Презентация slides topic2






















- Размер: 2.1 Mегабайта
- Количество слайдов: 25
Описание презентации Презентация slides topic2 по слайдам
 1 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic 2 Power Converter Systems Graduate Course EE 8407 Ryerson Campus. Bin Wu Ph. D, PEng Professor ELCE Department Ryerson University Contact Info Office: ENG 328 Tel: (416) 979 -5000 ext: 6484 Email: bwu@ee. ryerson. ca http: //www. ee. ryerson. ca/~bwu/
1 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic 2 Power Converter Systems Graduate Course EE 8407 Ryerson Campus. Bin Wu Ph. D, PEng Professor ELCE Department Ryerson University Contact Info Office: ENG 328 Tel: (416) 979 -5000 ext: 6484 Email: bwu@ee. ryerson. ca http: //www. ee. ryerson. ca/~bwu/
 2 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic 2 High-Power Semiconductor Devices
2 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic 2 High-Power Semiconductor Devices
 3 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic 2 • Power Diode • SCR Thyristor • Gate Turn-Off Thyristor (GTO) • Integrated Gate Commutated Thyristor (GCT) • Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT) • Switch Series Operation Lecture Topics. High-Power Semiconductor Devices
3 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic 2 • Power Diode • SCR Thyristor • Gate Turn-Off Thyristor (GTO) • Integrated Gate Commutated Thyristor (GCT) • Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT) • Switch Series Operation Lecture Topics. High-Power Semiconductor Devices
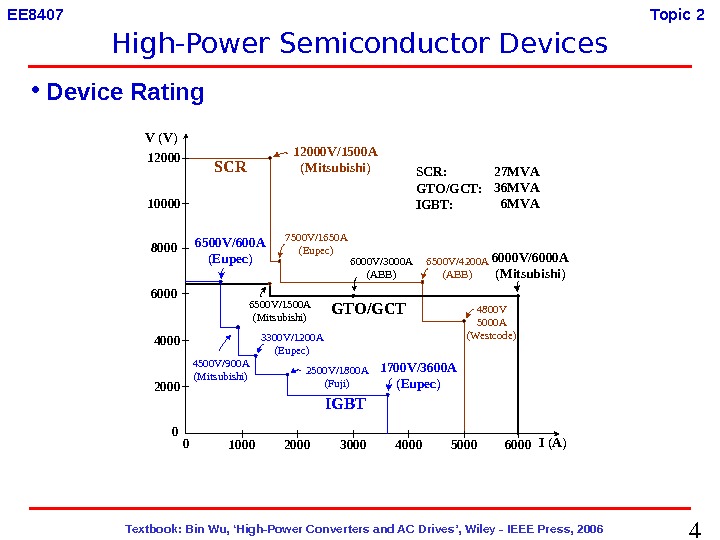
 4 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic 2 12000 10000 8000 SCR 12000 V/1500 A (Mitsubishi)4500 V/900 A (Mitsubishi) 6500 V/1500 A (Mitsubishi) GTO/GCT 7500 V/1650 A (Eupec)6500 V/600 A (Eupec) 6000 4000 2000 1000 2000 3000 4000 3300 V/1200 A (Eupec) 2500 V/1800 A (Fuji)1700 V/3600 A (Eupec) IGBT SCR: GTO/GCT: IGBT: 27 MVA 36 MVA 6000 V/3000 A (ABB) 6500 V/4200 A (ABB) 6000 V/6000 A (Mitsubishi) 4800 V 5000 A (Westcode) 5000 6000 I (A)V (V) 00 • Device Rating High-Power Semiconductor Devices
4 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic 2 12000 10000 8000 SCR 12000 V/1500 A (Mitsubishi)4500 V/900 A (Mitsubishi) 6500 V/1500 A (Mitsubishi) GTO/GCT 7500 V/1650 A (Eupec)6500 V/600 A (Eupec) 6000 4000 2000 1000 2000 3000 4000 3300 V/1200 A (Eupec) 2500 V/1800 A (Fuji)1700 V/3600 A (Eupec) IGBT SCR: GTO/GCT: IGBT: 27 MVA 36 MVA 6000 V/3000 A (ABB) 6500 V/4200 A (ABB) 6000 V/6000 A (Mitsubishi) 4800 V 5000 A (Westcode) 5000 6000 I (A)V (V) 00 • Device Rating High-Power Semiconductor Devices
 5 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic 2 4500 V/800 A press pack and 1700 V/1200 A module diodes Power Diode
5 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic 2 4500 V/800 A press pack and 1700 V/1200 A module diodes Power Diode
