1f80f023c6e05e2fe394ce169b5e85b8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 Matakuliah Tahun Versi : F 0392/Simulasi Perdagangan di Bursa Efek : 2005 : 1/3 Pertemuan 05 Harga Wajar Saham 1
Matakuliah Tahun Versi : F 0392/Simulasi Perdagangan di Bursa Efek : 2005 : 1/3 Pertemuan 05 Harga Wajar Saham 1
 Learning Outcomes Pada akhir pertemuan ini, diharapkan mahasiswa akan mampu : • Menentukan harga wajar saham dengan beberapa pendekatan 2
Learning Outcomes Pada akhir pertemuan ini, diharapkan mahasiswa akan mampu : • Menentukan harga wajar saham dengan beberapa pendekatan 2
 Outline Materi • • Net Asset Valuation Dividend Valuation Stock Valuation CAPM 3
Outline Materi • • Net Asset Valuation Dividend Valuation Stock Valuation CAPM 3
 Equity Valuation Models • Balance Sheet Book Value per share Equity ÷ # shares Book value reflects acctg entries only Does not include: Brand name Customer loyalty Expertise; reputation Future growth opportunities Liquidation Value Replacement Value 4
Equity Valuation Models • Balance Sheet Book Value per share Equity ÷ # shares Book value reflects acctg entries only Does not include: Brand name Customer loyalty Expertise; reputation Future growth opportunities Liquidation Value Replacement Value 4
 Intrinsic Value • Value today = Present Value of Future CF’s • V 0 = [D 1 + P 1] / (1+R) • Also: R = [P 1 - P 0]/P 0 + D 1/P 0 • Returns: Expected - given price & expected CF’s Required - based on risk Realized - actual return; after the fact 5
Intrinsic Value • Value today = Present Value of Future CF’s • V 0 = [D 1 + P 1] / (1+R) • Also: R = [P 1 - P 0]/P 0 + D 1/P 0 • Returns: Expected - given price & expected CF’s Required - based on risk Realized - actual return; after the fact 5
