Презентация lect.6-7 GRAMMATICAL ASPECTS OF TRANSLATION






































































lect.6-7_grammatical_aspects_of_translation.ppt
- Размер: 1.9 Mегабайта
- Количество слайдов: 79
Описание презентации Презентация lect.6-7 GRAMMATICAL ASPECTS OF TRANSLATION по слайдам
 GRAMMATICAL ASPECTS OF TRANSLATION Lectures 6 —
GRAMMATICAL ASPECTS OF TRANSLATION Lectures 6 —
 Problems for discussion Handling equivalent forms and structures Handling equivalent-lacking forms and structures Handling modal forms Key words: Correspondence, grammatical forms, syntactic order, permanent grammatical equivalent, grammatical transformations, similarity/dissimilarity, a lack of equivalence.
Problems for discussion Handling equivalent forms and structures Handling equivalent-lacking forms and structures Handling modal forms Key words: Correspondence, grammatical forms, syntactic order, permanent grammatical equivalent, grammatical transformations, similarity/dissimilarity, a lack of equivalence.
 HANDLING EQUIVALENT FORMS AND STRUCTURES Every word in the text is used in a _____________and all the words are arranged in sentences in a_____________. _______is an important feature of speech units. Grammatical forms and structures, except for providing___________, also convey some information which is part of its_________.
HANDLING EQUIVALENT FORMS AND STRUCTURES Every word in the text is used in a _____________and all the words are arranged in sentences in a_____________. _______is an important feature of speech units. Grammatical forms and structures, except for providing___________, also convey some information which is part of its_________.
 HANDLING EQUIVALENT FORMS AND STRUCTURES They reveal the____________, clauses and sentences in the text, they can make ______________that is of particular significance for the______. The __________of the text is an important ___________ either the ____of the text or its______.
HANDLING EQUIVALENT FORMS AND STRUCTURES They reveal the____________, clauses and sentences in the text, they can make ______________that is of particular significance for the______. The __________of the text is an important ___________ either the ____of the text or its______.
 HANDLING EQUIVALENT FORMS AND STRUCTURES Though the __________in the original text is___________, the semantic role of grammatical forms and structures should not be____________. The importance of the _________________is often reflected in the choice of the_______________.
HANDLING EQUIVALENT FORMS AND STRUCTURES Though the __________in the original text is___________, the semantic role of grammatical forms and structures should not be____________. The importance of the _________________is often reflected in the choice of the_______________.
 HANDLING EQUIVALENT FORMS AND STRUCTURES Equivalence in translation can be best achieved if the translator_______________________________________________.
HANDLING EQUIVALENT FORMS AND STRUCTURES Equivalence in translation can be best achieved if the translator_______________________________________________.
 The principal types of grammatical correspondences between two languages are as follows: -_______________________; -______________.
The principal types of grammatical correspondences between two languages are as follows: -_______________________; -______________.
 HANDLING EQUIVALENT FORMS AND STRUCTURES NB There are _______________________and the translator can choose between the ________and various________________. There is never an _______ between the meaning and __________in SL and TL. F. e. , both English and Russian verbs have their __________________.
HANDLING EQUIVALENT FORMS AND STRUCTURES NB There are _______________________and the translator can choose between the ________and various________________. There is never an _______ between the meaning and __________in SL and TL. F. e. , both English and Russian verbs have their __________________.
 HANDLING EQUIVALENT FORMS AND STRUCTURES The English infinitive has__________________, which are absent in the _____________________in Russian. The idea of __________action expressed by the _______is not present in the meaning of the Russian Infinitive and has to be rendered in translation by____________.
HANDLING EQUIVALENT FORMS AND STRUCTURES The English infinitive has__________________, which are absent in the _____________________in Russian. The idea of __________action expressed by the _______is not present in the meaning of the Russian Infinitive and has to be rendered in translation by____________.
 HANDLING EQUIVALENT FORMS AND STRUCTURES ‘The train seems to arrive at 5. » _____________ ‘The train seems to have arrived at 5. “ _______________
HANDLING EQUIVALENT FORMS AND STRUCTURES ‘The train seems to arrive at 5. » _____________ ‘The train seems to have arrived at 5. “ _______________
 HANDLING EQUIVALENT FORMS AND STRUCTURES A ________of the English and Russian Infinitives can be also found in the______________. (for example, the ______Infinitive which in English _______following that indicated by the_______):
HANDLING EQUIVALENT FORMS AND STRUCTURES A ________of the English and Russian Infinitives can be also found in the______________. (for example, the ______Infinitive which in English _______following that indicated by the_______):
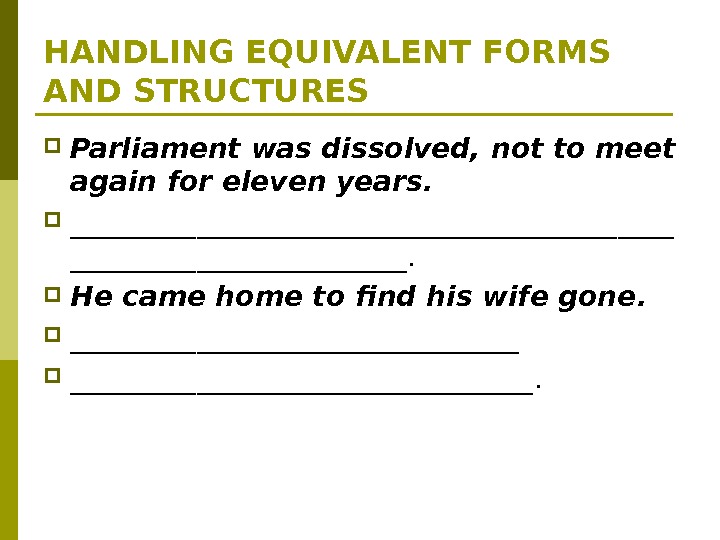
 HANDLING EQUIVALENT FORMS AND STRUCTURES Parliament was dissolved, not to meet again for eleven years. ______________________. Не came home to find his wife gone. _________________________________.
