lecture 1 Proteins.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 60
 Protein Chemistry
Protein Chemistry
 Amino acid classification 1. Non-polar (hydrophobic) 2. Polar (hydrophilic)
Amino acid classification 1. Non-polar (hydrophobic) 2. Polar (hydrophilic)
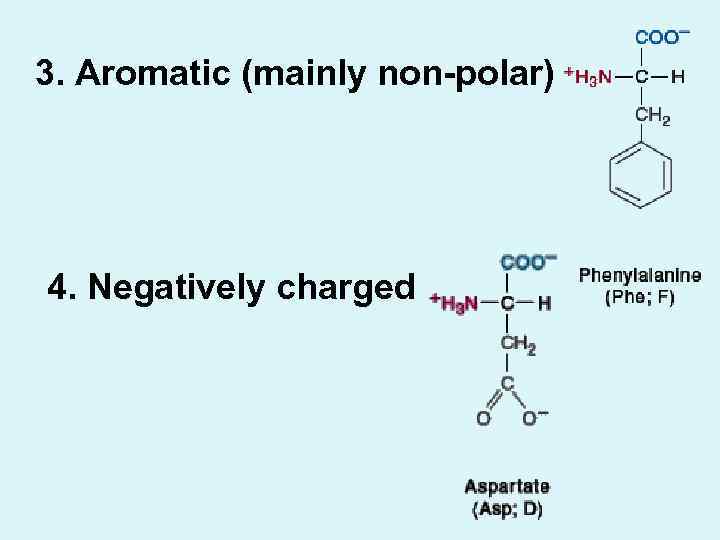 3. Aromatic (mainly non-polar) 4. Negatively charged
3. Aromatic (mainly non-polar) 4. Negatively charged
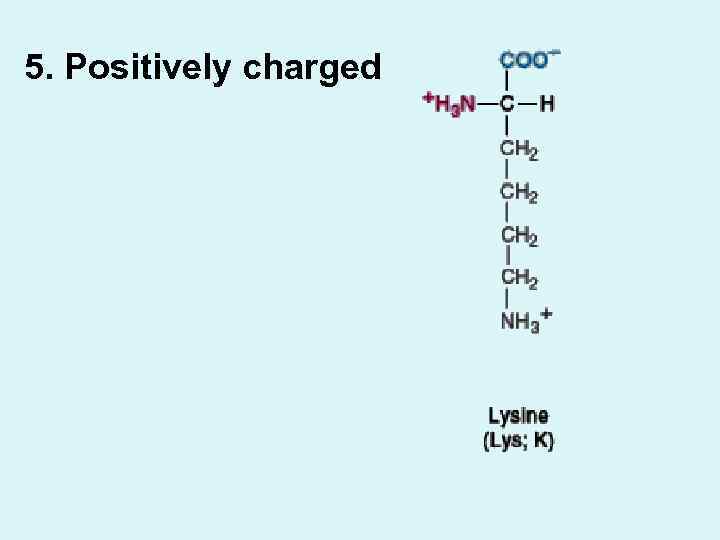 5. Positively charged
5. Positively charged
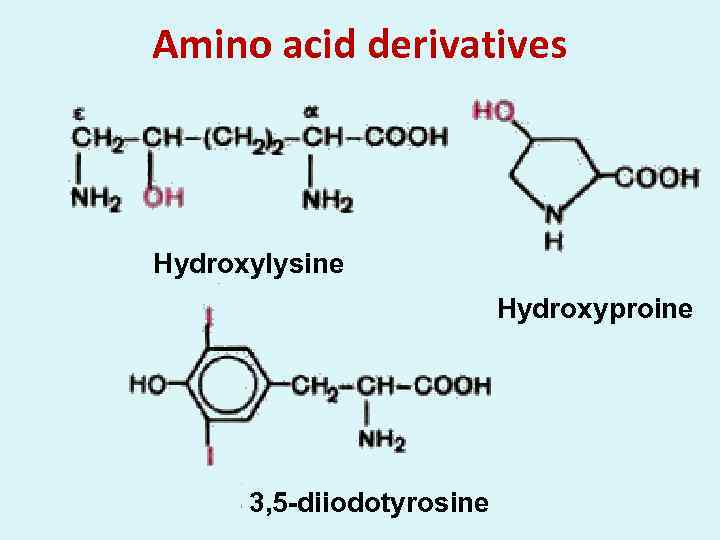 Amino acid derivatives Hydroxylysine Hydroxyproine 3, 5 -diiodotyrosine
Amino acid derivatives Hydroxylysine Hydroxyproine 3, 5 -diiodotyrosine
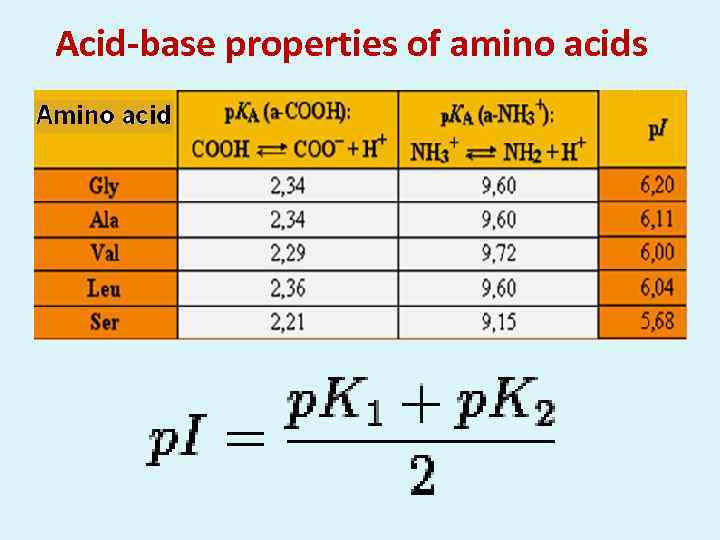 Acid-base properties of amino acids
Acid-base properties of amino acids
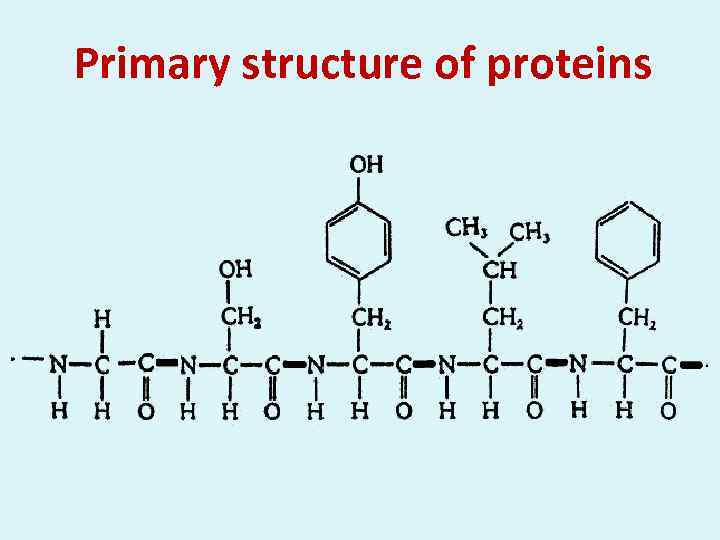 Primary structure of proteins
Primary structure of proteins
