SEWP ZC 241: PRINCIPLES OF MANAGEMENT Human





















































00_human_resource_management_amp_selection.ppt
- Размер: 4.9 Mегабайта
- Количество слайдов: 75
Описание презентации SEWP ZC 241: PRINCIPLES OF MANAGEMENT Human по слайдам
 SEWP ZC 241: PRINCIPLES OF MANAGEMENT Human Resource Management & Selection
SEWP ZC 241: PRINCIPLES OF MANAGEMENT Human Resource Management & Selection
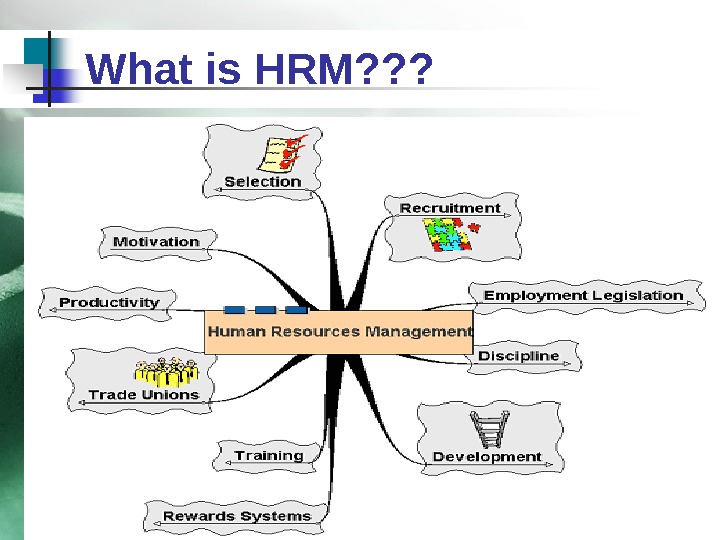
 What is HRM? ? ?
What is HRM? ? ?
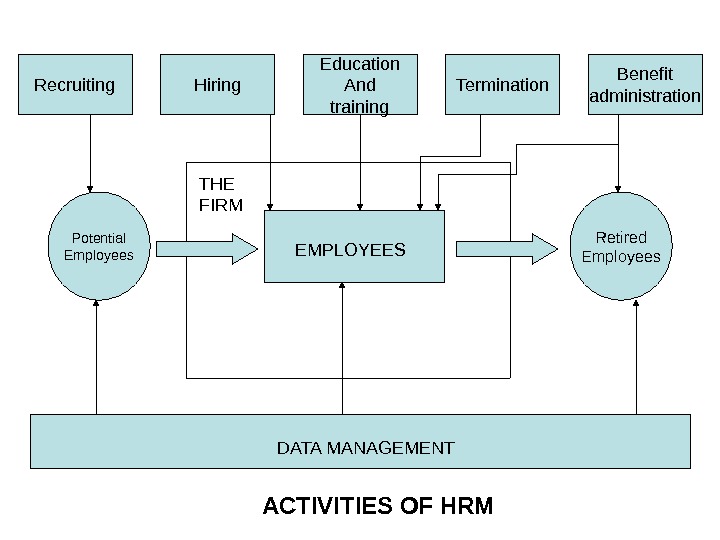
 Potential Employees Retired Employees. Recruiting Hiring Education And training Termination Benefit administration ACTIVITIES OF HRM DATA MANAGEMENT EMPLOYEESTHE FIRM
Potential Employees Retired Employees. Recruiting Hiring Education And training Termination Benefit administration ACTIVITIES OF HRM DATA MANAGEMENT EMPLOYEESTHE FIRM
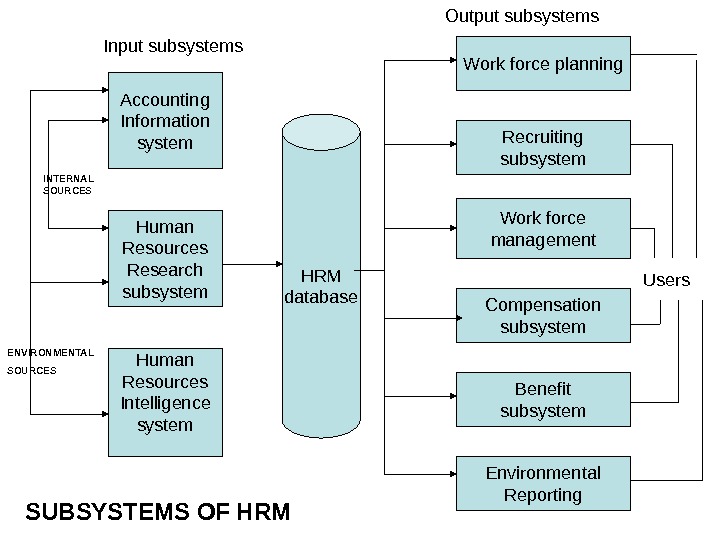
 Work force planning Recruiting subsystem Work force management Compensation subsystem Benefit subsystem Environmental Reporting. HRM database. Accounting Information system Human Resources Research subsystem Human Resources Intelligence system Users. Input subsystems Output subsystems SUBSYSTEMS OF HRMENVIRONMENTAL SOURCES INTERNAL SOURCES
Work force planning Recruiting subsystem Work force management Compensation subsystem Benefit subsystem Environmental Reporting. HRM database. Accounting Information system Human Resources Research subsystem Human Resources Intelligence system Users. Input subsystems Output subsystems SUBSYSTEMS OF HRMENVIRONMENTAL SOURCES INTERNAL SOURCES
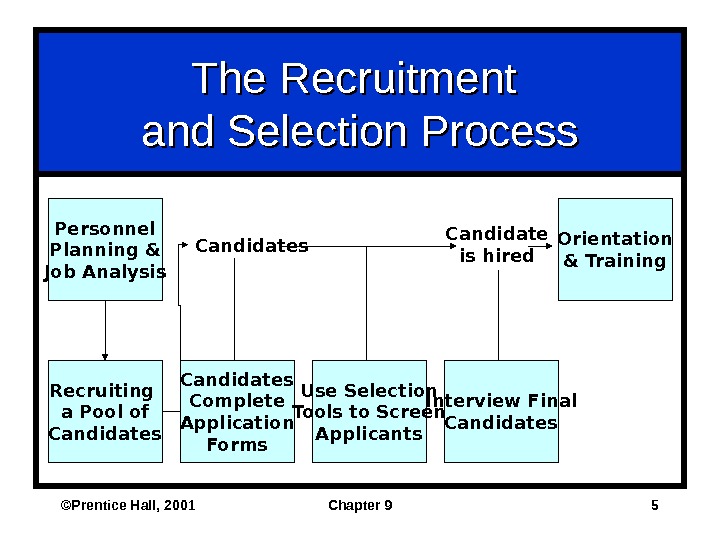
 ©Prentice Hall, 2001 Chapter 9 5 The Recruitment and Selection Process Personnel Planning & Job Analysis Recruiting a Pool of Candidates Orientation & Training. Candidate is hired Candidates Complete Application Forms Use Selection Tools to Screen Applicants Interview Final Candidates
©Prentice Hall, 2001 Chapter 9 5 The Recruitment and Selection Process Personnel Planning & Job Analysis Recruiting a Pool of Candidates Orientation & Training. Candidate is hired Candidates Complete Application Forms Use Selection Tools to Screen Applicants Interview Final Candidates
 ©Prentice Hall, 2001 Chapter 9 6 Staffing the Organization
©Prentice Hall, 2001 Chapter 9 6 Staffing the Organization
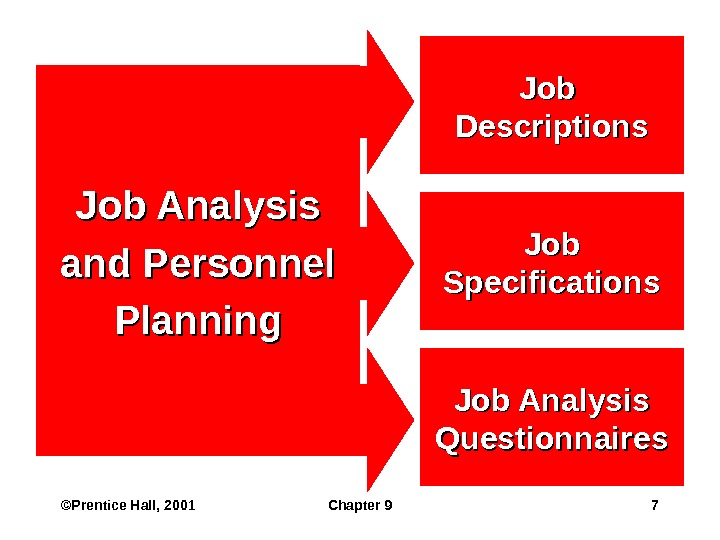
 ©Prentice Hall, 2001 Chapter 9 7 Job Analysis and Personnel Planning Job Specifications Job Descriptions Job Analysis Questionnaires
©Prentice Hall, 2001 Chapter 9 7 Job Analysis and Personnel Planning Job Specifications Job Descriptions Job Analysis Questionnaires