HANDLING EQUIVALENT FORMS AND STRUCTURES Parliament was dissolved, not to meet again for eleven years. ______________________. Не came home to find his wife gone. _________________________________.
 HANDLING EQUIVALENT FORMS AND STRUCTURES A _________can be observed if one compares ___________of the verb in English and in Russian. The English and the Russian _______both have____________, but in English the _______________________and are more often used. As a result, the meaning of the __________________is often rendered by an _____in the translation:
HANDLING EQUIVALENT FORMS AND STRUCTURES A _________can be observed if one compares ___________of the verb in English and in Russian. The English and the Russian _______both have____________, but in English the _______________________and are more often used. As a result, the meaning of the __________________is often rendered by an _____in the translation:
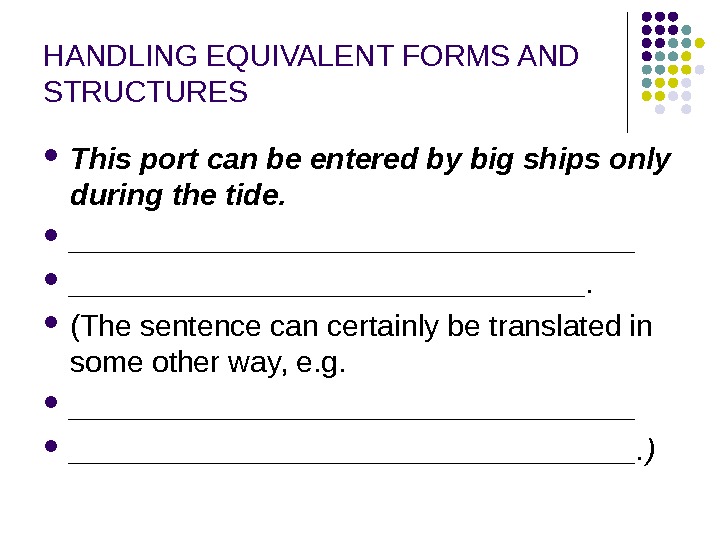
 HANDLING EQUIVALENT FORMS AND STRUCTURES This port can be entered by big ships only during the tide. _________________. (The sentence can certainly be translated in some other way, e. g. __________________________________. )
HANDLING EQUIVALENT FORMS AND STRUCTURES This port can be entered by big ships only during the tide. _________________. (The sentence can certainly be translated in some other way, e. g. __________________________________. )
 HANDLING EQUIVALENT FORMS AND STRUCTURES A most common example of _______________________in the two languages is the role of ____________in English and in Russian/Ukrainian. Both languages use a “______» and an “_____» word order. But the English word order____, in most cases___________: the predicate is ___________and followed___________.
HANDLING EQUIVALENT FORMS AND STRUCTURES A most common example of _______________________in the two languages is the role of ____________in English and in Russian/Ukrainian. Both languages use a “______» and an “_____» word order. But the English word order____, in most cases___________: the predicate is ___________and followed___________.
 HANDLING EQUIVALENT FORMS AND STRUCTURES This order of words is often changed in the Russian/Ukrainian translation since in Russian/Ukrainian______________________, the elements conveying new information (the_______) leaning______________.
HANDLING EQUIVALENT FORMS AND STRUCTURES This order of words is often changed in the Russian/Ukrainian translation since in Russian/Ukrainian______________________, the elements conveying new information (the_______) leaning______________.
 HANDLING EQUIVALENT FORMS AND STRUCTURES Thus if the English sentence «My son entered the room» is intended to inform us__________, its Russian/Ukrainian equivalent will be «____________________» but in case ______is to tell us ______, the word order will be preserved: ____________________
HANDLING EQUIVALENT FORMS AND STRUCTURES Thus if the English sentence «My son entered the room» is intended to inform us__________, its Russian/Ukrainian equivalent will be «____________________» but in case ______is to tell us ______, the word order will be preserved: ____________________
 HANDLING EQUIVALENT FORMS AND STRUCTURES The predominantly ________in the English sentence means that _________________the object carry a______________. This emphasis _________in translation by such a ______as the _____________in the Russian sentence and the translator has to use some _______________________ Money he had none. ________________.