 Example 1 • Suppose: P 1 = 52 (expected) D 1 = 4. 00 (expected) P 0 = 48 Beta = 1. 2 Rf = 6%; Rm - Rf = 5% • Recall: R = Rf + B(Rm - Rf) 6
Example 1 • Suppose: P 1 = 52 (expected) D 1 = 4. 00 (expected) P 0 = 48 Beta = 1. 2 Rf = 6%; Rm - Rf = 5% • Recall: R = Rf + B(Rm - Rf) 6
![Example 2 • Expected Return: R = [52 - 48]/48 + 4/48 = 16. Example 2 • Expected Return: R = [52 - 48]/48 + 4/48 = 16.](https://present5.com/presentation/1f80f023c6e05e2fe394ce169b5e85b8/image-7.jpg) Example 2 • Expected Return: R = [52 - 48]/48 + 4/48 = 16. 67% • Required: R = 6 + 1. 2(5) = 12% • Is Stock Over or Under valued? => undervalued; stock price has to rise • Intrinsic Value: P 0 = [52 + 4] / (1+12%) = $50 > 48 7
Example 2 • Expected Return: R = [52 - 48]/48 + 4/48 = 16. 67% • Required: R = 6 + 1. 2(5) = 12% • Is Stock Over or Under valued? => undervalued; stock price has to rise • Intrinsic Value: P 0 = [52 + 4] / (1+12%) = $50 > 48 7
 Dividend Discount Model • P 0 = D 1/(1+R) + D 2/(1+R)2 + D 3/(1+R)3 +. . . If Dividends are expected to grow at the constant rate g, then: P 0 = D 1/(R-g) or: P 0 = Do(1+g)/(R-g) • Price will be higher: The higher the expected dividend The lower the capitalization rate, R The higher the expected growth rate, g The model is extremely sensitive to inputs 8
Dividend Discount Model • P 0 = D 1/(1+R) + D 2/(1+R)2 + D 3/(1+R)3 +. . . If Dividends are expected to grow at the constant rate g, then: P 0 = D 1/(R-g) or: P 0 = Do(1+g)/(R-g) • Price will be higher: The higher the expected dividend The lower the capitalization rate, R The higher the expected growth rate, g The model is extremely sensitive to inputs 8
