© SAP AGSales and Distribution (SD)SAP University Alliances













































04_intro_erp_using_gbi_slides_sd_en_v2_01_aris.ppt
- Размер: 756 Кб
- Количество слайдов: 49
Описание презентации © SAP AGSales and Distribution (SD)SAP University Alliances по слайдам
 © SAP AGSales and Distribution (SD)SAP University Alliances Version 2. 01 Authors Bret Wagner Stefan Weidner Hans-Jürgen Scheruhn Product SAP ERP 6. 0 Eh. P 4 Global Bike Inc. Level Beginner Focus Cross-functional integration Sales and Distribution In addition to the standard Sales and Distribution slides, this presentation includes links to business process models provided by a team at Hochschule Harz in Germany led by Prof. Dr. Hans-Jürgen Scheruhn. These business models represent the processes in the case study 100% and thus facilitate an integrated view on data, functions and persons responsible. Each link in the presentation is indicated by the symbol . A list of all links can be found on the second last page.
© SAP AGSales and Distribution (SD)SAP University Alliances Version 2. 01 Authors Bret Wagner Stefan Weidner Hans-Jürgen Scheruhn Product SAP ERP 6. 0 Eh. P 4 Global Bike Inc. Level Beginner Focus Cross-functional integration Sales and Distribution In addition to the standard Sales and Distribution slides, this presentation includes links to business process models provided by a team at Hochschule Harz in Germany led by Prof. Dr. Hans-Jürgen Scheruhn. These business models represent the processes in the case study 100% and thus facilitate an integrated view on data, functions and persons responsible. Each link in the presentation is indicated by the symbol . A list of all links can be found on the second last page.
 SAP ERPPage 4 — 2 © SAP AG Course Overview Introduction to SAP Navigation Introduction to GBI Sales & Distribution Materials Management Production Planning Financial Accounting Controlling
SAP ERPPage 4 — 2 © SAP AG Course Overview Introduction to SAP Navigation Introduction to GBI Sales & Distribution Materials Management Production Planning Financial Accounting Controlling
 SAP ERPPage 4 — 3 © SAP AG Functionality Sales Support Sales Shipping and Transportation Billing Credit Management Foreign Trade
SAP ERPPage 4 — 3 © SAP AG Functionality Sales Support Sales Shipping and Transportation Billing Credit Management Foreign Trade
 SAP ERPPage 4 — 4 © SAP AG Unit Overview SD Organizational Structure SD Master Data SD Processes — Order-to-Cash Process
SAP ERPPage 4 — 4 © SAP AG Unit Overview SD Organizational Structure SD Master Data SD Processes — Order-to-Cash Process
 SAP ERPPage 4 — 5 © SAP AG SD Organizational Structure Client — An independent environment in the system Company Code — Smallest org unit for which you can maintain a legal set of books Credit Control Area — An organizational entity which grants and monitors a credit limit for customers. — It can include one or more company codes Sales Organization — An organizational unit responsible for the sale of certain products or services. — The responsibility of a sales organization may include legal liability for products and customer claims Distribution Channel — The way in which products or services reach the customer — Typical examples of distribution channels are wholesale, retail, or direct sales
SAP ERPPage 4 — 5 © SAP AG SD Organizational Structure Client — An independent environment in the system Company Code — Smallest org unit for which you can maintain a legal set of books Credit Control Area — An organizational entity which grants and monitors a credit limit for customers. — It can include one or more company codes Sales Organization — An organizational unit responsible for the sale of certain products or services. — The responsibility of a sales organization may include legal liability for products and customer claims Distribution Channel — The way in which products or services reach the customer — Typical examples of distribution channels are wholesale, retail, or direct sales
 SAP ERPPage 4 — 6 © SAP AG SD Organizational Structure Division — A way of grouping materials, products, or services Sales Area — Combination of Sales Organization, Distribution Channel and Division — Determines conditions (i. e. pricing) for sales activities Plant (here: Delivering Plant) — Plant from which the goods should be delivered to the customer Other SD organization units: — Shipping Point — Loading Point — Sales Office — Sales Group — Sales Person
SAP ERPPage 4 — 6 © SAP AG SD Organizational Structure Division — A way of grouping materials, products, or services Sales Area — Combination of Sales Organization, Distribution Channel and Division — Determines conditions (i. e. pricing) for sales activities Plant (here: Delivering Plant) — Plant from which the goods should be delivered to the customer Other SD organization units: — Shipping Point — Loading Point — Sales Office — Sales Group — Sales Person
 SAP ERPPage 4 — 7 © SAP AG GBI 2. 0 Structure for Sales and Distribution Global Bike Inc. Global Bike Germany Gmb. H US West US East San Diego Germany North Germany South Dallas Miami Hamburg Heidelberg Client Company Code Sales Organization Sales Office
SAP ERPPage 4 — 7 © SAP AG GBI 2. 0 Structure for Sales and Distribution Global Bike Inc. Global Bike Germany Gmb. H US West US East San Diego Germany North Germany South Dallas Miami Hamburg Heidelberg Client Company Code Sales Organization Sales Office
 SAP ERPPage 4 — 8 © SAP AG GBI 2. 0 Enterprise Structure in SAP ERP (Sales) Client GBI Credit Control Area (global) GL 00 CC US 00 US East UE 00 US West UW 00 CC CA 00 CA East CE 00 CA West CW 00 CC DE 00 DE South DS 00 DE North DN 00 CC GB 00 GB South GS 00 GB North GN 00 CC AU 00 AU South AS 00 AU North AN 00 Distribution Channel Wholesale WH Distribution Channel Internet IN D ivision B icycles B I D ivision A ccessories A S Sales Organisation Company Code