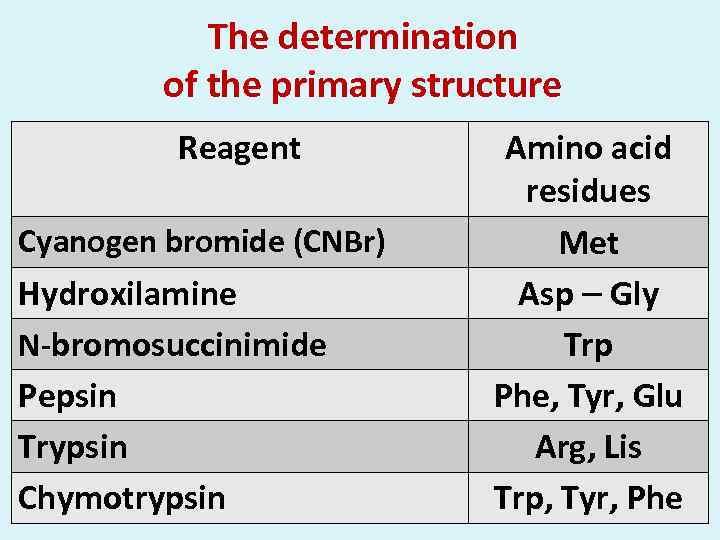 The determination of the primary structure Reagent Cyanogen bromide (CNBr) Hydroxilamine N-bromosuccinimide Pepsin Trypsin Chymotrypsin Amino acid residues Met Asp Gly Trp Phe, Tyr, Glu Arg, Lis Trp, Tyr, Phe
The determination of the primary structure Reagent Cyanogen bromide (CNBr) Hydroxilamine N-bromosuccinimide Pepsin Trypsin Chymotrypsin Amino acid residues Met Asp Gly Trp Phe, Tyr, Glu Arg, Lis Trp, Tyr, Phe
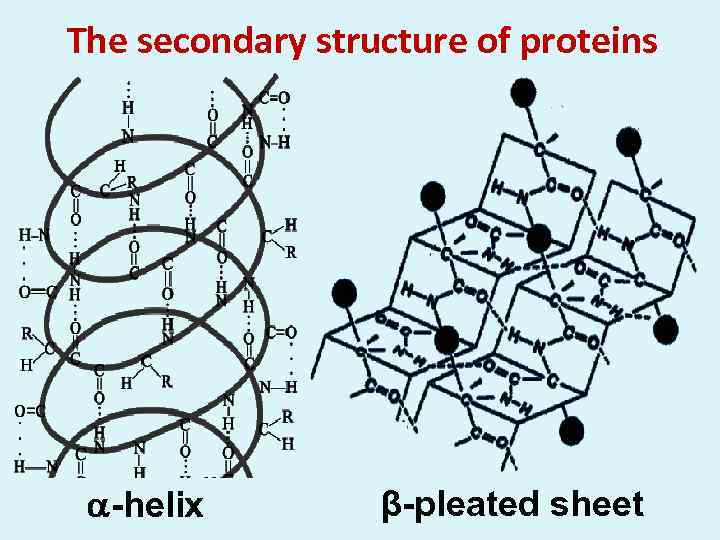 The secondary structure of proteins -helix β-pleated sheet
The secondary structure of proteins -helix β-pleated sheet
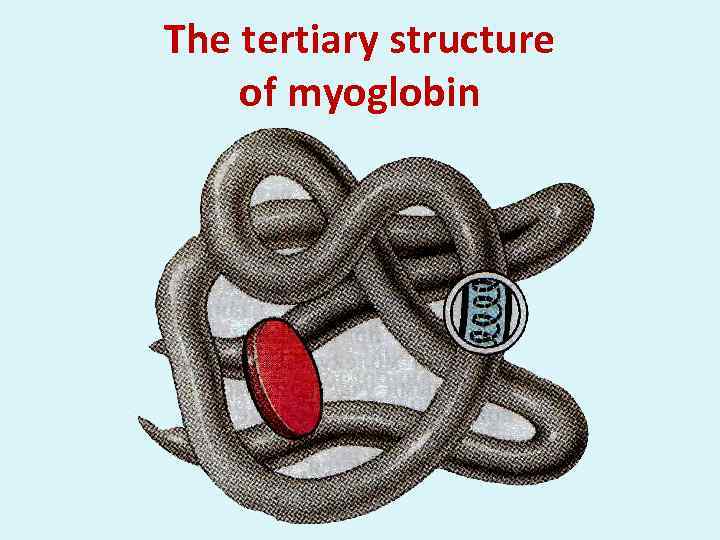 The tertiary structure of myoglobin
The tertiary structure of myoglobin
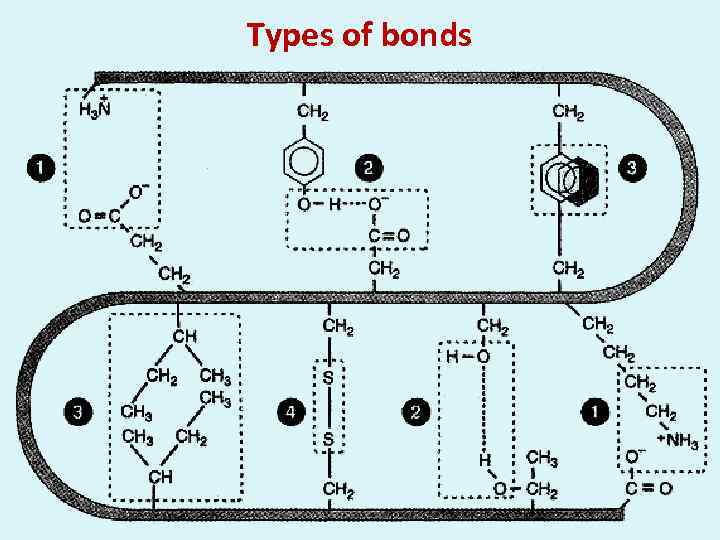 Types of bonds
Types of bonds
 Chaperone
Chaperone
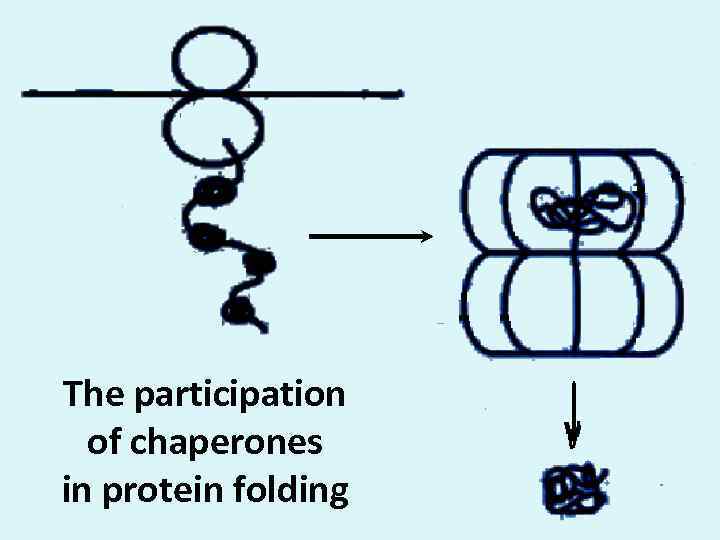 The participation of chaperones in protein folding
The participation of chaperones in protein folding
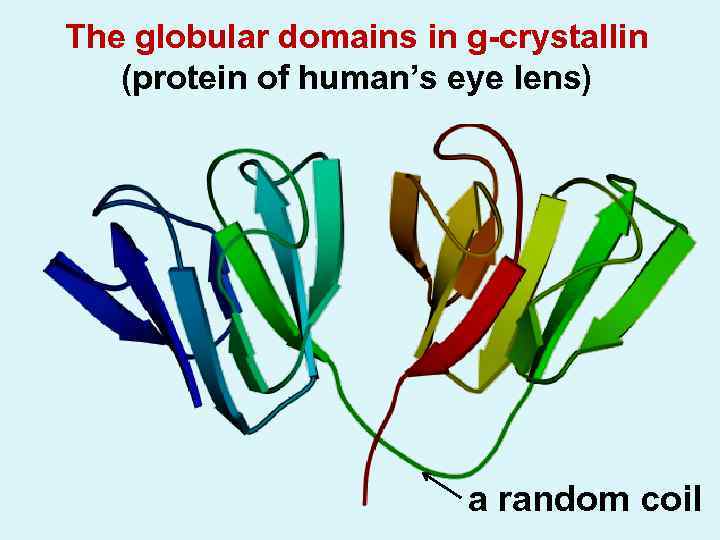 The globular domains in g-crystallin (protein of human’s eye lens) a random coil
