Ядерное Оружие.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 Nuclear Weapon
Nuclear Weapon
 Motivation and History
Motivation and History
 History o o In 1939, the French physicist Joliot-Curie concluded that it is possible chain reaction which will lead to an explosion of terrible destructive power and that uranium can be a source of energy as usual explosives. This conclusion became a push for the development of a nuclear weapon. In April 1939, six leading German nuclear physicists: Professor Zhoos, Ganly, Geiger, Mattauh, Bothe and Hoffman found organization called "Uranium Club“ The United States government decided as soon as possible to build an atomic bomb. The project was called as the "Manhattan Project". It was headed by Leslie Groves. In the United States in Los Alamos in the desert expanses of New Mexico in 1942 was created the U. S. nuclear center.
History o o In 1939, the French physicist Joliot-Curie concluded that it is possible chain reaction which will lead to an explosion of terrible destructive power and that uranium can be a source of energy as usual explosives. This conclusion became a push for the development of a nuclear weapon. In April 1939, six leading German nuclear physicists: Professor Zhoos, Ganly, Geiger, Mattauh, Bothe and Hoffman found organization called "Uranium Club“ The United States government decided as soon as possible to build an atomic bomb. The project was called as the "Manhattan Project". It was headed by Leslie Groves. In the United States in Los Alamos in the desert expanses of New Mexico in 1942 was created the U. S. nuclear center.
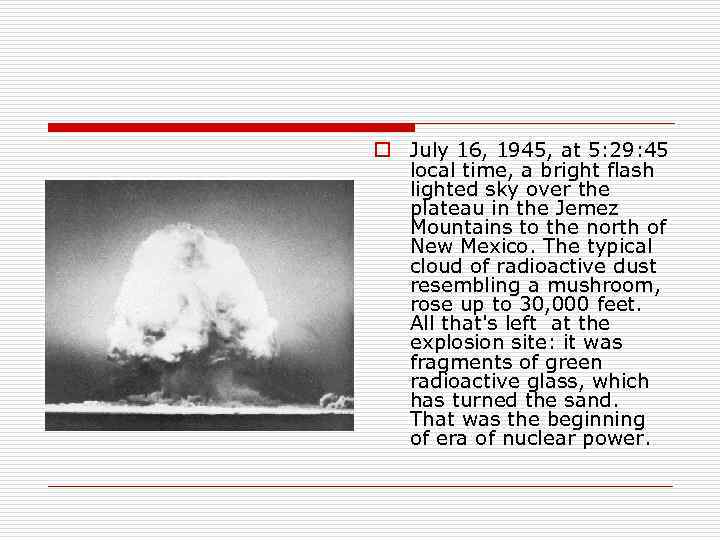 o July 16, 1945, at 5: 29: 45 local time, a bright flash lighted sky over the plateau in the Jemez Mountains to the north of New Mexico. The typical cloud of radioactive dust resembling a mushroom, rose up to 30, 000 feet. All that's left at the explosion site: it was fragments of green radioactive glass, which has turned the sand. That was the beginning of era of nuclear power.
o July 16, 1945, at 5: 29: 45 local time, a bright flash lighted sky over the plateau in the Jemez Mountains to the north of New Mexico. The typical cloud of radioactive dust resembling a mushroom, rose up to 30, 000 feet. All that's left at the explosion site: it was fragments of green radioactive glass, which has turned the sand. That was the beginning of era of nuclear power.
