7c9a6376f64161676c2cef853f95e6b9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 Matakuliah Tahun Versi : M 0284/Teknologi & Infrastruktur E-Business : 2005 : <
Matakuliah Tahun Versi : M 0284/Teknologi & Infrastruktur E-Business : 2005 : <
 Learning Objectives • Describe what software agents are • Differentiate between various classes of software agents • Understand the use of artificial intelligence and statistical reasoning • Describe the range of agents available to assist in the buying process • Identify various activities in e-commerce where software agents can be used 2
Learning Objectives • Describe what software agents are • Differentiate between various classes of software agents • Understand the use of artificial intelligence and statistical reasoning • Describe the range of agents available to assist in the buying process • Identify various activities in e-commerce where software agents can be used 2
 Overview • • • What are software agents? Logic of agent behavior Types of agents Information agents E-Commerce agents Mobile agents 3
Overview • • • What are software agents? Logic of agent behavior Types of agents Information agents E-Commerce agents Mobile agents 3
 What are software agents? • Software entities – Autonomy/agency - without detailed commands – Purposeful - goal-driven – Reactive - react to changes in environment. Exhibit intelligence – Social and Mobility skill - travel around and interact with other agents 4
What are software agents? • Software entities – Autonomy/agency - without detailed commands – Purposeful - goal-driven – Reactive - react to changes in environment. Exhibit intelligence – Social and Mobility skill - travel around and interact with other agents 4
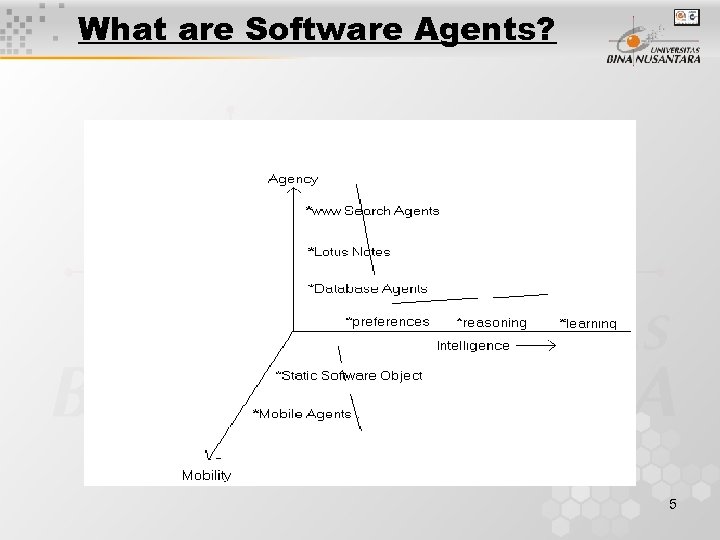 What are Software Agents? 5
What are Software Agents? 5
 Logic of Agent Behavior • Symbolic Reasoning if
Logic of Agent Behavior • Symbolic Reasoning if
 Logic of Agent Behavior • Statistical Reasoning – Market Segmentation • Clustering according to some characteristics such a buying behavior, demographic data – Also called Collaborative filtering – Used by Amazon. com to predict books that might prove to be your favorite 7