The globular domains in g-crystallin (protein of human’s eye lens) a random coil
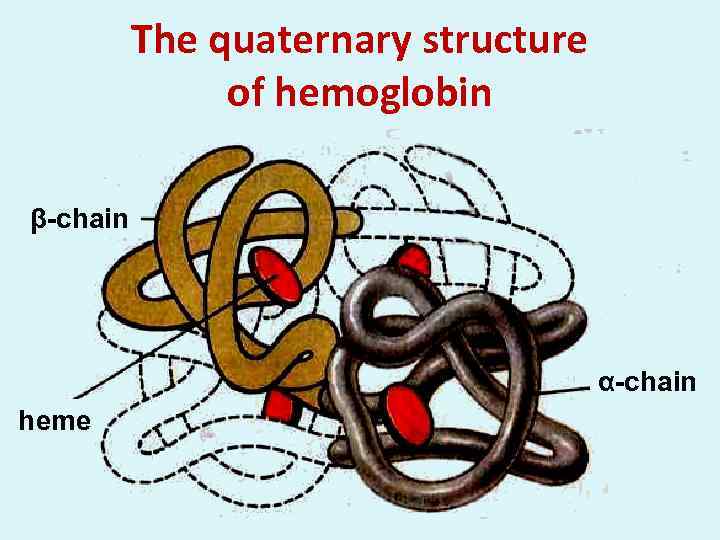 The quaternary structure of hemoglobin β-chain α-chain heme
The quaternary structure of hemoglobin β-chain α-chain heme
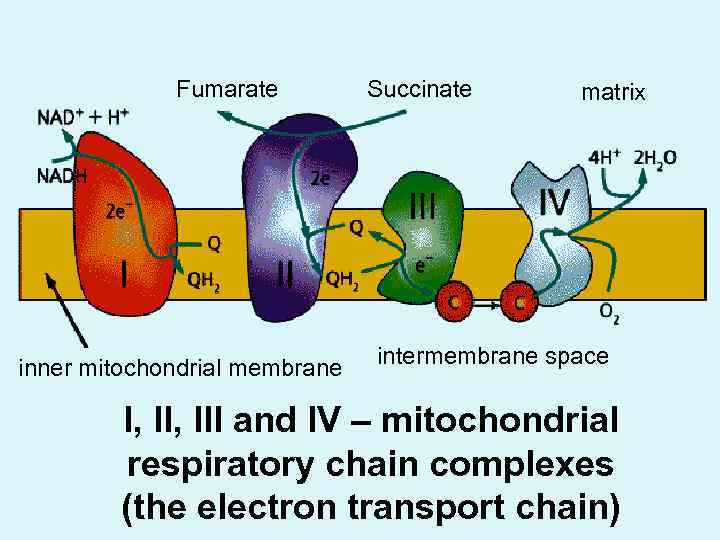 Fumarate inner mitochondrial membrane Succinate matrix intermembrane space I, III and IV – mitochondrial respiratory chain complexes (the electron transport chain)
Fumarate inner mitochondrial membrane Succinate matrix intermembrane space I, III and IV – mitochondrial respiratory chain complexes (the electron transport chain)
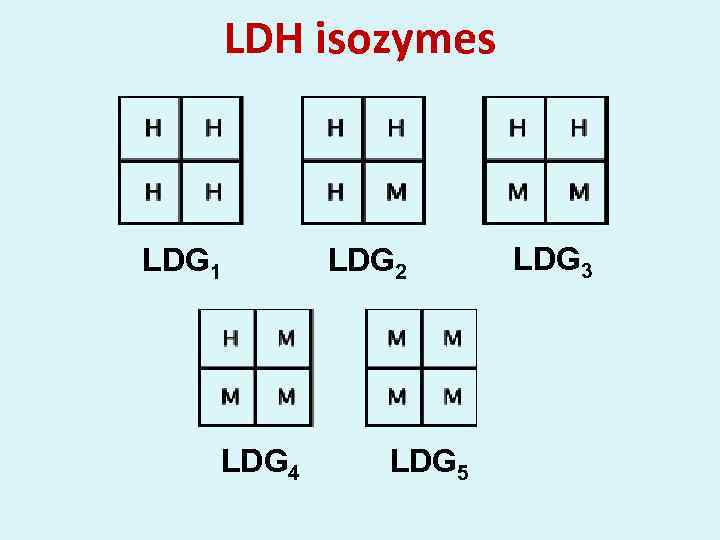 LDH isozymes LDG 1 LDG 4 LDG 2 LDG 5 LDG 3
LDH isozymes LDG 1 LDG 4 LDG 2 LDG 5 LDG 3
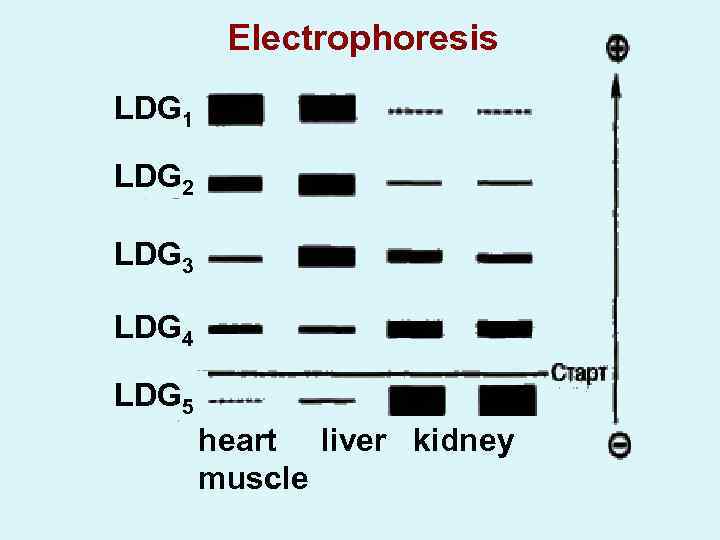 Electrophoresis LDG 1 LDG 2 LDG 3 LDG 4 LDG 5 heart liver kidney muscle
Electrophoresis LDG 1 LDG 2 LDG 3 LDG 4 LDG 5 heart liver kidney muscle
 Classification of proteins Simple proteins
Classification of proteins Simple proteins