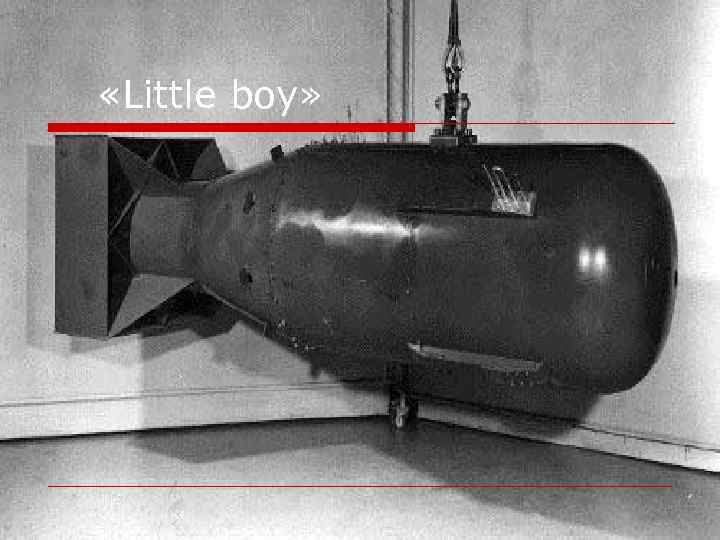 «Little boy»
«Little boy»
 «Fat man»
«Fat man»
 Hiroshima and Nagasaki o Instantly killed by thermal heat (about 5000 degrees C) and shock 300 thousand people o 200, 000 people were injured, burns, exposed to radiation o On the area of 12 sq. km have been completely destroyed all the buildings
Hiroshima and Nagasaki o Instantly killed by thermal heat (about 5000 degrees C) and shock 300 thousand people o 200, 000 people were injured, burns, exposed to radiation o On the area of 12 sq. km have been completely destroyed all the buildings
 Nuclear Weapon in USSR o In August 20, 1945 was formed a special committee on nuclear energy under the direction of Beria. His deputy was appointed Commissar of ammunition B. L. Vannikov. The committee consisted of prominent scientists A. F. Joffe, P. L. Kapitza and I. V. Kurchatov. o In the area of the Semipalatinsk testing ground was built. Exactly at 7. 00 am on 29 August 1949, in this testing ground was undermined the first Soviet nuclear device, code-named "RDS-1".
Nuclear Weapon in USSR o In August 20, 1945 was formed a special committee on nuclear energy under the direction of Beria. His deputy was appointed Commissar of ammunition B. L. Vannikov. The committee consisted of prominent scientists A. F. Joffe, P. L. Kapitza and I. V. Kurchatov. o In the area of the Semipalatinsk testing ground was built. Exactly at 7. 00 am on 29 August 1949, in this testing ground was undermined the first Soviet nuclear device, code-named "RDS-1".
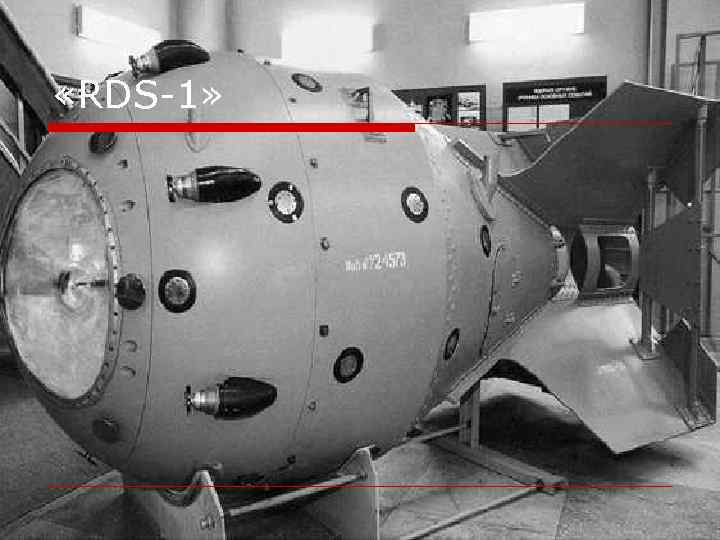 «RDS-1»
«RDS-1»
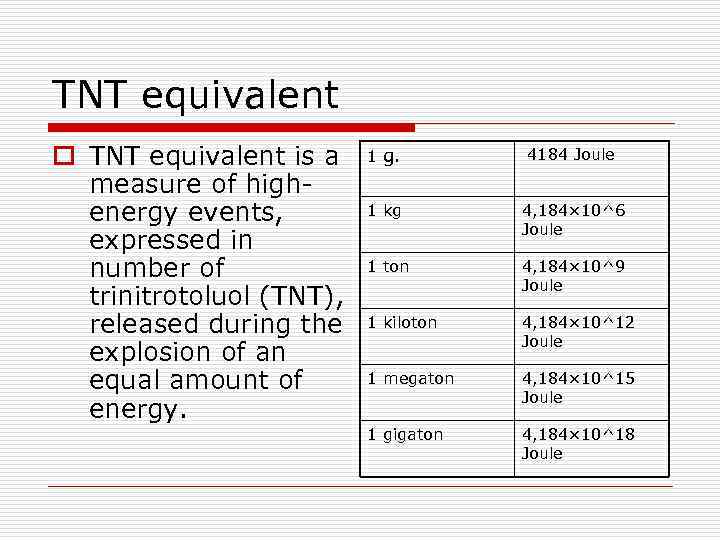 TNT equivalent o TNT equivalent is a measure of highenergy events, expressed in number of trinitrotoluol (TNT), released during the explosion of an equal amount of energy. 1 g. 4184 Joule 1 kg 4, 184× 10^6 Joule 1 ton 4, 184× 10^9 Joule 1 kiloton 4, 184× 10^12 Joule 1 megaton 4, 184× 10^15 Joule 1 gigaton 4, 184× 10^18 Joule
