5c0c56df8eb940ddf26d52516b833a53.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29
 Money and Financial Institutions
Money and Financial Institutions
 n n Make a list of the things you have bought in the last week. If money didn’t exist, how would you pay for them?
n n Make a list of the things you have bought in the last week. If money didn’t exist, how would you pay for them?
 The History of Money n n Monetary system- A system in which goods and services are exchanged indirectly using money as a medium Money- can be anything that people accept as a standard for payment
The History of Money n n Monetary system- A system in which goods and services are exchanged indirectly using money as a medium Money- can be anything that people accept as a standard for payment
 Functions of Money has 3 basic functions n Medium of exchange n Standard of Value- a fixed means for measuring the weight, amount, or value for something n Store of Value- it holds its value over time and can be stored or saved
Functions of Money has 3 basic functions n Medium of exchange n Standard of Value- a fixed means for measuring the weight, amount, or value for something n Store of Value- it holds its value over time and can be stored or saved
 Characteristics of Money n n n Money must be stable To be used as money, it must be scarce Money must be accepted Money must be divisible into parts Money has to be portable and durable
Characteristics of Money n n n Money must be stable To be used as money, it must be scarce Money must be accepted Money must be divisible into parts Money has to be portable and durable
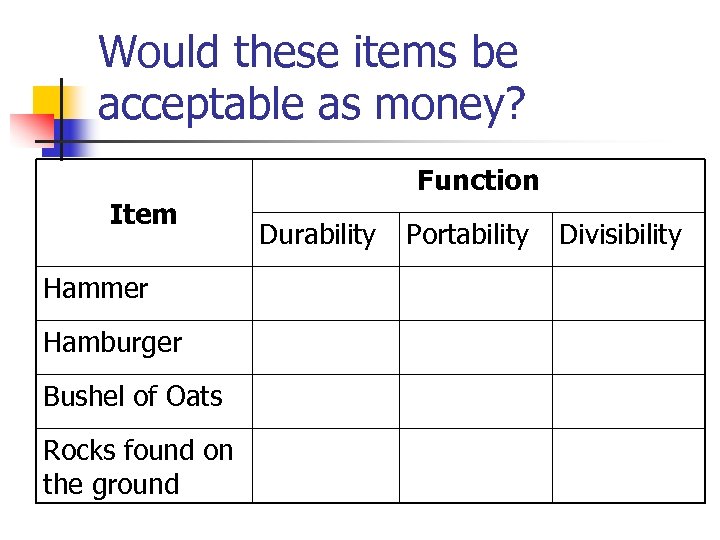 Would these items be acceptable as money? Item Hammer Hamburger Bushel of Oats Rocks found on the ground Function Durability Portability Divisibility
Would these items be acceptable as money? Item Hammer Hamburger Bushel of Oats Rocks found on the ground Function Durability Portability Divisibility
 Banking n n Financial Institution- An organization for managing money, such as a bank, credit union, or brokerage firm Banks manage money, move it around, and maintain a supply of it as well as keeping money safe and gives you access where ever you go
Banking n n Financial Institution- An organization for managing money, such as a bank, credit union, or brokerage firm Banks manage money, move it around, and maintain a supply of it as well as keeping money safe and gives you access where ever you go
 Storing Money n n n Bank account- a record of how much money a customer has put in to or taken out of a bank Deposit- money put in a bank Withdrawal- money taken out of a bank
Storing Money n n n Bank account- a record of how much money a customer has put in to or taken out of a bank Deposit- money put in a bank Withdrawal- money taken out of a bank
 Storing Money 2 main types of accounts n Checking accounts- used for saving money in the short term n Savings accounts- usually used for storing money over a long period of time n Interest-rate a bank pays you for keeping your money there
Storing Money 2 main types of accounts n Checking accounts- used for saving money in the short term n Savings accounts- usually used for storing money over a long period of time n Interest-rate a bank pays you for keeping your money there
 Transferring Money n n n Every single business transaction involves the transfer of money Electronic funds transfer- the transfer of money from one account to another using computers Used to pay employees, pay bills, withdraw money
Transferring Money n n n Every single business transaction involves the transfer of money Electronic funds transfer- the transfer of money from one account to another using computers Used to pay employees, pay bills, withdraw money
 Lending Money n n The money you deposit in a bank makes it possible for the bank to lend money to other customers Collateral- something valuable you put up for a loan, so the bank can take it if you fail to pay back the loan.
Lending Money n n The money you deposit in a bank makes it possible for the bank to lend money to other customers Collateral- something valuable you put up for a loan, so the bank can take it if you fail to pay back the loan.