SAP ERPPage 4 — 8 © SAP AG GBI 2. 0 Enterprise Structure in SAP ERP (Sales) Client GBI Credit Control Area (global) GL 00 CC US 00 US East UE 00 US West UW 00 CC CA 00 CA East CE 00 CA West CW 00 CC DE 00 DE South DS 00 DE North DN 00 CC GB 00 GB South GS 00 GB North GN 00 CC AU 00 AU South AS 00 AU North AN 00 Distribution Channel Wholesale WH Distribution Channel Internet IN D ivision B icycles B I D ivision A ccessories A S Sales Organisation Company Code
 SAP ERPPage 4 — 9 © SAP AG SD Master Data Customer Master Material Master Sales Condition
SAP ERPPage 4 — 9 © SAP AG SD Master Data Customer Master Material Master Sales Condition
 SAP ERPPage 4 — 10 © SAP AG Customer Master Data Customer Master — Contains all of the information necessary for processing orders, deliveries, invoices and customer payment — Every customer MUST have a master record Created by Sales Area — Sales Organization — Distribution Channel — Division
SAP ERPPage 4 — 10 © SAP AG Customer Master Data Customer Master — Contains all of the information necessary for processing orders, deliveries, invoices and customer payment — Every customer MUST have a master record Created by Sales Area — Sales Organization — Distribution Channel — Division
 SAP ERPPage 4 — 11 © SAP AG Customer Master Data The customer master information is divided into 3 areas: — General Data — Company Code Data — Sales Area Data
SAP ERPPage 4 — 11 © SAP AG Customer Master Data The customer master information is divided into 3 areas: — General Data — Company Code Data — Sales Area Data
 SAP ERPPage 4 — 12 © SAP AG Customer Master Company Code US 00 Company Code DE 00 Client XXXGeneral Information relevant for the entire organization: Name Address Communication Company Code specific information : Acc. Mgmt Payment Bank Sales Area specific information : Sales Office Currency Sales Org. UW 00 Sales Org. DS
SAP ERPPage 4 — 12 © SAP AG Customer Master Company Code US 00 Company Code DE 00 Client XXXGeneral Information relevant for the entire organization: Name Address Communication Company Code specific information : Acc. Mgmt Payment Bank Sales Area specific information : Sales Office Currency Sales Org. UW 00 Sales Org. DS
 SAP ERPPage 4 — 13 © SAP AG Material Master Data Material Master — Contains all the information a company needs to manage about a material — It is used by most components within the SAP system • Sales and Distribution • Materials Management • Production • Plant Maintenance • Accounting/Controlling • Quality Management — Material master data is stored in functional segments called Views
SAP ERPPage 4 — 13 © SAP AG Material Master Data Material Master — Contains all the information a company needs to manage about a material — It is used by most components within the SAP system • Sales and Distribution • Materials Management • Production • Plant Maintenance • Accounting/Controlling • Quality Management — Material master data is stored in functional segments called Views
 SAP ERPPage 4 — 14 © SAP AG Material Master Views Material Master. Basic Data Sales Data Controlling Data Forecasting Data. Purchasing Data Mat. Plan. Data Accounting Data Storage Data Quality Data
SAP ERPPage 4 — 14 © SAP AG Material Master Views Material Master. Basic Data Sales Data Controlling Data Forecasting Data. Purchasing Data Mat. Plan. Data Accounting Data Storage Data Quality Data
 SAP ERPPage 4 — 15 © SAP AG Sales Org. UW 00 Sales Org. UE 00 Material Master Client XXXGeneral Information relevant for the entire organization: Name Weight Unit of Measure Sales specific information : Delivering Plant Loading Grp Storage Location specific information : Stock Qty Storage Loc. FG 00 Storage Loc. TG
SAP ERPPage 4 — 15 © SAP AG Sales Org. UW 00 Sales Org. UE 00 Material Master Client XXXGeneral Information relevant for the entire organization: Name Weight Unit of Measure Sales specific information : Delivering Plant Loading Grp Storage Location specific information : Stock Qty Storage Loc. FG 00 Storage Loc. TG
 SAP ERPPage 4 — 16 © SAP AG Condition Master Data (Pricing) Condition master data includes: — Prices — Surcharges — Discounts — Freights — Taxes You can define the condition master to be dependent on various data: — Material specific — Customer specific Conditions can be dependent on any document field
SAP ERPPage 4 — 16 © SAP AG Condition Master Data (Pricing) Condition master data includes: — Prices — Surcharges — Discounts — Freights — Taxes You can define the condition master to be dependent on various data: — Material specific — Customer specific Conditions can be dependent on any document field
 SAP ERPPage 4 — 17 © SAP AG Output is information that is sent to the customer using various media, such as: — E-mail — Mail — EDI — Fax — XML Output examples: — Quotation — Confirmation — Invoice
SAP ERPPage 4 — 17 © SAP AG Output is information that is sent to the customer using various media, such as: — E-mail — Mail — EDI — Fax — XML Output examples: — Quotation — Confirmation — Invoice
 SAP ERPPage 4 — 18 © SAP AG Sales Order Process Sales Order Entry Post Goods Issue. Invoice Customer Pick Materials Receipt of Customer Payment Pack Materials. Check Availability. Pre-sales Activities
SAP ERPPage 4 — 18 © SAP AG Sales Order Process Sales Order Entry Post Goods Issue. Invoice Customer Pick Materials Receipt of Customer Payment Pack Materials. Check Availability. Pre-sales Activities
 SAP ERPPage 4 — 19 © SAP AG Pre-Sales Activities (CRM Light) Sales Support is a component of SD that assists in the sales, distribution, and marketing of a companies products and services to its customers. It contains the following functionality: — Creating and tracking customer contacts and communications (sales activity) • Phone call records • On-site meeting • Letters • Campaign communication — Implementing and tracking direct mailing, internet, and trade fair campaigns based on customer attributes Pre-sales documents need to be managed within the presales activities: Inquiries and Quotations. These documents help identify possible sales related activity and determine sales probability.