 ©Prentice Hall, 2001 Chapter 9 8 Employee Recruiting • Current employees • Advertising • Employment agencies • Temporary help agencies • Executive recruiters • Referrals and walk-ins • College recruiting • Workforce diversity
©Prentice Hall, 2001 Chapter 9 8 Employee Recruiting • Current employees • Advertising • Employment agencies • Temporary help agencies • Executive recruiters • Referrals and walk-ins • College recruiting • Workforce diversity
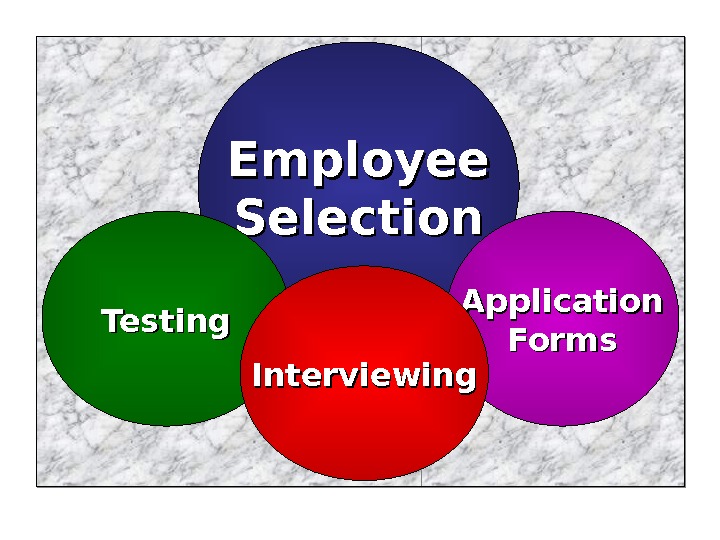
 Employee Selection Application Forms. Testing Interviewing
Employee Selection Application Forms. Testing Interviewing
 Interviewing Guidelines Plan the Interview Establish Rapport Ask Questions Close the Interview Review
Interviewing Guidelines Plan the Interview Establish Rapport Ask Questions Close the Interview Review
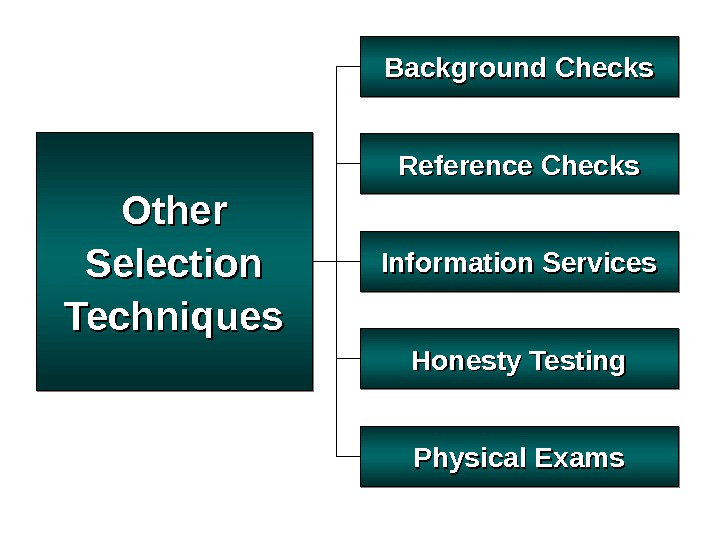
 Other Selection Techniques Background Checks Physical Exams. Reference Checks Honesty Testing. Information Services
Other Selection Techniques Background Checks Physical Exams. Reference Checks Honesty Testing. Information Services
 Preparing Employees to Do Their Jobs Orientation Training
Preparing Employees to Do Their Jobs Orientation Training
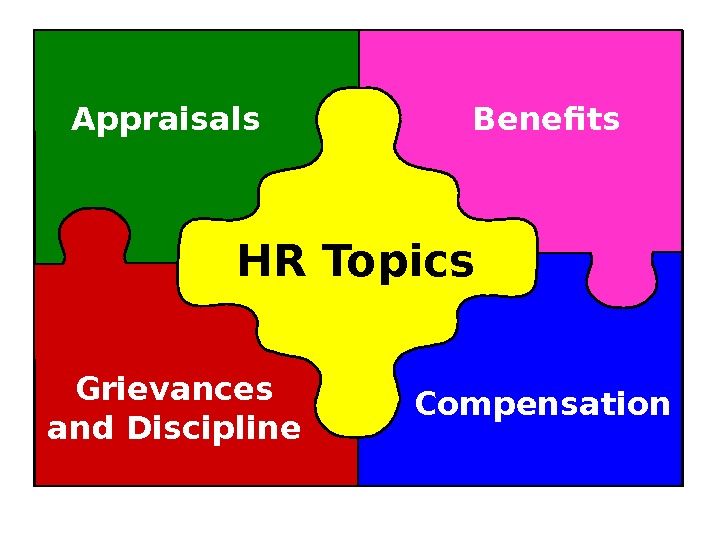
 HR Topics. Appraisals Benefits Compensation. Grievances and Discipline
HR Topics. Appraisals Benefits Compensation. Grievances and Discipline
 ©Prentice Hall, 2001 Chapter 9 14 • Equal Employment Laws • Affirmative Action Programs • Sexual Harassment • Occupational Safety and Health • Labor-Management Relations • Other Employment Law Issues Human Resources Legal Framework
©Prentice Hall, 2001 Chapter 9 14 • Equal Employment Laws • Affirmative Action Programs • Sexual Harassment • Occupational Safety and Health • Labor-Management Relations • Other Employment Law Issues Human Resources Legal Framework
 Human Resource Management (HRM) concerns with getting, training, motivating and keeping competent employees. Human Resource Management. Overview: definition and significance
Human Resource Management (HRM) concerns with getting, training, motivating and keeping competent employees. Human Resource Management. Overview: definition and significance
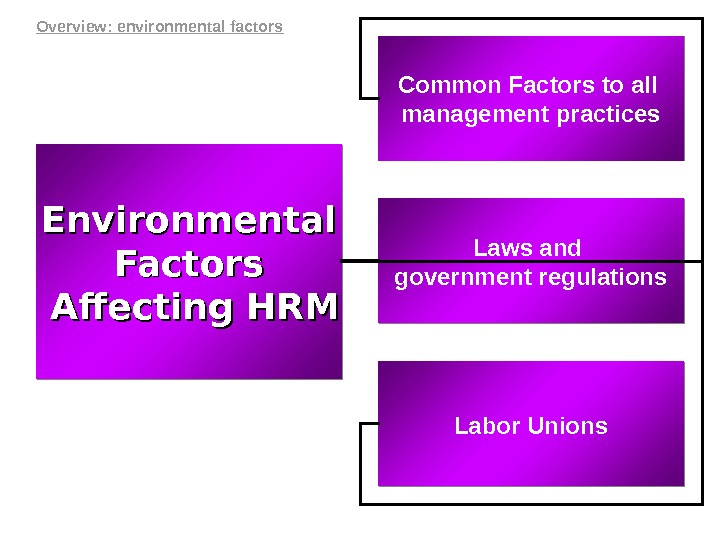
 Common Factors to all management practices Environmental Factors Affecting HRMAffecting HRM Laws and government regulations Labor Unions. Overview: environmental factors
Common Factors to all management practices Environmental Factors Affecting HRMAffecting HRM Laws and government regulations Labor Unions. Overview: environmental factors
 The Legal Environment of HRM Affirmative Action Employment Training Retention. Overview: environmental factors
The Legal Environment of HRM Affirmative Action Employment Training Retention. Overview: environmental factors
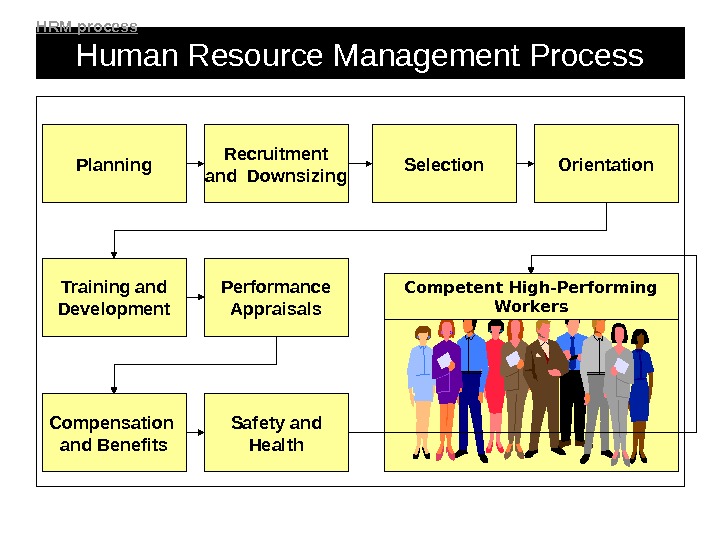