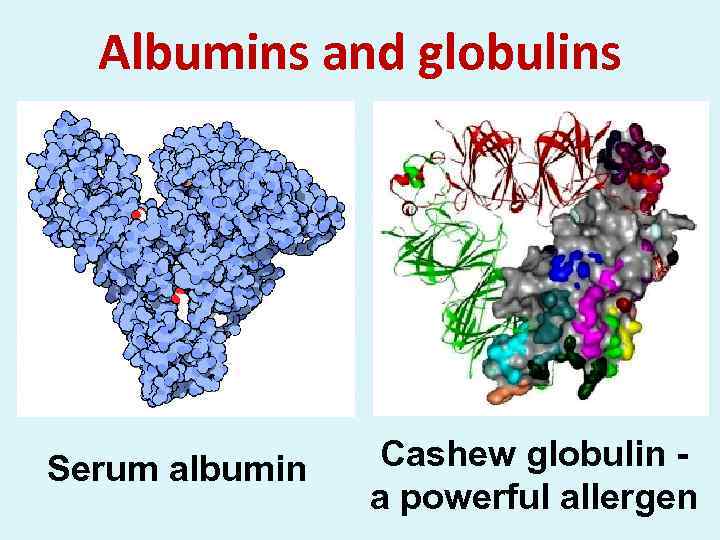 Albumins and globulins Serum albumin Cashew globulin - a powerful allergen
Albumins and globulins Serum albumin Cashew globulin - a powerful allergen
 Hystones and DNA
Hystones and DNA
 Prolamin
Prolamin
 Conjugative proteins
Conjugative proteins
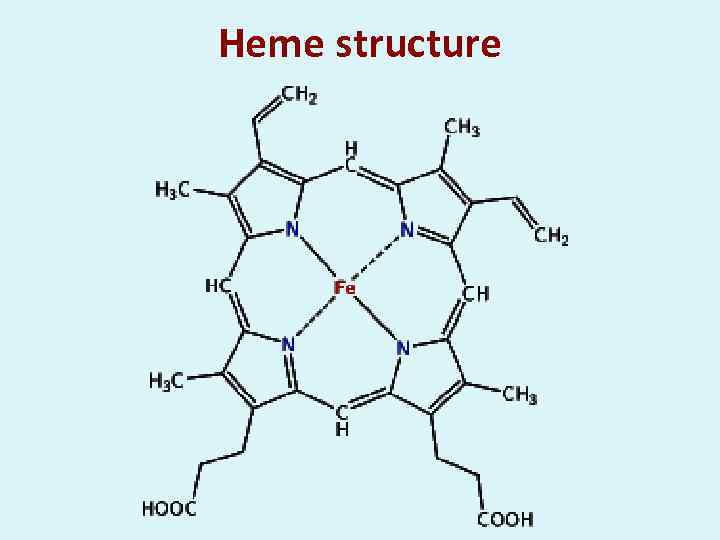 Heme structure
Heme structure
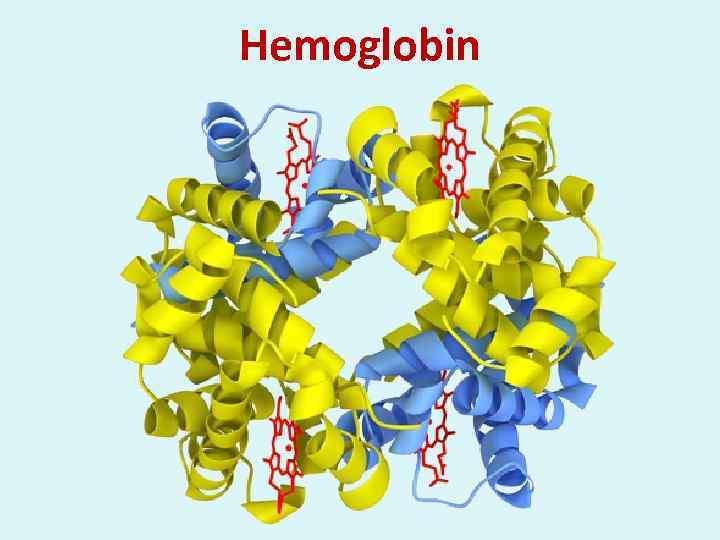 Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin
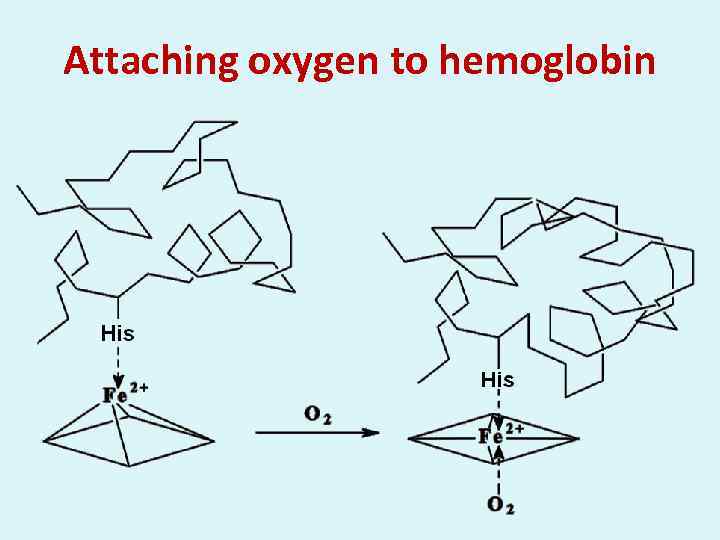 Attaching oxygen to hemoglobin
Attaching oxygen to hemoglobin
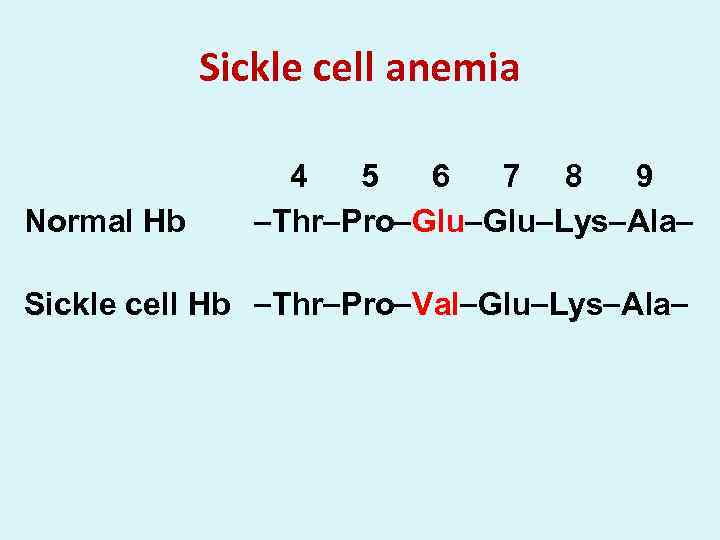 Sickle cell anemia Normal Hb 4 5 6 7 8 9 Thr Pro Glu Lys Ala Sickle cell Hb Thr Pro Val Glu Lys Ala
Sickle cell anemia Normal Hb 4 5 6 7 8 9 Thr Pro Glu Lys Ala Sickle cell Hb Thr Pro Val Glu Lys Ala
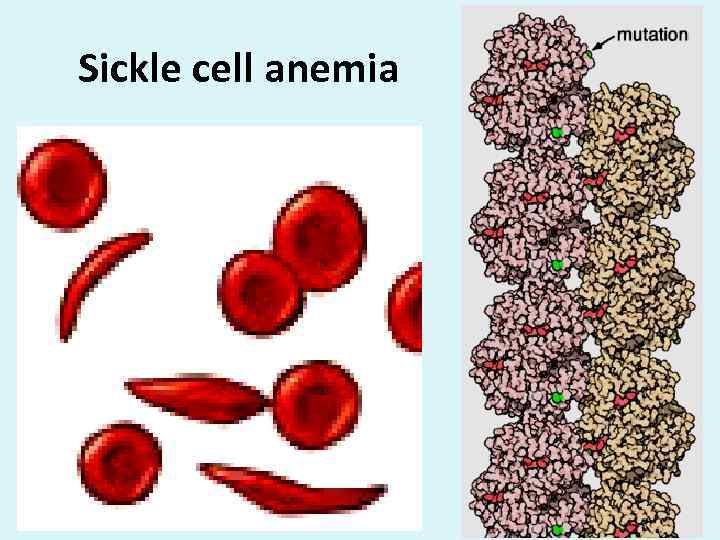 Sickle cell anemia
Sickle cell anemia
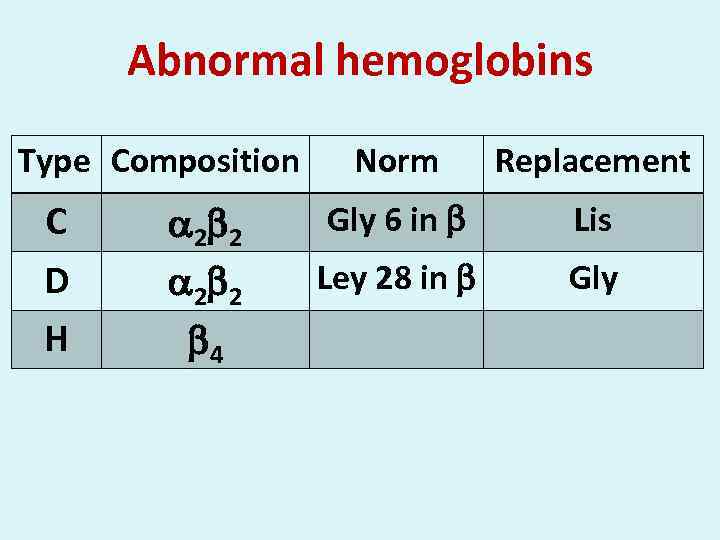 Abnormal hemoglobins Type Composition С D Н 2 2 4 Norm Replacement Gly 6 in Lis Ley 28 in Gly