HANDLING EQUIVALENT FORMS AND STRUCTURES The predominantly ________in the English sentence means that _________________the object carry a______________. This emphasis _________in translation by such a ______as the _____________in the Russian sentence and the translator has to use some _______________________ Money he had none. ________________.
 HANDLING EQUIVALENT-LACKING FORMS AND STRUCTURES The English grammatical form that has __ ___________in Russian/Ukrainian may be a part of speech, a ___________or a____________. The _____ is part of the English grammar and is ________in Russian and Ukrainian.
HANDLING EQUIVALENT-LACKING FORMS AND STRUCTURES The English grammatical form that has __ ___________in Russian/Ukrainian may be a part of speech, a ___________or a____________. The _____ is part of the English grammar and is ________in Russian and Ukrainian.
 HANDLING EQUIVALENT-LACKING FORMS AND STRUCTURES As a rule, English ___________into Russian and Ukrainian for their ______is expressed by ____________and needn’t be reproduced___________. Translating the phrase «the man who gave me the book» with the Russian «__________» the translator needn’t worry about the definite article since the _____________due to the presence of the ______________clause.
HANDLING EQUIVALENT-LACKING FORMS AND STRUCTURES As a rule, English ___________into Russian and Ukrainian for their ______is expressed by ____________and needn’t be reproduced___________. Translating the phrase «the man who gave me the book» with the Russian «__________» the translator needn’t worry about the definite article since the _____________due to the presence of the ______________clause.
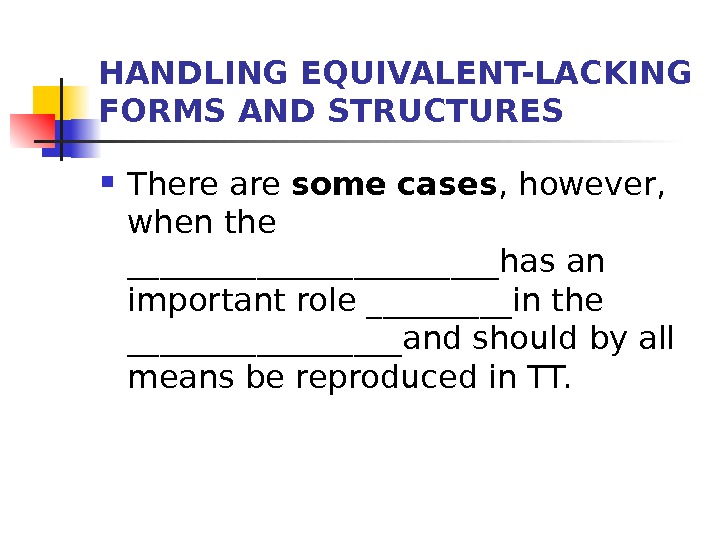
 HANDLING EQUIVALENT-LACKING FORMS AND STRUCTURES There are some cases , however, when the ____________has an important role _____in the _________and should by all means be reproduced in TT.
HANDLING EQUIVALENT-LACKING FORMS AND STRUCTURES There are some cases , however, when the ____________has an important role _____in the _________and should by all means be reproduced in TT.
 HANDLING EQUIVALENT-LACKING FORMS AND STRUCTURES A passenger was looking for a place to put his bag. – _________________________. I have found a fellow student who agreed to help me. – _______________________. A Mr. Brown has left a message for you. – _________________________________.
HANDLING EQUIVALENT-LACKING FORMS AND STRUCTURES A passenger was looking for a place to put his bag. – _________________________. I have found a fellow student who agreed to help me. – _______________________. A Mr. Brown has left a message for you. – _________________________________.
 HANDLING EQUIVALENT-LACKING FORMS AND STRUCTURES The __________may correspond either to the _______________Russian forms and the choice is largely__________. After supper he usually smoked in the garden. _________________. After supper he smoked a cigarette in the garden and went to bed. ____________________.
HANDLING EQUIVALENT-LACKING FORMS AND STRUCTURES The __________may correspond either to the _______________Russian forms and the choice is largely__________. After supper he usually smoked in the garden. _________________. After supper he smoked a cigarette in the garden and went to bed. ____________________.
 HANDLING EQUIVALENT-LACKING FORMS AND STRUCTURES The _______forms!!! — referring to an action ___________ or a_________. I hoped he had read that book. (а) _______________ , (б) ________________. And, again, the ________will enable the translator to make the correct choice.
HANDLING EQUIVALENT-LACKING FORMS AND STRUCTURES The _______forms!!! — referring to an action ___________ or a_________. I hoped he had read that book. (а) _______________ , (б) ________________. And, again, the ________will enable the translator to make the correct choice.
 HANDLING EQUIVALENT-LACKING FORMS AND STRUCTURES English ______________________ have no parallels in Russian and Ukrainian. Translating sentences with such complexes always_____________.
HANDLING EQUIVALENT-LACKING FORMS AND STRUCTURES English ______________________ have no parallels in Russian and Ukrainian. Translating sentences with such complexes always_____________.