 6 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic 2 Press pack device: • Double sided cooling • Low assembly cost and high power density • Preferred choice for high voltage high power applications • Heatsink Assembly A B Cd. V P N (a) Diode Rectifier (b) Press pack (c) Module. Heatsink A P NP NAPower Diode
6 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic 2 Press pack device: • Double sided cooling • Low assembly cost and high power density • Preferred choice for high voltage high power applications • Heatsink Assembly A B Cd. V P N (a) Diode Rectifier (b) Press pack (c) Module. Heatsink A P NP NAPower Diode
 7 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic 2 4500 V/800 A and 4500 V/1500 A SCRs SCR Thyristor
7 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic 2 4500 V/800 A and 4500 V/1500 A SCRs SCR Thyristor
 8 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic 2 • Switching Characteristics. DI 9. 0 DI 1. 0 rrt rr. I 1. 0 rr. I on. V don t ont rt. Gi Ti Tv GMI 1. 0 t t t DI offt rr. Q DV DV 1. 0 Ti T v Gi. SCR Thyristor
8 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic 2 • Switching Characteristics. DI 9. 0 DI 1. 0 rrt rr. I 1. 0 rr. I on. V don t ont rt. Gi Ti Tv GMI 1. 0 t t t DI offt rr. Q DV DV 1. 0 Ti T v Gi. SCR Thyristor
 9 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic 2 DRMV RRMV TAVMI TRMSI — Maximum Rating 12000 V 1500 A 2360 A — Turn — on Time Turn — off Time /dtdi T /dtdv. T rr. Q Switching Characteristics son t 14 s offt 1200 s. A/100 s. V /2000 C 7000 DRMV – Repetitive peak off — state voltage RRMV – Repetitive peak re verse voltage TAVMI – Maximum average on — state current RRMSI – Maximum rms on — state current 2 rrrr rr It Q – Reverse recovery Charge Part number – FT 1500 AU — 240 (Mitsubishi) • Main Specifications 12000 V/1500 A SCR Thyristor
9 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic 2 DRMV RRMV TAVMI TRMSI — Maximum Rating 12000 V 1500 A 2360 A — Turn — on Time Turn — off Time /dtdi T /dtdv. T rr. Q Switching Characteristics son t 14 s offt 1200 s. A/100 s. V /2000 C 7000 DRMV – Repetitive peak off — state voltage RRMV – Repetitive peak re verse voltage TAVMI – Maximum average on — state current RRMSI – Maximum rms on — state current 2 rrrr rr It Q – Reverse recovery Charge Part number – FT 1500 AU — 240 (Mitsubishi) • Main Specifications 12000 V/1500 A SCR Thyristor
 10 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic 2 4500 V/800 A and 4500 V/1500 A GTOs. Gate Turn-Off (GTO) Thyristor
10 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic 2 4500 V/800 A and 4500 V/1500 A GTOs. Gate Turn-Off (GTO) Thyristor
 11 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic 2 • Symmetrical versus Asymmetrical GTOs Type Blocking Voltage Example (6000 V GTOs) Applications Asymmetrical GTO DRMRRMVV VV DRM 6000 VV RRM 22 For use in voltage source inverters with anti — parallel diodes. Symmetrical GTO DRMRRM VV DRM 6000 VV RRM 6500 For use in current source inverters. DRMV — Maximum repetitive peak (forward) off — state voltage RRMV — Maximum repetitive peak reverse voltage Gate Turn-Off (GTO) Thyristor
