L3 Directions.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 MINISTRY OF EDUCATION AND SCIENCE RK INTERNATIONAL EDUCATION CORPORATION GEODESY Lecture 3: Reading a Grid & Determining Direction Shoganbekova Daniya A. Assistant of professor FCTIM
MINISTRY OF EDUCATION AND SCIENCE RK INTERNATIONAL EDUCATION CORPORATION GEODESY Lecture 3: Reading a Grid & Determining Direction Shoganbekova Daniya A. Assistant of professor FCTIM
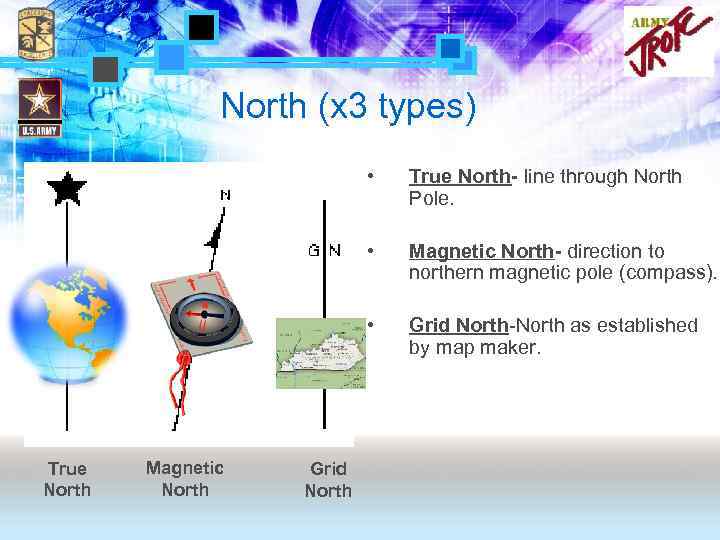 North (x 3 types) • • Magnetic North Grid North Magnetic North- direction to northern magnetic pole (compass). • True North- line through North Pole. Grid North-North as established by map maker.
North (x 3 types) • • Magnetic North Grid North Magnetic North- direction to northern magnetic pole (compass). • True North- line through North Pole. Grid North-North as established by map maker.
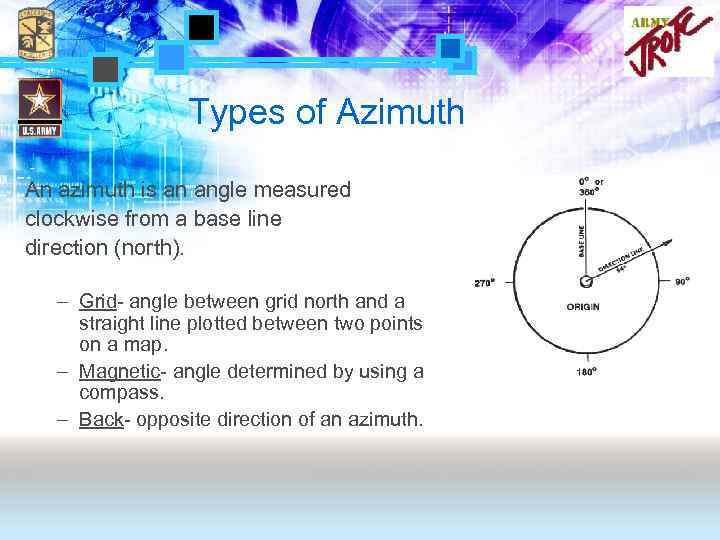 Types of Azimuth An azimuth is an angle measured clockwise from a base line direction (north). – Grid- angle between grid north and a straight line plotted between two points on a map. – Magnetic- angle determined by using a compass. – Back- opposite direction of an azimuth.
Types of Azimuth An azimuth is an angle measured clockwise from a base line direction (north). – Grid- angle between grid north and a straight line plotted between two points on a map. – Magnetic- angle determined by using a compass. – Back- opposite direction of an azimuth.