TNT equivalent o TNT equivalent is a measure of highenergy events, expressed in number of trinitrotoluol (TNT), released during the explosion of an equal amount of energy. 1 g. 4184 Joule 1 kg 4, 184× 10^6 Joule 1 ton 4, 184× 10^9 Joule 1 kiloton 4, 184× 10^12 Joule 1 megaton 4, 184× 10^15 Joule 1 gigaton 4, 184× 10^18 Joule
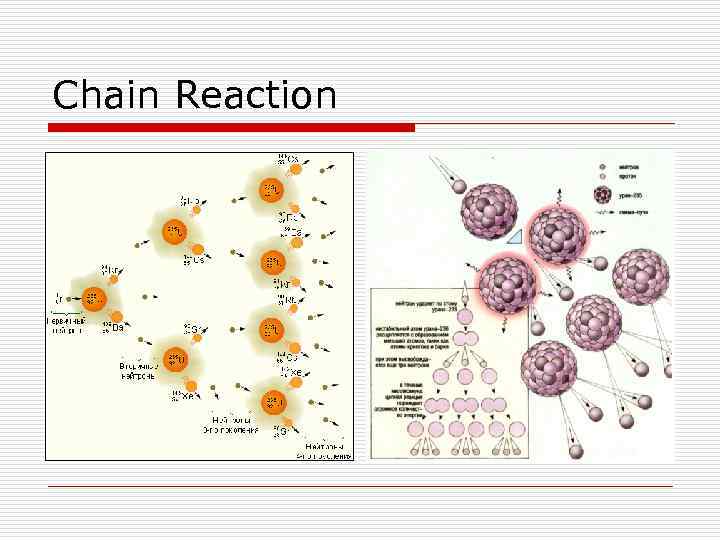 Chain Reaction
Chain Reaction
 Classification of nuclear weapon Atomic Hydrogen Neutron weapon
Classification of nuclear weapon Atomic Hydrogen Neutron weapon
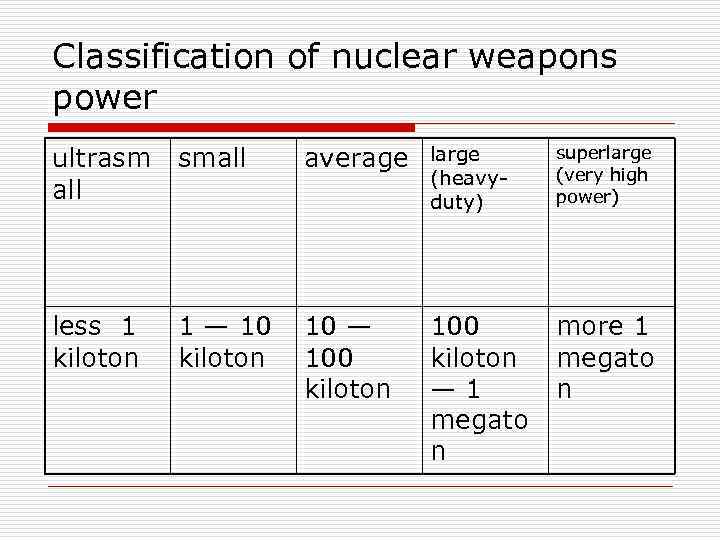 Classification of nuclear weapons power ultrasm all small average large (heavyduty) superlarge (very high power) less 1 kiloton 1 — 10 kiloton 10 — 100 kiloton — 1 megato n more 1 megato n
Classification of nuclear weapons power ultrasm all small average large (heavyduty) superlarge (very high power) less 1 kiloton 1 — 10 kiloton 10 — 100 kiloton — 1 megato n more 1 megato n
 Uranium bomb o Uranium bomb is an explosive device, in which the role of the main source of energy is nuclear fission of uranium - nuclear reaction o To combat-ready nuclear bomb, the concentration of uranium-235 in nuclear fuel should not be below 80%, otherwise the uranium 238 would quickly stop the established nuclear chain reaction o Bomb based on uranium was the first nuclear weapons which human used in military settings
Uranium bomb o Uranium bomb is an explosive device, in which the role of the main source of energy is nuclear fission of uranium - nuclear reaction o To combat-ready nuclear bomb, the concentration of uranium-235 in nuclear fuel should not be below 80%, otherwise the uranium 238 would quickly stop the established nuclear chain reaction o Bomb based on uranium was the first nuclear weapons which human used in military settings
 o There are two main schemes to undermine fissile charge: the gun (ballistic) and implosion
o There are two main schemes to undermine fissile charge: the gun (ballistic) and implosion