 Human Resource Management Process Planning Recruitment and Downsizing Selection Orientation Training and Development Performance Appraisals Safety and Health. Compensation and Benefits Competent High-Performing Workers. HRM process
Human Resource Management Process Planning Recruitment and Downsizing Selection Orientation Training and Development Performance Appraisals Safety and Health. Compensation and Benefits Competent High-Performing Workers. HRM process
 Human Resource. Human Resource Planning Making a Future Assessment. Making a Current Assessment Designing a Future Program. HRM process: planning
Human Resource. Human Resource Planning Making a Future Assessment. Making a Current Assessment Designing a Future Program. HRM process: planning
 Human Resource Inventory Report Job Description. Job Analysis Job Specification
Human Resource Inventory Report Job Description. Job Analysis Job Specification
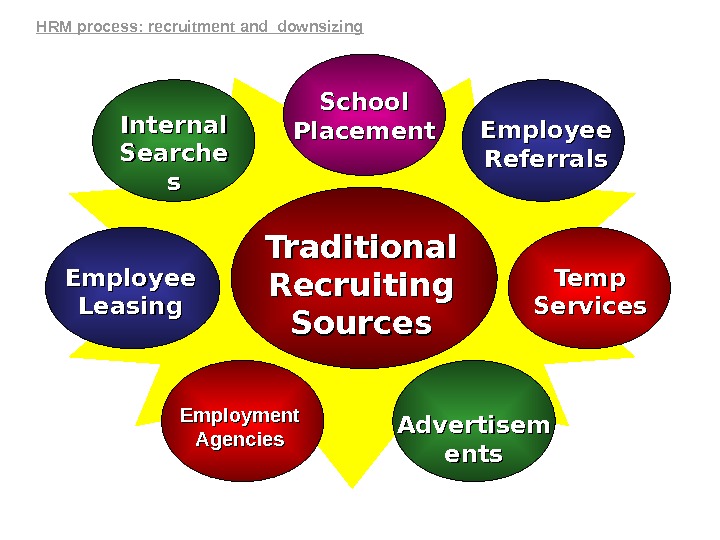
 Traditional Recruiting Sources. Internal Searche ss Employee Referrals Employee Leasing Temp Services Employment Agencies Advertisem ents. School Placement. HRM process: recruitment and downsizing
Traditional Recruiting Sources. Internal Searche ss Employee Referrals Employee Leasing Temp Services Employment Agencies Advertisem ents. School Placement. HRM process: recruitment and downsizing
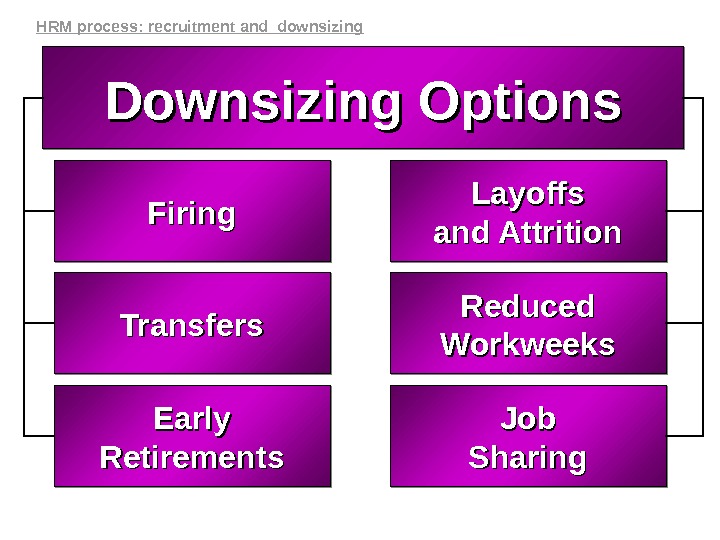
 Firing Layoffs and Attritionand Attrition Transfers Reduced Workweeks Job Sharing. Early Retirements Downsizing Options. HRM process: recruitment and downsizing
Firing Layoffs and Attritionand Attrition Transfers Reduced Workweeks Job Sharing. Early Retirements Downsizing Options. HRM process: recruitment and downsizing
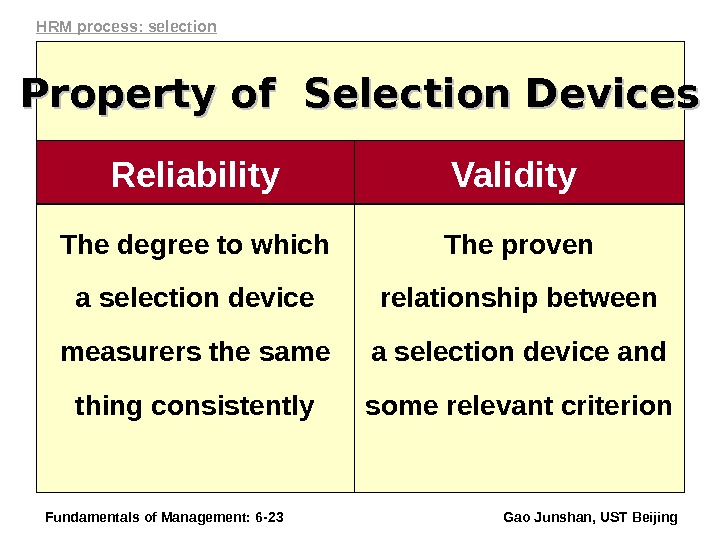
 Fundamentals of Management: 6 — 23 Gao Junshan, UST Beijing. The proven relationship between a selection device and some relevant criterion Validity Reliability The degree to which a selection device measurers the same thing consistently. Property of Selection Devices HRM process: selection
Fundamentals of Management: 6 — 23 Gao Junshan, UST Beijing. The proven relationship between a selection device and some relevant criterion Validity Reliability The degree to which a selection device measurers the same thing consistently. Property of Selection Devices HRM process: selection
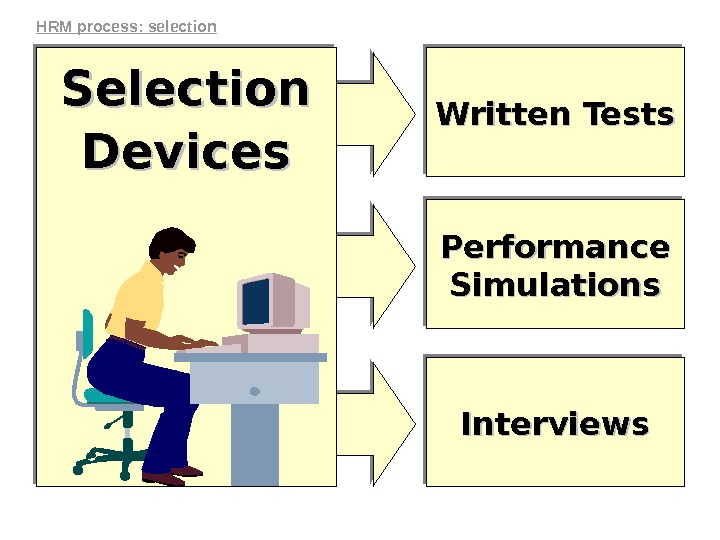
 Written Tests Performance Simulations Interviews. Selection Devices. HRM process: selection
Written Tests Performance Simulations Interviews. Selection Devices. HRM process: selection