Logic of Agent Behavior • Statistical Reasoning – Market Segmentation • Clustering according to some characteristics such a buying behavior, demographic data – Also called Collaborative filtering – Used by Amazon. com to predict books that might prove to be your favorite 7
 Logic of Agent Behavior • Multi-attribute utility theory used to rank-order different choices such as items to buy Utility is related to various quality, price and delivery attributes Utility numbers are calculated for various choices Various formulas used: U(x)= log( x+ b) U(x)= a + bx + cx 2 U(x) = (1/k) (1 - e –kx) where U is the utility and x is the measure of the attribute. In the case of an automobile, x could be price, quality or fuel economy. 8
Logic of Agent Behavior • Multi-attribute utility theory used to rank-order different choices such as items to buy Utility is related to various quality, price and delivery attributes Utility numbers are calculated for various choices Various formulas used: U(x)= log( x+ b) U(x)= a + bx + cx 2 U(x) = (1/k) (1 - e –kx) where U is the utility and x is the measure of the attribute. In the case of an automobile, x could be price, quality or fuel economy. 8
 Logic of Agent Behavior • Constraint Satisfaction Approach • A way to prune a large set of choices – Hard and Soft constraints – Options/ choices that violate hard constraints are removed – Options left are evaluated in terms of how far soft constraints violated 9
Logic of Agent Behavior • Constraint Satisfaction Approach • A way to prune a large set of choices – Hard and Soft constraints – Options/ choices that violate hard constraints are removed – Options left are evaluated in terms of how far soft constraints violated 9
 Logic of Agent Behavior • Auction Protocols – English auction move up – Dutch auction move low – Sealed-bid auction envelopes price start low and price start high and offers in sealed 10