 HANDLING EQUIVALENT-LACKING FORMS AND STRUCTURES ______________ 1 -st. An __________must be ________by the translator. The identification problem is particularly _________in the case of the “_____»- structures which may___________________________.
HANDLING EQUIVALENT-LACKING FORMS AND STRUCTURES ______________ 1 -st. An __________must be ________by the translator. The identification problem is particularly _________in the case of the “_____»- structures which may___________________________.
 HANDLING EQUIVALENT-LACKING FORMS AND STRUCTURES The phrase «How can you play with your brother lying sick in bed» can be understood in _______: as an __________and then its Russian equivalent will be «________________» or as a ____________which should be translated as «_______________» .
HANDLING EQUIVALENT-LACKING FORMS AND STRUCTURES The phrase «How can you play with your brother lying sick in bed» can be understood in _______: as an __________and then its Russian equivalent will be «________________» or as a ____________which should be translated as «_______________» .
 HANDLING EQUIVALENT-LACKING FORMS AND STRUCTURES Then the translator should consider the _____________________equivalents. The meaning of the ___________________can be rendered into Russian with the help of_____________________.
HANDLING EQUIVALENT-LACKING FORMS AND STRUCTURES Then the translator should consider the _____________________equivalents. The meaning of the ___________________can be rendered into Russian with the help of_____________________.
 HANDLING EQUIVALENT-LACKING FORMS AND STRUCTURES Using a _____ involves the identification of the ___________________ of the construction: «Business disposed of, we went for a walk. » -_________________.
HANDLING EQUIVALENT-LACKING FORMS AND STRUCTURES Using a _____ involves the identification of the ___________________ of the construction: «Business disposed of, we went for a walk. » -_________________.
 HANDLING EQUIVALENT-LACKING FORMS AND STRUCTURES This can be avoided by using an_______, but then care should be taken to refer it to the subject: ____________________________. (__________are common in English but are usually not used in__________. «But coming from West Indies, his chances were very slim» and «__________________» . )
HANDLING EQUIVALENT-LACKING FORMS AND STRUCTURES This can be avoided by using an_______, but then care should be taken to refer it to the subject: ____________________________. (__________are common in English but are usually not used in__________. «But coming from West Indies, his chances were very slim» and «__________________» . )
 HANDLING EQUIVALENT-LACKING FORMS AND STRUCTURES The same sentence can be rendered into Russian by _________ sentences: _________________________. This method is not________, whenever it___ _____________.
HANDLING EQUIVALENT-LACKING FORMS AND STRUCTURES The same sentence can be rendered into Russian by _________ sentences: _________________________. This method is not________, whenever it___ _____________.
 HANDLING EQUIVALENT-LACKING FORMS AND STRUCTURES Specific translation problems emerge when the translator has to handle a _______________introduced by the verb “ ______ » or “______», such as: «I shall have him do it» or «I shall have him punished».
HANDLING EQUIVALENT-LACKING FORMS AND STRUCTURES Specific translation problems emerge when the translator has to handle a _______________introduced by the verb “ ______ » or “______», such as: «I shall have him do it» or «I shall have him punished».
 HANDLING EQUIVALENT-LACKING FORMS AND STRUCTURES First, the translator has to ____what Russian ________should be used as a _______for the English “_____» or “_______». Depending on the _______of the___________, the phrase «I shall have him do it» may be rendered into Russian as «_________________» or even «__________________» .
HANDLING EQUIVALENT-LACKING FORMS AND STRUCTURES First, the translator has to ____what Russian ________should be used as a _______for the English “_____» or “_______». Depending on the _______of the___________, the phrase «I shall have him do it» may be rendered into Russian as «_________________» or even «__________________» .
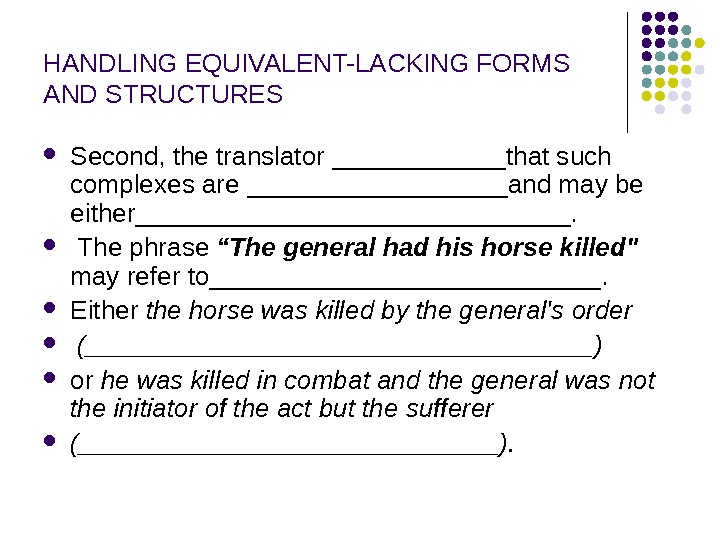
 HANDLING EQUIVALENT-LACKING FORMS AND STRUCTURES Second, the translator ______that such complexes are _________and may be either_______________. The phrase “The general had his horse killed» may refer to______________. Either the horse was killed by the general’s order (__________________) or he was killed in combat and the general was not the initiator of the act but the sufferer (_______________).