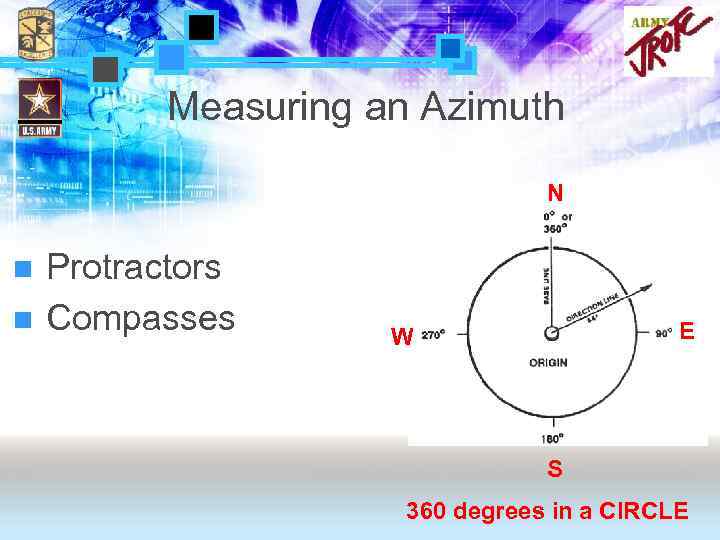 Measuring an Azimuth N n Protractors n Compasses E W S 360 degrees in a CIRCLE
Measuring an Azimuth N n Protractors n Compasses E W S 360 degrees in a CIRCLE
 Measuring an Azimuth Protractors
Measuring an Azimuth Protractors
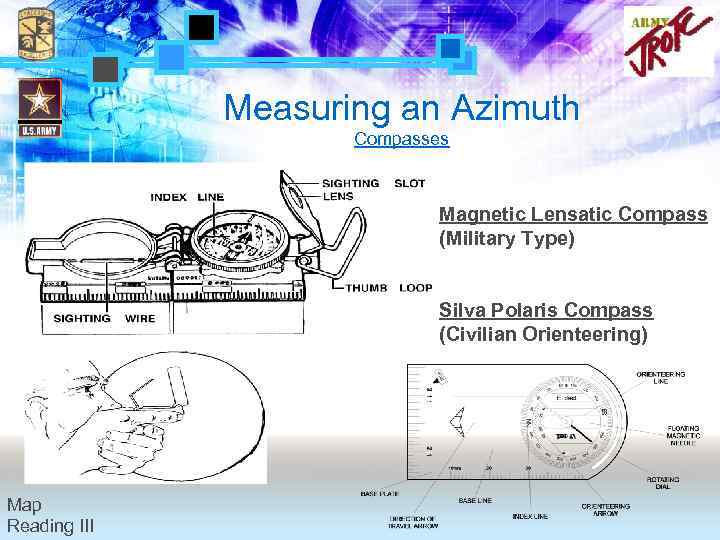 Measuring an Azimuth Compasses Magnetic Lensatic Compass (Military Type) Silva Polaris Compass (Civilian Orienteering) Map Reading III
Measuring an Azimuth Compasses Magnetic Lensatic Compass (Military Type) Silva Polaris Compass (Civilian Orienteering) Map Reading III
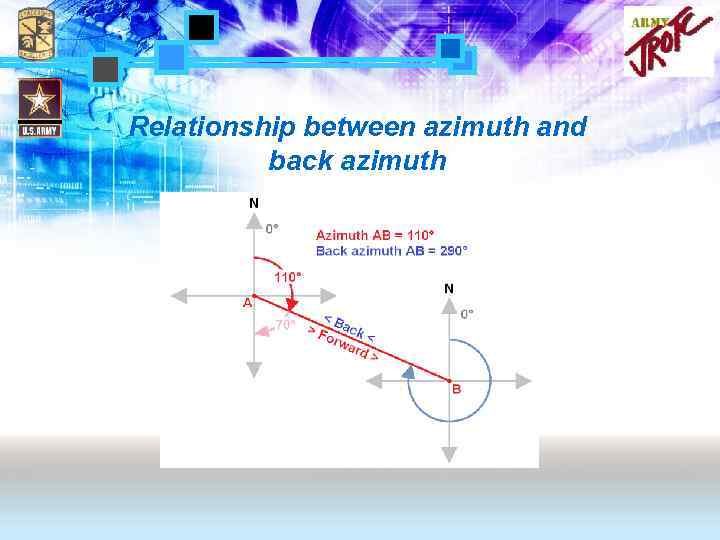 Relationship between azimuth and back azimuth
Relationship between azimuth and back azimuth
 BACK AZIMUTH RULE #1: IF THE AZIMUTH IS MORE THAN 180 DEGREES, THEN SUBTRACT 180 DEGREES. EXAMPLE: AZIMUTH 215 DEGREES -180 DEGREES BACK AZIMUTH 35 DEGREES RULE #2: IF THE AZIMUTH IS 180 DEGREES OR LESS, THEN ADD 180 DEGREES. EXAMPLE: AZIMUTH 180 DEGREES +180 DEGREES BACK AZIMUTH 360 DEGREES Map Reading III