 The Effectiveness of Interviews • Prior knowledge about an applicant • Attitude of the interviewer • The order of the interview • Negative information • The first five minutes • The content of the interview • The validity of the interview • Structured versus unstructured interviews. HRM process: selection
The Effectiveness of Interviews • Prior knowledge about an applicant • Attitude of the interviewer • The order of the interview • Negative information • The first five minutes • The content of the interview • The validity of the interview • Structured versus unstructured interviews. HRM process: selection
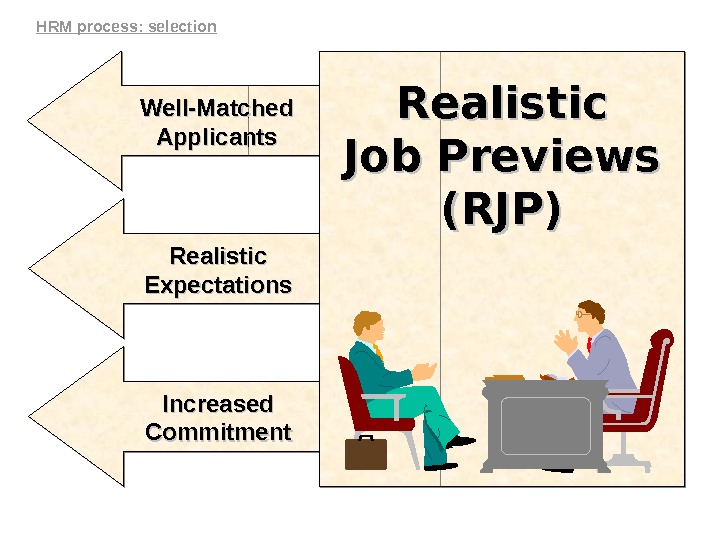
 Well-Matched. Well-Matched Applicants Realistic Expectations Increased Commitment Realistic Job Previews (RJP)(RJP)HRM process: selection
Well-Matched. Well-Matched Applicants Realistic Expectations Increased Commitment Realistic Job Previews (RJP)(RJP)HRM process: selection
 Fundamentals of Management: 6 — 27 Gao Junshan, UST Beijing. Employee Orientation Smooth Insider-Outsider Transition Familiar with the job and its environment Reduce initial anxiety. HRM process: orientation
Fundamentals of Management: 6 — 27 Gao Junshan, UST Beijing. Employee Orientation Smooth Insider-Outsider Transition Familiar with the job and its environment Reduce initial anxiety. HRM process: orientation
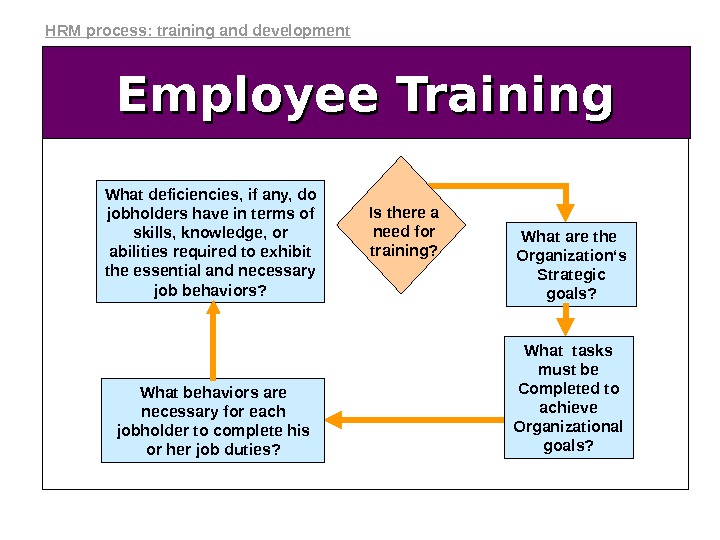
 Employee Training What deficiencies, if any, do jobholders have in terms of skills, knowledge, or abilities required to exhibit the essential and necessary job behaviors? What behaviors are necessary for each jobholder to complete his or her job duties? What tasks must be Completed to achieve Organizational goals? What are the Organization‘s Strategic goals? Is there a need for training? HRM process: training and development
Employee Training What deficiencies, if any, do jobholders have in terms of skills, knowledge, or abilities required to exhibit the essential and necessary job behaviors? What behaviors are necessary for each jobholder to complete his or her job duties? What tasks must be Completed to achieve Organizational goals? What are the Organization‘s Strategic goals? Is there a need for training? HRM process: training and development
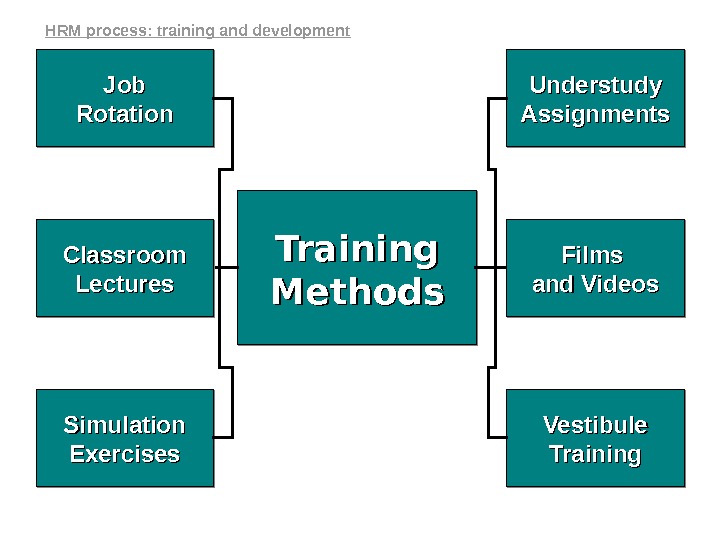
 Training Methods. Job Rotation Simulation Exercises. Classroom Lectures Understudy Assignments Vestibule Training Films and Videosand Videos. HRM process: training and development
Training Methods. Job Rotation Simulation Exercises. Classroom Lectures Understudy Assignments Vestibule Training Films and Videosand Videos. HRM process: training and development