HANDLING EQUIVALENT-LACKING FORMS AND STRUCTURES Second, the translator ______that such complexes are _________and may be either_______________. The phrase “The general had his horse killed» may refer to______________. Either the horse was killed by the general’s order (__________________) or he was killed in combat and the general was not the initiator of the act but the sufferer (_______________).
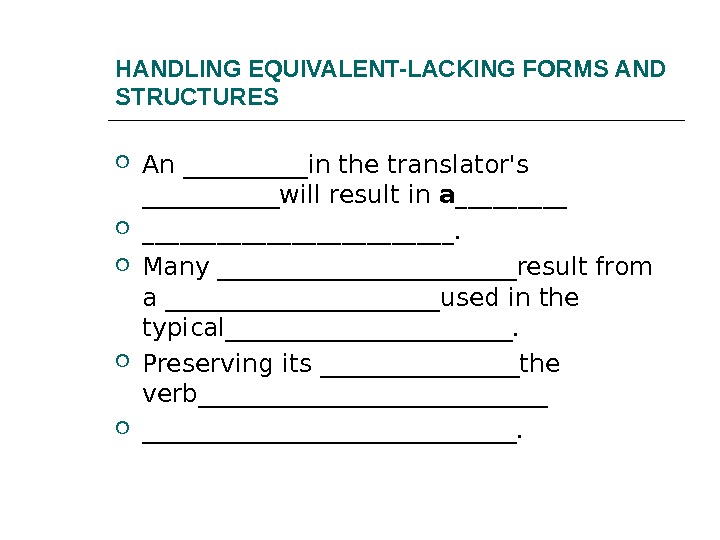
 HANDLING EQUIVALENT-LACKING FORMS AND STRUCTURES An _____in the translator’s ______will result in a_____________. Many ____________result from a ___________used in the typical____________. Preserving its ________the verb_______________.
HANDLING EQUIVALENT-LACKING FORMS AND STRUCTURES An _____in the translator’s ______will result in a_____________. Many ____________result from a ___________used in the typical____________. Preserving its ________the verb_______________.
 HANDLING EQUIVALENT-LACKING FORMS AND STRUCTURES They laughed merrily. ____________. They laughed him out of the room. _________________. In such cases the translator has to choose among _____________relationships in TL.
HANDLING EQUIVALENT-LACKING FORMS AND STRUCTURES They laughed merrily. ____________. They laughed him out of the room. _________________. In such cases the translator has to choose among _____________relationships in TL.
 HANDLING MODAL FORMS _______is a semantic category indicating the __________that the speaker _______to his message. A message can be presented by its author as________, a request______, or something that_______, possible or ________but not an established fact. _________make up an important part of the information__________.
HANDLING MODAL FORMS _______is a semantic category indicating the __________that the speaker _______to his message. A message can be presented by its author as________, a request______, or something that_______, possible or ________but not an established fact. _________make up an important part of the information__________.
 HANDLING MODAL FORMS The translator must be able to understand various __________expressed by ____________and to choose the __________in TL. English makes use of ________of language units to express modal relationships: ______________________.
HANDLING MODAL FORMS The translator must be able to understand various __________expressed by ____________and to choose the __________in TL. English makes use of ________of language units to express modal relationships: ______________________.
 HANDLING MODAL FORMS ______are widely used in English to _________of modality. The translator should be ___________that an English __________can be found in some phrases the Russian ______of which have _______forms.
HANDLING MODAL FORMS ______are widely used in English to _________of modality. The translator should be ___________that an English __________can be found in some phrases the Russian ______of which have _______forms.
 HANDLING MODAL FORMS She can speak and write English. _______________. I can see the English coast already. _______________. Why should you say it? _____________?
HANDLING MODAL FORMS She can speak and write English. _______________. I can see the English coast already. _______________. Why should you say it? _____________?
 HANDLING MODAL FORMS There is ___________ between the English and the Russian _________and the translator should choose the _______ which_____________.
HANDLING MODAL FORMS There is ___________ between the English and the Russian _________and the translator should choose the _______ which_____________.
 HANDLING MODAL FORMS Most English ________are ___________. So “_____» can express _____or a high degree of__________. “ _____» implies either ______or moral ________(permission). “ ____» denotes physical or______, etc.
HANDLING MODAL FORMS Most English ________are ___________. So “_____» can express _____or a high degree of__________. “ _____» implies either ______or moral ________(permission). “ ____» denotes physical or______, etc.
 HANDLING MODAL FORMS You must go there at once. _______________. You must be very tired. ________________. Не may know what has happened. ________________. Не may come in now. _________________.
HANDLING MODAL FORMS You must go there at once. _______________. You must be very tired. ________________. Не may know what has happened. ________________. Не may come in now. _________________.
 HANDLING MODAL FORMS But when a ______is used with a ________form, it loses, as a rule, its______________. Thus, “______» always implies certainty, “________ «, probability, while “________», improbability. It should also be noted that the _________ may indicate either _________after «must», «may», «cannot») or an action that _______(after_ ________________).
