Olshansk i y V. M. (1), Volkov













- Размер: 3.1 Mегабайта
- Количество слайдов: 14
Описание презентации Olshansk i y V. M. (1), Volkov по слайдам
 Olshansk i y V. M. (1), Volkov S. V. (2) Institute of Ecology and Evolution Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow 1. vmolsh@yandex. ru, 2. mendur@mail. ru . Mashkin P. V. Pushchino State Institute of Natural Sciences, Pushchino, Moscow region. pmashkin@yandex. ru Development of system for «on line» water quality monitoring in rivers, lakes, fish farms, sewage treat plants with biosensors: fresh water mussels.
Olshansk i y V. M. (1), Volkov S. V. (2) Institute of Ecology and Evolution Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow 1. vmolsh@yandex. ru, 2. mendur@mail. ru . Mashkin P. V. Pushchino State Institute of Natural Sciences, Pushchino, Moscow region. pmashkin@yandex. ru Development of system for «on line» water quality monitoring in rivers, lakes, fish farms, sewage treat plants with biosensors: fresh water mussels.
 Chemical methods. The methods are common for all countries. It provide s the determin ation of different substances t y pe s and concentration in water. The methods have rish methodic and device s base. BUT: it is impossible estimate biological effect of sinergetic influence of all chemical substances and physical factors on living organizms using only chemical methods we can appreciate the real danger of water pollution only when testing the viability of aquatic organisms . W ater quality monitoring methods
Chemical methods. The methods are common for all countries. It provide s the determin ation of different substances t y pe s and concentration in water. The methods have rish methodic and device s base. BUT: it is impossible estimate biological effect of sinergetic influence of all chemical substances and physical factors on living organizms using only chemical methods we can appreciate the real danger of water pollution only when testing the viability of aquatic organisms . W ater quality monitoring methods
 Methods of biotests. The methods use quick physiological or living organizms behavi o r reactions (moving activity, respiration, reaction of shells closing, changes in heart rate or electrical activity) on differents types of water pollution. Water organisms – fish and mussels – re sponse «on line» on total influence — chemical and physical factors. The biological methods can’t detect type of pollution, it signals only about dangerous level for water animals.
Methods of biotests. The methods use quick physiological or living organizms behavi o r reactions (moving activity, respiration, reaction of shells closing, changes in heart rate or electrical activity) on differents types of water pollution. Water organisms – fish and mussels – re sponse «on line» on total influence — chemical and physical factors. The biological methods can’t detect type of pollution, it signals only about dangerous level for water animals.
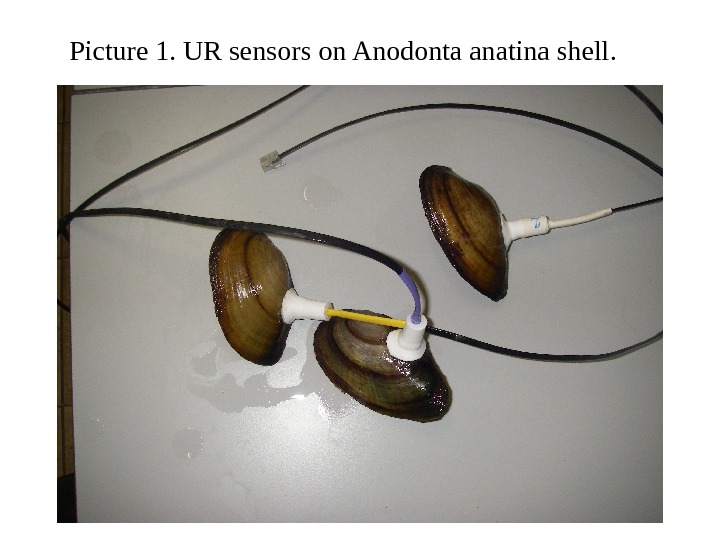
 l Why mussels? • Big fresh water mussels are most important part of river self purification system. It dominates in benthos biomass. • They are species — indicator in rivers, can live in aquarium long time. They live under limit moving activity under experimental conditions, can live long time without food. • It is possible to registrate cardio rate s of each shell by infrared optocouples (picture 1). Sensors could be fixed on shell s near pericard without of injury. • It is possible to registrate shells valves disclosure with Hall sensor s. Difficulties of mussels viability monitoring: sometimes mussels clos e it shells for one — two h ours even in clear water. They have individual physiological features, such as the shape and rate of cardio rhithm.