11 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic 2 • Symmetrical versus Asymmetrical GTOs Type Blocking Voltage Example (6000 V GTOs) Applications Asymmetrical GTO DRMRRMVV VV DRM 6000 VV RRM 22 For use in voltage source inverters with anti — parallel diodes. Symmetrical GTO DRMRRM VV DRM 6000 VV RRM 6500 For use in current source inverters. DRMV — Maximum repetitive peak (forward) off — state voltage RRMV — Maximum repetitive peak reverse voltage Gate Turn-Off (GTO) Thyristor
 12 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic 2 • Switching Characteristics Tv. DV dofft tailt f t. D V 9. 0 D V 1. 0 DI D I 9. 0 DI 1. 0 r tdont dtdi. G/1 MGI 11. 0 MGI 21. 0 MG I 2 T i TTiv, Gi t t dtdi. G/2 0 0 Ti T v. Gi. Gate Turn-Off (GTO) Thyristor
12 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic 2 • Switching Characteristics Tv. DV dofft tailt f t. D V 9. 0 D V 1. 0 DI D I 9. 0 DI 1. 0 r tdont dtdi. G/1 MGI 11. 0 MGI 21. 0 MG I 2 T i TTiv, Gi t t dtdi. G/2 0 0 Ti T v. Gi. Gate Turn-Off (GTO) Thyristor
 13 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic 2 • Main Specifications DRMV RRMV TGQMI TAVMI TRMSI — Maximum Rating 4500 V 17 V 4000 A 1570 A — Turn — on Switching Turn — off Switching /dtdi T /dtdv. T /dtdi. G 1 /dtdi. G 2 Switching Characteristics sdont 5. 2 srt 0. 5 sdofft 0. 25 sft 0. 3 s. A/500 s. V/1000 s. A/40 On — state Voltage VVstateon. T 4. 4)( at AIT 4000 DRMV — Repetitive peak off — state voltage RRMV — Repetitive peak reverse voltage TGQMI — Repetitive co ntrollable on — state current TAVMI — Maximum average on — state current RRMSI — Maximum rms on — state current Part number — 5 SGA 40 L 4501 (ABB) 4500 V/4000 A Asymmetrical GTO Thyristor Gate Turn-Off (GTO) Thyristor
13 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic 2 • Main Specifications DRMV RRMV TGQMI TAVMI TRMSI — Maximum Rating 4500 V 17 V 4000 A 1570 A — Turn — on Switching Turn — off Switching /dtdi T /dtdv. T /dtdi. G 1 /dtdi. G 2 Switching Characteristics sdont 5. 2 srt 0. 5 sdofft 0. 25 sft 0. 3 s. A/500 s. V/1000 s. A/40 On — state Voltage VVstateon. T 4. 4)( at AIT 4000 DRMV — Repetitive peak off — state voltage RRMV — Repetitive peak reverse voltage TGQMI — Repetitive co ntrollable on — state current TAVMI — Maximum average on — state current RRMSI — Maximum rms on — state current Part number — 5 SGA 40 L 4501 (ABB) 4500 V/4000 A Asymmetrical GTO Thyristor Gate Turn-Off (GTO) Thyristor
 14 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic 2 6500 V/1500 A Symmetrical GCT = Improved GTO + Integrated Gate + Anti-parallel Diode (optional) Integrated Gate Commutated Thyristor (GCT)
14 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic 2 6500 V/1500 A Symmetrical GCT = Improved GTO + Integrated Gate + Anti-parallel Diode (optional) Integrated Gate Commutated Thyristor (GCT)
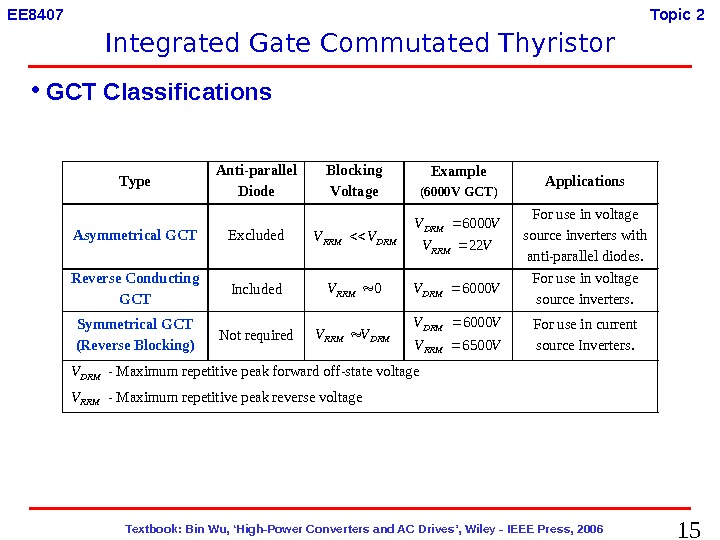