HANDLING MODAL FORMS But when a ______is used with a ________form, it loses, as a rule, its______________. Thus, “______» always implies certainty, “________ «, probability, while “________», improbability. It should also be noted that the _________ may indicate either _________after «must», «may», «cannot») or an action that _______(after_ ________________).
 HANDLING MODAL FORMS He must have told her about it yesterday. _____________. Не should have told her about it yesterday. _______________.
HANDLING MODAL FORMS He must have told her about it yesterday. _____________. Не should have told her about it yesterday. _______________.
 HANDLING MODAL FORMS Special attention should be given to the form “____________» where the ___________can have ____different meanings: _________________________.
HANDLING MODAL FORMS Special attention should be given to the form “____________» where the ___________can have ____different meanings: _________________________.
 HANDLING MODAL FORMS I might have spoken too strongly. ______________. You might have done it yourself. ______________.
HANDLING MODAL FORMS I might have spoken too strongly. ______________. You might have done it yourself. ______________.
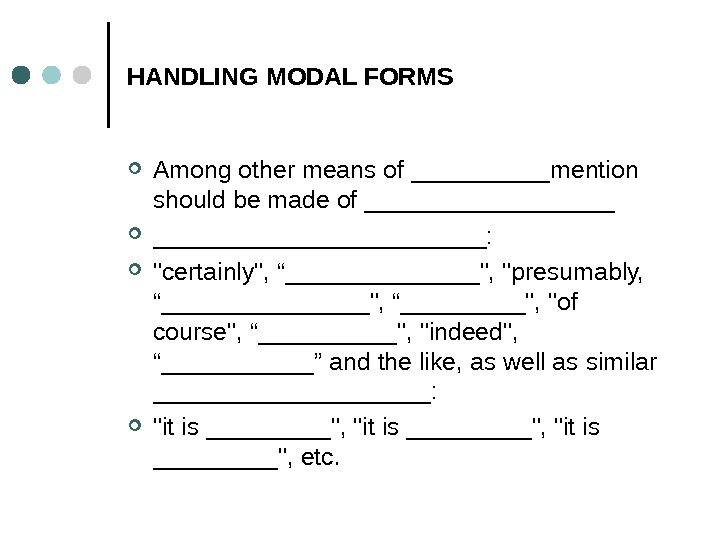
 HANDLING MODAL FORMS Among other means of _____mention should be made of ________________________: «certainly», “_______», «presumably, “________», “_____», «of course», “_____», «indeed», “______” and the like, as well as similar __________: «it is _________», «it is _____», etc.
HANDLING MODAL FORMS Among other means of _____mention should be made of ________________________: «certainly», “_______», «presumably, “________», “_____», «of course», “_____», «indeed», “______” and the like, as well as similar __________: «it is _________», «it is _____», etc.
 HANDLING MODAL FORMS They may all ____________of _____ relationships. For instance, “ _______” may be rendered as « ___________ » и т. п. , « ______ » — « __________________ » и т. п. , « ________ » — « ____________________ » .
HANDLING MODAL FORMS They may all ____________of _____ relationships. For instance, “ _______” may be rendered as « ___________ » и т. п. , « ______ » — « __________________ » и т. п. , « ________ » — « ____________________ » .
 HANDLING MODAL FORMS Some of the ________(«surely», “____», “_____» and the like) have____________. What should he do if she failed him? Surely die of disappointment and despair. _________________________________. ( Неге «surely» is______. )
HANDLING MODAL FORMS Some of the ________(«surely», “____», “_____» and the like) have____________. What should he do if she failed him? Surely die of disappointment and despair. _________________________________. ( Неге «surely» is______. )
 HANDLING MODAL FORMS The English ________give relatively little trouble to the translator since he can, as a rule, make use of the____________. Note should be taken, however, of those forms of the _________(the_______) which are purely structural and express _______________that should be reproduced in translation:
HANDLING MODAL FORMS The English ________give relatively little trouble to the translator since he can, as a rule, make use of the____________. Note should be taken, however, of those forms of the _________(the_______) which are purely structural and express _______________that should be reproduced in translation:
 HANDLING MODAL FORMS It is important that everyone should do his duty. ______________. I suggest that we all should go home. ______________!
HANDLING MODAL FORMS It is important that everyone should do his duty. ______________. I suggest that we all should go home. ______________!
 HANDLING MODAL FORMS Do not forget that while the English language has practically__________, the Russian language has. Whenever necessary, Russian _______ (________________) should be used to _______which is expressed in the _____by other means or only _______:
HANDLING MODAL FORMS Do not forget that while the English language has practically__________, the Russian language has. Whenever necessary, Russian _______ (________________) should be used to _______which is expressed in the _____by other means or only _______:
 HANDLING MODAL FORMS After us the deluge. __________. Не was in wild spirits, shouting that you might dissuade him for twenty-four hours. ______________________________.
HANDLING MODAL FORMS After us the deluge. __________. Не was in wild spirits, shouting that you might dissuade him for twenty-four hours. ______________________________.
 Causes of Grammatical transformations Causes : Grammatical transformations are motivated by the ________________________of the two languages. Grammatical transformations are___________– the ________________ in the _____of the two languages.
