Prezentatsia_1_1.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 16
 The World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) The Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) Viktoriia Muraviova Nastassia Laktsiyonava Palina Sivitskaya
The World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) The Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) Viktoriia Muraviova Nastassia Laktsiyonava Palina Sivitskaya
 WIPO The World Intellectual Property Organization
WIPO The World Intellectual Property Organization
 What is WIPO? WIPO is the global forum for intellectual property services, policy, information and cooperation. We are a self-funding agency of the United Nations, with 188 member states. Our mission is to lead the development of a balanced and effective international intellectual property (IP) system that enables innovation and creativity for the benefit of all.
What is WIPO? WIPO is the global forum for intellectual property services, policy, information and cooperation. We are a self-funding agency of the United Nations, with 188 member states. Our mission is to lead the development of a balanced and effective international intellectual property (IP) system that enables innovation and creativity for the benefit of all.
 What is Intellectual Property? Intellectual property (IP) refers to creations of the mind, such as inventions; literary and artistic works; designs; and symbols, names and images used in commerce.
What is Intellectual Property? Intellectual property (IP) refers to creations of the mind, such as inventions; literary and artistic works; designs; and symbols, names and images used in commerce.
 What WIPO does? They provide: • • a policy forum to shape balanced international IP rules for a changing world; global services to protect IP across borders and to resolve disputes; technical infrastructure to connect IP systems and share knowledge; cooperation and capacity-building programs to enable all countries to use IP for economic, social and cultural development; • a world reference source for IP information
What WIPO does? They provide: • • a policy forum to shape balanced international IP rules for a changing world; global services to protect IP across borders and to resolve disputes; technical infrastructure to connect IP systems and share knowledge; cooperation and capacity-building programs to enable all countries to use IP for economic, social and cultural development; • a world reference source for IP information
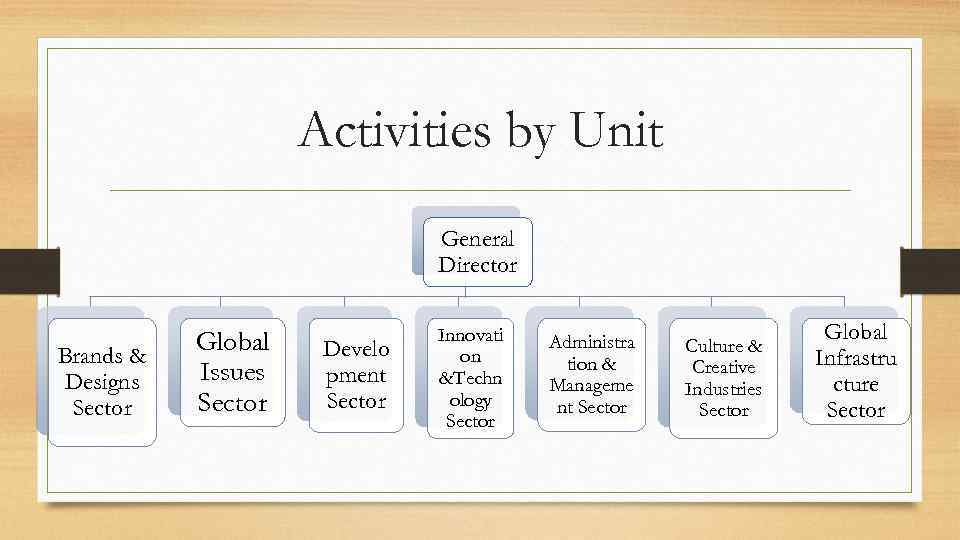 Activities by Unit General Director Brands & Designs Sector Global Issues Sector Develo pment Sector Innovati on &Techn ology Sector Administra tion & Manageme nt Sector Culture & Creative Industries Sector Global Infrastru cture Sector
Activities by Unit General Director Brands & Designs Sector Global Issues Sector Develo pment Sector Innovati on &Techn ology Sector Administra tion & Manageme nt Sector Culture & Creative Industries Sector Global Infrastru cture Sector
 TRIPS The Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights
TRIPS The Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights
 What is TRIPS? • The Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) is an international agreement administered by the World Trade Organization (WTO) that sets down minimum standards for many forms of intellectual property (IP) regulation as applied to nationals of other WTO Members. • The TRIPS agreement introduced intellectual property law into the international trading system for the first time and remains the most comprehensive international agreement on intellectual property to date.
What is TRIPS? • The Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) is an international agreement administered by the World Trade Organization (WTO) that sets down minimum standards for many forms of intellectual property (IP) regulation as applied to nationals of other WTO Members. • The TRIPS agreement introduced intellectual property law into the international trading system for the first time and remains the most comprehensive international agreement on intellectual property to date.
 Background and history • TRIPS was negotiated at the end of the Uruguay Round of the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) in 1994 • After the Uruguay round, the GATT became the basis for the establishment of the World Trade Orgnization. Because ratification of TRIPS is a compulsory requirement of World Trade Organization membership, any country seeking to obtain easy access to the numerous international markets opened by the World Trade Organization must enact the strict intellectual property laws mandated by TRIPS. For this reason, TRIPS is the most important multilateral instrument for the globalization of intellectual property laws.
