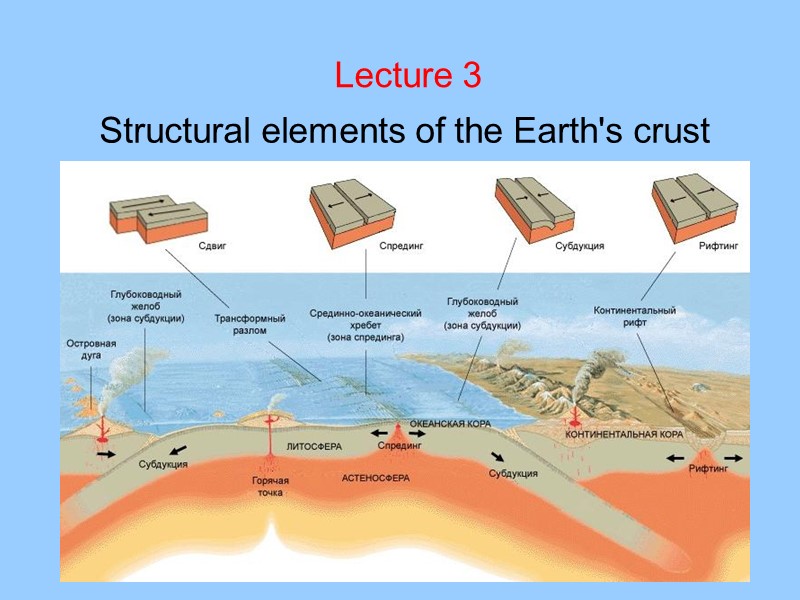
Structural elements of the Earth’s crust Lecture 3













29184-lektsia_3_strukturnye_elementy_zemnoy_kory.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 Structural elements of the Earth's crust Lecture 3
Structural elements of the Earth's crust Lecture 3
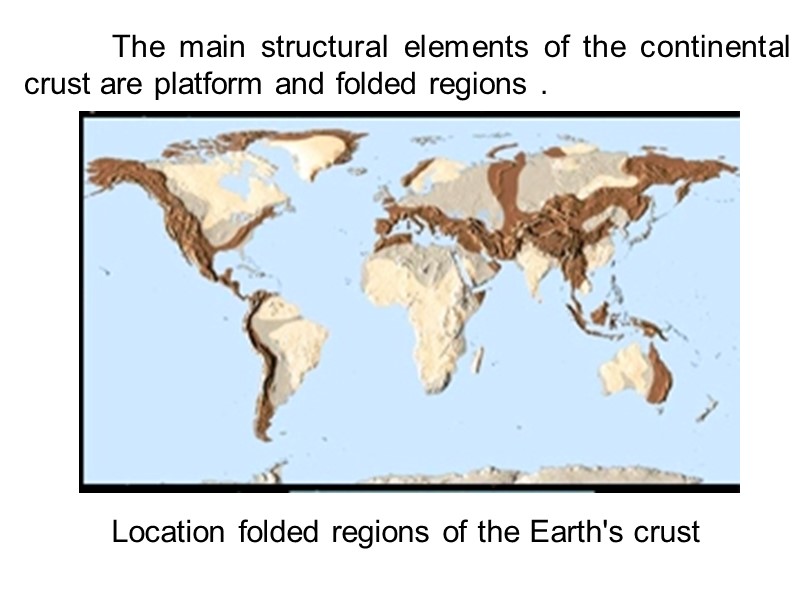
 The main structural elements of the continental crust are platform and folded regions . Location folded regions of the Earth's crust
The main structural elements of the continental crust are platform and folded regions . Location folded regions of the Earth's crust
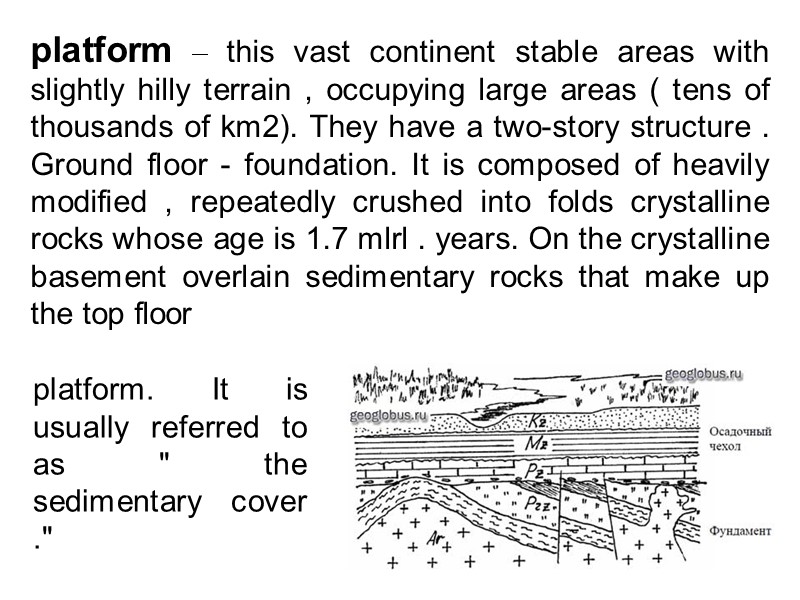
 platform – this vast continent stable areas with slightly hilly terrain , occupying large areas ( tens of thousands of km2). They have a two-story structure . Ground floor - foundation. It is composed of heavily modified , repeatedly crushed into folds crystalline rocks whose age is 1.7 mlrl . years. On the crystalline basement overlain sedimentary rocks that make up the top floor platform. It is usually referred to as " the sedimentary cover ."