Abnormal hemoglobins Type Composition С D Н 2 2 4 Norm Replacement Gly 6 in Lis Ley 28 in Gly
 Myoglobin
Myoglobin
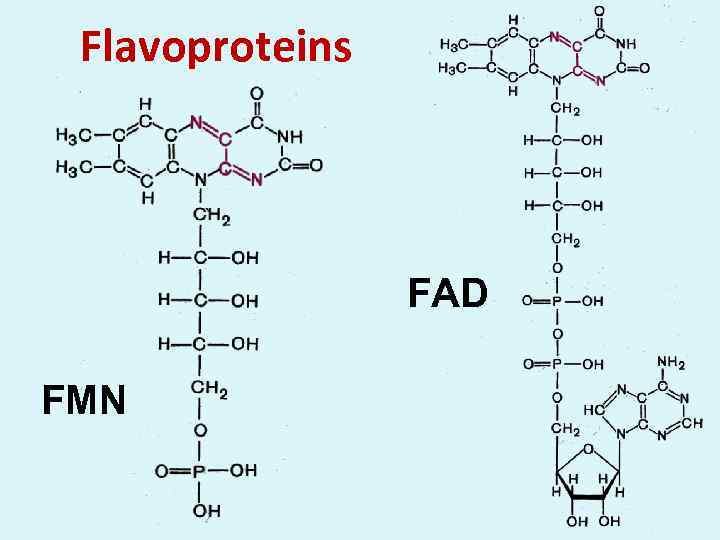 Flavoproteins FAD FMN
Flavoproteins FAD FMN
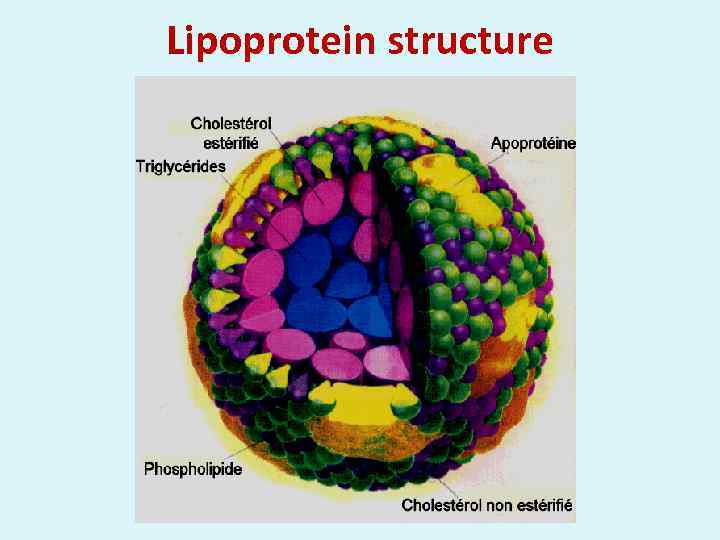 Lipoprotein structure
Lipoprotein structure
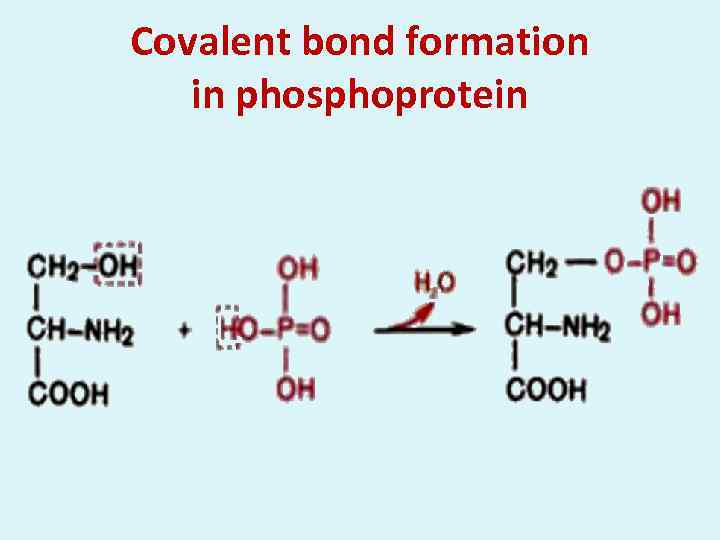 Covalent bond formation in phosphoprotein
Covalent bond formation in phosphoprotein
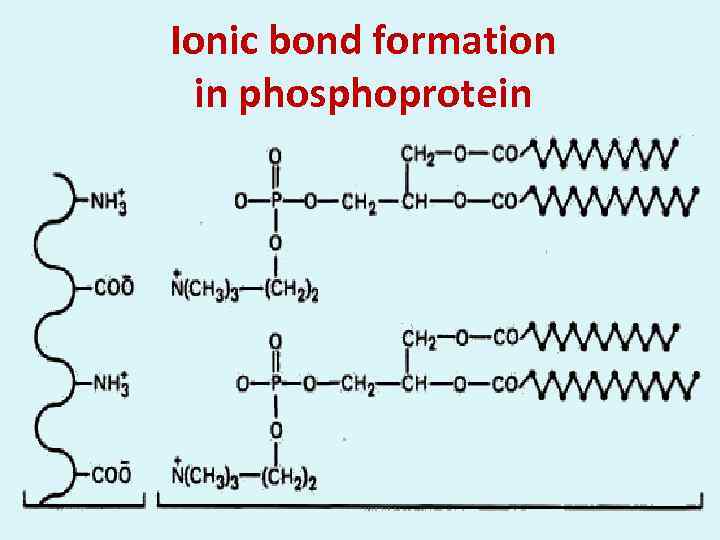 Ionic bond formation in phosphoprotein
Ionic bond formation in phosphoprotein
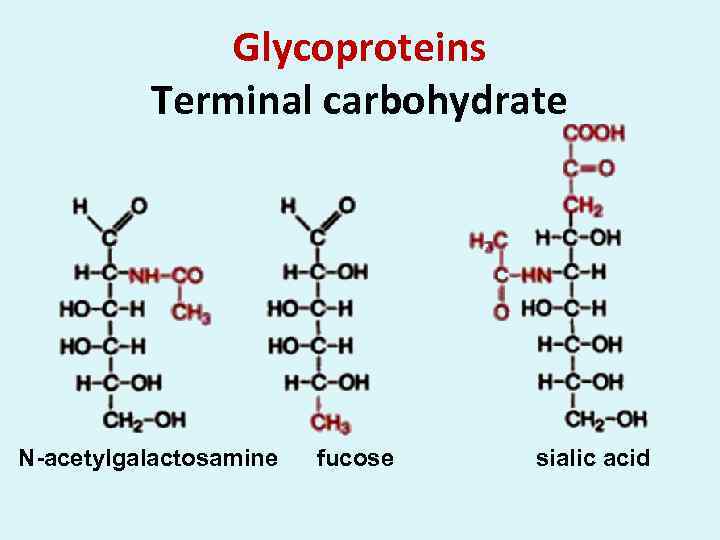 Glycoproteins Terminal carbohydrate N-acetylgalactosamine fucose sialic acid
Glycoproteins Terminal carbohydrate N-acetylgalactosamine fucose sialic acid
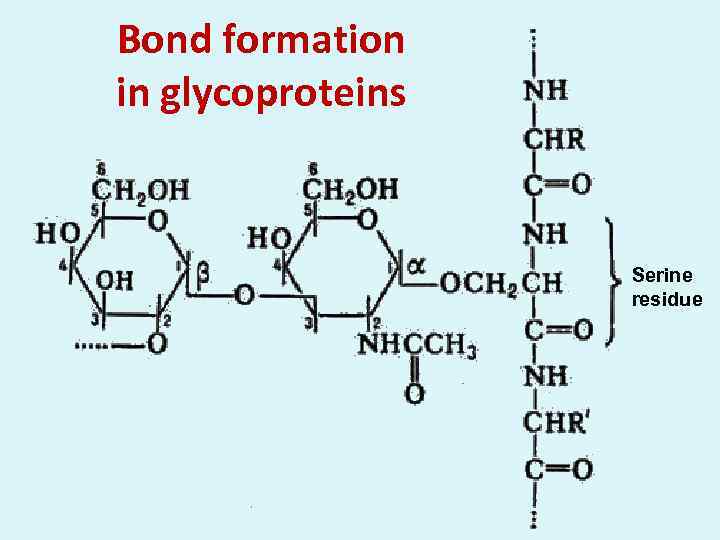 Bond formation in glycoproteins Serine residue
Bond formation in glycoproteins Serine residue
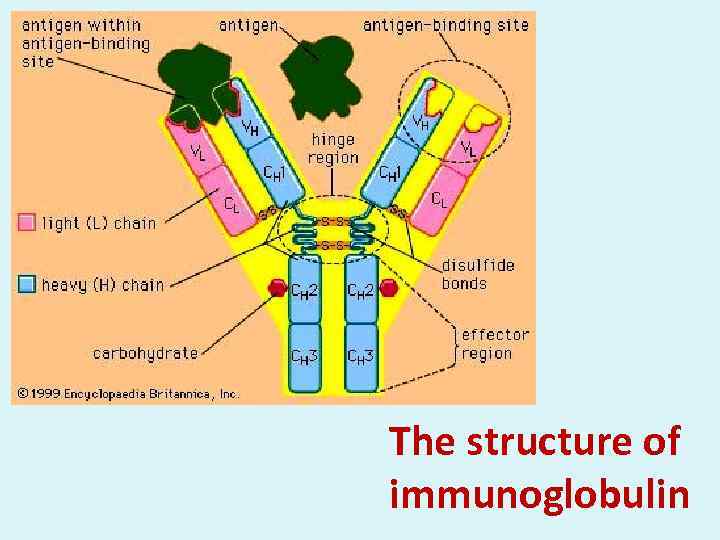 The structure of immunoglobulin
The structure of immunoglobulin