BACK AZIMUTH RULE #1: IF THE AZIMUTH IS MORE THAN 180 DEGREES, THEN SUBTRACT 180 DEGREES. EXAMPLE: AZIMUTH 215 DEGREES -180 DEGREES BACK AZIMUTH 35 DEGREES RULE #2: IF THE AZIMUTH IS 180 DEGREES OR LESS, THEN ADD 180 DEGREES. EXAMPLE: AZIMUTH 180 DEGREES +180 DEGREES BACK AZIMUTH 360 DEGREES Map Reading III
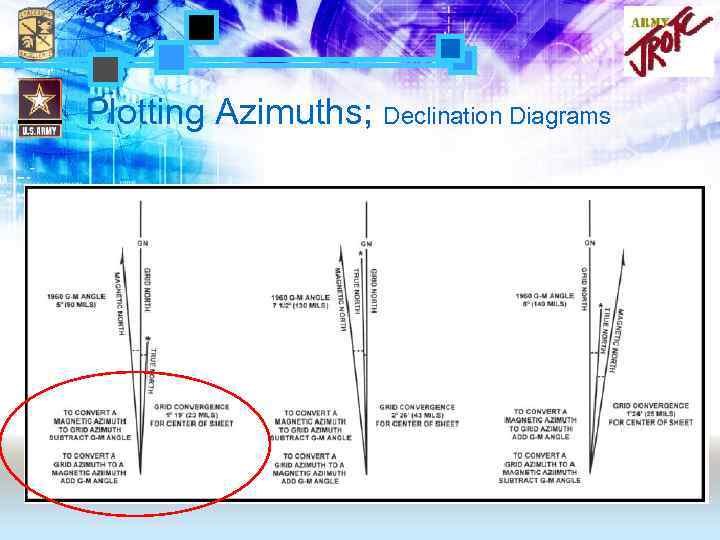
 Plotting Azimuths • Azimuths must be converted to the environment they will be used in. – Grid to Magnetic (map-to-compass) – Magnetic to Grid (compass-to-map). • Use the Declination Diagram to find the conversion angle
Plotting Azimuths • Azimuths must be converted to the environment they will be used in. – Grid to Magnetic (map-to-compass) – Magnetic to Grid (compass-to-map). • Use the Declination Diagram to find the conversion angle
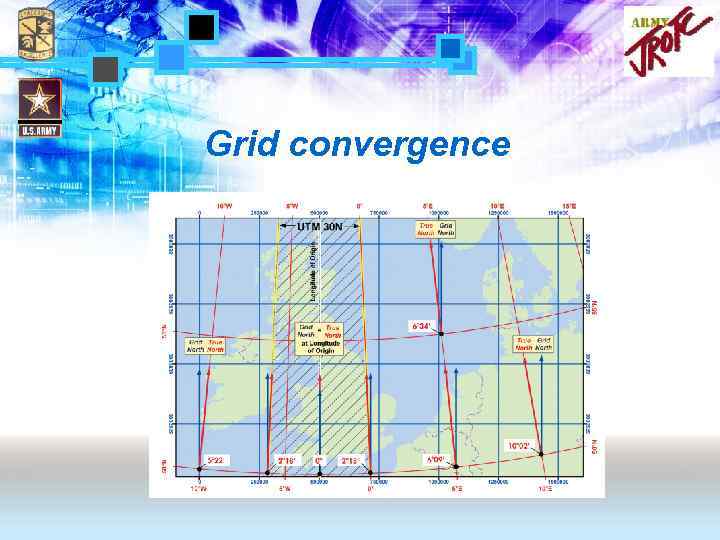 Grid convergence
Grid convergence
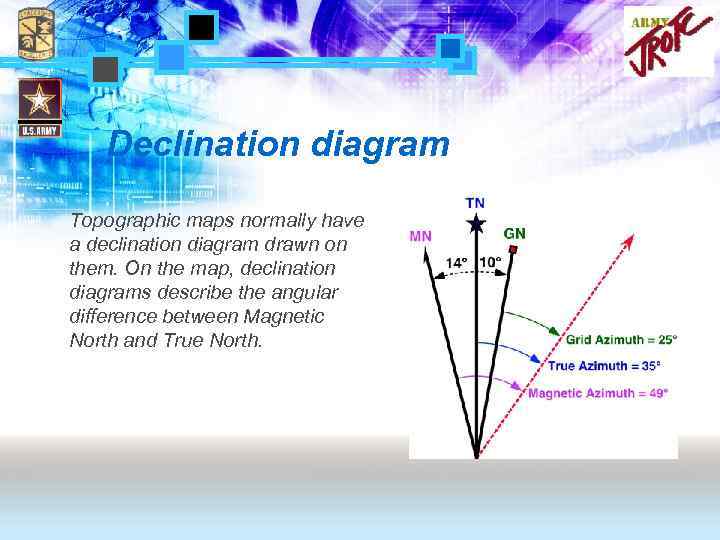 Declination diagram Topographic maps normally have a declination diagram drawn on them. On the map, declination diagrams describe the angular difference between Magnetic North and True North.
Declination diagram Topographic maps normally have a declination diagram drawn on them. On the map, declination diagrams describe the angular difference between Magnetic North and True North.