 15 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic 2 • GCT Classifications Type Anti-parallel Diode Blocking Voltage Example (6000 V GCT) Applications Asymmetrical GCT Excluded DRMRRMVV VVDRM 6000 VVRRM 22 For use in voltage source inverters with anti-parallel diodes. Reverse Conducting GCT Included 0 RRMV VVDRM 6000 For use in voltage source inverters. Symmetrical GCT (Reverse Blocking) Not required DRMRRMVV VVDRM 6000 VVRRM 6500 For use in current source Inverters. DRMV — Maximum repetitive peak forward off-state voltage RRMV — Maximum repetitive peak reverse voltage Integrated Gate Commutated Thyristor
15 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic 2 • GCT Classifications Type Anti-parallel Diode Blocking Voltage Example (6000 V GCT) Applications Asymmetrical GCT Excluded DRMRRMVV VVDRM 6000 VVRRM 22 For use in voltage source inverters with anti-parallel diodes. Reverse Conducting GCT Included 0 RRMV VVDRM 6000 For use in voltage source inverters. Symmetrical GCT (Reverse Blocking) Not required DRMRRMVV VVDRM 6000 VVRRM 6500 For use in current source Inverters. DRMV — Maximum repetitive peak forward off-state voltage RRMV — Maximum repetitive peak reverse voltage Integrated Gate Commutated Thyristor
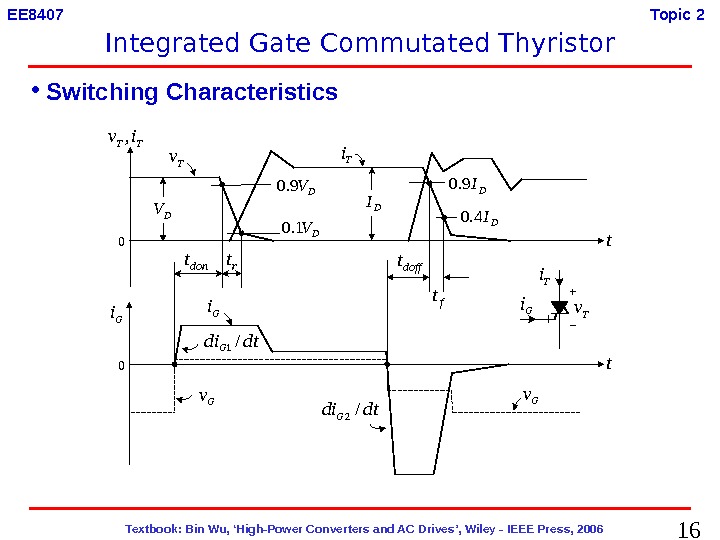
 16 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic 2 • Switching Characteristics. DI 9. 0 DI 4. 0 DV 9. 0 DV 1. 0 Gi Gv t t TTiv, Tv DV T i DI r tdont dtdi. G/1 dtdi. G/2 doff t G v 0 0 Gi Ti T v. Gi. Integrated Gate Commutated Thyristor
16 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic 2 • Switching Characteristics. DI 9. 0 DI 4. 0 DV 9. 0 DV 1. 0 Gi Gv t t TTiv, Tv DV T i DI r tdont dtdi. G/1 dtdi. G/2 doff t G v 0 0 Gi Ti T v. Gi. Integrated Gate Commutated Thyristor
 17 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic 2 • Main Specifications. DRMV RRMV TQRMI TAVMI TRMSI — Maximum Rating 6000 V 22 V 6000 A 2000 A 3100 A — Turn-on Switching Turn-off Switching /dtdi. T /dtdv. T /dtdi. G 1 /dtdi. G 2 Switching Characteristics stdon 0. 1 srt 0. 2 s dofft 0. 3 ft — N/A s. A/1000 s. V/3000 s. A/200 10, 000 s. A / On-state Voltage VV stateon. T 4 )( at AIT 6000 DRMV — Repetitive peak off-state voltage RRMV — Repetitive peak reverse voltage TGRMI — Repetitive controllable on-state current TAVMI — Maximum average on-state current RRMSI — Maximum rms on-state current Part number – FGC 6000 AX 120 DS (Mitsubishi) 6000 V/6000 A Asymmetrical GCTIntegrated Gate Commutated Thyristor
17 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic 2 • Main Specifications. DRMV RRMV TQRMI TAVMI TRMSI — Maximum Rating 6000 V 22 V 6000 A 2000 A 3100 A — Turn-on Switching Turn-off Switching /dtdi. T /dtdv. T /dtdi. G 1 /dtdi. G 2 Switching Characteristics stdon 0. 1 srt 0. 2 s dofft 0. 3 ft — N/A s. A/1000 s. V/3000 s. A/200 10, 000 s. A / On-state Voltage VV stateon. T 4 )( at AIT 6000 DRMV — Repetitive peak off-state voltage RRMV — Repetitive peak reverse voltage TGRMI — Repetitive controllable on-state current TAVMI — Maximum average on-state current RRMSI — Maximum rms on-state current Part number – FGC 6000 AX 120 DS (Mitsubishi) 6000 V/6000 A Asymmetrical GCTIntegrated Gate Commutated Thyristor