 Lending Money n n n Mortgage loan- used to buy real estate, such as a house Mortgage-a deed to give the lender back the property if the loan is not paid back Commercial loan- loan made to businesses to buy supplies and equipment
Lending Money n n n Mortgage loan- used to buy real estate, such as a house Mortgage-a deed to give the lender back the property if the loan is not paid back Commercial loan- loan made to businesses to buy supplies and equipment
 Lending Money n n Individual Loan- a loan made to an individual to pay for personal items, such as a car, home repairs, or a vacation. Line of Credit- an amount set aside by a bank for preferred customers that is available on demand.
Lending Money n n Individual Loan- a loan made to an individual to pay for personal items, such as a car, home repairs, or a vacation. Line of Credit- an amount set aside by a bank for preferred customers that is available on demand.
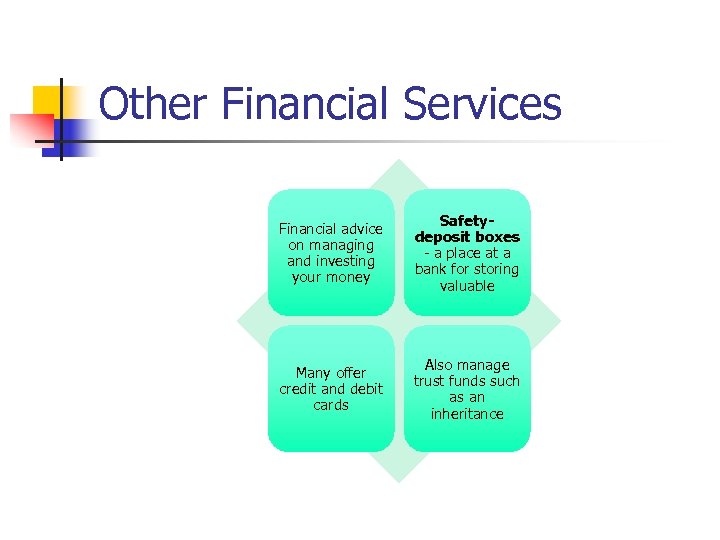 Other Financial Services Financial advice on managing and investing your money Safetydeposit boxes - a place at a bank for storing valuable Many offer credit and debit cards Also manage trust funds such as an inheritance
Other Financial Services Financial advice on managing and investing your money Safetydeposit boxes - a place at a bank for storing valuable Many offer credit and debit cards Also manage trust funds such as an inheritance
 Types of banks n n Banks operate on a state, national, and international level There are strict rules for starting a bank n n n Meet special requirements Apply for a charter Prove you have enough capital
Types of banks n n Banks operate on a state, national, and international level There are strict rules for starting a bank n n n Meet special requirements Apply for a charter Prove you have enough capital
 Commercial Banks n n Most US banks are commercial banks Offer the entire range of services Often called full-service banks In business to make a profit
Commercial Banks n n Most US banks are commercial banks Offer the entire range of services Often called full-service banks In business to make a profit
 Savings and Loan Associations n n n Originally set up to offer savings accounts and home mortgage loans Purpose was to encourage people to save money and make it easier to buy a home Charged lower interest on loans, paid higher interest on savings
Savings and Loan Associations n n n Originally set up to offer savings accounts and home mortgage loans Purpose was to encourage people to save money and make it easier to buy a home Charged lower interest on loans, paid higher interest on savings
