6b4e22e632965e0875a4f345336c38f5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39
 MGT 301 Principles of Marketing Lecture-13
MGT 301 Principles of Marketing Lecture-13
 Summary of Lecture-12
Summary of Lecture-12
 Marketing Research
Marketing Research
 Steps in the Marketing Research Process
Steps in the Marketing Research Process
 1. Problem Definition and the 2. Research Objectives 2. Developing the Research Plan 3. Implementation 4. Interpretation and Reporting of Findings
1. Problem Definition and the 2. Research Objectives 2. Developing the Research Plan 3. Implementation 4. Interpretation and Reporting of Findings
 Today’s Topics u u Marketing Research (cont. . ) Consumer Market-understanding the consumer
Today’s Topics u u Marketing Research (cont. . ) Consumer Market-understanding the consumer
 Research Instruments – Questionnaires u Include open-ended and closed-ended questions u Phrasing and question order are key – Mechanical instrument
Research Instruments – Questionnaires u Include open-ended and closed-ended questions u Phrasing and question order are key – Mechanical instrument
 Contact Methods u Mail questionnaires u Telephonic Interview u u Personal interview – Group interview…Focus group interview Online Research
Contact Methods u Mail questionnaires u Telephonic Interview u u Personal interview – Group interview…Focus group interview Online Research
 Step-3 Implementing the Research Plan Collecting the Data
Step-3 Implementing the Research Plan Collecting the Data
 Analyzing the Data
Analyzing the Data
 C C After the data have been collected, the next step in the research process is data analysis. The purpose of data analysis is to interpret and draw conclusions from the data that has been collected.
C C After the data have been collected, the next step in the research process is data analysis. The purpose of data analysis is to interpret and draw conclusions from the data that has been collected.
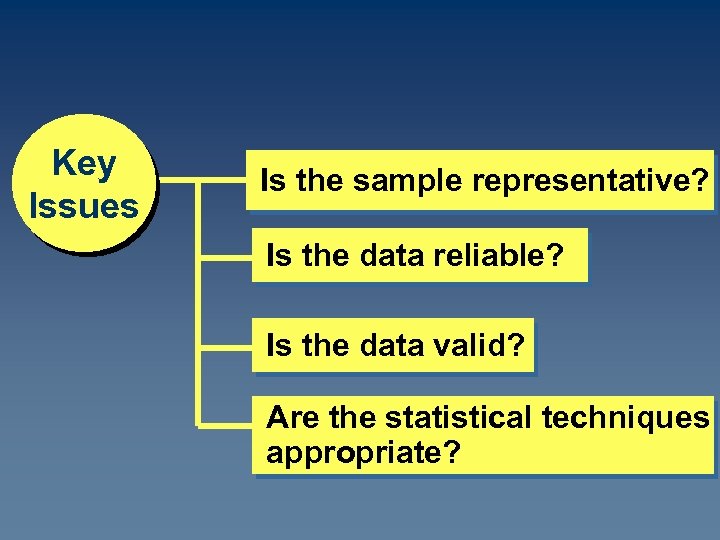 Key Issues Is the sample representative? Is the data reliable? Is the data valid? Are the statistical techniques appropriate?
Key Issues Is the sample representative? Is the data reliable? Is the data valid? Are the statistical techniques appropriate?
 Step-4 Interpretation and Reporting of Findings u u After data analysis is completed, the researcher must prepare the report and communicate the conclusions and recommendations to management. The research will ordinarily be required to present both written and oral reports on the project.
Step-4 Interpretation and Reporting of Findings u u After data analysis is completed, the researcher must prepare the report and communicate the conclusions and recommendations to management. The research will ordinarily be required to present both written and oral reports on the project.
 Research Is Useful If: § We put thought into it before we do it § We do the right kind of research § We use judgment in interpreting and using the results
Research Is Useful If: § We put thought into it before we do it § We do the right kind of research § We use judgment in interpreting and using the results
 Consumer Market § All individuals and households who buy or acquire goods and services for personal consumption
Consumer Market § All individuals and households who buy or acquire goods and services for personal consumption
 – Firm needs to know – Who buys? – How they buy? – When and where they buy? ? – Why they buy? – How they respond to marketing stimuli?
– Firm needs to know – Who buys? – How they buy? – When and where they buy? ? – Why they buy? – How they respond to marketing stimuli?
 Why do you think marketers know these things? ?
Why do you think marketers know these things? ?
 Because they study consumer behavior (CB)
Because they study consumer behavior (CB)
 What is Consumer Behavior about?
What is Consumer Behavior about?
 C How, why, where and when consumers make purchase decisions? C Considers who influences the decisions? C How are purchases made? C What information is needed for those decisions? C What factors affect these decisions?