Background and history • TRIPS was negotiated at the end of the Uruguay Round of the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) in 1994 • After the Uruguay round, the GATT became the basis for the establishment of the World Trade Orgnization. Because ratification of TRIPS is a compulsory requirement of World Trade Organization membership, any country seeking to obtain easy access to the numerous international markets opened by the World Trade Organization must enact the strict intellectual property laws mandated by TRIPS. For this reason, TRIPS is the most important multilateral instrument for the globalization of intellectual property laws.
 The requirements of TRIPS (1) • TRIPS requires member states to provide strong protection for intellectual property rights. For example, under TRIPS: v Copyright terms must extend at least 20 years, unless based on the life of the author. v. Copyright must be granted automatically, and not based upon any "formality, " such as registrations, as specified in the Berne Convention. v. Computer programs must be regarded as "literary works" under copyright law and receive the same terms of protection.
The requirements of TRIPS (1) • TRIPS requires member states to provide strong protection for intellectual property rights. For example, under TRIPS: v Copyright terms must extend at least 20 years, unless based on the life of the author. v. Copyright must be granted automatically, and not based upon any "formality, " such as registrations, as specified in the Berne Convention. v. Computer programs must be regarded as "literary works" under copyright law and receive the same terms of protection.
 The requirements of TRIPS (2) v National exceptions to copyright (such as "fair use" in the United States) are constrained by the Berne three-step test v Patents must be granted for "inventions" in all "fields of technology" provided they meet all other patentability requirements (although exceptions for certain public interests are allowed and must be enforceable for at least 20 years. v Exceptions to exclusive rights must be limited, provided that a normal exploitation of the work and normal exploitation of the patent is not in conflict.
The requirements of TRIPS (2) v National exceptions to copyright (such as "fair use" in the United States) are constrained by the Berne three-step test v Patents must be granted for "inventions" in all "fields of technology" provided they meet all other patentability requirements (although exceptions for certain public interests are allowed and must be enforceable for at least 20 years. v Exceptions to exclusive rights must be limited, provided that a normal exploitation of the work and normal exploitation of the patent is not in conflict.
 The requirements of TRIPS (3) • No unreasonable prejudice to the legitimate interests of the right holders of computer programs and patents is allowed. • Legitimate interests of third parties have to be taken into account by patent rights. • In each state, intellectual property laws may not offer any benefits to local citizens which are not available to citizens of other TRIPS signatories under the principle of national treatment (with certain limited exceptions). TRIPS also has a most favored nation clause.
The requirements of TRIPS (3) • No unreasonable prejudice to the legitimate interests of the right holders of computer programs and patents is allowed. • Legitimate interests of third parties have to be taken into account by patent rights. • In each state, intellectual property laws may not offer any benefits to local citizens which are not available to citizens of other TRIPS signatories under the principle of national treatment (with certain limited exceptions). TRIPS also has a most favored nation clause.
 Implementation in developing countries • The obligations under TRIPS apply equally to all member states, however developing countries were allowed extra time to implement the applicable changes to their national laws, in two tiers of transition according to their level of development.
Implementation in developing countries • The obligations under TRIPS apply equally to all member states, however developing countries were allowed extra time to implement the applicable changes to their national laws, in two tiers of transition according to their level of development.
 Post-TRIPS expansion General objectives of these agreements include: v The creation of anti-circumvention laws to protect Digital Rights Management systems. This was achieved through the 1996 World Intellectual Property Organization Copyright Treaty (WIPO Treaty) and the WIPO Performances and Phonograms Treaty. v More stringent restrictions on compulsory licenses for patents. v More aggressive patent enforcement. This effort has been observed more broadly in proposals for WIPO and European Union rules on intellectual property enforcement. The 2001 EU Copyright Directive was to implement the 1996 WIPO Copyright Treaty. v The campaign for the creation of a WIPO Broadcasting Treaty that would give broadcasters (and possibly webcasters) exclusive rights over the copies of works they have distributed.
Post-TRIPS expansion General objectives of these agreements include: v The creation of anti-circumvention laws to protect Digital Rights Management systems. This was achieved through the 1996 World Intellectual Property Organization Copyright Treaty (WIPO Treaty) and the WIPO Performances and Phonograms Treaty. v More stringent restrictions on compulsory licenses for patents. v More aggressive patent enforcement. This effort has been observed more broadly in proposals for WIPO and European Union rules on intellectual property enforcement. The 2001 EU Copyright Directive was to implement the 1996 WIPO Copyright Treaty. v The campaign for the creation of a WIPO Broadcasting Treaty that would give broadcasters (and possibly webcasters) exclusive rights over the copies of works they have distributed.
 Criticism • Since TRIPS came into force it has received a growing level of criticism from developing countries, academics, and non-governmental organizations. Some of this criticism is against the WTO as a whole, but many advocates of trade liberalization also regard TRIPS as bad policy. TRIPS's wealth concentration effects (moving money from people in developing countries to copyright and patent owners in developed countries) and its imposition of artificial scarcity on the citizens of countries that would otherwise have had weaker intellectual property laws, are common bases for such criticisms.
Criticism • Since TRIPS came into force it has received a growing level of criticism from developing countries, academics, and non-governmental organizations. Some of this criticism is against the WTO as a whole, but many advocates of trade liberalization also regard TRIPS as bad policy. TRIPS's wealth concentration effects (moving money from people in developing countries to copyright and patent owners in developed countries) and its imposition of artificial scarcity on the citizens of countries that would otherwise have had weaker intellectual property laws, are common bases for such criticisms.
 Thanks For Your Attention!!!
Thanks For Your Attention!!!