 Fundamentals of Management: 6 — 30 Gao Junshan, UST Beijing. Performance Management • Performance management system is a process of – Establishing standards and – Evaluating performance • The purpose of performance management is to – Arrive at objective human resource decisions and – Provide documentation to support any personnel actions • Evaluation of the employees performance can be done by – Comparing against some set of performance standards – Comparing employees with one another – Measuring the work on the bases of preset objectives. HRM process: performance management
Fundamentals of Management: 6 — 30 Gao Junshan, UST Beijing. Performance Management • Performance management system is a process of – Establishing standards and – Evaluating performance • The purpose of performance management is to – Arrive at objective human resource decisions and – Provide documentation to support any personnel actions • Evaluation of the employees performance can be done by – Comparing against some set of performance standards – Comparing employees with one another – Measuring the work on the bases of preset objectives. HRM process: performance management
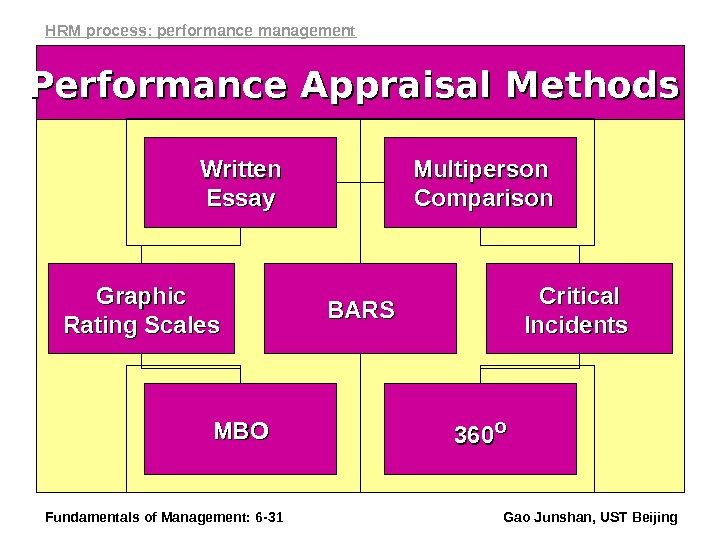
 Fundamentals of Management: 6 — 31 Gao Junshan, UST Beijing. Performance Appraisal Methods Critical Incidents Graphic Rating Scales Multiperson Comparison. Written Essay BARS 360360 oo MBOMBOHRM process: performance management
Fundamentals of Management: 6 — 31 Gao Junshan, UST Beijing. Performance Appraisal Methods Critical Incidents Graphic Rating Scales Multiperson Comparison. Written Essay BARS 360360 oo MBOMBOHRM process: performance management
 Employee Counseling. Discipline Actions Performance Problems on the Job. HRM process: performance management
Employee Counseling. Discipline Actions Performance Problems on the Job. HRM process: performance management
 Determining Benefits. Determining Pay Levels Administration of Employee Compensation. HRM process: compensation and benefits
Determining Benefits. Determining Pay Levels Administration of Employee Compensation. HRM process: compensation and benefits
 Factors Influencing Pay Level • Knowledge, skills, abilities • Authority and responsibility • Nature of the business • The environment • Geographic location • Performance levels • Seniority of the employee • Compensation philosophy. HRM process: compensation and benefits
Factors Influencing Pay Level • Knowledge, skills, abilities • Authority and responsibility • Nature of the business • The environment • Geographic location • Performance levels • Seniority of the employee • Compensation philosophy. HRM process: compensation and benefits
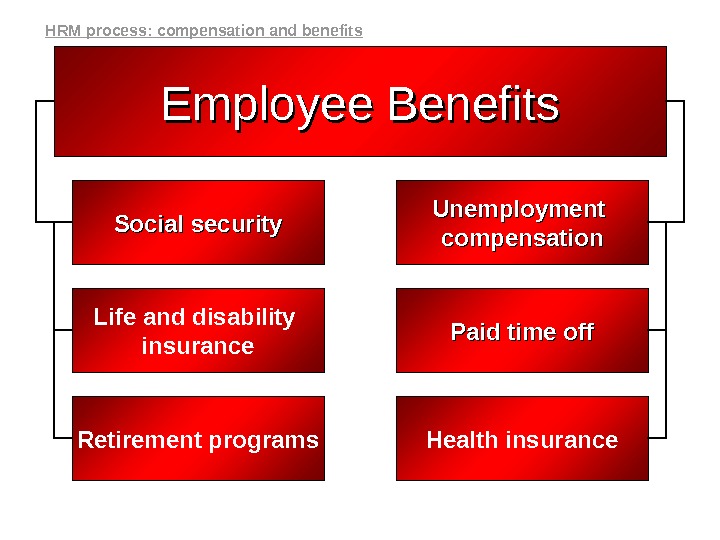
 Employee Benefits Social security Unemployment compensation Life and disability insurance Paid time off Retirement programs Health insurance. HRM process: compensation and benefits