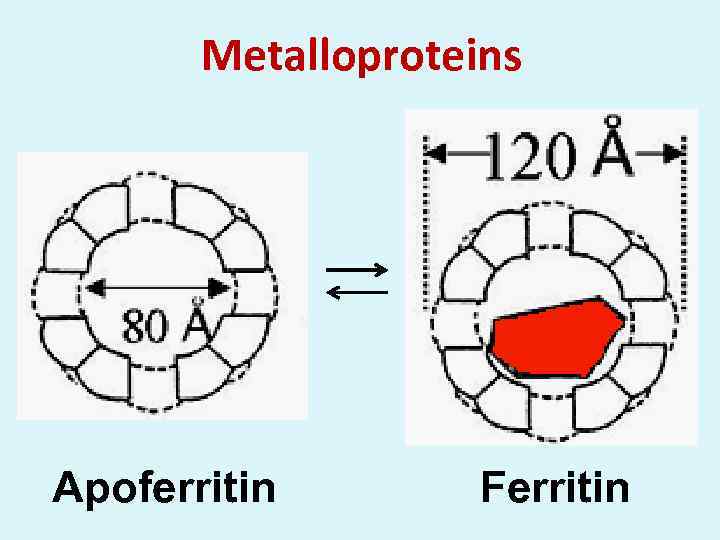 Metalloproteins Apoferritin Ferritin
Metalloproteins Apoferritin Ferritin
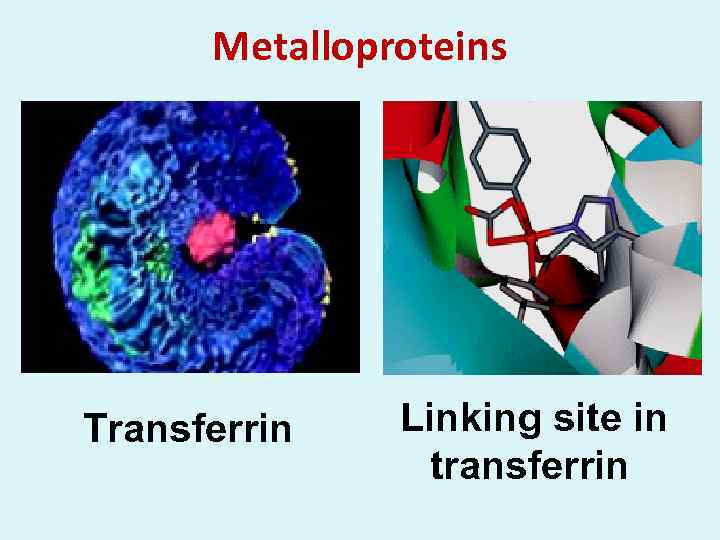 Metalloproteins Transferrin Linking site in transferrin
Metalloproteins Transferrin Linking site in transferrin
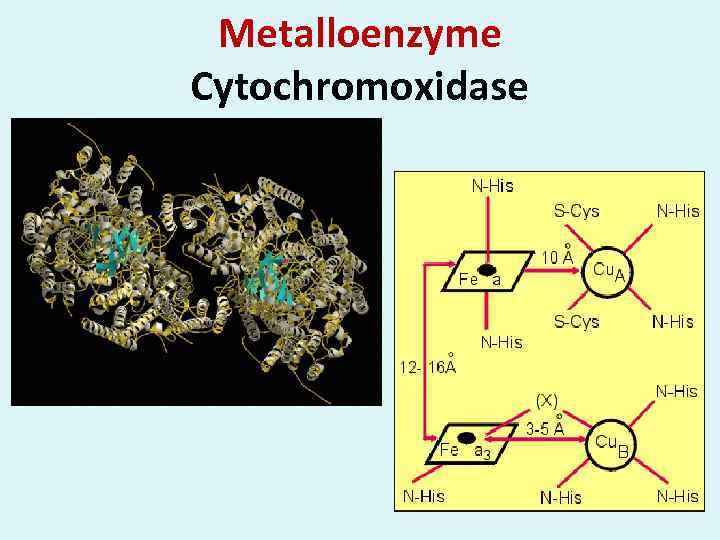 Metalloenzyme Cytochromoxidase
Metalloenzyme Cytochromoxidase
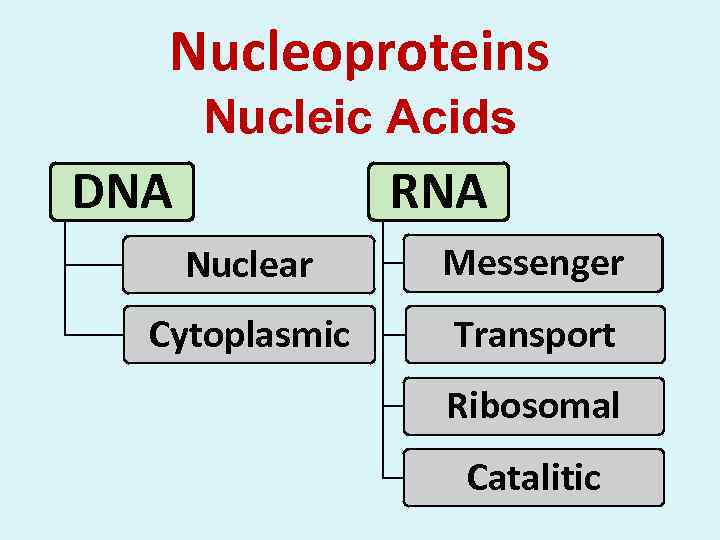 Nucleoproteins Nucleic Acids DNA RNA Nuclear Messenger Cytoplasmic Transport Ribosomal Catalitic
Nucleoproteins Nucleic Acids DNA RNA Nuclear Messenger Cytoplasmic Transport Ribosomal Catalitic
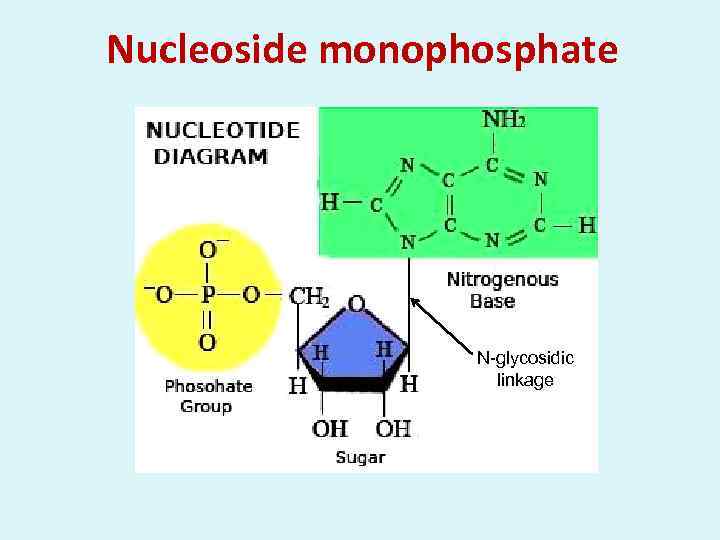 Nucleoside monophosphate N-glycosidic linkage
Nucleoside monophosphate N-glycosidic linkage
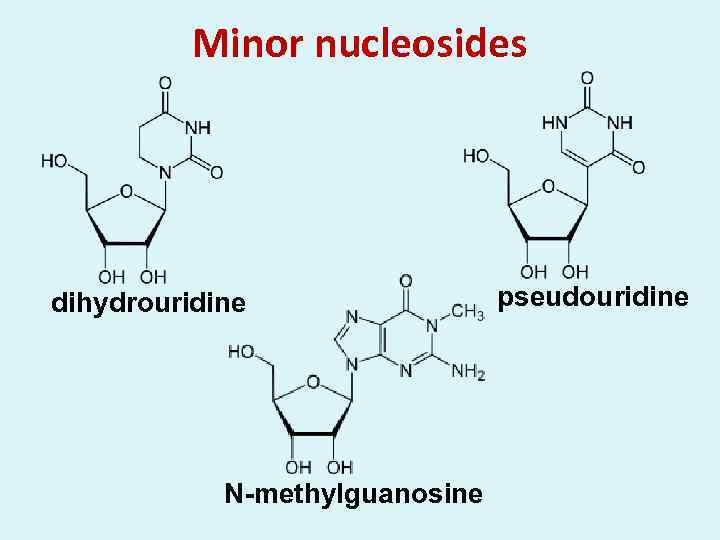 Minor nucleosides dihydrouridine N-methylguanosine pseudouridine
Minor nucleosides dihydrouridine N-methylguanosine pseudouridine
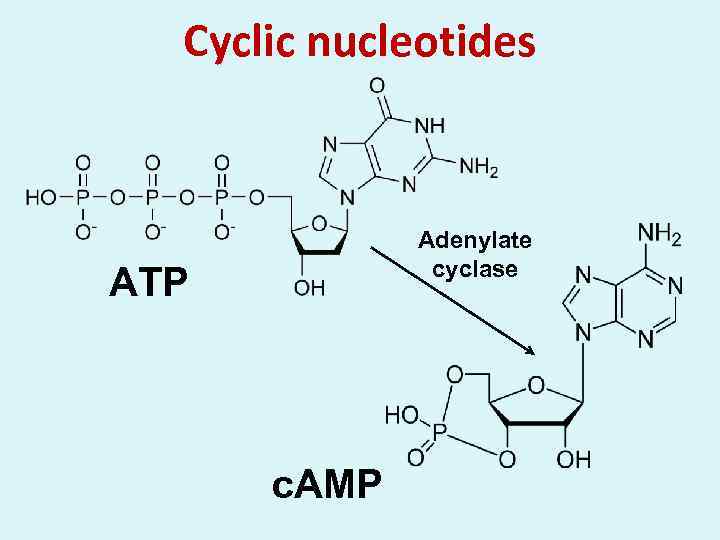 Cyclic nucleotides Adenylate cyclase ATP c. AMP