SAP ERPPage 4 — 19 © SAP AG Pre-Sales Activities (CRM Light) Sales Support is a component of SD that assists in the sales, distribution, and marketing of a companies products and services to its customers. It contains the following functionality: — Creating and tracking customer contacts and communications (sales activity) • Phone call records • On-site meeting • Letters • Campaign communication — Implementing and tracking direct mailing, internet, and trade fair campaigns based on customer attributes Pre-sales documents need to be managed within the presales activities: Inquiries and Quotations. These documents help identify possible sales related activity and determine sales probability.
 SAP ERPPage 4 — 20 © SAP AG Pre-Sales Activities (CRM Light) The ultimate goal of all pre-sales activities is to equip the sales technician with all the information necessary to negotiate and complete the potential sale. Information needed: — Past sales activity — Past communication — Contact information — General Company info — Credit limits and usage — Current backorders 360º view of your customer
SAP ERPPage 4 — 20 © SAP AG Pre-Sales Activities (CRM Light) The ultimate goal of all pre-sales activities is to equip the sales technician with all the information necessary to negotiate and complete the potential sale. Information needed: — Past sales activity — Past communication — Contact information — General Company info — Credit limits and usage — Current backorders 360º view of your customer
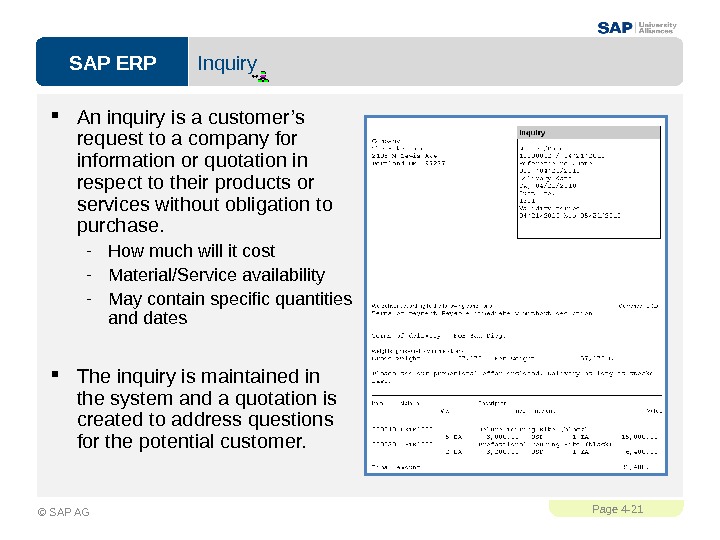
 SAP ERPPage 4 — 21 © SAP AG Inquiry An inquiry is a customer’s request to a company for information or quotation in respect to their products or services without obligation to purchase. — How much will it cost — Material/Service availability — May contain specific quantities and dates The inquiry is maintained in the system and a quotation is created to address questions for the potential customer.
SAP ERPPage 4 — 21 © SAP AG Inquiry An inquiry is a customer’s request to a company for information or quotation in respect to their products or services without obligation to purchase. — How much will it cost — Material/Service availability — May contain specific quantities and dates The inquiry is maintained in the system and a quotation is created to address questions for the potential customer.
 SAP ERPPage 4 — 22 © SAP AG Quotation The quotation presents the customer with a legally binding offer to deliver specific products or a selection of a certain amount of products in a specified timeframe at a pre-defined price.
SAP ERPPage 4 — 22 © SAP AG Quotation The quotation presents the customer with a legally binding offer to deliver specific products or a selection of a certain amount of products in a specified timeframe at a pre-defined price.