platform – this vast continent stable areas with slightly hilly terrain , occupying large areas ( tens of thousands of km2). They have a two-story structure . Ground floor - foundation. It is composed of heavily modified , repeatedly crushed into folds crystalline rocks whose age is 1.7 mlrl . years. On the crystalline basement overlain sedimentary rocks that make up the top floor platform. It is usually referred to as " the sedimentary cover ."
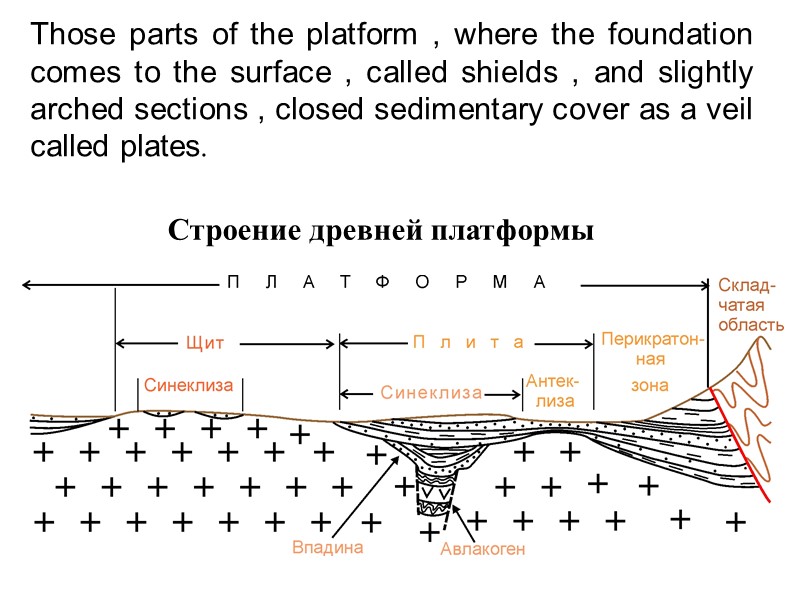
 Строение древней платформы Those parts of the platform , where the foundation comes to the surface , called shields , and slightly arched sections , closed sedimentary cover as a veil called plates.
Строение древней платформы Those parts of the platform , where the foundation comes to the surface , called shields , and slightly arched sections , closed sedimentary cover as a veil called plates.