Employee Benefits Social security Unemployment compensation Life and disability insurance Paid time off Retirement programs Health insurance. HRM process: compensation and benefits
 Workforce Diversity Sexual Harassment. Current HRM Issues. Current issues: Workforce diversity, sexual harassment
Workforce Diversity Sexual Harassment. Current HRM Issues. Current issues: Workforce diversity, sexual harassment
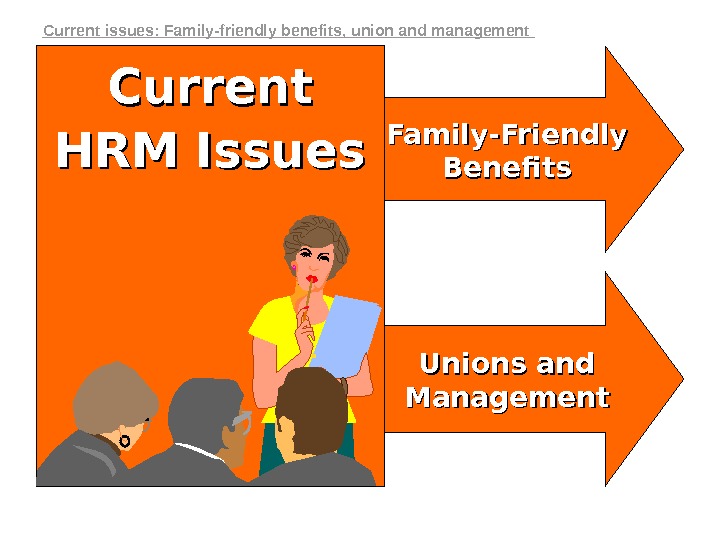
 Family-Friendly Benefits Unions and Management. Current HRM Issues. Current issues: Family-friendly benefits, union and management
Family-Friendly Benefits Unions and Management. Current HRM Issues. Current issues: Family-friendly benefits, union and management
 Workplace Violence Survivors of Layoffs. Current HRM Issues. Current issues: Workforce violence, survivors of layoffs
Workplace Violence Survivors of Layoffs. Current HRM Issues. Current issues: Workforce violence, survivors of layoffs
 Outsourcing Contingent Workforce. Current HRM Issues. Current issues: Outsourcing and use of contingent workforce (See chap 2 p 66)
Outsourcing Contingent Workforce. Current HRM Issues. Current issues: Outsourcing and use of contingent workforce (See chap 2 p 66)
 HUMAN RESOURCES MANAGEMENT • Set of Organizational activities directed at attracting, developing, and maintaining an effective workforce • The process of acquiring, training, terminating, developing, and properly using the human resources in an organization
HUMAN RESOURCES MANAGEMENT • Set of Organizational activities directed at attracting, developing, and maintaining an effective workforce • The process of acquiring, training, terminating, developing, and properly using the human resources in an organization
 The HRM Process 1. Human Resource Planning: Forecasting Demand Supply and Job Analysis 2. Staffing the Organization: Recruitment, Selecting, and Orientation 3. Developing the Workforce: Training and Performance Appraisal 4. Compensation and Benefit: Wages and Salaries, Incentive and Benefit Program
The HRM Process 1. Human Resource Planning: Forecasting Demand Supply and Job Analysis 2. Staffing the Organization: Recruitment, Selecting, and Orientation 3. Developing the Workforce: Training and Performance Appraisal 4. Compensation and Benefit: Wages and Salaries, Incentive and Benefit Program
 Human Resource Planning Job Analysis – determining the tasks, the skills, abilities and responsibilities needed to perform the job • Job Description – a statement about a job’s duties • Job Specification – A statement of the human qualification needed to perform a job
Human Resource Planning Job Analysis – determining the tasks, the skills, abilities and responsibilities needed to perform the job • Job Description – a statement about a job’s duties • Job Specification – A statement of the human qualification needed to perform a job