 SAP ERPPage 4 — 23 © SAP AG Sales Order Sales order processing can originate from a variety of documents and activities — Customer contacts us for order: phone, internet, email — Existing Contract — Quotations The electronic document that is created should contain the following basic information: — Customer Information — Material/service and quantity — Pricing (conditions) — Specific delivery dates and quantities — Shipping information — Billing Information
SAP ERPPage 4 — 23 © SAP AG Sales Order Sales order processing can originate from a variety of documents and activities — Customer contacts us for order: phone, internet, email — Existing Contract — Quotations The electronic document that is created should contain the following basic information: — Customer Information — Material/service and quantity — Pricing (conditions) — Specific delivery dates and quantities — Shipping information — Billing Information
 SAP ERPPage 4 — 24 © SAP AG Sales Order The sales document is made up of three primary areas: — Header • Data relevant for the entire sales order: Ex: customer data, total cost of the order — Line Item(s) • Information about the specific product: Ex: material and quantity, cost of an individual line — Schedule Line(s) • Uniquely belongs to a Line Item, contains delivery quantities and dates for partial deliveries
SAP ERPPage 4 — 24 © SAP AG Sales Order The sales document is made up of three primary areas: — Header • Data relevant for the entire sales order: Ex: customer data, total cost of the order — Line Item(s) • Information about the specific product: Ex: material and quantity, cost of an individual line — Schedule Line(s) • Uniquely belongs to a Line Item, contains delivery quantities and dates for partial deliveries
 SAP ERPPage 4 — 25 © SAP AG Sales Order The sales order contains all of the information needed to process your customers request, the following information is determined for each sales order: — Delivering Schedule — Shipping point and route determination — Availability Check — Transfer of requirements to MRP — Pricing — Credit limit check
SAP ERPPage 4 — 25 © SAP AG Sales Order The sales order contains all of the information needed to process your customers request, the following information is determined for each sales order: — Delivering Schedule — Shipping point and route determination — Availability Check — Transfer of requirements to MRP — Pricing — Credit limit check
 SAP ERPPage 4 — 26 © SAP AG Delivery Scheduling When an order is created you must enter a requested delivery date for the order or each line item. The system will then determine a delivery timeline, this will be used when determining our material availability, or ATP (Availability to Promise) date. The system will determine this date using forward and backward scheduling rules you have defined.
SAP ERPPage 4 — 26 © SAP AG Delivery Scheduling When an order is created you must enter a requested delivery date for the order or each line item. The system will then determine a delivery timeline, this will be used when determining our material availability, or ATP (Availability to Promise) date. The system will determine this date using forward and backward scheduling rules you have defined.
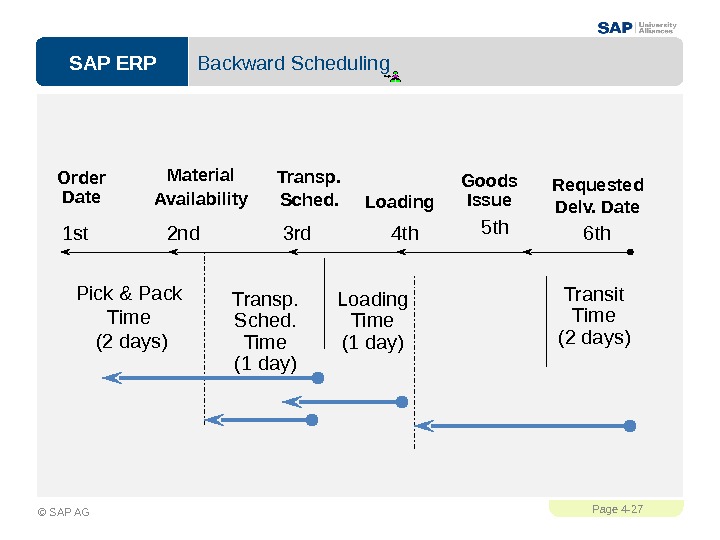
 SAP ERPPage 4 — 27 © SAP AG Backward Scheduling Requested Delv. Date. Goods Issue Loading. Material Availability. Order Date Transp. Sched. Transit Time (2 days)Loading Time (1 day)Pick & Pack Time (2 days) Transp. Sched. Time (1 day)2 nd 3 rd 4 th 5 th 6 th 1 st
SAP ERPPage 4 — 27 © SAP AG Backward Scheduling Requested Delv. Date. Goods Issue Loading. Material Availability. Order Date Transp. Sched. Transit Time (2 days)Loading Time (1 day)Pick & Pack Time (2 days) Transp. Sched. Time (1 day)2 nd 3 rd 4 th 5 th 6 th 1 st
 SAP ERPPage 4 — 28 © SAP AG Forward Scheduling Transit Time (2 days)Loading Time (1 day)Transp. Sched. Time (1 day) New Delv. Date 1 st 3 rd 4 th 5 th 6 th 2 nd Pick & Pack Time (2 days) 7 th Requested Delv. Date. Goods Issue Loading. Material Availability. Order Date Transp. Sched.
SAP ERPPage 4 — 28 © SAP AG Forward Scheduling Transit Time (2 days)Loading Time (1 day)Transp. Sched. Time (1 day) New Delv. Date 1 st 3 rd 4 th 5 th 6 th 2 nd Pick & Pack Time (2 days) 7 th Requested Delv. Date. Goods Issue Loading. Material Availability. Order Date Transp. Sched.
 SAP ERPPage 4 — 29 © SAP AG Shipping & Route Determination During the creation of the sales order the system must determine the shipping point from which the material will be shipped and the route the material will take to get from your warehouse to your customers location. A shipping point is determined for each line item within the order. The route determination will is used to define the transit time of the material that we used in scheduling.
SAP ERPPage 4 — 29 © SAP AG Shipping & Route Determination During the creation of the sales order the system must determine the shipping point from which the material will be shipped and the route the material will take to get from your warehouse to your customers location. A shipping point is determined for each line item within the order. The route determination will is used to define the transit time of the material that we used in scheduling.