 18 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic 2 1700 V/1200 A and 3300 V/1200 A IGBT modules Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT)
18 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic 2 1700 V/1200 A and 3300 V/1200 A IGBT modules Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT)
 19 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic 2 Static V-I Characteristicst +15 V 90% t +15 V 10% t dont rt dofft f t 90% 0 GEv Gv. C i 0 0 Switching characteristics 5 GEV 4 GEV 3 GEV 2 GEV 1 GEV CEV 2 V 0 CI CEv. G C E Ci • IGBT Characteristics Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT)
19 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic 2 Static V-I Characteristicst +15 V 90% t +15 V 10% t dont rt dofft f t 90% 0 GEv Gv. C i 0 0 Switching characteristics 5 GEV 4 GEV 3 GEV 2 GEV 1 GEV CEV 2 V 0 CI CEv. G C E Ci • IGBT Characteristics Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT)
 20 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic 2 • Main Specifications CEV CI CMI — Maximum Rating 3300 V 1200 A 2400 A — don t rt dofft ft Switching Characteristics 0. 35 s 0. 27 s 1. 7 s 0. 2 s Saturation Voltage V 3. 4 sat. CEI at AIC 1200 CE V — Rated collector-emitter voltage CI — Rated dc collector current CMI — Maximum repetitive peak collector current Part number – FZ 1200 R 33 KF 2 (Eupec) 3300 V/1200 A IGBTInsulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT)
20 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic 2 • Main Specifications CEV CI CMI — Maximum Rating 3300 V 1200 A 2400 A — don t rt dofft ft Switching Characteristics 0. 35 s 0. 27 s 1. 7 s 0. 2 s Saturation Voltage V 3. 4 sat. CEI at AIC 1200 CE V — Rated collector-emitter voltage CI — Rated dc collector current CMI — Maximum repetitive peak collector current Part number – FZ 1200 R 33 KF 2 (Eupec) 3300 V/1200 A IGBTInsulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT)
 21 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic 2 • Cause of Voltage Imbalance 1 S 2 S 3 S 1 v 2 v 3 v Type Causes of Voltage Imbalance Static Voltage Sharing lk. I – Device off-state leakage current j. T – Junction temperature Device dont – Turn-on delay time dofft – Turn-off delay time rr. Q – Reverse recovery charge of anti-parallel diode j. T – Junction temperature Gate Driver GDont – Gate driver turn-on delay time GDofft – Gate driver turn-off delay time wire. L – Wiring inductance between the the gate driver and the device gate Dynamic Voltage Sharing – Differences between series connected devices. Device Series Operation
21 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic 2 • Cause of Voltage Imbalance 1 S 2 S 3 S 1 v 2 v 3 v Type Causes of Voltage Imbalance Static Voltage Sharing lk. I – Device off-state leakage current j. T – Junction temperature Device dont – Turn-on delay time dofft – Turn-off delay time rr. Q – Reverse recovery charge of anti-parallel diode j. T – Junction temperature Gate Driver GDont – Gate driver turn-on delay time GDofft – Gate driver turn-off delay time wire. L – Wiring inductance between the the gate driver and the device gate Dynamic Voltage Sharing – Differences between series connected devices. Device Series Operation