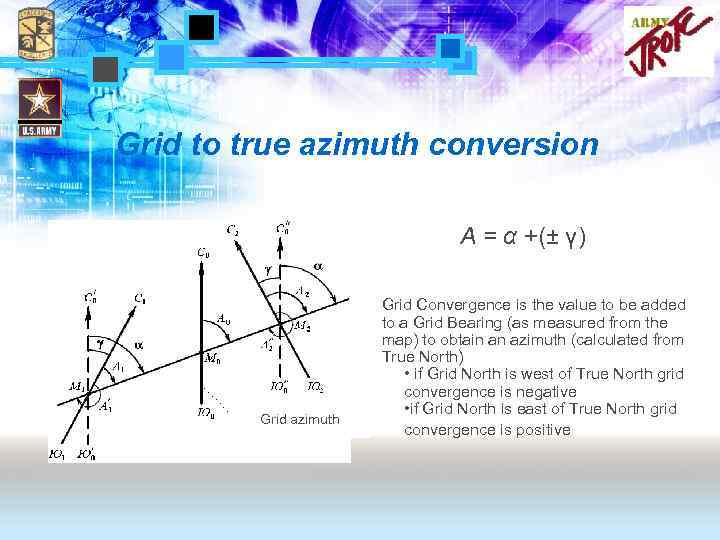 Grid to true azimuth conversion А = α +(± γ) Grid azimuth Grid Convergence is the value to be added to a Grid Bearing (as measured from the map) to obtain an azimuth (calculated from True North) • if Grid North is west of True North grid convergence is negative • if Grid North is east of True North grid convergence is positive
Grid to true azimuth conversion А = α +(± γ) Grid azimuth Grid Convergence is the value to be added to a Grid Bearing (as measured from the map) to obtain an azimuth (calculated from True North) • if Grid North is west of True North grid convergence is negative • if Grid North is east of True North grid convergence is positive
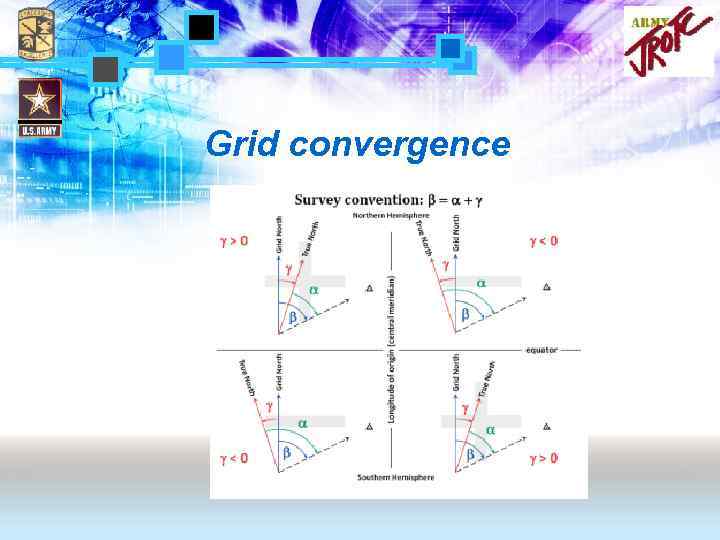 Grid convergence
Grid convergence
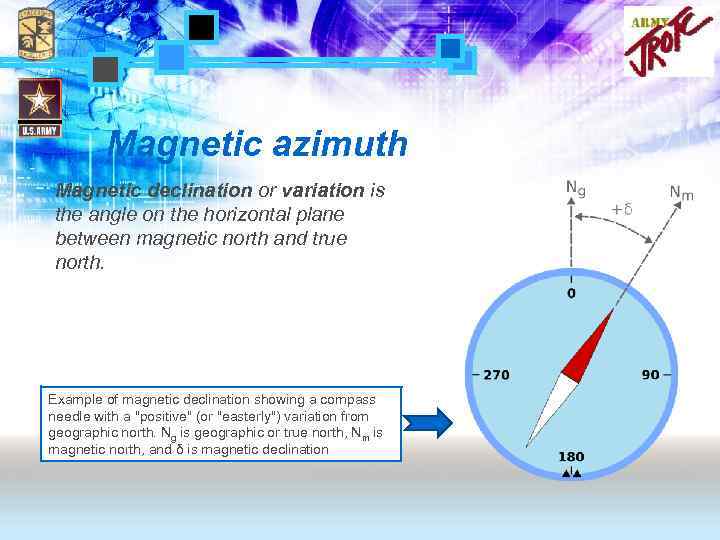 Magnetic azimuth Magnetic declination or variation is the angle on the horizontal plane between magnetic north and true north. Example of magnetic declination showing a compass needle with a "positive" (or "easterly") variation from geographic north. Ng is geographic or true north, Nm is magnetic north, and δ is magnetic declination