 SAP ERPPage 4 — 30 © SAP AG Availability Check — Determines the material availability date — Considers all inward and outward inventory movements Proposes 3 methods of delivery — One-time delivery — Complete delivery — Delayed proposal Rules are created by YOU
SAP ERPPage 4 — 30 © SAP AG Availability Check — Determines the material availability date — Considers all inward and outward inventory movements Proposes 3 methods of delivery — One-time delivery — Complete delivery — Delayed proposal Rules are created by YOU
 SAP ERPPage 4 — 31 © SAP AG Pricing The system displays pricing information for all sales documents on the pricing screens at both the header and the line item level. — Header pricing is valid for the whole order it is the cumulative of all line items within the order — Line item pricing is for each specific material. The system will automatically search for price, discounts, surcharges, calculate taxes and freight. You have the ability to manually manipulate the pricing at both the header and line item level within the sales order by entering a condition type and amount. — Taxes and freight can be set-up so we can’t manually enter
SAP ERPPage 4 — 31 © SAP AG Pricing The system displays pricing information for all sales documents on the pricing screens at both the header and the line item level. — Header pricing is valid for the whole order it is the cumulative of all line items within the order — Line item pricing is for each specific material. The system will automatically search for price, discounts, surcharges, calculate taxes and freight. You have the ability to manually manipulate the pricing at both the header and line item level within the sales order by entering a condition type and amount. — Taxes and freight can be set-up so we can’t manually enter
 SAP ERPPage 4 — 32 © SAP AG Credit Check Allows your company to manage its credit exposure and risk for each customer by specifying credit limits. During the sales order process the system will alert the sales rep about the customers credit situation that arises, if necessary the system can be configured to block orders and deliveries.
SAP ERPPage 4 — 32 © SAP AG Credit Check Allows your company to manage its credit exposure and risk for each customer by specifying credit limits. During the sales order process the system will alert the sales rep about the customers credit situation that arises, if necessary the system can be configured to block orders and deliveries.
 SAP ERPPage 4 — 33 © SAP AG Shipping & Transportation The shipping process begins when you create the delivery document for the sales order. This document controls, supports, and monitors numerous sub-processes for shipping processing: — Picking — Packing — Post Goods Issue Integrated with the Material Management (MM) and Finance (FI) modules
SAP ERPPage 4 — 33 © SAP AG Shipping & Transportation The shipping process begins when you create the delivery document for the sales order. This document controls, supports, and monitors numerous sub-processes for shipping processing: — Picking — Packing — Post Goods Issue Integrated with the Material Management (MM) and Finance (FI) modules
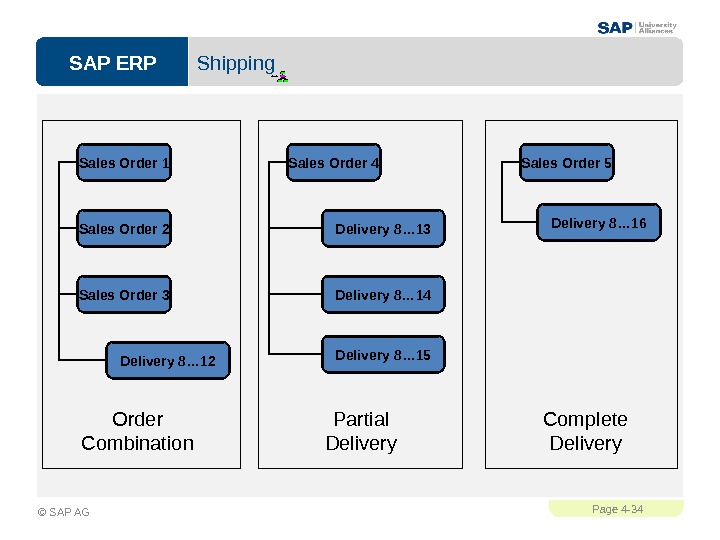
 SAP ERPPage 4 — 34 © SAP AG Shipping Order Combination. Sales Order 1 Sales Order 2 Sales Order 3 Delivery 8… 12 Partial Delivery. Sales Order 4 Delivery 8… 13 Delivery 8… 14 Delivery 8… 15 Complete Delivery. Sales Order 5 Delivery 8…
SAP ERPPage 4 — 34 © SAP AG Shipping Order Combination. Sales Order 1 Sales Order 2 Sales Order 3 Delivery 8… 12 Partial Delivery. Sales Order 4 Delivery 8… 13 Delivery 8… 14 Delivery 8… 15 Complete Delivery. Sales Order 5 Delivery 8…
 SAP ERPPage 4 — 35 © SAP AG Delivery Creation Checks order and materials to determine if a delivery is possible — delivery block (hold), completeness Confirms availability Confirms export/foreign trade requirements Determines total weight & volume
SAP ERPPage 4 — 35 © SAP AG Delivery Creation Checks order and materials to determine if a delivery is possible — delivery block (hold), completeness Confirms availability Confirms export/foreign trade requirements Determines total weight & volume
 SAP ERPPage 4 — 36 © SAP AG Delivery Creation Generates packing proposal Calculates weight and volume Checks scheduling Considers partial deliveries Updates route assignment Assigns picking location Updates sales order Determines batches Quality check (if needed) Updates sales order
SAP ERPPage 4 — 36 © SAP AG Delivery Creation Generates packing proposal Calculates weight and volume Checks scheduling Considers partial deliveries Updates route assignment Assigns picking location Updates sales order Determines batches Quality check (if needed) Updates sales order