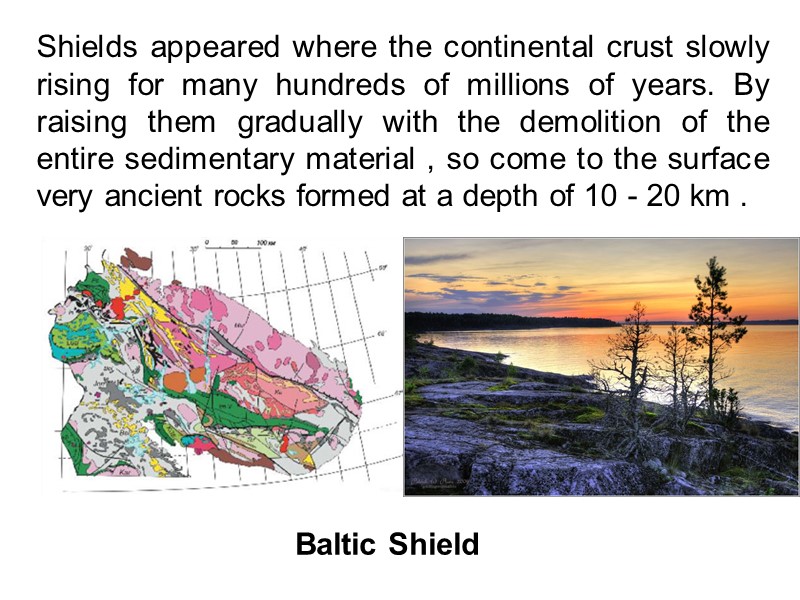
 Shields appeared where the continental crust slowly rising for many hundreds of millions of years. By raising them gradually with the demolition of the entire sedimentary material , so come to the surface very ancient rocks formed at a depth of 10 - 20 km . Baltic Shield
Shields appeared where the continental crust slowly rising for many hundreds of millions of years. By raising them gradually with the demolition of the entire sedimentary material , so come to the surface very ancient rocks formed at a depth of 10 - 20 km . Baltic Shield
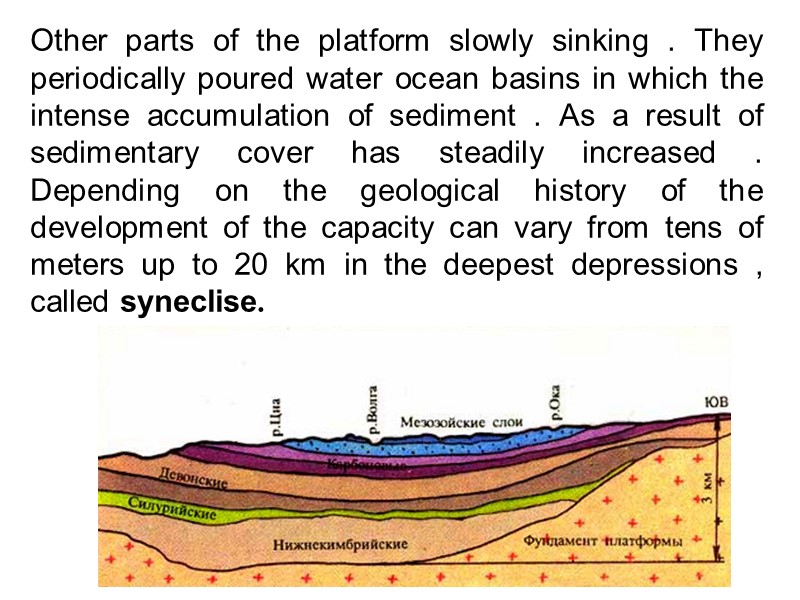
 Other parts of the platform slowly sinking . They periodically poured water ocean basins in which the intense accumulation of sediment . As a result of sedimentary cover has steadily increased . Depending on the geological history of the development of the capacity can vary from tens of meters up to 20 km in the deepest depressions , called syneclise.
Other parts of the platform slowly sinking . They periodically poured water ocean basins in which the intense accumulation of sediment . As a result of sedimentary cover has steadily increased . Depending on the geological history of the development of the capacity can vary from tens of meters up to 20 km in the deepest depressions , called syneclise.