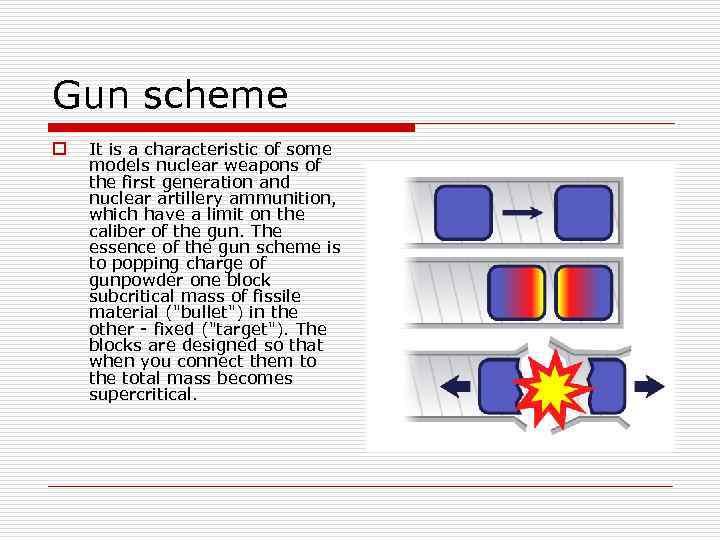 Gun scheme o It is a characteristic of some models nuclear weapons of the first generation and nuclear artillery ammunition, which have a limit on the caliber of the gun. The essence of the gun scheme is to popping charge of gunpowder one block subcritical mass of fissile material ("bullet") in the other - fixed ("target"). The blocks are designed so that when you connect them to the total mass becomes supercritical.
Gun scheme o It is a characteristic of some models nuclear weapons of the first generation and nuclear artillery ammunition, which have a limit on the caliber of the gun. The essence of the gun scheme is to popping charge of gunpowder one block subcritical mass of fissile material ("bullet") in the other - fixed ("target"). The blocks are designed so that when you connect them to the total mass becomes supercritical.
 Implosive scheme o Implosive scheme meant to receive supercritical state by compression of fissile material focused shock wave created by the explosion of ordinary chemical explosives. To focus the shock wave used so-called explosive lenses, and undermining performed simultaneously at many points with precise accuracy.
Implosive scheme o Implosive scheme meant to receive supercritical state by compression of fissile material focused shock wave created by the explosion of ordinary chemical explosives. To focus the shock wave used so-called explosive lenses, and undermining performed simultaneously at many points with precise accuracy.
 Thermonuclear weapon o It is type of weapon of mass destruction, destructive power is based on the energy of nuclear fusion of light elements into heavier ones (for example, the synthesis of a nucleus of a helium atom of the two nuclei of deuterium (heavy hydrogen)), in which a colossal amount of energy is released. Thermonuclear weapon has much more explosive power than nuclear weapons.
Thermonuclear weapon o It is type of weapon of mass destruction, destructive power is based on the energy of nuclear fusion of light elements into heavier ones (for example, the synthesis of a nucleus of a helium atom of the two nuclei of deuterium (heavy hydrogen)), in which a colossal amount of energy is released. Thermonuclear weapon has much more explosive power than nuclear weapons.