 Dividend Discount Model • Example: D 1 = $4. 00 g = 5% R = 12% P 0 = D 1/(R-g) = 4/(12%-5%) = $57. 14 • Note: Since P 1 = D 2/(R-g) = D 1(1+g)/(R-g) P 1 = [D 1/(R-g)] x (1+g) P 1 = P 0 x (1+g) Price grows at constant rate 9
Dividend Discount Model • Example: D 1 = $4. 00 g = 5% R = 12% P 0 = D 1/(R-g) = 4/(12%-5%) = $57. 14 • Note: Since P 1 = D 2/(R-g) = D 1(1+g)/(R-g) P 1 = [D 1/(R-g)] x (1+g) P 1 = P 0 x (1+g) Price grows at constant rate 9
 Dividend Discount Model • Suppose D 1 = $4. 00 g increases from 5% to 6% • What happens to price? • What happens to expected return? P 0 = 4/(12%-6%) = $66. 67 E(R) = D 1/P 0 + g = 4/66. 67 + 6% = 12% (unchanged) 10
Dividend Discount Model • Suppose D 1 = $4. 00 g increases from 5% to 6% • What happens to price? • What happens to expected return? P 0 = 4/(12%-6%) = $66. 67 E(R) = D 1/P 0 + g = 4/66. 67 + 6% = 12% (unchanged) 10
 Stock Prices & Investment Opportunities • Sustainable Growth Rate: rate of growth such that D/E remains constant & no new equity is needed SGR = r x ROE • R = retention ratio = (1 -DPS)/EPS • DPS = Dividends per share 11
Stock Prices & Investment Opportunities • Sustainable Growth Rate: rate of growth such that D/E remains constant & no new equity is needed SGR = r x ROE • R = retention ratio = (1 -DPS)/EPS • DPS = Dividends per share 11
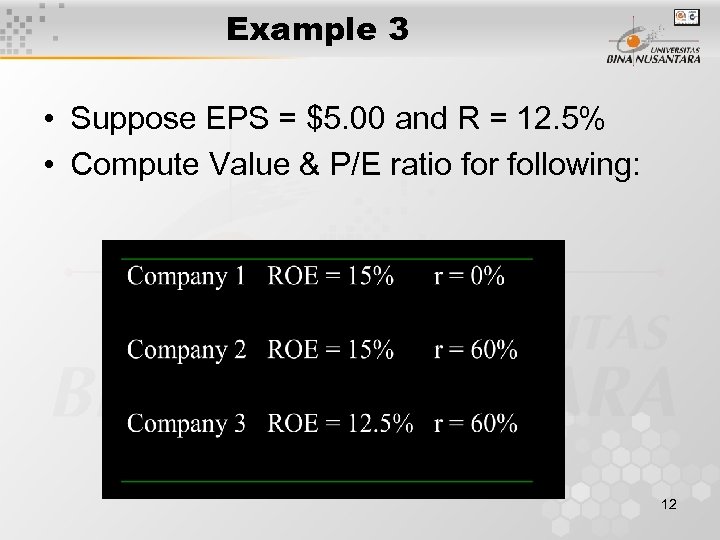 Example 3 • Suppose EPS = $5. 00 and R = 12. 5% • Compute Value & P/E ratio for following: 12
Example 3 • Suppose EPS = $5. 00 and R = 12. 5% • Compute Value & P/E ratio for following: 12
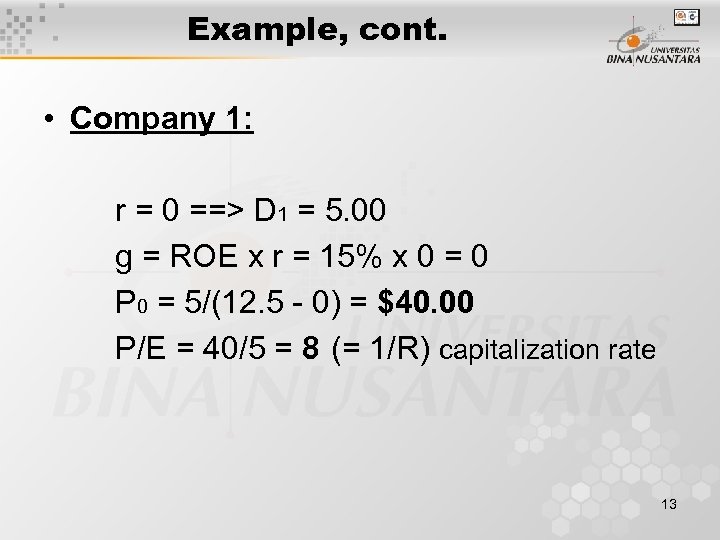 Example, cont. • Company 1: r = 0 ==> D 1 = 5. 00 g = ROE x r = 15% x 0 = 0 P 0 = 5/(12. 5 - 0) = $40. 00 P/E = 40/5 = 8 (= 1/R) capitalization rate 13
Example, cont. • Company 1: r = 0 ==> D 1 = 5. 00 g = ROE x r = 15% x 0 = 0 P 0 = 5/(12. 5 - 0) = $40. 00 P/E = 40/5 = 8 (= 1/R) capitalization rate 13