Magnetic azimuth Magnetic declination or variation is the angle on the horizontal plane between magnetic north and true north. Example of magnetic declination showing a compass needle with a "positive" (or "easterly") variation from geographic north. Ng is geographic or true north, Nm is magnetic north, and δ is magnetic declination
 Magnetic declination • The Grid Magnetic angle is calculated from the magnetic declination and the grid convergence, and is the angle between Grid North and Magnetic North - this value must be subtracted from a grid bearing to obtain a magnetic bearing The magnetic poles move with time, and the Magnetic Variation is the amount the magnetic declination changes each year
Magnetic declination • The Grid Magnetic angle is calculated from the magnetic declination and the grid convergence, and is the angle between Grid North and Magnetic North - this value must be subtracted from a grid bearing to obtain a magnetic bearing The magnetic poles move with time, and the Magnetic Variation is the amount the magnetic declination changes each year
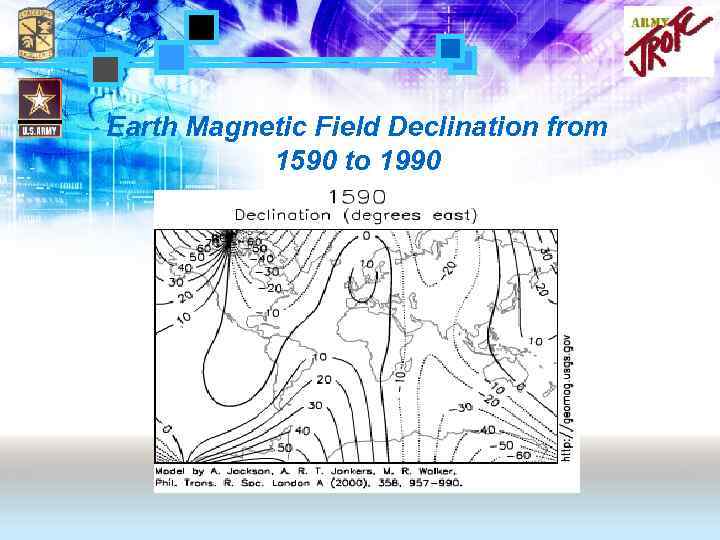 Earth Magnetic Field Declination from 1590 to 1990
Earth Magnetic Field Declination from 1590 to 1990
 Plotting Azimuths; Declination Diagrams
Plotting Azimuths; Declination Diagrams
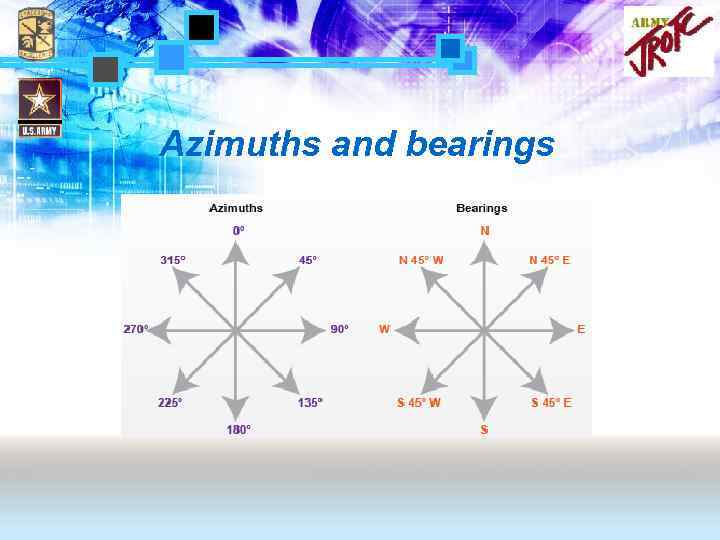
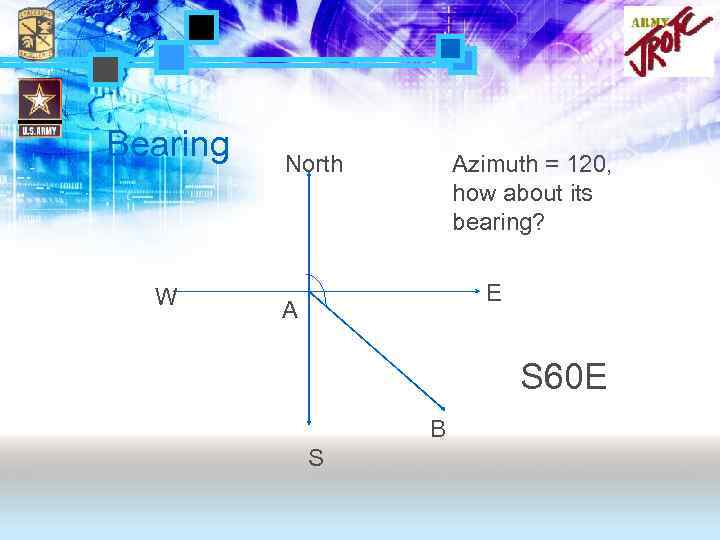
 Bearing • Another way to describe the direction of two points. – – Baseline (N or S) Angle between the baseline and direction Direction of travel E. g. N 30 W, S 18 E…
Bearing • Another way to describe the direction of two points. – – Baseline (N or S) Angle between the baseline and direction Direction of travel E. g. N 30 W, S 18 E…
 Azimuths and bearings
Azimuths and bearings
 Bearing W North Azimuth = 120, how about its bearing? E A S 60 E B S
Bearing W North Azimuth = 120, how about its bearing? E A S 60 E B S
 Back bearing • Bearing can be calculated from azimuth • Back bearing can be calculated from back azimuth • When azimuth = 30, how about back azimuth, bearing, and back bearing?
