates paid for jobs in each pay grade, relative to the points or rankings assigned to each job or grade by the job evaluation. Shows the relationships between the value of the job as determined by one of the job evaluation methods and the current average pay rates for your grades.
 Step 5: Fine-Tune Pay Rates Developing Pay Ranges Flexibility in meeting external job market rates Easier for employees to move into higher pay grades Allows for rewarding performance differences and seniority Correcting Out-of-Line Rates Raising underpaid jobs to the minimum of the rate range for their pay grade Freezing rates or cutting pay rates for overpaid (“red circle”) jobs to maximum in the pay range for their pay grade
Step 5: Fine-Tune Pay Rates Developing Pay Ranges Flexibility in meeting external job market rates Easier for employees to move into higher pay grades Allows for rewarding performance differences and seniority Correcting Out-of-Line Rates Raising underpaid jobs to the minimum of the rate range for their pay grade Freezing rates or cutting pay rates for overpaid (“red circle”) jobs to maximum in the pay range for their pay grade
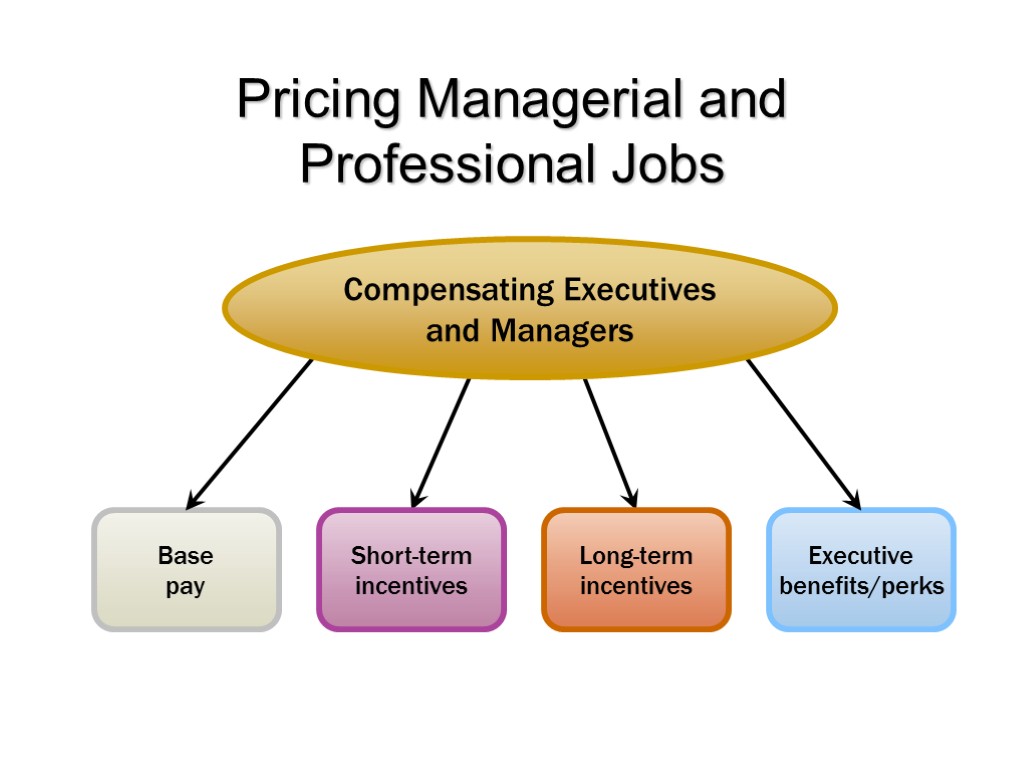
 Pricing Managerial and Professional Jobs
Pricing Managerial and Professional Jobs
 Pricing Managerial and Professional Jobs What Determines Executive Pay? CEO pay is set by the board of directors taking into account factors such as the business strategy, corporate trends, and where they want to be in the short and long term. CEOs can have considerable influence over the boards that determine their pay. Firms pay CEOs based on the complexity of the jobs they fill. Shareholder activism and government oversight have tightened the restrictions on what companies pay top executives. Boards are reducing the relative importance of base salary while boosting the emphasis on performance-based pay.
Pricing Managerial and Professional Jobs What Determines Executive Pay? CEO pay is set by the board of directors taking into account factors such as the business strategy, corporate trends, and where they want to be in the short and long term. CEOs can have considerable influence over the boards that determine their pay. Firms pay CEOs based on the complexity of the jobs they fill. Shareholder activism and government oversight have tightened the restrictions on what companies pay top executives. Boards are reducing the relative importance of base salary while boosting the emphasis on performance-based pay.