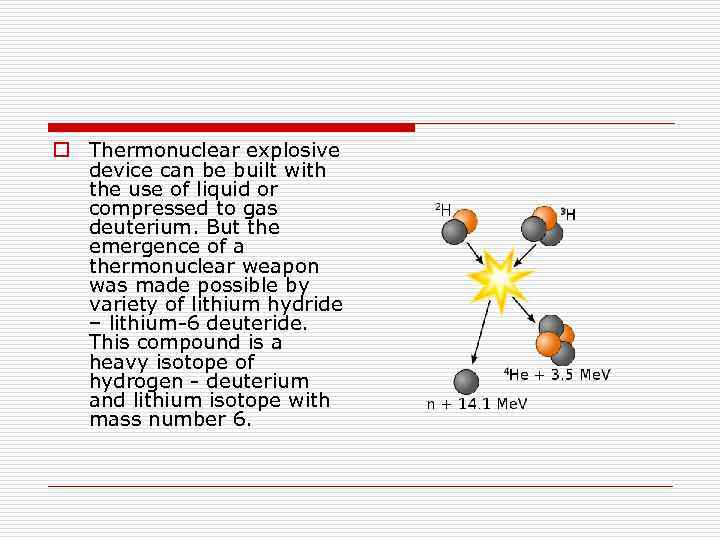 o Thermonuclear explosive device can be built with the use of liquid or compressed to gas deuterium. But the emergence of a thermonuclear weapon was made possible by variety of lithium hydride – lithium-6 deuteride. This compound is a heavy isotope of hydrogen - deuterium and lithium isotope with mass number 6.
o Thermonuclear explosive device can be built with the use of liquid or compressed to gas deuterium. But the emergence of a thermonuclear weapon was made possible by variety of lithium hydride – lithium-6 deuteride. This compound is a heavy isotope of hydrogen - deuterium and lithium isotope with mass number 6.
 RDS-6 s
RDS-6 s
 o o o A. Warhead before the explosion, the first step above, the second step below. Both components of a thermonuclear bomb. B. The explosive undermines first step, compressing the plutonium core to supercritical state and initiating a chain reaction of splitting. C. In the process of splitting in the first step there is x-ray emission, which extends along the inside of the shell, penetrating through the filler of polystyrene foam. D. The second step is compressed due to ablation (evaporation) under the influence of X-ray radiation, and plutonium rod inside the second step goes into a supercritical state, triggering a chain reaction, releasing large amounts of heat. E. In the compressed and warmed lithium-6 deuteride fusion reaction occurs, the emitted neutron flux is the initiator of the splitting reaction of tampere. Fireball expands. . .
o o o A. Warhead before the explosion, the first step above, the second step below. Both components of a thermonuclear bomb. B. The explosive undermines first step, compressing the plutonium core to supercritical state and initiating a chain reaction of splitting. C. In the process of splitting in the first step there is x-ray emission, which extends along the inside of the shell, penetrating through the filler of polystyrene foam. D. The second step is compressed due to ablation (evaporation) under the influence of X-ray radiation, and plutonium rod inside the second step goes into a supercritical state, triggering a chain reaction, releasing large amounts of heat. E. In the compressed and warmed lithium-6 deuteride fusion reaction occurs, the emitted neutron flux is the initiator of the splitting reaction of tampere. Fireball expands. . .
 Neutron weapons o It is kind of nuclear weapons, which artificially increased the share of the explosive energy, which release in the form of neutron radiation to defeat manpower, weapons of the enemy and radioactive contamination with the limited damaging effects of the shock waves and light. Because of the neutrons are absorpted by atmosphere quickly ineffective neutron large capacity ammunition; equivalent tonnage of neutron warheads usually no more than a few kilotons, and they are classified in tactical nuclear weapons.
Neutron weapons o It is kind of nuclear weapons, which artificially increased the share of the explosive energy, which release in the form of neutron radiation to defeat manpower, weapons of the enemy and radioactive contamination with the limited damaging effects of the shock waves and light. Because of the neutrons are absorpted by atmosphere quickly ineffective neutron large capacity ammunition; equivalent tonnage of neutron warheads usually no more than a few kilotons, and they are classified in tactical nuclear weapons.