 22 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic 2 s. R s. C v. R 1 S 2 S 3 S 1 v 2 v 3 v • Equal Voltage Sharing • S 1 , S 2 , S 3 : GTO, GCT or IGBT • Voltage Sharing: v 1 = v 2 = v 3 in steady state and transients • Static Voltage Sharing: R v • Dynamic Voltage Sharing: R s and C s Device Series Operation
22 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic 2 s. R s. C v. R 1 S 2 S 3 S 1 v 2 v 3 v • Equal Voltage Sharing • S 1 , S 2 , S 3 : GTO, GCT or IGBT • Voltage Sharing: v 1 = v 2 = v 3 in steady state and transients • Static Voltage Sharing: R v • Dynamic Voltage Sharing: R s and C s Device Series Operation
 23 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic 2 • Active Overvoltage Clamping (AOC) • Assumption: S 1 is turned off earlier than S 2 • V CE 1 is clamed to V m due to active clamping. Gate Signal Conditioning inv Gate Signal Conditioningg. R Amp Active Overvoltage Clamping AOC Vm Vm 1 CEv 2 CEv 1 S 2 S- Suitable for series IGBTs — Not applicable to GCTs 1 CE v 2 CEv Ci dt 0 m V t Device Series Operation
23 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic 2 • Active Overvoltage Clamping (AOC) • Assumption: S 1 is turned off earlier than S 2 • V CE 1 is clamed to V m due to active clamping. Gate Signal Conditioning inv Gate Signal Conditioningg. R Amp Active Overvoltage Clamping AOC Vm Vm 1 CEv 2 CEv 1 S 2 S- Suitable for series IGBTs — Not applicable to GCTs 1 CE v 2 CEv Ci dt 0 m V t Device Series Operation
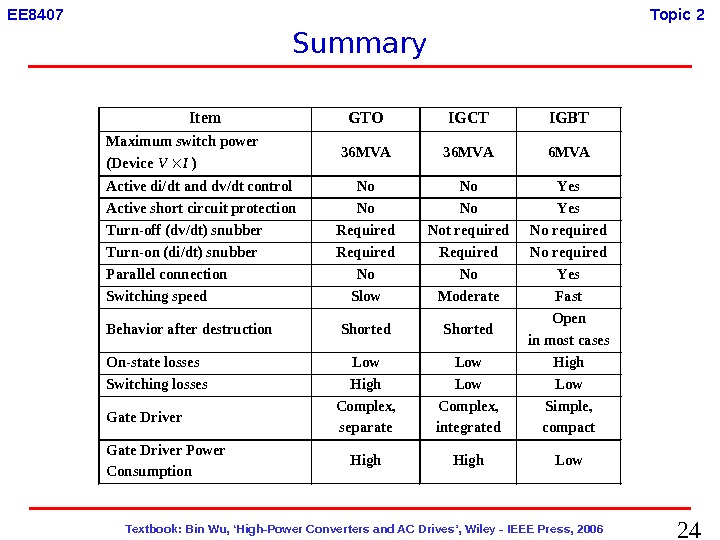
 24 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic 2 Item GTO IGCT IGBT Maximum switch power (Device IV) 36 MVA Active di/dt and dv/dt control No No Yes Active short circuit protection No No Yes Turn-off (dv/dt) snubber Required Not required No required Turn-on (di/dt) snubber Required No required Parallel connection No No Yes Switching speed Slow Moderate Fast Behavior after destruction Shorted Open in most cases On-state losses Low High Switching losses High Low Gate Driver Complex, separate Complex, integrated Simple, compact Gate Driver Power Consumption High Low Summary
24 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic 2 Item GTO IGCT IGBT Maximum switch power (Device IV) 36 MVA Active di/dt and dv/dt control No No Yes Active short circuit protection No No Yes Turn-off (dv/dt) snubber Required Not required No required Turn-on (di/dt) snubber Required No required Parallel connection No No Yes Switching speed Slow Moderate Fast Behavior after destruction Shorted Open in most cases On-state losses Low High Switching losses High Low Gate Driver Complex, separate Complex, integrated Simple, compact Gate Driver Power Consumption High Low Summary
 25 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic
25 Textbook: Bin Wu, ‘High-Power Converters and AC Drives’, Wiley — IEEE Press, 2006 EE 8407 Topic