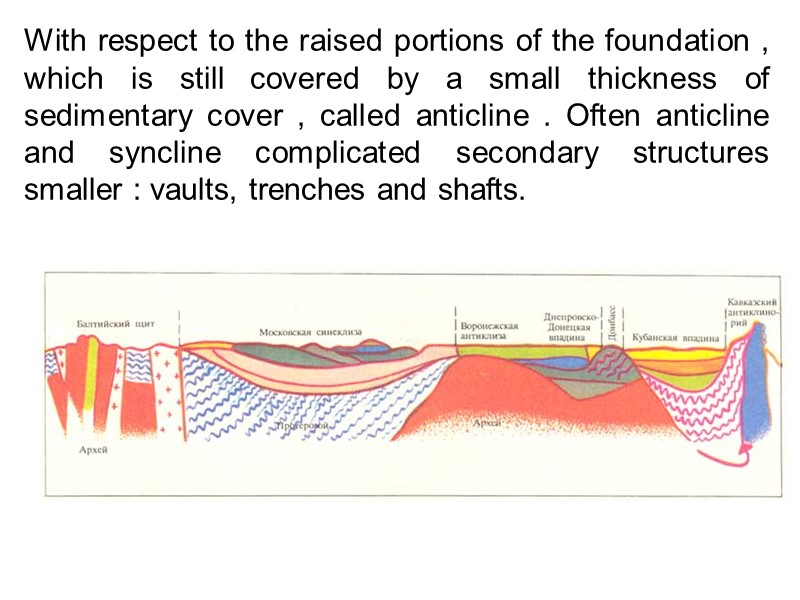
 With respect to the raised portions of the foundation , which is still covered by a small thickness of sedimentary cover , called anticline . Often anticline and syncline complicated secondary structures smaller : vaults, trenches and shafts.
With respect to the raised portions of the foundation , which is still covered by a small thickness of sedimentary cover , called anticline . Often anticline and syncline complicated secondary structures smaller : vaults, trenches and shafts.
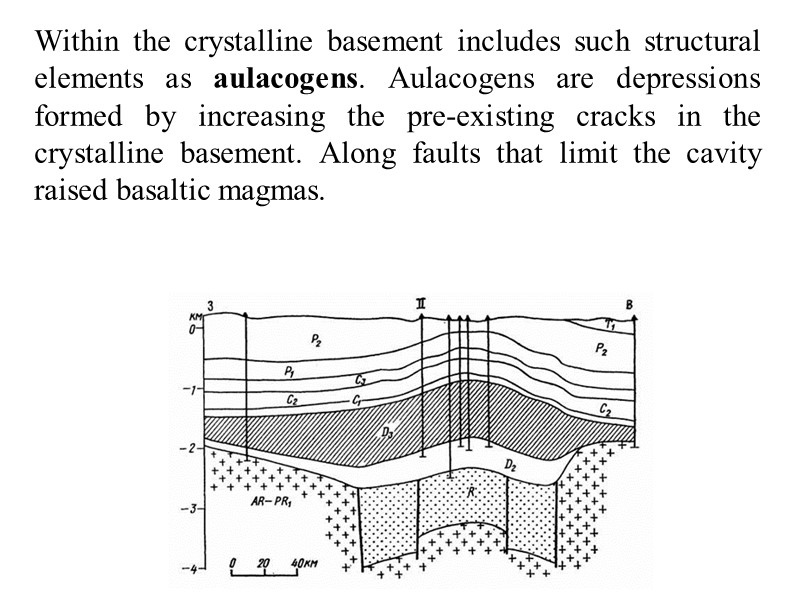
 Within the crystalline basement includes such structural elements as aulacogens. Aulacogens are depressions formed by increasing the pre-existing cracks in the crystalline basement. Along faults that limit the cavity raised basaltic magmas.
Within the crystalline basement includes such structural elements as aulacogens. Aulacogens are depressions formed by increasing the pre-existing cracks in the crystalline basement. Along faults that limit the cavity raised basaltic magmas.