 Design o Neutron charge is designed as a usual nuclear charge of low power with box containing a small amount of thermonuclear fuel (a mix of deuterium and tritium, with a high content of the latter as a source of fast neutrons). At undermining the basic nuclear weapon explodes, the energy used to run thermonuclear reaction. Most of the energy of the explosion in the application of neutron weapons liberated by running the fusion reaction. The design of the charge is such that 80% of the explosion energy is the energy of the fast neutron flux, and only 20% are other striking factors
Design o Neutron charge is designed as a usual nuclear charge of low power with box containing a small amount of thermonuclear fuel (a mix of deuterium and tritium, with a high content of the latter as a source of fast neutrons). At undermining the basic nuclear weapon explodes, the energy used to run thermonuclear reaction. Most of the energy of the explosion in the application of neutron weapons liberated by running the fusion reaction. The design of the charge is such that 80% of the explosion energy is the energy of the fast neutron flux, and only 20% are other striking factors
 The development of nuclear weapons (Sarov) o Russian Federal Nuclear Center - All-Russian Research Institute of Experimental Physics (RFNC-ARRIEP)Federal State Unitary Enterprise of the State Atomic Energy Corporation "Rosatom". The Institute was founded in 1946 to realize the Soviet atomic project. It developed the first Soviet atomic and hydrogen bombs. o Currently RFNC-ARRIEP - the largest research and development center in Russia, which successfully addresses the defense, scientific and industrial problems. The main objective of RFNC-ARRIEP was and is to ensure reliability and security of nuclear weapons in Russia.
The development of nuclear weapons (Sarov) o Russian Federal Nuclear Center - All-Russian Research Institute of Experimental Physics (RFNC-ARRIEP)Federal State Unitary Enterprise of the State Atomic Energy Corporation "Rosatom". The Institute was founded in 1946 to realize the Soviet atomic project. It developed the first Soviet atomic and hydrogen bombs. o Currently RFNC-ARRIEP - the largest research and development center in Russia, which successfully addresses the defense, scientific and industrial problems. The main objective of RFNC-ARRIEP was and is to ensure reliability and security of nuclear weapons in Russia.
 Yulii Borisovich Khariton
Yulii Borisovich Khariton
 The development of nuclear weapons (Snezhinsk) o Russian Federal Nuclear Center - All-Russian Research Institute of Technical Physics named by E. I. Zababakhin (RFNC-ARRITP) - Federal State Unitary Enterprise of the State Atomic Energy Corporation "Rosatom". o In 1955 the second-grade nuclear center of the Soviet Union created (now RFNC-ARRITP). This provided the acceleration of development of nuclear weapons, created the preconditions to preserve one of the two nuclear centers in the event of war, made it possible to more objectively judge the level of building a nuclear weapon, as healthy competition engendered development.
The development of nuclear weapons (Snezhinsk) o Russian Federal Nuclear Center - All-Russian Research Institute of Technical Physics named by E. I. Zababakhin (RFNC-ARRITP) - Federal State Unitary Enterprise of the State Atomic Energy Corporation "Rosatom". o In 1955 the second-grade nuclear center of the Soviet Union created (now RFNC-ARRITP). This provided the acceleration of development of nuclear weapons, created the preconditions to preserve one of the two nuclear centers in the event of war, made it possible to more objectively judge the level of building a nuclear weapon, as healthy competition engendered development.
 Dmitry Efimovich Vasilyev
Dmitry Efimovich Vasilyev
 Lominsky Georgi Pavlovich
Lominsky Georgi Pavlovich
 Nechay Vladimir Zinovievich
Nechay Vladimir Zinovievich
 Rykovanov Georgi Nikolaevich
Rykovanov Georgi Nikolaevich
 Boris Vasilyevich Litvinov o Chief Designer in the 1961 -1997 years.
Boris Vasilyevich Litvinov o Chief Designer in the 1961 -1997 years.