Logic of Agent Behavior • Auction Protocols – English auction move up – Dutch auction move low – Sealed-bid auction envelopes price start low and price start high and offers in sealed 10
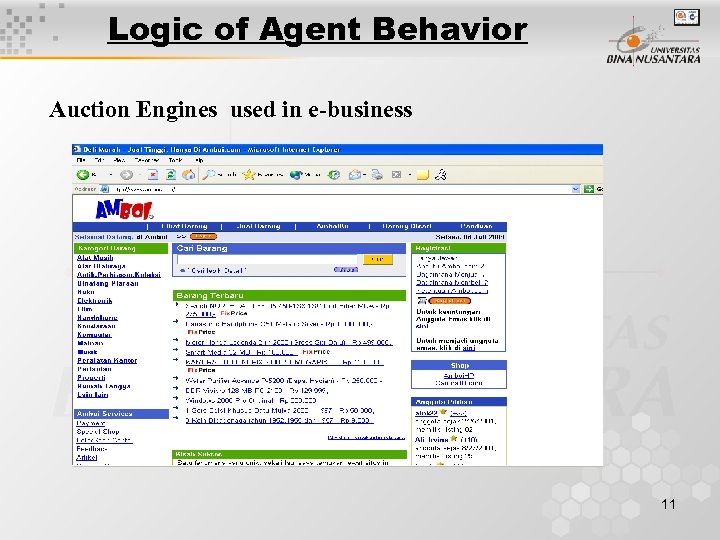 Logic of Agent Behavior Auction Engines used in e-business 11
Logic of Agent Behavior Auction Engines used in e-business 11
 Types of Software Agents • Information Agents • E-Commerce Agents • Mobile Agents 12
Types of Software Agents • Information Agents • E-Commerce Agents • Mobile Agents 12
 Information Agents • Information Search Agents search engines • Information filtering agents search few specific web site and retrieve information relevant to a user 13
Information Agents • Information Search Agents search engines • Information filtering agents search few specific web site and retrieve information relevant to a user 13
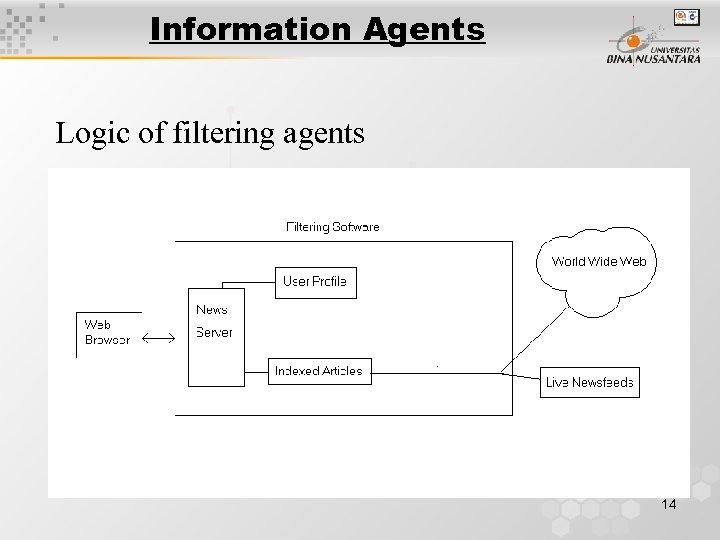 Information Agents Logic of filtering agents 14
Information Agents Logic of filtering agents 14
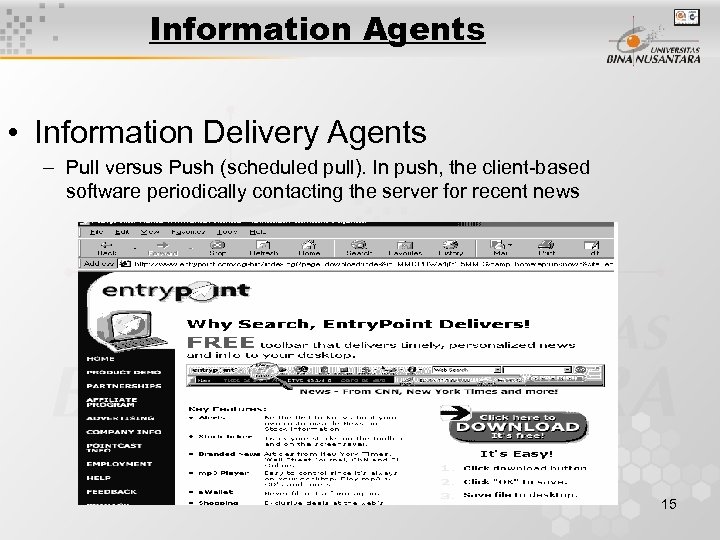 Information Agents • Information Delivery Agents – Pull versus Push (scheduled pull). In push, the client-based software periodically contacting the server for recent news 15
Information Agents • Information Delivery Agents – Pull versus Push (scheduled pull). In push, the client-based software periodically contacting the server for recent news 15
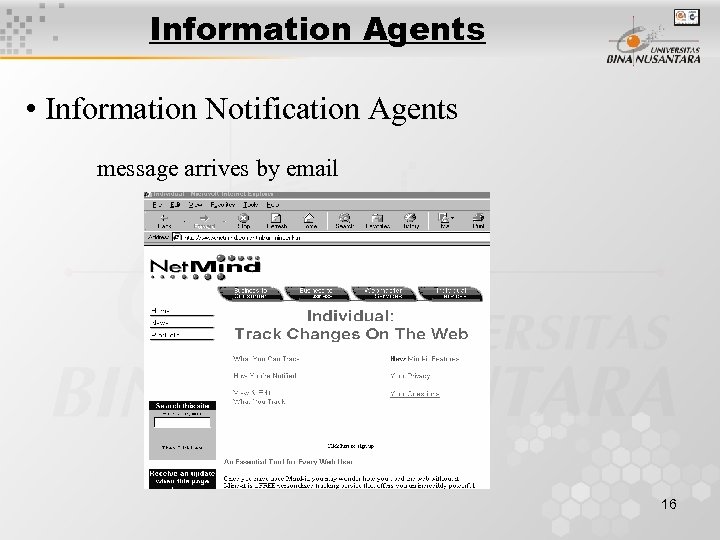 Information Agents • Information Notification Agents message arrives by email 16
Information Agents • Information Notification Agents message arrives by email 16
 Information Agents • Information Reconnaissance Agents – Letizia at MIT brings to attention to users pages of interest that are only a few links away from the current page – The system builds up a interest profile of the user and searches neighboring pages of interest 17
Information Agents • Information Reconnaissance Agents – Letizia at MIT brings to attention to users pages of interest that are only a few links away from the current page – The system builds up a interest profile of the user and searches neighboring pages of interest 17