 Mountain-folded regions or geosynclinal belt– this large linearly extended, most mobile parts of the earth's crust. Usually they are located in the contact zones of lithospheric plates. On the surface of the Earth are seven major geosynclinal belts: Mediterranean, Pacific, Atlantic, Brazil, the Arctic, Ural-Mongolian, within the African.
Mountain-folded regions or geosynclinal belt– this large linearly extended, most mobile parts of the earth's crust. Usually they are located in the contact zones of lithospheric plates. On the surface of the Earth are seven major geosynclinal belts: Mediterranean, Pacific, Atlantic, Brazil, the Arctic, Ural-Mongolian, within the African.
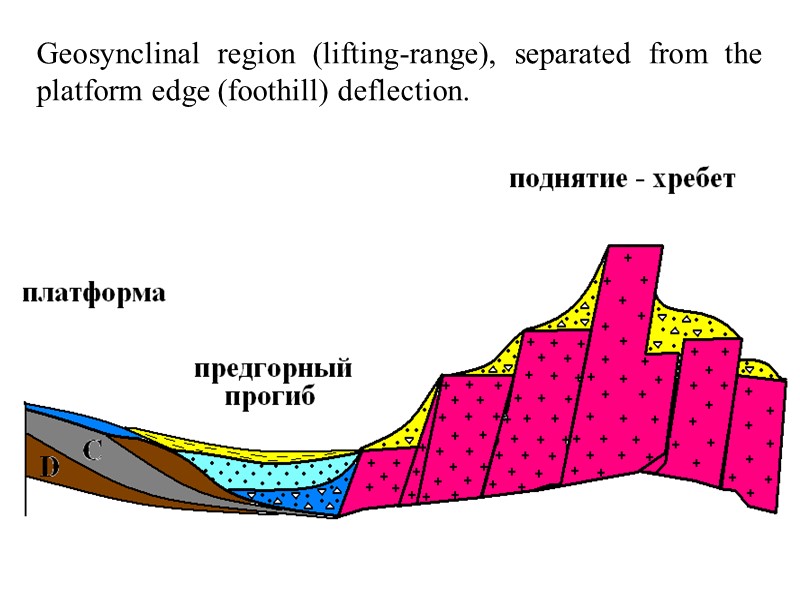
 Geosynclinal belt, in turn, are divided into smaller parts - geosynclinal area. Geosynclinal area separated from the platform edge deflections. In the middle of the geosynclinal regions are often observed median massifs that divide the region in geosynclinal system. The main structural unit of geosynclinal region is geosyncline. This section of the earth's crust, where intensive appear or manifest magmatic processes.
Geosynclinal belt, in turn, are divided into smaller parts - geosynclinal area. Geosynclinal area separated from the platform edge deflections. In the middle of the geosynclinal regions are often observed median massifs that divide the region in geosynclinal system. The main structural unit of geosynclinal region is geosyncline. This section of the earth's crust, where intensive appear or manifest magmatic processes.
 Geosynclinal region (lifting-range), separated from the platform edge (foothill) deflection.
Geosynclinal region (lifting-range), separated from the platform edge (foothill) deflection.
 In the development of geosynclines there are three stages of development. The first stage - the inception of geosynclinal belt. At this time, a large area of the earth's crust bends and at this point formed a saltwater pool. The second stage - folding. At this time, there is an intensive horizontal and vertical tectonic movements that crushes rocks into folds. The third stage - the formation of mountain ranges. At this stage in geosynclinal areas appeared deep breaks that seem to be divided into separate blocks geosyncline. For these faults, some blocks fell, others - were raised. So there were all well-known mountain ranges.
In the development of geosynclines there are three stages of development. The first stage - the inception of geosynclinal belt. At this time, a large area of the earth's crust bends and at this point formed a saltwater pool. The second stage - folding. At this time, there is an intensive horizontal and vertical tectonic movements that crushes rocks into folds. The third stage - the formation of mountain ranges. At this stage in geosynclinal areas appeared deep breaks that seem to be divided into separate blocks geosyncline. For these faults, some blocks fell, others - were raised. So there were all well-known mountain ranges.