l Why mussels? • Big fresh water mussels are most important part of river self purification system. It dominates in benthos biomass. • They are species — indicator in rivers, can live in aquarium long time. They live under limit moving activity under experimental conditions, can live long time without food. • It is possible to registrate cardio rate s of each shell by infrared optocouples (picture 1). Sensors could be fixed on shell s near pericard without of injury. • It is possible to registrate shells valves disclosure with Hall sensor s. Difficulties of mussels viability monitoring: sometimes mussels clos e it shells for one — two h ours even in clear water. They have individual physiological features, such as the shape and rate of cardio rhithm.
 Sea Waters: Biota Guard company, Norway. ( www. biotaguard. no ) The devices used for control of sea pollution with oil. No research data about sensitivity blue mussels to oil, only reclaim information. Fresh waters: Aqua. Dect company ( www. mermayde. nl ) ( Holland). Device : Mosselmonitor, Dreissena monitor ( 35 years on market) Device was modificate in Poland. Used in Hungary (sewage treat factory). In Russia used in Vladyvostok, Ekaterinburg on drinking water inlets. Used old prinsiple: it control only closing -opening shells. Now not in eploitation. Device: Laser opto — fiber foto pletismograph Russia St. Petreburg. Used fresh water cray fishes. Besids, in different countries there are experimental devices in the only exemplar. Our experiments with Anodonta and Unio show that for effective water quality control have to use both parameteres: cardiograms and level of opening shells. World analog of the devices
Sea Waters: Biota Guard company, Norway. ( www. biotaguard. no ) The devices used for control of sea pollution with oil. No research data about sensitivity blue mussels to oil, only reclaim information. Fresh waters: Aqua. Dect company ( www. mermayde. nl ) ( Holland). Device : Mosselmonitor, Dreissena monitor ( 35 years on market) Device was modificate in Poland. Used in Hungary (sewage treat factory). In Russia used in Vladyvostok, Ekaterinburg on drinking water inlets. Used old prinsiple: it control only closing -opening shells. Now not in eploitation. Device: Laser opto — fiber foto pletismograph Russia St. Petreburg. Used fresh water cray fishes. Besids, in different countries there are experimental devices in the only exemplar. Our experiments with Anodonta and Unio show that for effective water quality control have to use both parameteres: cardiograms and level of opening shells. World analog of the devices
 Picture 1. UR sensors on Anodonta anatina shell.
Picture 1. UR sensors on Anodonta anatina shell.
 Sample of real form of cardiograms (left side screen) and histogram of distribution time intervals between beads (right)
Sample of real form of cardiograms (left side screen) and histogram of distribution time intervals between beads (right)
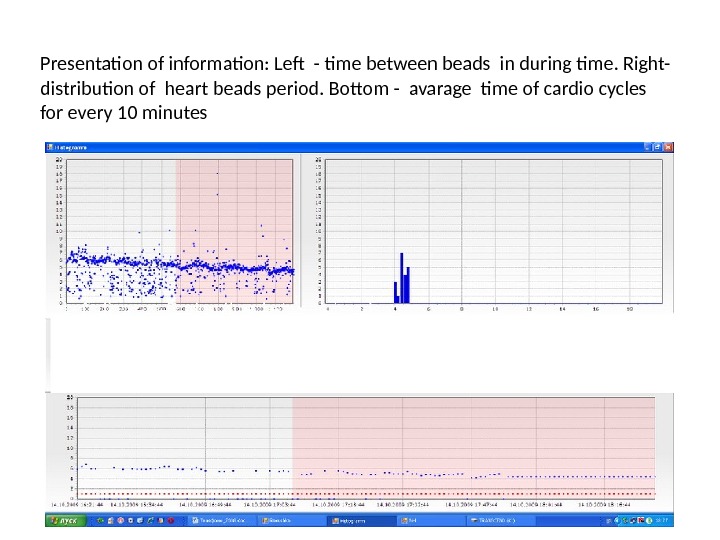
 Presentation of information: Left — time between beads in during time. Right- distribution of heart beads period. Bottom — avarage time of cardio cycles for every 10 minutes
Presentation of information: Left — time between beads in during time. Right- distribution of heart beads period. Bottom — avarage time of cardio cycles for every 10 minutes
 General view of equipment for water inlet in Rublevo, Moscow.