Causes of Grammatical transformations Causes : Grammatical transformations are motivated by the ________________________of the two languages. Grammatical transformations are___________– the ________________ in the _____of the two languages.
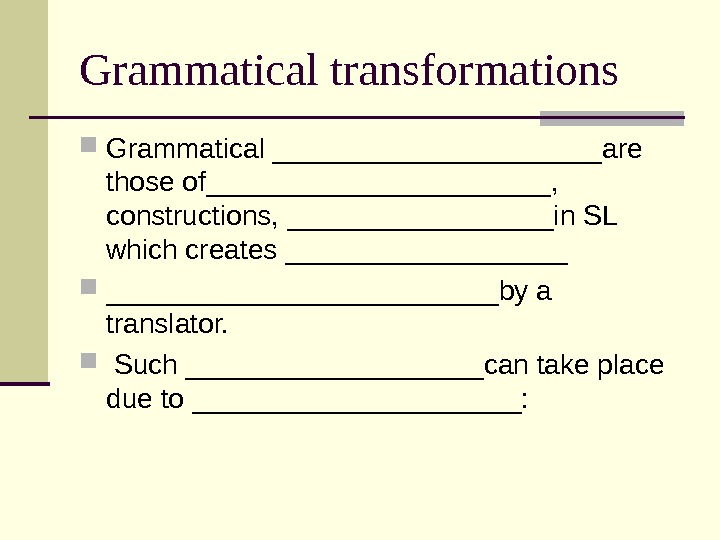
 Grammatical transformations Grammatical ___________are those of___________, constructions, _________in SL which creates _________________________by a translator. Such __________can take place due to ___________:
Grammatical transformations Grammatical ___________are those of___________, constructions, _________in SL which creates _________________________by a translator. Such __________can take place due to ___________:
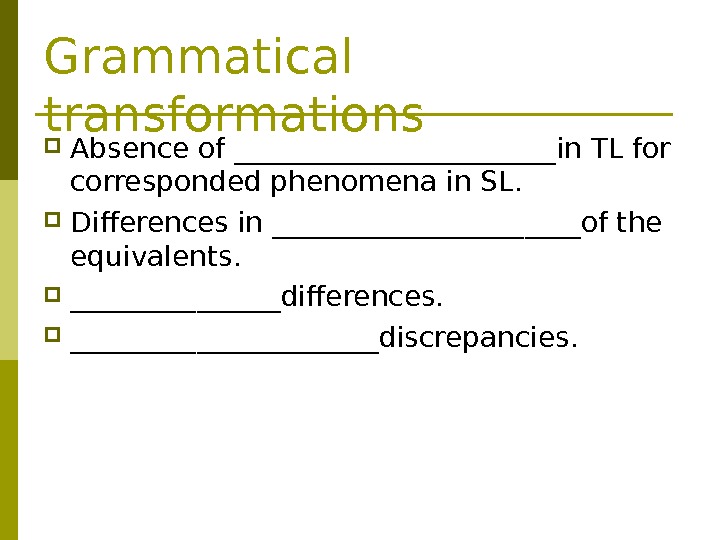
 Grammatical transformations Absence of ____________in TL for corresponded phenomena in SL. Differences in ___________of the equivalents. ________differences. ___________discrepancies.
Grammatical transformations Absence of ____________in TL for corresponded phenomena in SL. Differences in ___________of the equivalents. ________differences. ___________discrepancies.
 Grammatical transformations e. g. They say-_______ you see-______
Grammatical transformations e. g. They say-_______ you see-______
 Grammatical transformations ________; Replacement; _______; Omission; _____________: — Inner fragmentation; — Outer fragmentation ; Sentence__________.
Grammatical transformations ________; Replacement; _______; Omission; _____________: — Inner fragmentation; — Outer fragmentation ; Sentence__________.
 Using grammatical transformations Factors that depend on using grammatical transformations: _________of the sentence; ___________coloring; sense__________________; ____________________.
Using grammatical transformations Factors that depend on using grammatical transformations: _________of the sentence; ___________coloring; sense__________________; ____________________.
 Grammatical transformations Transposition — is a _________________(Subject , Predicate, Object, etc. ) as compared with that of the source sentence dictated either by peculiarities of the target language syntax or by the______________.
Grammatical transformations Transposition — is a _________________(Subject , Predicate, Object, etc. ) as compared with that of the source sentence dictated either by peculiarities of the target language syntax or by the______________.
 Grammatical transformations It is performed usually due to the _____________________ of the sentence as in Russian_____, as a rule, at______________.
Grammatical transformations It is performed usually due to the _____________________ of the sentence as in Russian_____, as a rule, at______________.
 Grammatical transformations e. g. The flight will be boarding at Gate 17 in about fifteen minutes. _______________________________.
Grammatical transformations e. g. The flight will be boarding at Gate 17 in about fifteen minutes. _______________________________.
 Grammatical transformations Replacement — is ______in the target text at the _______, lexical and _________of the language when the _____of the certain _________are replaced by ________of target________.
Grammatical transformations Replacement — is ______in the target text at the _______, lexical and _________of the language when the _____of the certain _________are replaced by ________of target________.
 Grammatical transformations e. g. He used to come to Italy each spring. _______________.