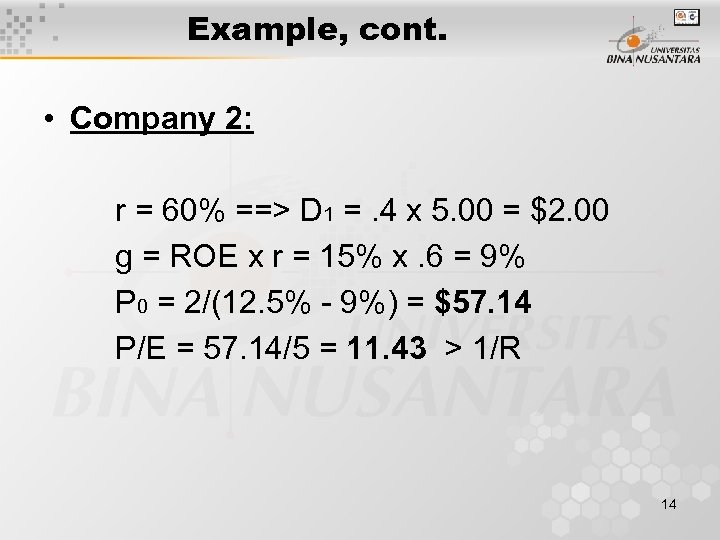 Example, cont. • Company 2: r = 60% ==> D 1 =. 4 x 5. 00 = $2. 00 g = ROE x r = 15% x. 6 = 9% P 0 = 2/(12. 5% - 9%) = $57. 14 P/E = 57. 14/5 = 11. 43 > 1/R 14
Example, cont. • Company 2: r = 60% ==> D 1 =. 4 x 5. 00 = $2. 00 g = ROE x r = 15% x. 6 = 9% P 0 = 2/(12. 5% - 9%) = $57. 14 P/E = 57. 14/5 = 11. 43 > 1/R 14
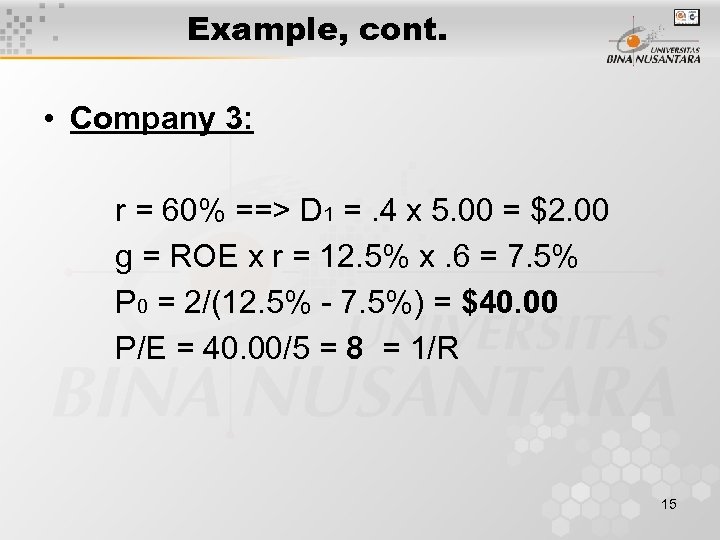 Example, cont. • Company 3: r = 60% ==> D 1 =. 4 x 5. 00 = $2. 00 g = ROE x r = 12. 5% x. 6 = 7. 5% P 0 = 2/(12. 5% - 7. 5%) = $40. 00 P/E = 40. 00/5 = 8 = 1/R 15
Example, cont. • Company 3: r = 60% ==> D 1 =. 4 x 5. 00 = $2. 00 g = ROE x r = 12. 5% x. 6 = 7. 5% P 0 = 2/(12. 5% - 7. 5%) = $40. 00 P/E = 40. 00/5 = 8 = 1/R 15
 Summary • Expected EPS same for all three firms • Only positive NPV growth leads to increase in share value (ROE > R) • P/E = 1/R for no growth • P/E > 1/R for positive NPV growth firms • P 0 = E/R + PVGO • P 0 = 40 + 17. 14 16
Summary • Expected EPS same for all three firms • Only positive NPV growth leads to increase in share value (ROE > R) • P/E = 1/R for no growth • P/E > 1/R for positive NPV growth firms • P 0 = E/R + PVGO • P 0 = 40 + 17. 14 16
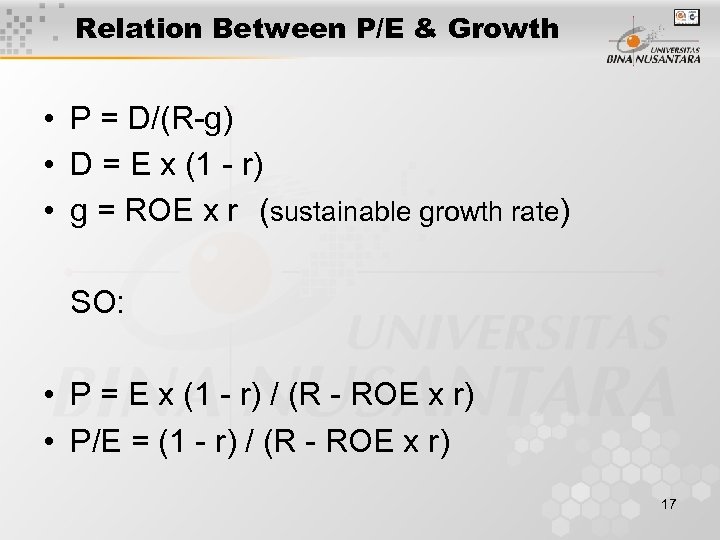 Relation Between P/E & Growth • P = D/(R-g) • D = E x (1 - r) • g = ROE x r (sustainable growth rate) SO: • P = E x (1 - r) / (R - ROE x r) • P/E = (1 - r) / (R - ROE x r) 17
Relation Between P/E & Growth • P = D/(R-g) • D = E x (1 - r) • g = ROE x r (sustainable growth rate) SO: • P = E x (1 - r) / (R - ROE x r) • P/E = (1 - r) / (R - ROE x r) 17