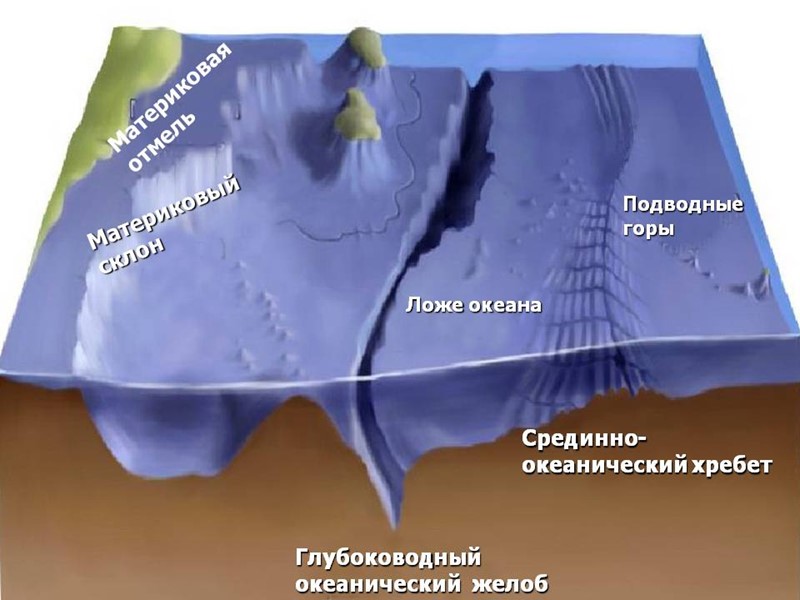
 Structural elements of the oceanic crust The topography of the ocean floor are the following most major structural elements: 1) underwater continental margins; 2) the seafloor; 3) mid-ocean ridges.
Structural elements of the oceanic crust The topography of the ocean floor are the following most major structural elements: 1) underwater continental margins; 2) the seafloor; 3) mid-ocean ridges.
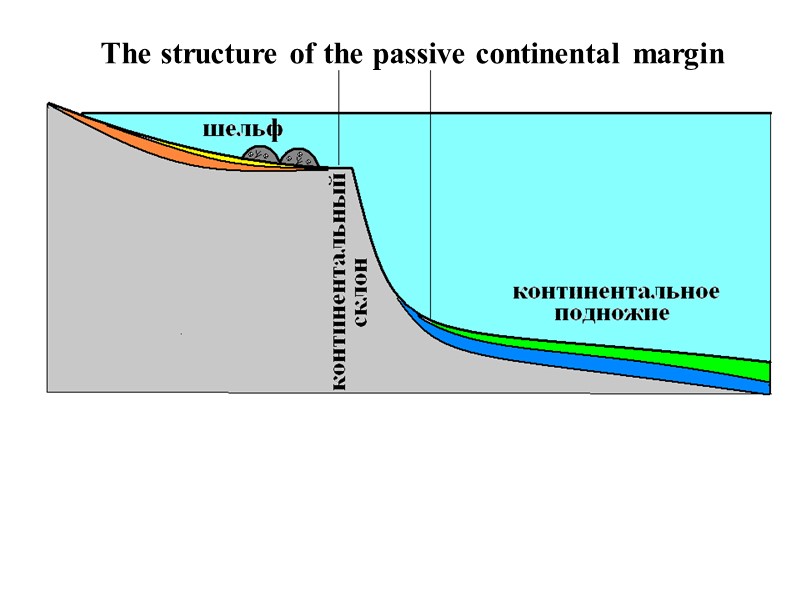
 Underwater continental margins are divided into two types - Atlantic (passive) and Pacific (active). In the morphology of the passive type of submarine continental margins distinguished: 1) shelf; 2) the continental slope; 3) Continental foot. shelf immediately adjacent to the land and is a shallow part of the sea basin. Slope of the bottom shelf is about 1 °. continental slope is a narrow zone of the seabed, limiting the shelf from the ocean and lowered to a depth of 2.0-2.5 km.