C How, why, where and when consumers make purchase decisions? C Considers who influences the decisions? C How are purchases made? C What information is needed for those decisions? C What factors affect these decisions?

 Why is it Important? u u Consumers determine the sales and profits of a firm by their purchase decisions, thus the economic viability of the firm. In late 1990, US consumers were spending enough dollar bills to stretch from the Earth to the Sun and back, with enough left over for over 600 lines to the moon!
Why is it Important? u u Consumers determine the sales and profits of a firm by their purchase decisions, thus the economic viability of the firm. In late 1990, US consumers were spending enough dollar bills to stretch from the Earth to the Sun and back, with enough left over for over 600 lines to the moon!
 Customer vs. Consumer Behavior u u Customer behavior Includes both individual consumers who buy goods and services for their own use and organizational buyers who purchase business products. Consumer behavior Is the process through which the ultimate buyer makes purchase decisions.
Customer vs. Consumer Behavior u u Customer behavior Includes both individual consumers who buy goods and services for their own use and organizational buyers who purchase business products. Consumer behavior Is the process through which the ultimate buyer makes purchase decisions.
 Consumer Behavior Defined l l l The study of the processes involved when individuals or groups select, purchase, use, or dispose of products, services, ideas, or experiences to satisfy needs and desires (Solomon, 1996). Those actions directly involved in obtaining, consuming and disposing of products and services, including the decision processes that precede and follow those actions (Engel et al. 1995). Examines mental and emotional processes in addition to the physical activities (Wilkie 1990).
Consumer Behavior Defined l l l The study of the processes involved when individuals or groups select, purchase, use, or dispose of products, services, ideas, or experiences to satisfy needs and desires (Solomon, 1996). Those actions directly involved in obtaining, consuming and disposing of products and services, including the decision processes that precede and follow those actions (Engel et al. 1995). Examines mental and emotional processes in addition to the physical activities (Wilkie 1990).
 Consumer Behavior Deals With … C Actions in Purchasing and Using Products C Including Behavior and Thought Processes
Consumer Behavior Deals With … C Actions in Purchasing and Using Products C Including Behavior and Thought Processes
 The buying behavior of final consumers-individuals and households who buy goods and services for personal consumption.
The buying behavior of final consumers-individuals and households who buy goods and services for personal consumption.
 Marketing Applications
Marketing Applications
 C Positioning C Segmentation C Product development C Market development C International marketing
C Positioning C Segmentation C Product development C Market development C International marketing
 Consumer Spending Patterns
Consumer Spending Patterns
 C Disposable income C Discretionary income C Family life cycle: C Young C Teens C Empty nesters C Senior citizens