General view of equipment for water inlet in Rublevo, Moscow.
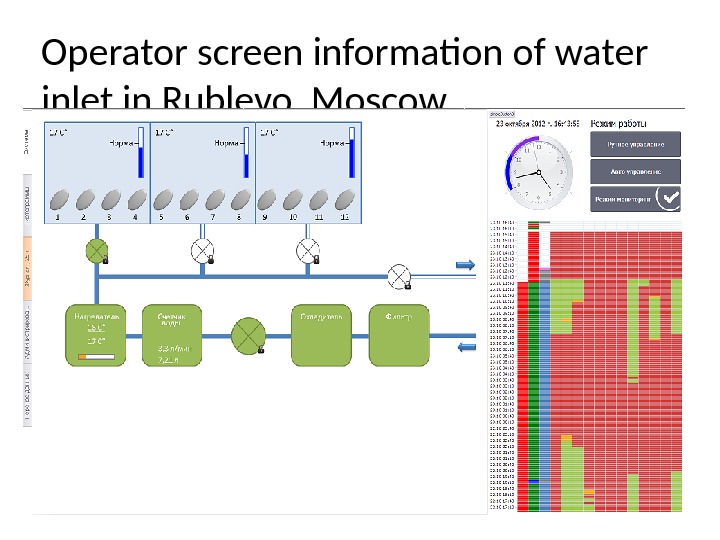
 Operator screen information of water inlet in Rublevo, Moscow.
Operator screen information of water inlet in Rublevo, Moscow.
 6 channel device for laboratory toxicity study and mussels with sensors
6 channel device for laboratory toxicity study and mussels with sensors
 Superiority our devices 1. The equipment operates in fully automatic mode. 2. The system supports the stability of the physical properties of water. 3. Redirecting of water flows through the various test tanks is done automatically every 10 minutes. 4. Heart rate and the disclosure are tested continuously separately for each mussle. 5. The information about the status of each mollusc is displayed in real time on the monitor. 6. A summary of the status of all shellfish is displayed on a separate monitor in the form of plain equipment operator.
Superiority our devices 1. The equipment operates in fully automatic mode. 2. The system supports the stability of the physical properties of water. 3. Redirecting of water flows through the various test tanks is done automatically every 10 minutes. 4. Heart rate and the disclosure are tested continuously separately for each mussle. 5. The information about the status of each mollusc is displayed in real time on the monitor. 6. A summary of the status of all shellfish is displayed on a separate monitor in the form of plain equipment operator.
 Stage of Russian-China collaboration 1 stage. Study type of cardio signals and sensitivity to different pollutants of China species. Growing most sensitive species in clear waters on fishery farms. 2 stage. Produce experimental seria new equipments: -for control drinking water quality on water inlet station ( mussels and electric fishes ). -sewage water treat station, toxicology and veterenarian laboratories (mussles). 3 stage. Sertification all kinds of the devices in China, marketing study. 4 stage. Industrial producing all kinds of equipments for China and other countries.
Stage of Russian-China collaboration 1 stage. Study type of cardio signals and sensitivity to different pollutants of China species. Growing most sensitive species in clear waters on fishery farms. 2 stage. Produce experimental seria new equipments: -for control drinking water quality on water inlet station ( mussels and electric fishes ). -sewage water treat station, toxicology and veterenarian laboratories (mussles). 3 stage. Sertification all kinds of the devices in China, marketing study. 4 stage. Industrial producing all kinds of equipments for China and other countries.
 Possible parthers: • China State Securaty organizations. • Province state environment protection organizations. • State toxicological and veterenarien laboratories. • Universities and institutes (for biological practicums) • Schools and colleges (devices for children research study) • Busness persons. (Production serial devices)
Possible parthers: • China State Securaty organizations. • Province state environment protection organizations. • State toxicological and veterenarien laboratories. • Universities and institutes (for biological practicums) • Schools and colleges (devices for children research study) • Busness persons. (Production serial devices)