Underwater continental margins are divided into two types - Atlantic (passive) and Pacific (active). In the morphology of the passive type of submarine continental margins distinguished: 1) shelf; 2) the continental slope; 3) Continental foot. shelf immediately adjacent to the land and is a shallow part of the sea basin. Slope of the bottom shelf is about 1 °. continental slope is a narrow zone of the seabed, limiting the shelf from the ocean and lowered to a depth of 2.0-2.5 km.
 The structure of the passive continental margin
The structure of the passive continental margin
 The surface of the continental slopes indented with numerous submarine canyons - a deep ravine with steep steep slopes and flat bottom. They are the result of the activity of bottom turbidity currents occurring at the edge of the shelf when the tsunami and earthquake. continental foot– пологонаклонная, slightly undulating plain, which occupies an intermediate position between the continental slope and ocean floor.
The surface of the continental slopes indented with numerous submarine canyons - a deep ravine with steep steep slopes and flat bottom. They are the result of the activity of bottom turbidity currents occurring at the edge of the shelf when the tsunami and earthquake. continental foot– пологонаклонная, slightly undulating plain, which occupies an intermediate position between the continental slope and ocean floor.
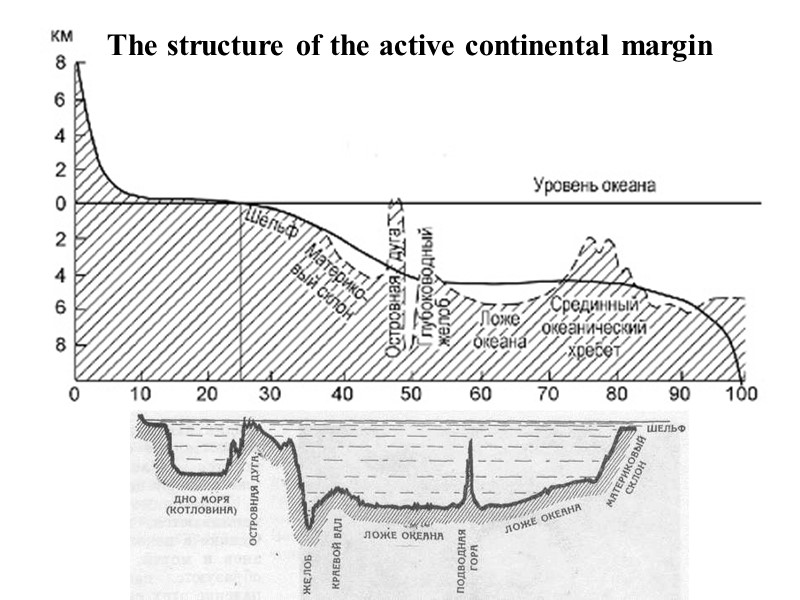
 Active continental margin characterized by high fragmentation of the topography and high tectonic activity, ie, intense volcanic eruptions, earthquakes. The transition from the continent to the seafloor is more complicated. It is implemented through the island arcs and trenches. island arc– mountain structures protruding above the level of the sea basin with their tops in the form of islands. trenches– narrow, deep depressions large extent.
Active continental margin characterized by high fragmentation of the topography and high tectonic activity, ie, intense volcanic eruptions, earthquakes. The transition from the continent to the seafloor is more complicated. It is implemented through the island arcs and trenches. island arc– mountain structures protruding above the level of the sea basin with their tops in the form of islands. trenches– narrow, deep depressions large extent.