 Human Resource Planning Forecasting the demand — estimating the personnel needs of organization Forecasting the supply of labour: • Internal Supply • External Supply Matching Demand with Supply
Human Resource Planning Forecasting the demand — estimating the personnel needs of organization Forecasting the supply of labour: • Internal Supply • External Supply Matching Demand with Supply

 Recruiting Recruitment – Steps taken to staff an organization with the best qualified people Sources: • Internal recruiting • External recruiting from worker unions, university, employment agencies
Recruiting Recruitment – Steps taken to staff an organization with the best qualified people Sources: • Internal recruiting • External recruiting from worker unions, university, employment agencies
 Selection and Orientation Selection – evaluating and choosing the candidates. Selection Process: application form, Tests, and Interview Orientation – A procedure for providing new employees with basic background information about the firm
Selection and Orientation Selection – evaluating and choosing the candidates. Selection Process: application form, Tests, and Interview Orientation – A procedure for providing new employees with basic background information about the firm
 Training and Development • Training – supplying the skills, knowledge, and attitudes needed by employees to improve their abilities to perform their job On-the Job Training Off-the Job Training • Development – preparing someone for the new and greater challenges and more demanding job
Training and Development • Training – supplying the skills, knowledge, and attitudes needed by employees to improve their abilities to perform their job On-the Job Training Off-the Job Training • Development – preparing someone for the new and greater challenges and more demanding job
 Performance Appraisal – appraising the employee’s performance in relation to job standards and then providing feedback to the employee Methods: • Subjective Performance appraisal – performance criteria and rating scale are not defined • Objective Performance Appraisal – performance criteria and the method of measurement are specifically defined
Performance Appraisal – appraising the employee’s performance in relation to job standards and then providing feedback to the employee Methods: • Subjective Performance appraisal – performance criteria and rating scale are not defined • Objective Performance Appraisal – performance criteria and the method of measurement are specifically defined
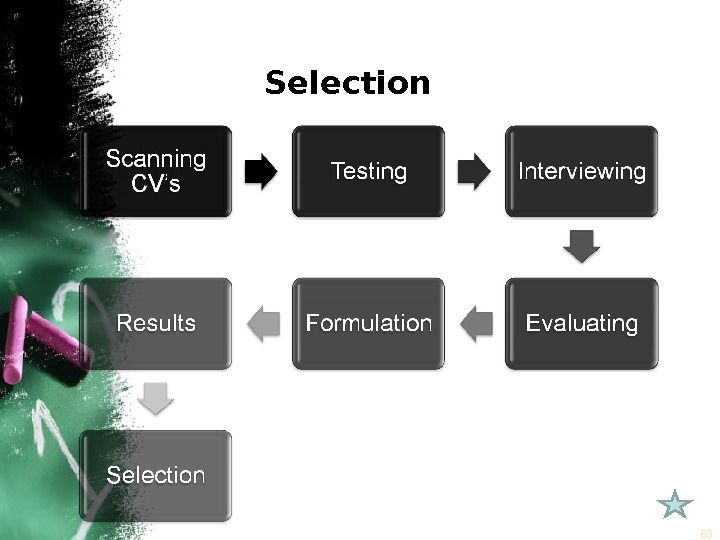
 SELECTION
SELECTION
 WHAT IS HUMAN RESOURCE?
WHAT IS HUMAN RESOURCE?
 Have a nice weekend!
Have a nice weekend!