 Compensating Professional Employees Employers can use job evaluation for professional jobs. Compensable factors focus on problem solving, creativity, job scope, and technical knowledge and expertise. Firms use the point method and factor comparison methods, although job classification is most popular. Professional jobs are market-priced to establish the values for benchmark jobs.
Compensating Professional Employees Employers can use job evaluation for professional jobs. Compensable factors focus on problem solving, creativity, job scope, and technical knowledge and expertise. Firms use the point method and factor comparison methods, although job classification is most popular. Professional jobs are market-priced to establish the values for benchmark jobs.
 Competency-Based Pay Competencies Demonstrable characteristics of a person, including knowledge, skills, and behaviors, that enable performance What is Competency-Based Pay? Paying for the employee’s range, depth, and types of skills and knowledge, rather than for the job title he or she holds
Competency-Based Pay Competencies Demonstrable characteristics of a person, including knowledge, skills, and behaviors, that enable performance What is Competency-Based Pay? Paying for the employee’s range, depth, and types of skills and knowledge, rather than for the job title he or she holds
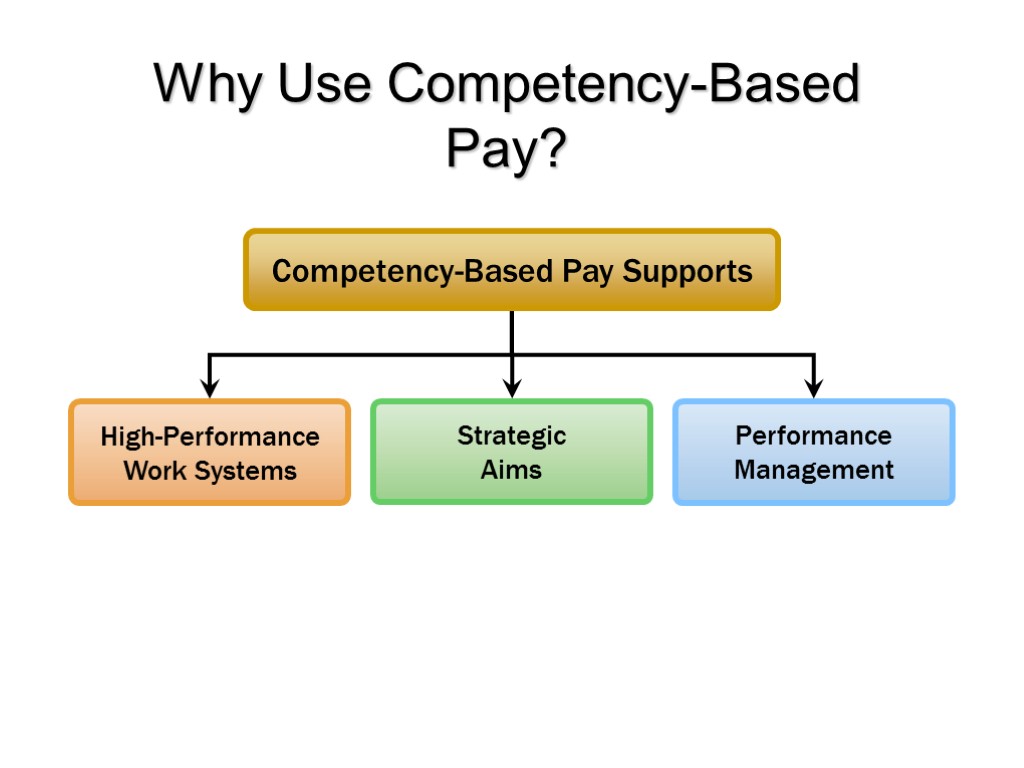
 Why Use Competency-Based Pay?
Why Use Competency-Based Pay?
 Competency-Based Pay in Practice Main elements of skill/competency/knowledge–based pay programs: A system that defines specific skills A process for tying the person’s pay to his or her skill A training system that lets employees seek and acquire skills A formal competency testing system A work design that lets employees move among jobs to permit work assignment flexibility
Competency-Based Pay in Practice Main elements of skill/competency/knowledge–based pay programs: A system that defines specific skills A process for tying the person’s pay to his or her skill A training system that lets employees seek and acquire skills A formal competency testing system A work design that lets employees move among jobs to permit work assignment flexibility