 Savings and Loan Associations n n n In the 1980 s, about 20% of S and L’s failed Government passed regulations allowing them to charge higher interest rates and offer more services Most S and L’s are like commercial banks
Savings and Loan Associations n n n In the 1980 s, about 20% of S and L’s failed Government passed regulations allowing them to charge higher interest rates and offer more services Most S and L’s are like commercial banks
 Credit Unions n n Nonprofit banks set up by organizations for their members to use Companies, labor unions, and professional groups have their own credit unions Offer members a full range of services Offer low interest loans, pay high interest rates
Credit Unions n n Nonprofit banks set up by organizations for their members to use Companies, labor unions, and professional groups have their own credit unions Offer members a full range of services Offer low interest loans, pay high interest rates
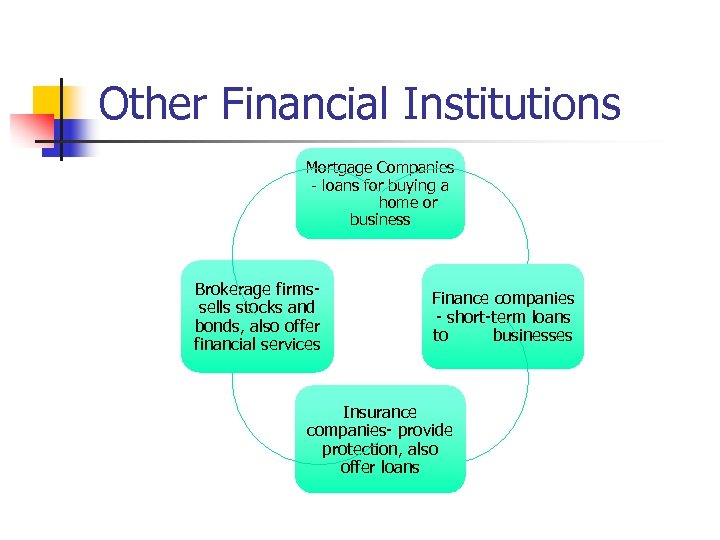 Other Financial Institutions Mortgage Companies - loans for buying a home or business Brokerage firmssells stocks and bonds, also offer financial services Finance companies - short-term loans to businesses Insurance companies- provide protection, also offer loans
Other Financial Institutions Mortgage Companies - loans for buying a home or business Brokerage firmssells stocks and bonds, also offer financial services Finance companies - short-term loans to businesses Insurance companies- provide protection, also offer loans
 The Federal Reserve System n n n Central banking organization in the US Set up in 1913 by congress Consists of: n n 12 Federal Reserve district banks 25 branch banks About 5, 000 member banks Run by board of governors, headed by a chairperson
The Federal Reserve System n n n Central banking organization in the US Set up in 1913 by congress Consists of: n n 12 Federal Reserve district banks 25 branch banks About 5, 000 member banks Run by board of governors, headed by a chairperson
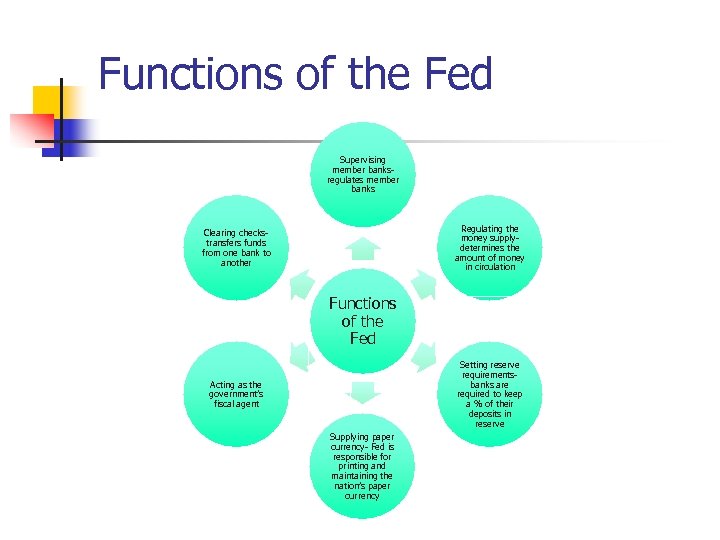 Functions of the Fed Supervising member banksregulates member banks Regulating the money supplydetermines the amount of money in circulation Clearing checkstransfers funds from one bank to another Functions of the Fed Setting reserve requirementsbanks are required to keep a % of their deposits in reserve Acting as the government’s fiscal agent Supplying paper currency- Fed is responsible for printing and maintaining the nation’s paper currency