Back bearing • Bearing can be calculated from azimuth • Back bearing can be calculated from back azimuth • When azimuth = 30, how about back azimuth, bearing, and back bearing?
 Homeassignment • SSW directions - ppt • SSWT DGW - “Work with map” / Task 4
Homeassignment • SSW directions - ppt • SSWT DGW - “Work with map” / Task 4
 Literature • • Rockville, Md. “Basic Geodesy”, reprint 2011/ 245 -246 pages Thomas, Willilam Norman. “Surveying”, 2009/ 113 -115 pages • Омиржанова Ж. Т. , Зубова О. А. , Инербаева Д. А. , учебное пособие «Геодезия» 2011/ 11 -15 стр
Literature • • Rockville, Md. “Basic Geodesy”, reprint 2011/ 245 -246 pages Thomas, Willilam Norman. “Surveying”, 2009/ 113 -115 pages • Омиржанова Ж. Т. , Зубова О. А. , Инербаева Д. А. , учебное пособие «Геодезия» 2011/ 11 -15 стр
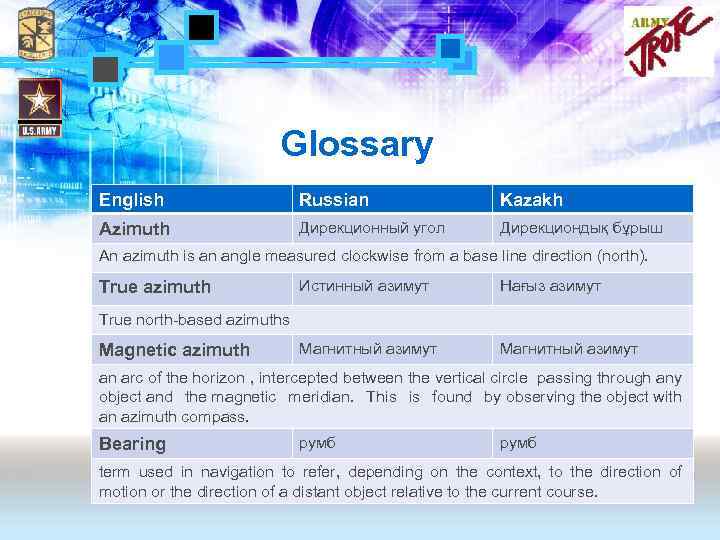 Glossary English Russian Kazakh Azimuth Дирекционный угол Дирекциондық бұрыш An azimuth is an angle measured clockwise from a base line direction (north). True azimuth Истинный азимут Нағыз азимут Магнитный азимут True north-based azimuths Magnetic azimuth an arc of the horizon , intercepted between the vertical circle passing through any object and the magnetic meridian. This is found by observing the object with an azimuth compass. Bearing румб term used in navigation to refer, depending on the context, to the direction of motion or the direction of a distant object relative to the current course.
Glossary English Russian Kazakh Azimuth Дирекционный угол Дирекциондық бұрыш An azimuth is an angle measured clockwise from a base line direction (north). True azimuth Истинный азимут Нағыз азимут Магнитный азимут True north-based azimuths Magnetic azimuth an arc of the horizon , intercepted between the vertical circle passing through any object and the magnetic meridian. This is found by observing the object with an azimuth compass. Bearing румб term used in navigation to refer, depending on the context, to the direction of motion or the direction of a distant object relative to the current course.