 SAP ERPPage 4 — 37 © SAP AG Delivery Document The Delivery Document initiates the delivery process and is the control mechanism for this process — Picking — Packing — Loading — Posting Goods Issue Changes to delivery are allowable — products, quantities
SAP ERPPage 4 — 37 © SAP AG Delivery Document The Delivery Document initiates the delivery process and is the control mechanism for this process — Picking — Packing — Loading — Posting Goods Issue Changes to delivery are allowable — products, quantities
 SAP ERPPage 4 — 38 © SAP AG Picking Quantities based on delivery note Assigned date when picking should begin Automated storage location assignment Supports serial number/lot number tracking and batch management Integrated with Warehouse Management (WM)
SAP ERPPage 4 — 38 © SAP AG Picking Quantities based on delivery note Assigned date when picking should begin Automated storage location assignment Supports serial number/lot number tracking and batch management Integrated with Warehouse Management (WM)
 SAP ERPPage 4 — 39 © SAP AG Loading and Packing Identifies which packaging is to be used for specified products (customer preference and UCC-128 considerations) Identifies and updates accounts associated with returnable packaging Tracks the packed product by container Insures weight/volume restrictions are enforced All packed items are assigned to the required means of transportation
SAP ERPPage 4 — 39 © SAP AG Loading and Packing Identifies which packaging is to be used for specified products (customer preference and UCC-128 considerations) Identifies and updates accounts associated with returnable packaging Tracks the packed product by container Insures weight/volume restrictions are enforced All packed items are assigned to the required means of transportation
 SAP ERPPage 4 — 40 © SAP AG Goods issue Event that indicates the legal change in ownership of the products Reduces inventory and enters Cost of Goods Sold Automatically updates the General Ledger (G/L) accounts Ends the shipping process and updates the status of the shipping documents
SAP ERPPage 4 — 40 © SAP AG Goods issue Event that indicates the legal change in ownership of the products Reduces inventory and enters Cost of Goods Sold Automatically updates the General Ledger (G/L) accounts Ends the shipping process and updates the status of the shipping documents
 SAP ERPPage 4 — 41 © SAP AG Billing The billing document is created by coping data from the sales order and/or delivery document. — Order-based billing — Delivery-based billing The billing process is used to generate the customer invoice. It will update the customer’s credit status.
SAP ERPPage 4 — 41 © SAP AG Billing The billing document is created by coping data from the sales order and/or delivery document. — Order-based billing — Delivery-based billing The billing process is used to generate the customer invoice. It will update the customer’s credit status.
 SAP ERPPage 4 — 42 © SAP AG Billing Documents The billing document will automatically create a debit posting to your customer sub-ledger account and credit your revenue account. It is at this point that the sales process is passed over to Financial Accounting to await payment.
SAP ERPPage 4 — 42 © SAP AG Billing Documents The billing document will automatically create a debit posting to your customer sub-ledger account and credit your revenue account. It is at this point that the sales process is passed over to Financial Accounting to await payment.
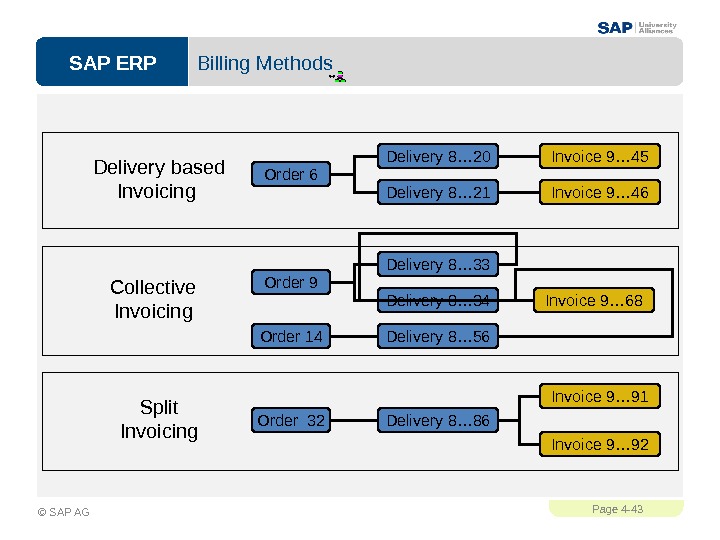
 SAP ERPPage 4 — 43 © SAP AG Billing Methods Collective Invoicing Delivery based Invoicing Delivery 8… 34 Delivery 8… 33 Order 14 Order 9 Delivery 8… 56 Invoice 9… 68 Order 6 Delivery 8… 20 Delivery 8… 21 Invoice 9… 45 Invoice 9… 46 Split Invoicing Order 32 Delivery 8… 86 Invoice 9… 92 Invoice 9…
SAP ERPPage 4 — 43 © SAP AG Billing Methods Collective Invoicing Delivery based Invoicing Delivery 8… 34 Delivery 8… 33 Order 14 Order 9 Delivery 8… 56 Invoice 9… 68 Order 6 Delivery 8… 20 Delivery 8… 21 Invoice 9… 45 Invoice 9… 46 Split Invoicing Order 32 Delivery 8… 86 Invoice 9… 92 Invoice 9…
 SAP ERPPage 4 — 44 © SAP AG Payment is the final step in the sales order process, this step is managed by the Financial Accounting department. Final payment includes: — Posting payments against invoices. — Reconciling differences between payment and invoice. Payment will create a posting clearing the liability in the A/R account and increases your bank account.
SAP ERPPage 4 — 44 © SAP AG Payment is the final step in the sales order process, this step is managed by the Financial Accounting department. Final payment includes: — Posting payments against invoices. — Reconciling differences between payment and invoice. Payment will create a posting clearing the liability in the A/R account and increases your bank account.