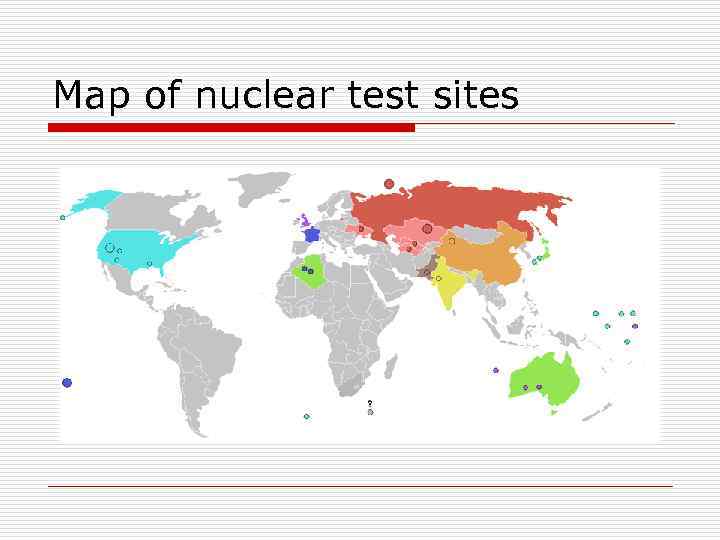 Map of nuclear test sites
Map of nuclear test sites
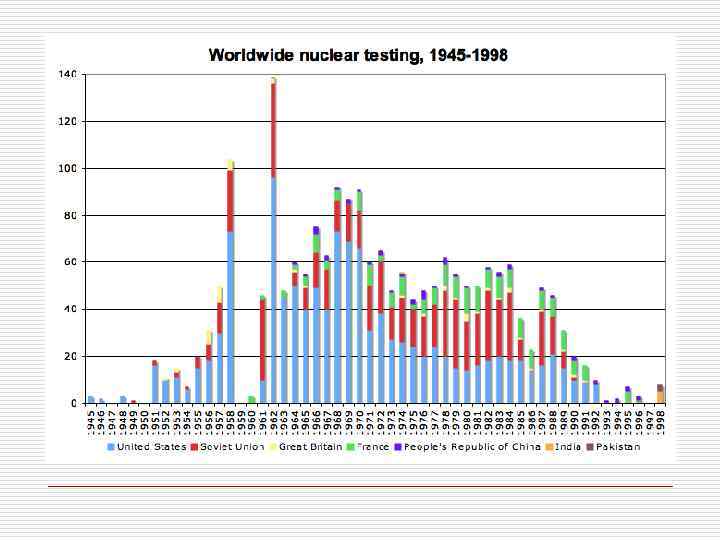
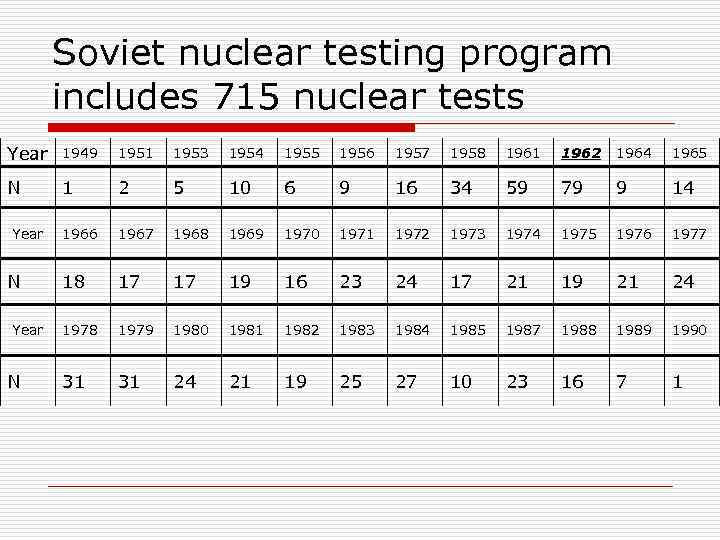 Soviet nuclear testing program includes 715 nuclear tests Year 1949 1951 1953 1954 1955 1956 1957 1958 1961 1962 1964 1965 N 1 2 5 10 6 9 16 34 59 79 9 14 1966 1967 1968 1969 1970 1971 1972 1973 1974 1975 1976 1977 18 17 17 19 16 23 24 17 21 19 21 24 1978 1979 1980 1981 1982 1983 1984 1985 1987 1988 1989 1990 31 31 24 21 19 25 27 10 23 16 7 1 Year N
Soviet nuclear testing program includes 715 nuclear tests Year 1949 1951 1953 1954 1955 1956 1957 1958 1961 1962 1964 1965 N 1 2 5 10 6 9 16 34 59 79 9 14 1966 1967 1968 1969 1970 1971 1972 1973 1974 1975 1976 1977 18 17 17 19 16 23 24 17 21 19 21 24 1978 1979 1980 1981 1982 1983 1984 1985 1987 1988 1989 1990 31 31 24 21 19 25 27 10 23 16 7 1 Year N