C Disposable income C Discretionary income C Family life cycle: C Young C Teens C Empty nesters C Senior citizens
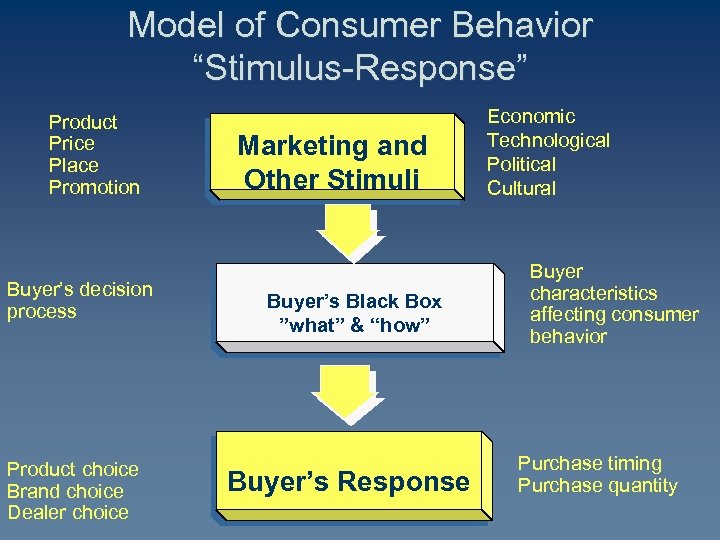 Model of Consumer Behavior “Stimulus-Response” Product Price Place Promotion Buyer’s decision process Product choice Brand choice Dealer choice Marketing and Other Stimuli Buyer’s Black Box ”what” & “how” Buyer’s Response Economic Technological Political Cultural Buyer characteristics affecting consumer behavior Purchase timing Purchase quantity
Model of Consumer Behavior “Stimulus-Response” Product Price Place Promotion Buyer’s decision process Product choice Brand choice Dealer choice Marketing and Other Stimuli Buyer’s Black Box ”what” & “how” Buyer’s Response Economic Technological Political Cultural Buyer characteristics affecting consumer behavior Purchase timing Purchase quantity
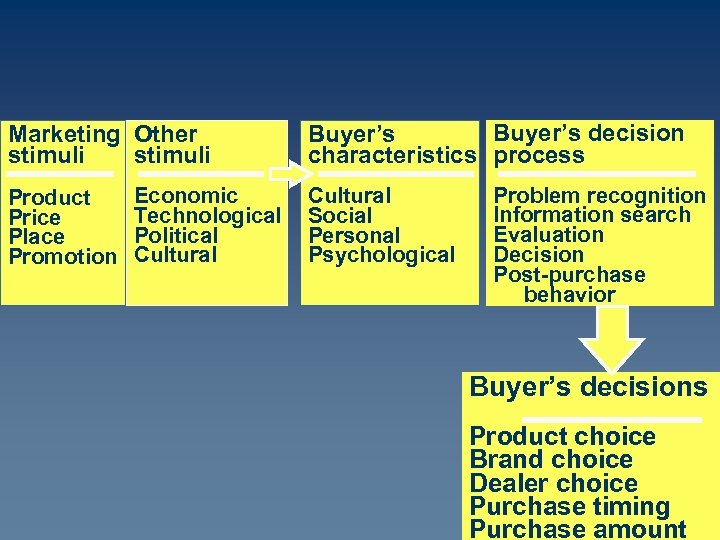 Marketing Other stimuli Product Price Place Promotion Economic Technological Political Cultural Buyer’s decision Buyer’s characteristics process Cultural Social Personal Psychological Problem recognition Information search Evaluation Decision Post-purchase behavior Buyer’s decisions Product choice Brand choice Dealer choice Purchase timing Purchase amount
Marketing Other stimuli Product Price Place Promotion Economic Technological Political Cultural Buyer’s decision Buyer’s characteristics process Cultural Social Personal Psychological Problem recognition Information search Evaluation Decision Post-purchase behavior Buyer’s decisions Product choice Brand choice Dealer choice Purchase timing Purchase amount
 Stimulus Response Model Marketing and other stimuli enter the buyer’s “black box” and produce certain choice/purchase responses. Marketers must figure out what is inside of the buyer’s “black box” and how stimuli are changed to responses.
Stimulus Response Model Marketing and other stimuli enter the buyer’s “black box” and produce certain choice/purchase responses. Marketers must figure out what is inside of the buyer’s “black box” and how stimuli are changed to responses.
 Enough for today. . .
Enough for today. . .
 Summary Consumer Market-understanding the consumer
Summary Consumer Market-understanding the consumer
 All individuals and households who buy or acquire goods and services for personal consumption
All individuals and households who buy or acquire goods and services for personal consumption
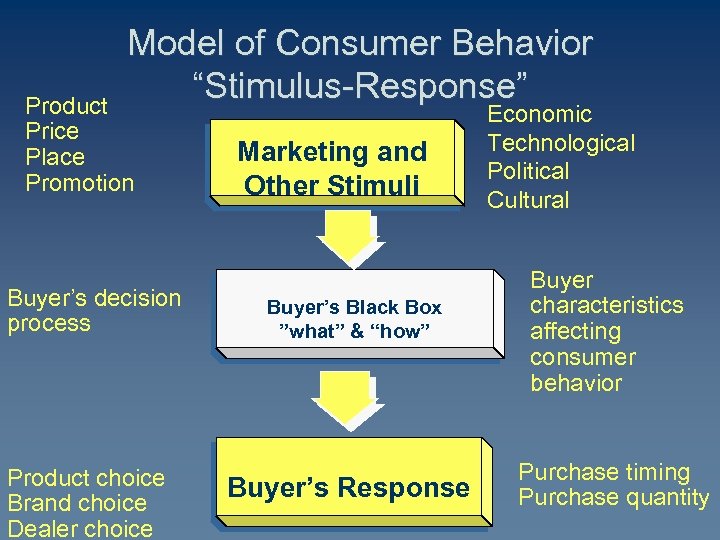 Model of Consumer Behavior “Stimulus-Response” Product Price Place Promotion Buyer’s decision process Product choice Brand choice Dealer choice Marketing and Other Stimuli Buyer’s Black Box ”what” & “how” Buyer’s Response Economic Technological Political Cultural Buyer characteristics affecting consumer behavior Purchase timing Purchase quantity
Model of Consumer Behavior “Stimulus-Response” Product Price Place Promotion Buyer’s decision process Product choice Brand choice Dealer choice Marketing and Other Stimuli Buyer’s Black Box ”what” & “how” Buyer’s Response Economic Technological Political Cultural Buyer characteristics affecting consumer behavior Purchase timing Purchase quantity
 Next…. Consumer Behavior (cont. . )
Next…. Consumer Behavior (cont. . )
 MGT 301 Principles of Marketing Lecture-13
MGT 301 Principles of Marketing Lecture-13