Cyclic nucleotides Adenylate cyclase ATP c. AMP
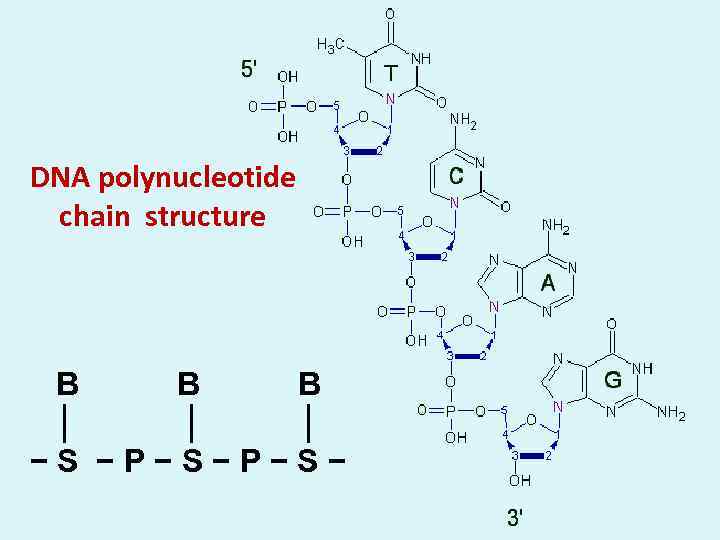 DNA polynucleotide chain structure B B B │ │ │ − S − P − S −
DNA polynucleotide chain structure B B B │ │ │ − S − P − S −
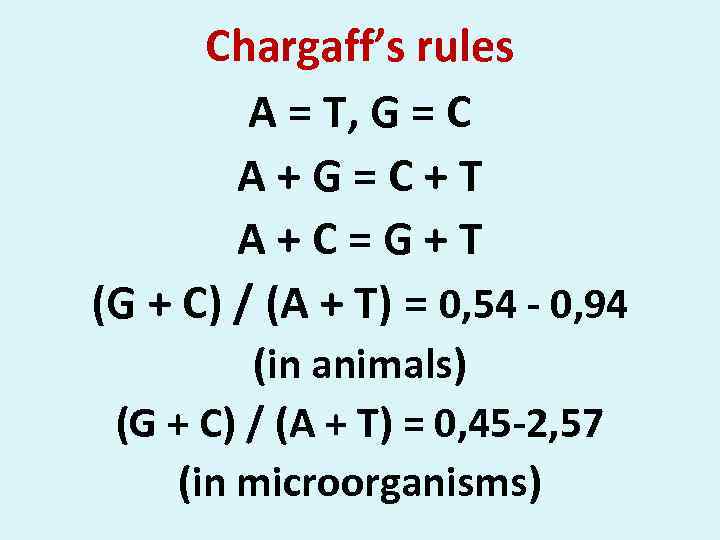 Chargaff’s rules A = T, G = C A + G = C + T A + C = G + T (G + C) / (A + T) = 0, 54 - 0, 94 (in animals) (G + C) / (A + T) = 0, 45 -2, 57 (in microorganisms)
Chargaff’s rules A = T, G = C A + G = C + T A + C = G + T (G + C) / (A + T) = 0, 54 - 0, 94 (in animals) (G + C) / (A + T) = 0, 45 -2, 57 (in microorganisms)
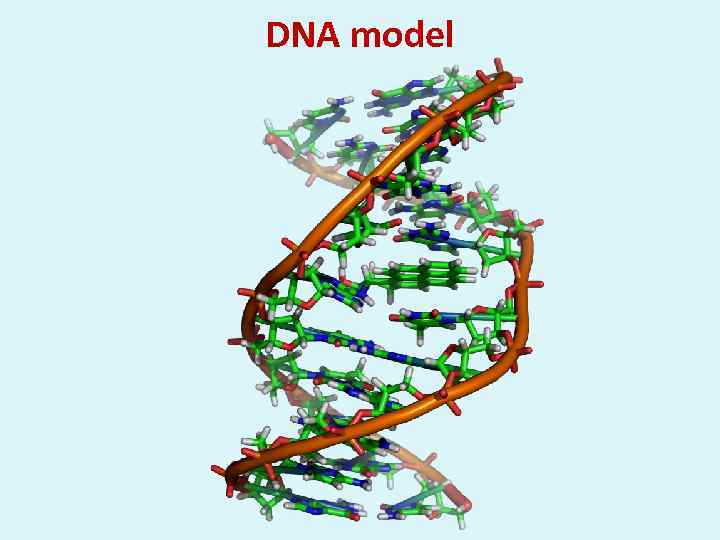 DNA model
DNA model
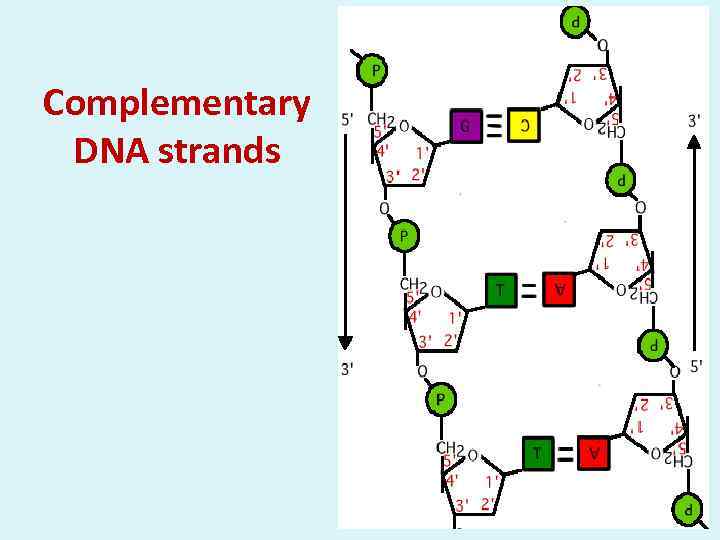 Complementary DNA strands
Complementary DNA strands
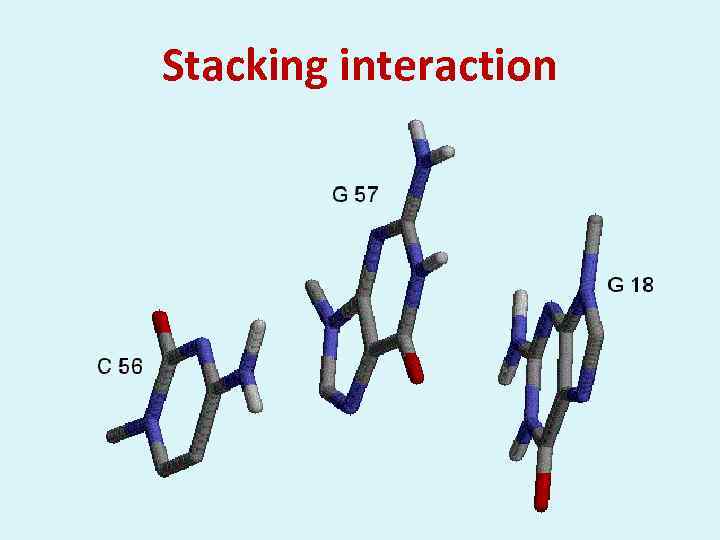 Stacking interaction
Stacking interaction
 The intensity of stacking Purine – Purine Pyrimidine – Pyrimidine
The intensity of stacking Purine – Purine Pyrimidine – Pyrimidine
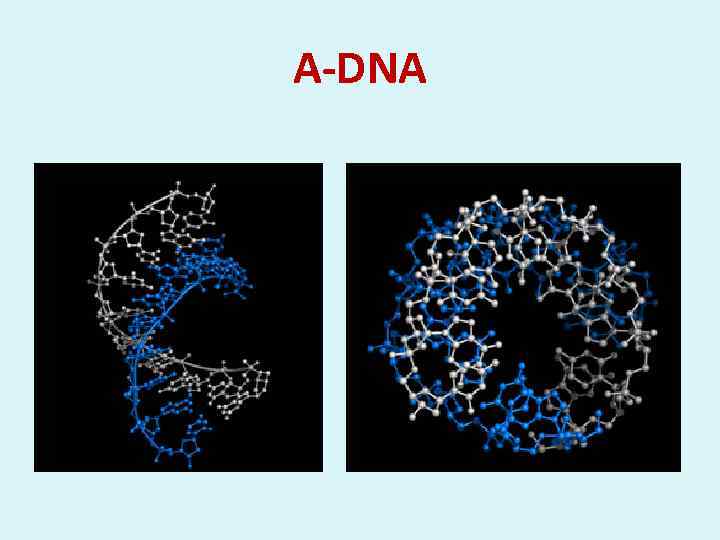 А-DNA
А-DNA