Grammatical transformations e. g. He used to come to Italy each spring. _______________.
 Grammatical transformations Addition — is a _____________of structural elements ___________in the source text or ________missing in the target language.
Grammatical transformations Addition — is a _____________of structural elements ___________in the source text or ________missing in the target language.
 Grammatical transformations e. g. The policeman waved me on. _________________________.
Grammatical transformations e. g. The policeman waved me on. _________________________.
 Grammatical transformations Sometimes ________available or implied in the ______________________when it is transformed into the_______. These semantic units should be _______________and ______________.
Grammatical transformations Sometimes ________available or implied in the ______________________when it is transformed into the_______. These semantic units should be _______________and ______________.
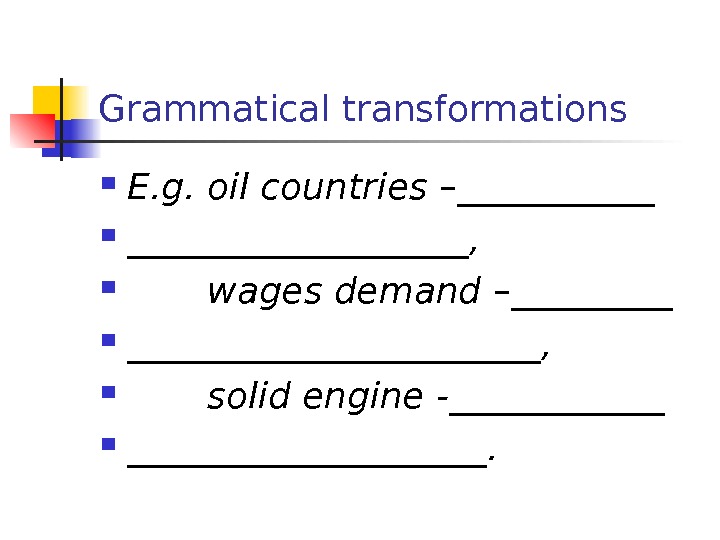
 Grammatical transformations E. g. oil countries – _______________ , wages demand – ________________ , solid engine — ________________.
Grammatical transformations E. g. oil countries – _______________ , wages demand – ________________ , solid engine — ________________.
 Grammatical transformations Omission — is __________of the source text considered ________________language structural ______and_____. e. g. Summer rains in Florida may be violent, while they last. ________________.
Grammatical transformations Omission — is __________of the source text considered ________________language structural ______and_____. e. g. Summer rains in Florida may be violent, while they last. ________________.
 Grammatical transformations We also ______that are not ______for understanding or expressing a_________. One of the cases or _____is the use in English of ______mostly typical of____________.
Grammatical transformations We also ______that are not ______for understanding or expressing a_________. One of the cases or _____is the use in English of ______mostly typical of____________.
 Grammatical transformations E. g. regular and normal session –_______; with the Advice and Consent of the Senate –_________.
Grammatical transformations E. g. regular and normal session –_______; with the Advice and Consent of the Senate –_________.
 Grammatical transformations Sentence _______ — implies ________________into the target sentence. e. g. Your presence is not required. It is not desirable. ________________.
Grammatical transformations Sentence _______ — implies ________________into the target sentence. e. g. Your presence is not required. It is not desirable. ________________.
 Grammatical transformations ______fragmentation — is either _______in translation of the source sentence by two or _________or _______a simple source sentence into a_____________.
Grammatical transformations ______fragmentation — is either _______in translation of the source sentence by two or _________or _______a simple source sentence into a_____________.
 Grammatical transformations e. g. Come along and see me play one evening. _______________.
Grammatical transformations e. g. Come along and see me play one evening. _______________.
 Grammatical transformations _____fragmentation — is a _______of a simple sentence into _____________one. e. g. C развитием промышленности появится много товаров. ______________________________.
Grammatical transformations _____fragmentation — is a _______of a simple sentence into _____________one. e. g. C развитием промышленности появится много товаров. ______________________________.
 Grammatical transformations Outer fragmentation — is a _____of a sentence in______________.
Grammatical transformations Outer fragmentation — is a _____of a sentence in______________.
 Grammatical transformations e. g. There was a real game too, not a party game played in the old school hall and invented by my eldest brother Herbert, who was always of an adventurous character until he was changed by the continual and sometimes shameful failures of his adult life. Была у нас и ___________ — мы играли в нее в старом ____ зале. Придумал ее наш ___________ — человек изобретательный и _________________ , пока постоянные и иногда __________ во взрослой жизни не изменили его натуру.
Grammatical transformations e. g. There was a real game too, not a party game played in the old school hall and invented by my eldest brother Herbert, who was always of an adventurous character until he was changed by the continual and sometimes shameful failures of his adult life. Была у нас и ___________ — мы играли в нее в старом ____ зале. Придумал ее наш ___________ — человек изобретательный и _________________ , пока постоянные и иногда __________ во взрослой жизни не изменили его натуру.
 Seminar: Definitions of all grammatical transformations. (In writing) N. Petrenko Pp.
Seminar: Definitions of all grammatical transformations. (In writing) N. Petrenko Pp.