 SAP ERPPage 4 — 45 © SAP AG Document Flow The document flow and order status feature allows you to find the status of an order at any point in time. The SAP updates the order status every time a change is made to any document created in the customer order management cycle (Order-to-Cash).
SAP ERPPage 4 — 45 © SAP AG Document Flow The document flow and order status feature allows you to find the status of an order at any point in time. The SAP updates the order status every time a change is made to any document created in the customer order management cycle (Order-to-Cash).
 SAP ERPPage 4 — 46 © SAP AG Sales Order Process Debugging “ Never again did I learn so much in such a short time, because twenty participants made mistakes for me! You cannot make so many mistakes all alone” SAP Co-founder Klaus Tschira, on his experiences teaching COBOL to clients at IBM.
SAP ERPPage 4 — 46 © SAP AG Sales Order Process Debugging “ Never again did I learn so much in such a short time, because twenty participants made mistakes for me! You cannot make so many mistakes all alone” SAP Co-founder Klaus Tschira, on his experiences teaching COBOL to clients at IBM.
 SAP ERPPage 4 — 47 © SAP AG Sales Order Process Debugging Document Flow — Gives Order Process Status List of Sales Orders (VA 05) — Tool to Find Order — Need student’s user id/data set number
SAP ERPPage 4 — 47 © SAP AG Sales Order Process Debugging Document Flow — Gives Order Process Status List of Sales Orders (VA 05) — Tool to Find Order — Need student’s user id/data set number
![SAP ERPPage 4 - 48 © SAP AG Overview of ARIS models (SD) [slide number] [slide SAP ERPPage 4 - 48 © SAP AG Overview of ARIS models (SD) [slide number] [slide](/docs//04_intro_erp_using_gbi_slides_sd_en_v2_01_aris_images/04_intro_erp_using_gbi_slides_sd_en_v2_01_aris_47.jpg) SAP ERPPage 4 — 48 © SAP AG Overview of ARIS models (SD) [slide number] [slide title] [model name assigned] [level of abstraction (1 -4)] 4 -5 SD Organizational Structure : “GBI System Organizational Model” MM, SD, FI(1 -3) 4 -6 SD Organizational Structure : “GBI System Organizational Model” MM, SD, FI(1 -3) 4 -7 Global Bike Inc. and Global Bike Germany Gmb. H : „GBI Org Chart US/DE „(1 -3) 4 -8 SD Organizational Structure : “GBI System Organizational Model” MM, SD, FI(1 -3) 4 -9 SD Master Data : Data Model (DM) “GBI Data Model” MM, SD, FI (3) 4 -10 Display Customer : General Data : Mask Diagram (MD) “Create Customer Address Data / XD 01”(4) 4 -11 General Data : Mask Diagram “Create Customer Address Data / XD 01”(4) 4 -11 Company Code Data : MD “Create Customer: Company Code Data / XD 01”(4) 4 -11 Sales Area Data : MD “Create Customer Sales Area Data / XD 01”(4) 4 -12 Customer Master : Event Process Chain (e. EPC) “Create New Customer“(3) 4 -13 Components Sales and Distribution , Materials Management , Accounting/Controlling and MD “Create Trading Goods: Basic Data 1 / MMH 1”(4) 4 -14 Material Master Views : e. EPC “Create Material Master for Trading Goods”(3) 4 -14 Basic Data and 2 more views: MD “Create Trading Goods: Basic Data 1 / MMH 1”(4) 4 -15 Material Master : e. EPC “Create Material Master for Trading Goods”(3) 4 -18 Sales Order Process : Value Added Chain Diagram “GBI_SD”(2) 4 -18 7 e. EPCs like Sales Order Entry (3) or Check Availability (3) and DM “Integration SD-FI”(3) 4 -21 Inquiry : e. EPC “Create Customer Inquiry“(3) 4 -22 Quotation : e. EPC “Create Customer Quotation“(3) 4 -23 Sales Order : e. EPC “Create Sales Order Referencing a Quotation”(3) 4 -24 sales document : Attribut Allocation Diagram “Sales Order”(4) 4 -27 Backward Scheduling : Attribut Allocation Diagram “Backward Scheduling“(4) 4 -30 Availability Check : e. EPC “Check Stock Status”(3) 4 -33 Shipping & Transportation e. EPC” Start Delivery Process“(3) 4 -34 Shipping DM “Integration SD-FI”(3) 4 -38 Picking : e. EPC” Pick Materials on Delivery Note”(3) 4 -40 Goods issue : e. EPC” Post Goods Issue“(3) 4 -41 Billing : e. EPC” Create Invoice for Customer“(3) 4 -42 Financial Accounting : Information Carirer Diagram “FI-SD Integration Point”(3) 4 -43 Billing Methods DM “Integration SD-FI”(3) 4 -44 Payment: e. EPC “Post Receipt of Customer Payment”(3) 4 -45 Document Flow : Information Carirer Diagram “GBI Document Flow MM, SD, FI” (3) All assigned models and its objects are linked to each other. This enables the model user to horizontally navigate (via Object Occurrences) within one level of abstraction and to vertically navigate (via Object Hierarchy) between the 4 levels of abstraction. Levels of abstraction (1 -4) (1) Core level (2) Overview level (3) Detailed level (4) Document level