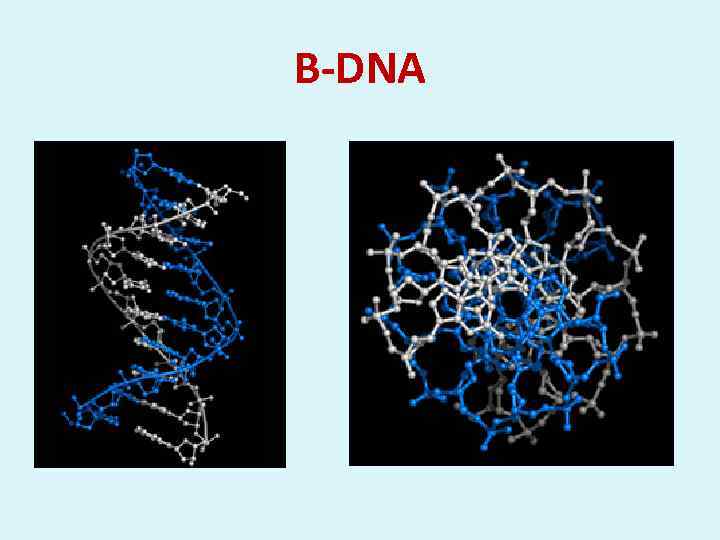 В-DNA
В-DNA
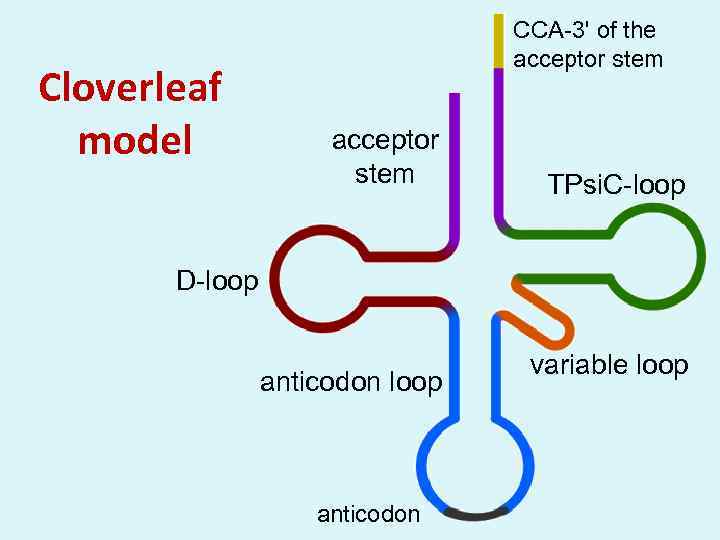 Cloverleaf model CCA-3' of the acceptor stem TPsi. C-loop D-loop anticodon variable loop
Cloverleaf model CCA-3' of the acceptor stem TPsi. C-loop D-loop anticodon variable loop
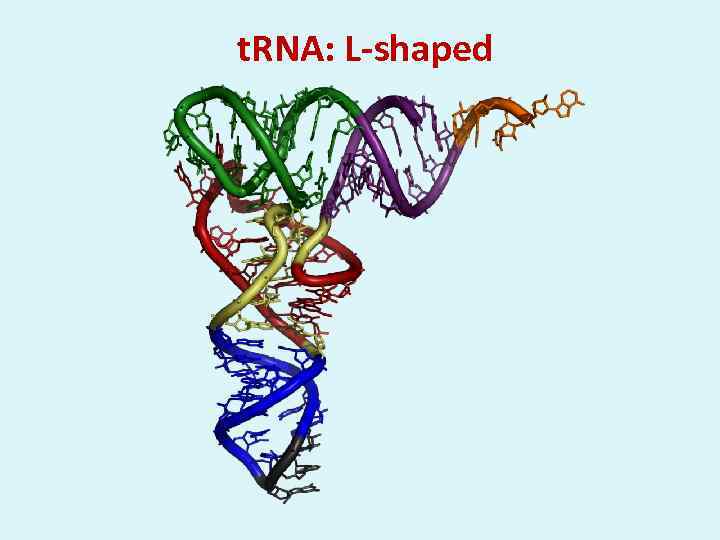 t. RNA: L-shaped
t. RNA: L-shaped
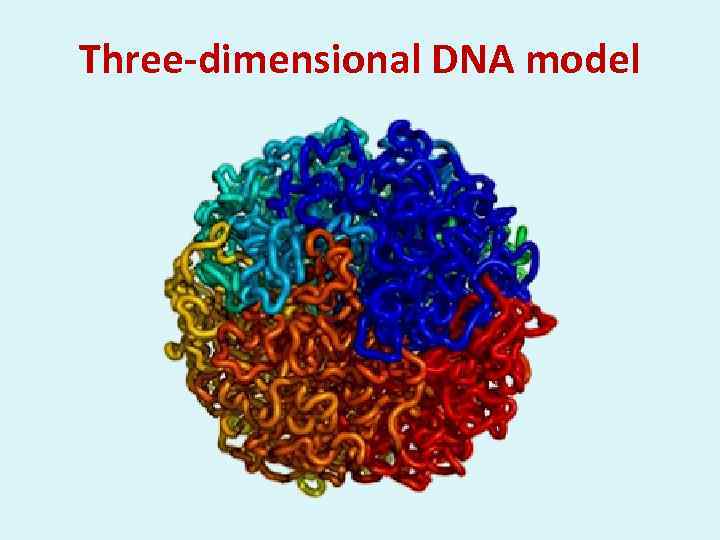 Three-dimensional DNA model
Three-dimensional DNA model
 Ribosome model
Ribosome model
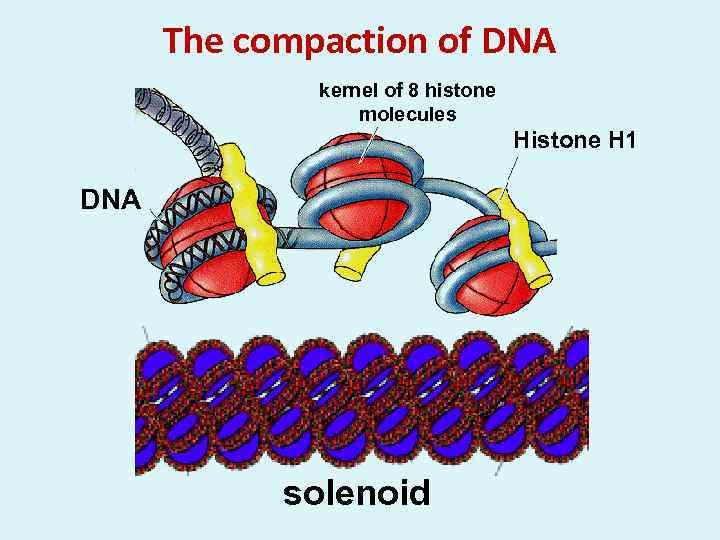 The compaction of DNA kernel of 8 histone molecules Histone H 1 DNA solenoid
The compaction of DNA kernel of 8 histone molecules Histone H 1 DNA solenoid
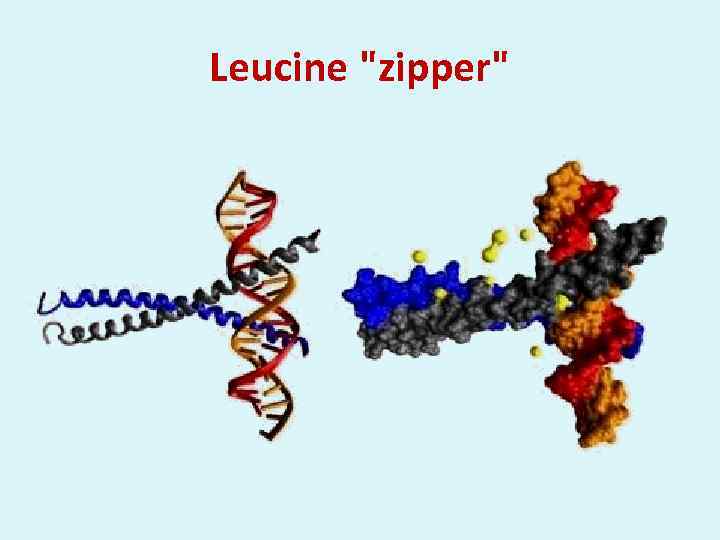 Leucine "zipper"
Leucine "zipper"
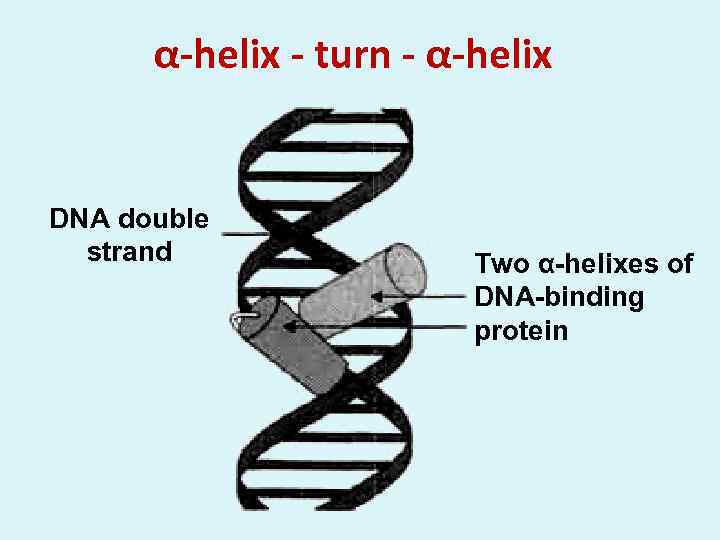 α-helix - turn - α-helix DNA double strand Two α-helixes of DNA-binding protein
α-helix - turn - α-helix DNA double strand Two α-helixes of DNA-binding protein
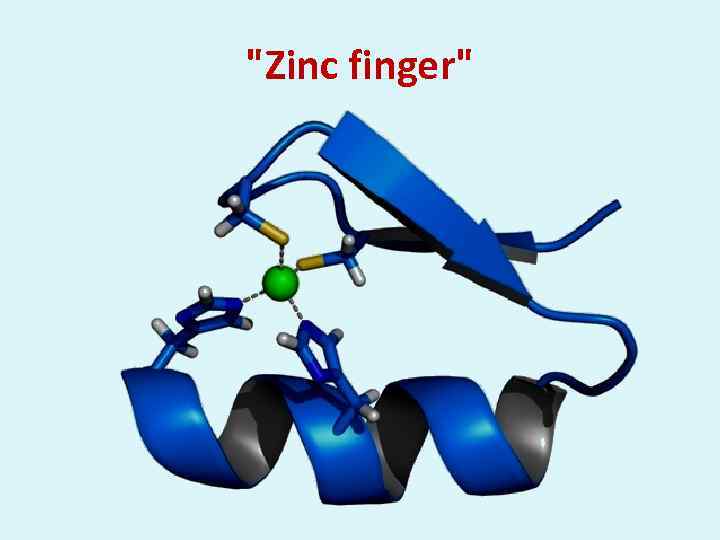 "Zinc finger"
"Zinc finger"