Functions of the Fed Supervising member banksregulates member banks Regulating the money supplydetermines the amount of money in circulation Clearing checkstransfers funds from one bank to another Functions of the Fed Setting reserve requirementsbanks are required to keep a % of their deposits in reserve Acting as the government’s fiscal agent Supplying paper currency- Fed is responsible for printing and maintaining the nation’s paper currency
 About Your Money http: //www. history. com/shows/modern-marvels/videos/playlists/money#makingmoney
About Your Money http: //www. history. com/shows/modern-marvels/videos/playlists/money#makingmoney
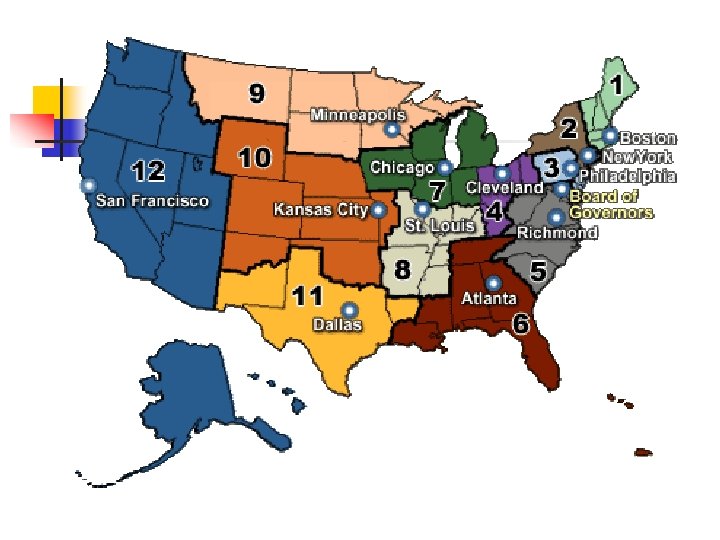
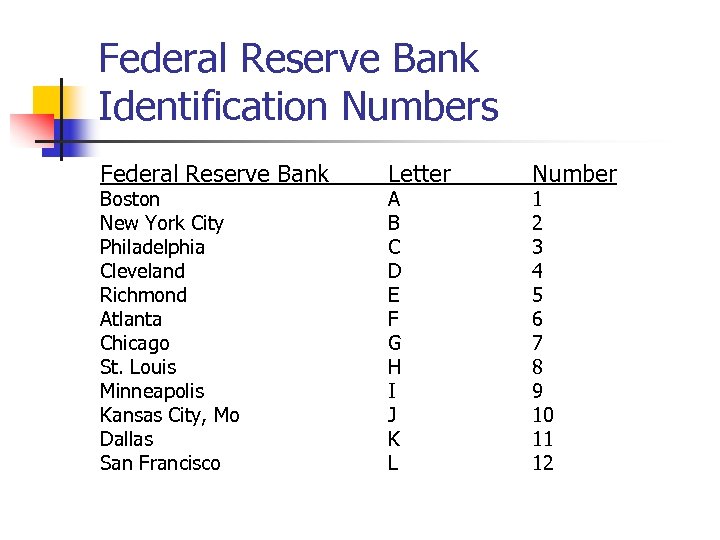 Federal Reserve Bank Identification Numbers Federal Reserve Bank Boston New York City Philadelphia Cleveland Richmond Atlanta Chicago St. Louis Minneapolis Kansas City, Mo Dallas San Francisco Letter A B C D E F G H I J K L Number 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
Federal Reserve Bank Identification Numbers Federal Reserve Bank Boston New York City Philadelphia Cleveland Richmond Atlanta Chicago St. Louis Minneapolis Kansas City, Mo Dallas San Francisco Letter A B C D E F G H I J K L Number 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
 Security Features of Notes n n n Inclusion of Watermarks Security Threads embedded into the paper Fine line Printing patterns Micro printing Color shifting Ink Low Vision Features
Security Features of Notes n n n Inclusion of Watermarks Security Threads embedded into the paper Fine line Printing patterns Micro printing Color shifting Ink Low Vision Features
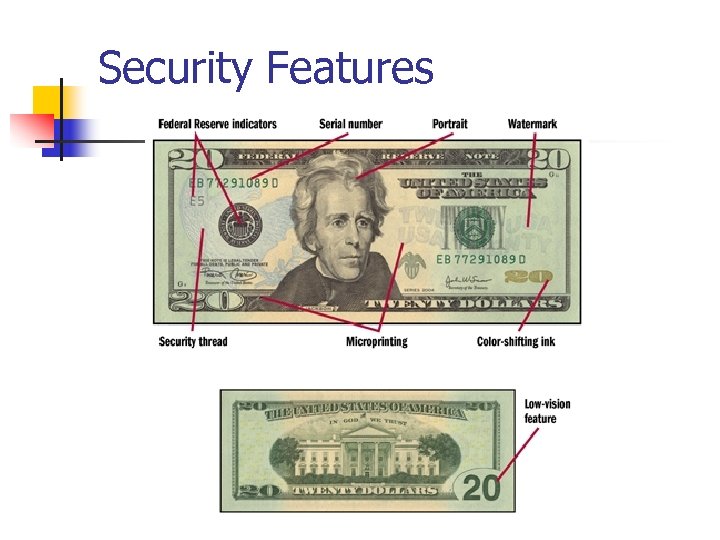 Security Features
Security Features
 Unique Paper n n Red and Blue threads part of formula Only one company has the formula and is able to produce the paper Made of 75% Cotton and 25% Linen Watermarks are included into the paper when it is produced
Unique Paper n n Red and Blue threads part of formula Only one company has the formula and is able to produce the paper Made of 75% Cotton and 25% Linen Watermarks are included into the paper when it is produced
 UV Light and Micro-printing n n n $100 glows red under the light $50 glows yellow under the light $20 glows green under the light $100 Micro-printing on the collar and lower left 100 $50 Micro-printing on the collar and side borders 50 $20 Micro-printing on the Lower Oval of portrait and lower left numeral
UV Light and Micro-printing n n n $100 glows red under the light $50 glows yellow under the light $20 glows green under the light $100 Micro-printing on the collar and lower left 100 $50 Micro-printing on the collar and side borders 50 $20 Micro-printing on the Lower Oval of portrait and lower left numeral