 The Flow • Definition • Approaches and their Implications • Functions • Emerging Roles • Challenges • Strategic HR Management • In a Nutshell 04/01/16 Free template from www. brainybetty. com
The Flow • Definition • Approaches and their Implications • Functions • Emerging Roles • Challenges • Strategic HR Management • In a Nutshell 04/01/16 Free template from www. brainybetty. com
 Definition Human resource management is the function performed in an organization that facilitates the most effective use of people(employees) to achieve organizational and individual goals 04/01/16 Free template from www. brainybetty. com
Definition Human resource management is the function performed in an organization that facilitates the most effective use of people(employees) to achieve organizational and individual goals 04/01/16 Free template from www. brainybetty. com
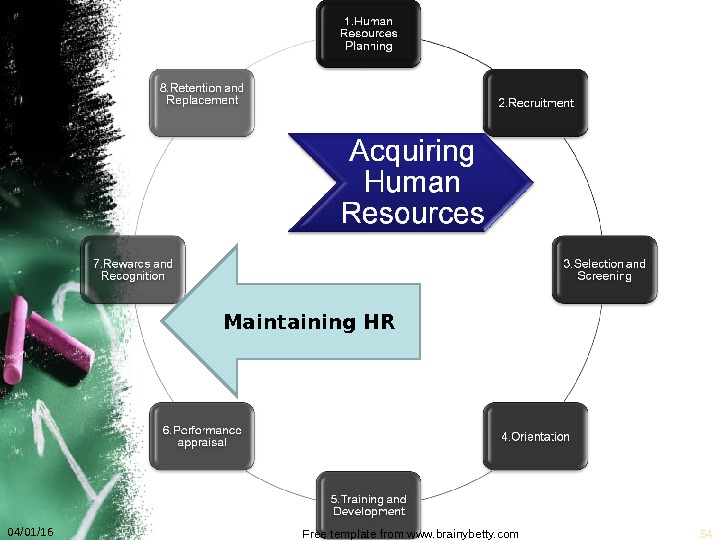
 04/01/16 Free template from www. brainybetty. com 54 Maintaining HR
04/01/16 Free template from www. brainybetty. com 54 Maintaining HR
 Scientific management approach 04/01/16 Free template from www. brainybetty. com
Scientific management approach 04/01/16 Free template from www. brainybetty. com
 Human relations approach 04/01/16 Free template from www. brainybetty. com
Human relations approach 04/01/16 Free template from www. brainybetty. com
 Why human relations approach Failed ? ? 04/01/16 Free template from www. brainybetty. com
Why human relations approach Failed ? ? 04/01/16 Free template from www. brainybetty. com
 Human Resources Approach • Organization goal & needs of employee are capable of existing in harmony • Employees are asset for organization • Organization should create contributive work environment to reap maximum benefit 04/01/16 Free template from www. brainybetty. com
Human Resources Approach • Organization goal & needs of employee are capable of existing in harmony • Employees are asset for organization • Organization should create contributive work environment to reap maximum benefit 04/01/16 Free template from www. brainybetty. com
 Challenges Before HR Manager 04/01/16 Free template from www. brainybetty. com
Challenges Before HR Manager 04/01/16 Free template from www. brainybetty. com
 Operative Functions
Operative Functions
 Employment
Employment
 Human Resource Planning • Present and future manpower requirements • Net human resource requirements • Mould, change and develop employees to meet future organizational requirements • Attract and acquire human resources from the market
Human Resource Planning • Present and future manpower requirements • Net human resource requirements • Mould, change and develop employees to meet future organizational requirements • Attract and acquire human resources from the market
 Selection
Selection
 Human Resource Development
Human Resource Development
 Compensation
Compensation
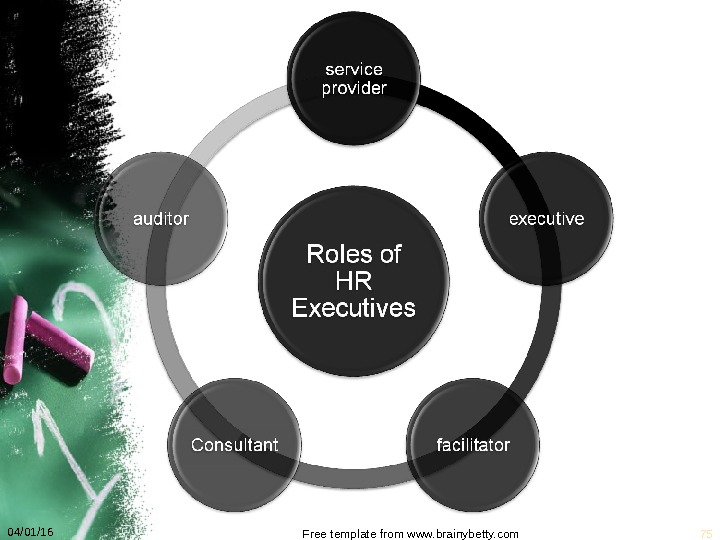
 Emerging Role of Human Resource Management It is the competence and attitude of the human resource that can make or break a business. 04/01/16 Free template from www. brainybetty. com
Emerging Role of Human Resource Management It is the competence and attitude of the human resource that can make or break a business. 04/01/16 Free template from www. brainybetty. com
 Value of Human Resources 04/01/16 Free template from www. brainybetty. com
Value of Human Resources 04/01/16 Free template from www. brainybetty. com
 Human resources- A competitive advantage 04/01/16 Free template from www. brainybetty. com
Human resources- A competitive advantage 04/01/16 Free template from www. brainybetty. com
 Human resource accounting 04/01/16 Free template from www. brainybetty. com
Human resource accounting 04/01/16 Free template from www. brainybetty. com
 04/01/16 Free template from www. brainybetty. com
04/01/16 Free template from www. brainybetty. com
 THE CHALLENGES 04/01/16 Free template from www. brainybetty. com
THE CHALLENGES 04/01/16 Free template from www. brainybetty. com
 04/01/16 Free template from www. brainybetty. com 72 STRATEGIC HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
04/01/16 Free template from www. brainybetty. com 72 STRATEGIC HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
 04/01/16 Free template from www. brainybetty. com
04/01/16 Free template from www. brainybetty. com
 IN A NUTSHELL 04/01/16 Free template from www. brainybetty. com
IN A NUTSHELL 04/01/16 Free template from www. brainybetty. com
 04/01/16 Free template from www. brainybetty. com
04/01/16 Free template from www. brainybetty. com