SAP ERPPage 4 — 48 © SAP AG Overview of ARIS models (SD) [slide number] [slide title] [model name assigned] [level of abstraction (1 -4)] 4 -5 SD Organizational Structure : “GBI System Organizational Model” MM, SD, FI(1 -3) 4 -6 SD Organizational Structure : “GBI System Organizational Model” MM, SD, FI(1 -3) 4 -7 Global Bike Inc. and Global Bike Germany Gmb. H : „GBI Org Chart US/DE „(1 -3) 4 -8 SD Organizational Structure : “GBI System Organizational Model” MM, SD, FI(1 -3) 4 -9 SD Master Data : Data Model (DM) “GBI Data Model” MM, SD, FI (3) 4 -10 Display Customer : General Data : Mask Diagram (MD) “Create Customer Address Data / XD 01”(4) 4 -11 General Data : Mask Diagram “Create Customer Address Data / XD 01”(4) 4 -11 Company Code Data : MD “Create Customer: Company Code Data / XD 01”(4) 4 -11 Sales Area Data : MD “Create Customer Sales Area Data / XD 01”(4) 4 -12 Customer Master : Event Process Chain (e. EPC) “Create New Customer“(3) 4 -13 Components Sales and Distribution , Materials Management , Accounting/Controlling and MD “Create Trading Goods: Basic Data 1 / MMH 1”(4) 4 -14 Material Master Views : e. EPC “Create Material Master for Trading Goods”(3) 4 -14 Basic Data and 2 more views: MD “Create Trading Goods: Basic Data 1 / MMH 1”(4) 4 -15 Material Master : e. EPC “Create Material Master for Trading Goods”(3) 4 -18 Sales Order Process : Value Added Chain Diagram “GBI_SD”(2) 4 -18 7 e. EPCs like Sales Order Entry (3) or Check Availability (3) and DM “Integration SD-FI”(3) 4 -21 Inquiry : e. EPC “Create Customer Inquiry“(3) 4 -22 Quotation : e. EPC “Create Customer Quotation“(3) 4 -23 Sales Order : e. EPC “Create Sales Order Referencing a Quotation”(3) 4 -24 sales document : Attribut Allocation Diagram “Sales Order”(4) 4 -27 Backward Scheduling : Attribut Allocation Diagram “Backward Scheduling“(4) 4 -30 Availability Check : e. EPC “Check Stock Status”(3) 4 -33 Shipping & Transportation e. EPC” Start Delivery Process“(3) 4 -34 Shipping DM “Integration SD-FI”(3) 4 -38 Picking : e. EPC” Pick Materials on Delivery Note”(3) 4 -40 Goods issue : e. EPC” Post Goods Issue“(3) 4 -41 Billing : e. EPC” Create Invoice for Customer“(3) 4 -42 Financial Accounting : Information Carirer Diagram “FI-SD Integration Point”(3) 4 -43 Billing Methods DM “Integration SD-FI”(3) 4 -44 Payment: e. EPC “Post Receipt of Customer Payment”(3) 4 -45 Document Flow : Information Carirer Diagram “GBI Document Flow MM, SD, FI” (3) All assigned models and its objects are linked to each other. This enables the model user to horizontally navigate (via Object Occurrences) within one level of abstraction and to vertically navigate (via Object Hierarchy) between the 4 levels of abstraction. Levels of abstraction (1 -4) (1) Core level (2) Overview level (3) Detailed level (4) Document level
 SAP ERPPage 4 — 49 © SAP AG Information Models Covering 4 Levels of IT Integration Presentation Processes Data Take GBI 2. 0 User Rolls and interact with GBI 2. 0 Processes via SAP GUI : Execute GBI 2. 0 Processes : Order of entire case study Single case study processes Execute GBI 2. 0 Transaction : All content of case studies at a glance GBI 2. 0 Data In- / Output : Entire SAP ERP document flow Description SAP ERP mask structure All SAP ERP master & transaction data All SAP ERP organizational units Kunde Anfrage Angebot Kundenauftrag (Org. units / Positions / Rolls/ User) : Level of Abstraction (LA) 1 to 3 Value added Chain (VAC) : LA 1 and 2 Event driven process chain : LA 3 Information carrier diagram : LA 3 Mask diagram : Level of Abstraction 4 Entity Relationsship Diagram : LA 3 Org. Chart : Level of Abstraction 1 — 3 Funktion Tree : Level of Abstr. 1 to 3 Functions Rolle. Process-Owner Execution in SAP ERP Model Presentation in ARIS Organizational View Process View Function View Data View
SAP ERPPage 4 — 49 © SAP AG Information Models Covering 4 Levels of IT Integration Presentation Processes Data Take GBI 2. 0 User Rolls and interact with GBI 2. 0 Processes via SAP GUI : Execute GBI 2. 0 Processes : Order of entire case study Single case study processes Execute GBI 2. 0 Transaction : All content of case studies at a glance GBI 2. 0 Data In- / Output : Entire SAP ERP document flow Description SAP ERP mask structure All SAP ERP master & transaction data All SAP ERP organizational units Kunde Anfrage Angebot Kundenauftrag (Org. units / Positions / Rolls/ User) : Level of Abstraction (LA) 1 to 3 Value added Chain (VAC) : LA 1 and 2 Event driven process chain : LA 3 Information carrier diagram : LA 3 Mask diagram : Level of Abstraction 4 Entity Relationsship Diagram : LA 3 Org. Chart : Level of Abstraction 1 — 3 Funktion Tree : Level of Abstr. 1 to 3 Functions Rolle. Process-Owner Execution in SAP ERP Model Presentation in ARIS Organizational View Process View Function View Data View