 Relation Between P/E & Growth • Now, take derivative of P/E w/r/t r: • (R - ROE x r) x (-1) - (1 - r) (-ROE) / (xx)2 • Denominator is always positive • Numerator = ROE - R • ROE > R => P/E increases when r increases • If ROE < R, growth reduces P/E & P • Growth must be value enhancing! 18
Relation Between P/E & Growth • Now, take derivative of P/E w/r/t r: • (R - ROE x r) x (-1) - (1 - r) (-ROE) / (xx)2 • Denominator is always positive • Numerator = ROE - R • ROE > R => P/E increases when r increases • If ROE < R, growth reduces P/E & P • Growth must be value enhancing! 18
 Example • Consider a takeover target w/ entrenched mgmt • r = 60%; ROE = 10%; R = 15% ; EPS = 5. 00 • D = (1 - 60%) x 5 = $2. 00 • g = 10% x 60% = 6% • P = 2 / (15% - 6%) = $22. 22 • PVGO = P 0 - E/R = 22. 22 - 5/. 15 = -11. 11 • Buy firm & increase value by setting r = 0 • P 0 = 5/. 15 = 33. 33 19
Example • Consider a takeover target w/ entrenched mgmt • r = 60%; ROE = 10%; R = 15% ; EPS = 5. 00 • D = (1 - 60%) x 5 = $2. 00 • g = 10% x 60% = 6% • P = 2 / (15% - 6%) = $22. 22 • PVGO = P 0 - E/R = 22. 22 - 5/. 15 = -11. 11 • Buy firm & increase value by setting r = 0 • P 0 = 5/. 15 = 33. 33 19
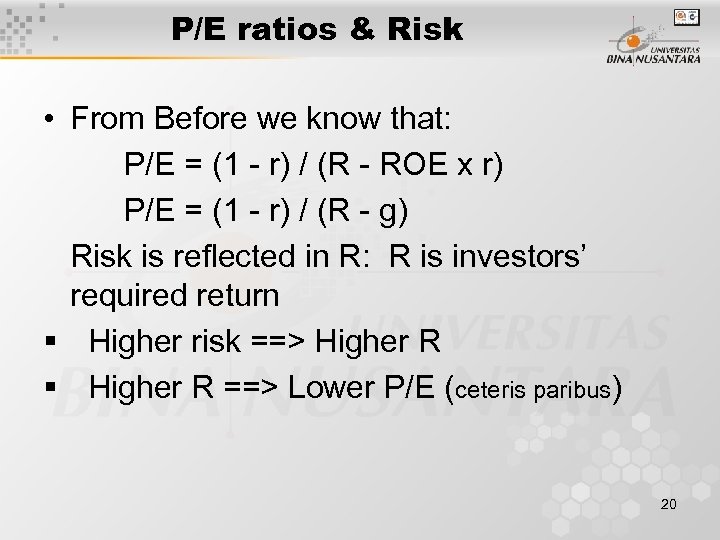 P/E ratios & Risk • From Before we know that: P/E = (1 - r) / (R - ROE x r) P/E = (1 - r) / (R - g) Risk is reflected in R: R is investors’ required return § Higher risk ==> Higher R § Higher R ==> Lower P/E (ceteris paribus) 20
P/E ratios & Risk • From Before we know that: P/E = (1 - r) / (R - ROE x r) P/E = (1 - r) / (R - g) Risk is reflected in R: R is investors’ required return § Higher risk ==> Higher R § Higher R ==> Lower P/E (ceteris paribus) 20
 Tugas Kerjakan dan kumpulkan pada Pert 06 • Tugas 05 -1 • Tugas 05 -2 • Tugas 05 -3 21
Tugas Kerjakan dan kumpulkan pada Pert 06 • Tugas 05 -1 • Tugas 05 -2 • Tugas 05 -3 21