 The structure of the active continental margin
The structure of the active continental margin
 ocean bed occupies more than 50% of the surface of the oceans. It is located at depths ranging from 3.5 to 6.0 thousand. M. Large areas of oceanic crust busy deep-water basin. Their relatively flat bottom is covered with a layer of red clay. On the ocean floor in places solitary hill climb with flat tops. This guyots - ancient volcanoes. Their cones once towered above the water, but as a result of tectonic processes they were at a considerable depth. Guyot especially numerous in the western Pacific Ocean. For example, the Hawaiian Islands are a basaltic volcanoes.
ocean bed occupies more than 50% of the surface of the oceans. It is located at depths ranging from 3.5 to 6.0 thousand. M. Large areas of oceanic crust busy deep-water basin. Their relatively flat bottom is covered with a layer of red clay. On the ocean floor in places solitary hill climb with flat tops. This guyots - ancient volcanoes. Their cones once towered above the water, but as a result of tectonic processes they were at a considerable depth. Guyot especially numerous in the western Pacific Ocean. For example, the Hawaiian Islands are a basaltic volcanoes.


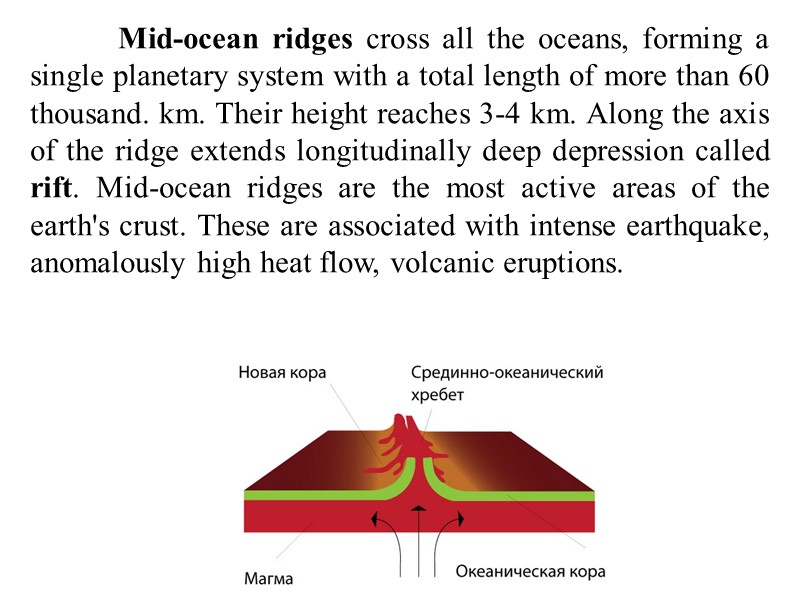
 Mid-ocean ridges cross all the oceans, forming a single planetary system with a total length of more than 60 thousand. km. Their height reaches 3-4 km. Along the axis of the ridge extends longitudinally deep depression called rift. Mid-ocean ridges are the most active areas of the earth's crust. These are associated with intense earthquake, anomalously high heat flow, volcanic eruptions.
Mid-ocean ridges cross all the oceans, forming a single planetary system with a total length of more than 60 thousand. km. Their height reaches 3-4 km. Along the axis of the ridge extends longitudinally deep depression called rift. Mid-ocean ridges are the most active areas of the earth's crust. These are associated with intense earthquake, anomalously high heat flow, volcanic eruptions.
 Quiz Structural-tectonic elements platforms. he structure and characteristics of the formation of geosynclinal regions. The structure of the active continental margins. The structure of the passive continental margins. The structure of the ocean floor. Mid-ocean ridges.
Quiz Structural-tectonic elements platforms. he structure and characteristics of the formation of geosynclinal regions. The structure of the active continental margins. The structure of the passive continental margins. The structure of the ocean floor. Mid-ocean ridges.
 http://zilant.kpfu.ru/kek/geotektonika/13.php http://kafgeo.igpu.ru/web-text-books/geology/r3-2.htm http://www.borshec.ru/pages-15.html http://egfak.narod.ru/eastplat.htm http://www.geoglobus.ru/info/review28/physiography_23.php При составлении презентации использовался материал с сайтов:
http://zilant.kpfu.ru/kek/geotektonika/13.php http://kafgeo.igpu.ru/web-text-books/geology/r3-2.htm http://www.borshec.ru/pages-15.html http://egfak.narod.ru/eastplat.htm http://www.geoglobus.ru/info/review28/physiography_23.php При составлении презентации использовался материал с сайтов:

