marketing research.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 Market research is to do with collecting information about consumers and the characteristics of markets It involves using surveys(опросы), polls, focus groups and other methods to gather information
Market research is to do with collecting information about consumers and the characteristics of markets It involves using surveys(опросы), polls, focus groups and other methods to gather information

 In the end, market research is about improving the marketing efforts of business organisations Research Purposes • To identify customer needs and then meet those needs • To learn about customer attitudes and values • To help develop products and services that meet identified needs
In the end, market research is about improving the marketing efforts of business organisations Research Purposes • To identify customer needs and then meet those needs • To learn about customer attitudes and values • To help develop products and services that meet identified needs
 Classifying Customers • A target market consists of a whole group of potential customers, drawn from the whole population • Classifying customers according to socio -economic status, lifestyle, family circumstances, gender and so on • It’s better to define the target market as a collection of ‘segments’ • Each segment will have different characteristics • Each segment’s needs and wants must be satisfied
Classifying Customers • A target market consists of a whole group of potential customers, drawn from the whole population • Classifying customers according to socio -economic status, lifestyle, family circumstances, gender and so on • It’s better to define the target market as a collection of ‘segments’ • Each segment will have different characteristics • Each segment’s needs and wants must be satisfied
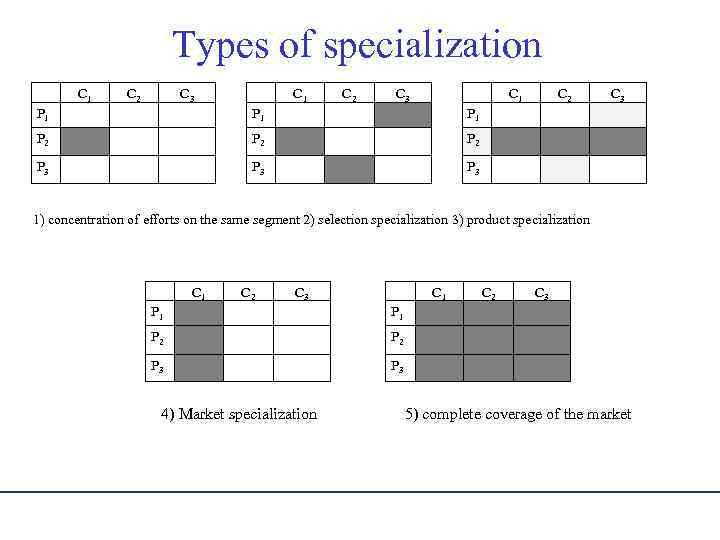 Types of specialization С 1 Р 1 Р 2 Р 3 С 2 С 3 С 1 Р 1 Р 2 Р 3 С 2 С 3 С 1 С 2 Р 1 Р 2 Р 3 С 3 1) concentration of efforts on the same segment 2) selection specialization 3) product specialization С 1 Р 1 Р 2 Р 3 С 2 С 3 С 1 Р 1 Р 2 Р 3 С 3 4) Market specialization С 2 5) complete coverage of the market
Types of specialization С 1 Р 1 Р 2 Р 3 С 2 С 3 С 1 Р 1 Р 2 Р 3 С 2 С 3 С 1 С 2 Р 1 Р 2 Р 3 С 3 1) concentration of efforts on the same segment 2) selection specialization 3) product specialization С 1 Р 1 Р 2 Р 3 С 2 С 3 С 1 Р 1 Р 2 Р 3 С 3 4) Market specialization С 2 5) complete coverage of the market
 Why Use Different Methods? • Each different method has its advantages and disadvantages • Each may only be appropriate in certain circumstances (обстоятельства) • Users need to work out if the method is right for them according to its cost, reliability, validity, accessibility and the time it will take to gather
Why Use Different Methods? • Each different method has its advantages and disadvantages • Each may only be appropriate in certain circumstances (обстоятельства) • Users need to work out if the method is right for them according to its cost, reliability, validity, accessibility and the time it will take to gather
 Secondary Research
Secondary Research
 Internal Sources • Company Accounts • Internal Reports and Analysis • Stock Analysis • Retail data - loyalty cards, till data, etc. External Sources • Government Statistics (ONS) • EU - Euro Stat • Trade publications • Commercial Data - Gallup, Mintel, etc. • Household Expenditure Survey • Magazine surveys • Other firms’ research • Research documents – publications, journals, etc.
Internal Sources • Company Accounts • Internal Reports and Analysis • Stock Analysis • Retail data - loyalty cards, till data, etc. External Sources • Government Statistics (ONS) • EU - Euro Stat • Trade publications • Commercial Data - Gallup, Mintel, etc. • Household Expenditure Survey • Magazine surveys • Other firms’ research • Research documents – publications, journals, etc.
 Information sources 1. Literature search Getting hold of all available material on a particular theme. Material is gathered from: • Internal company information • Relevant (соответствующая) tourism (trade) literature • Newspapers • Magazines • Firms’ annual reports
Information sources 1. Literature search Getting hold of all available material on a particular theme. Material is gathered from: • Internal company information • Relevant (соответствующая) tourism (trade) literature • Newspapers • Magazines • Firms’ annual reports
 Primary Research Characteristics - First hand information - Expensive to collect, analyse and evaluate - Can be highly focussed and relevant - Care needs to be taken with the approach and methodology to ensure accuracy (Необходимо проявлять осторожность при выборе подхода и методологии, чтобы обеспечить точность) - Types of question – closed – limited information gained; open – useful information but difficult to analyse
Primary Research Characteristics - First hand information - Expensive to collect, analyse and evaluate - Can be highly focussed and relevant - Care needs to be taken with the approach and methodology to ensure accuracy (Необходимо проявлять осторожность при выборе подхода и методологии, чтобы обеспечить точность) - Types of question – closed – limited information gained; open – useful information but difficult to analyse
 Quantitative and Qualitative Information: • Quantitative – based on numbers – 56% of 18 year olds drink alcohol at least four times a week - doesn’t tell you why, when, how • Qualitative – more detail – tells you why, when and how!
Quantitative and Qualitative Information: • Quantitative – based on numbers – 56% of 18 year olds drink alcohol at least four times a week - doesn’t tell you why, when, how • Qualitative – more detail – tells you why, when and how!
 Information sources 2. Talking to people Useful in the early stages Includes meetings with customers and suppliers It generates opinions and may be unrepresentative of the whole population
Information sources 2. Talking to people Useful in the early stages Includes meetings with customers and suppliers It generates opinions and may be unrepresentative of the whole population
 Information sources 3. Focus groups These are used to: • Explore ideas and attitudes • Test new approaches • Generate a discussion But they involve a small sample (выборка) and may not mirror the overall population
Information sources 3. Focus groups These are used to: • Explore ideas and attitudes • Test new approaches • Generate a discussion But they involve a small sample (выборка) and may not mirror the overall population
 Information sources 4. • • • Personal interviews Produce in depth information Are carried out face-to-face Can be very expensive Usually involve the interviewer asking questions from a written questionnaire or from a list of topics
Information sources 4. • • • Personal interviews Produce in depth information Are carried out face-to-face Can be very expensive Usually involve the interviewer asking questions from a written questionnaire or from a list of topics
 Information sources 5. Telephone surveys • The fastest way of gathering information, especially from large sample sizes • A prepared script (сценарий) is used as with written questionnaires, but a phone survey allows opinions to be tested further
Information sources 5. Telephone surveys • The fastest way of gathering information, especially from large sample sizes • A prepared script (сценарий) is used as with written questionnaires, but a phone survey allows opinions to be tested further
 Information sources 6. • • • Postal surveys Ideal for large sample sizes If sample covers wide area Generally cost less than telephone interviews • But take longer to complete • No interviewer, so less chance of personal bias (личная предвзятость) • Unable to probe for more detailed information
Information sources 6. • • • Postal surveys Ideal for large sample sizes If sample covers wide area Generally cost less than telephone interviews • But take longer to complete • No interviewer, so less chance of personal bias (личная предвзятость) • Unable to probe for more detailed information
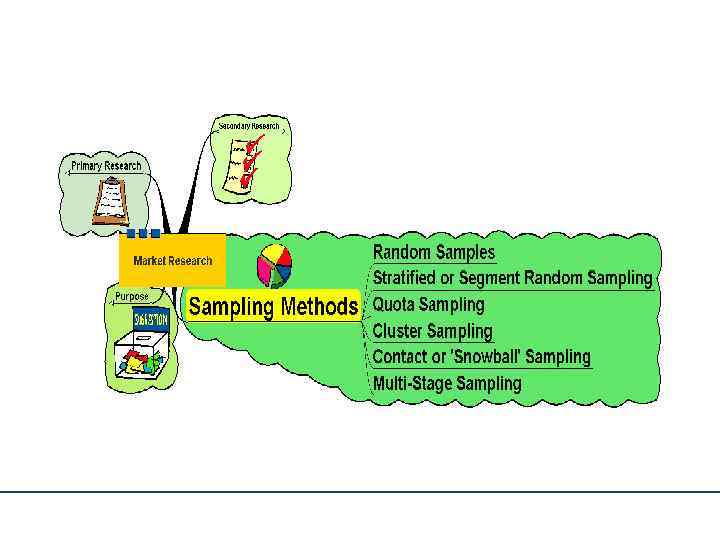
 • Random (случайная выборка) Samples – equal chance of anyone being picked – May select those not in the target group – indiscriminate – Sample sizes may need to be large to be representative – Can be very expensive • Stratified or Segment Random Sampling – Samples on the basis of a representative strata or segment – Still random but more focussed – May give more relevant information – May be more cost effective
• Random (случайная выборка) Samples – equal chance of anyone being picked – May select those not in the target group – indiscriminate – Sample sizes may need to be large to be representative – Can be very expensive • Stratified or Segment Random Sampling – Samples on the basis of a representative strata or segment – Still random but more focussed – May give more relevant information – May be more cost effective
 • Quota Sampling – Again – by segment – Not randomly selected – Specific number on each segment are interviewed, etc. – May not be fully representative – Cheaper method • Cluster Sampling – Primarily based on geographical areas or ‘clusters’ that can be seen as being representative of the whole population • Multi-Stage Sampling – Sample selected from multi stage sub-groups • Snowball Sampling – Samples developed from contacts of existing customers – ‘word of mouth’ type approach!
• Quota Sampling – Again – by segment – Not randomly selected – Specific number on each segment are interviewed, etc. – May not be fully representative – Cheaper method • Cluster Sampling – Primarily based on geographical areas or ‘clusters’ that can be seen as being representative of the whole population • Multi-Stage Sampling – Sample selected from multi stage sub-groups • Snowball Sampling – Samples developed from contacts of existing customers – ‘word of mouth’ type approach!
 Advantages of Market Research – Helps focus attention on objectives – Aids(помогает) forecasting, planning and strategic development – May help to reduce risk of new product development – Communicates image, vision, etc. – Globalisation makes market information valuable (HSBC adverts!!)
Advantages of Market Research – Helps focus attention on objectives – Aids(помогает) forecasting, planning and strategic development – May help to reduce risk of new product development – Communicates image, vision, etc. – Globalisation makes market information valuable (HSBC adverts!!)
 Disadvantages of Market Research – Information only as good as the methodology used – Can be inaccurate or unreliable(неточной или ненадежной) – Results may not be what the business wants to hear! – May stifle initiative and ‘gut feeling’ (Может подавить инициативу и 'шестое чувство') – Always a problem that we may never know enough to be sure!
Disadvantages of Market Research – Information only as good as the methodology used – Can be inaccurate or unreliable(неточной или ненадежной) – Results may not be what the business wants to hear! – May stifle initiative and ‘gut feeling’ (Может подавить инициативу и 'шестое чувство') – Always a problem that we may never know enough to be sure!
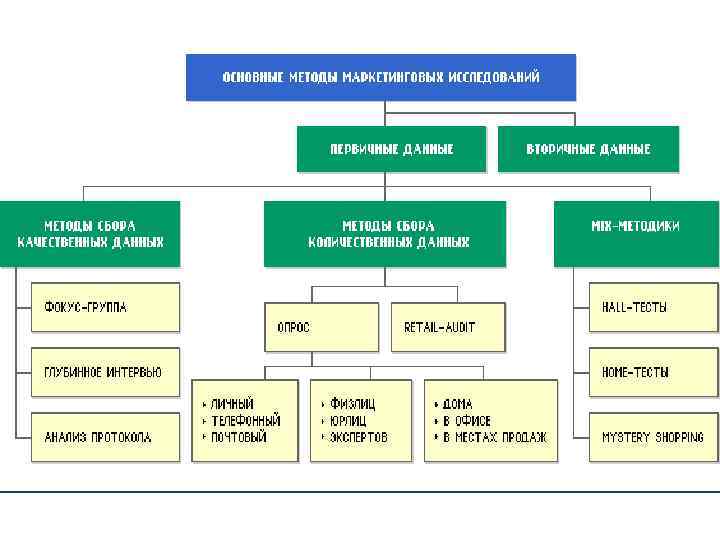
 Mix-methodologies - mixed methods research, rather successfully combining the advantages of qualitative and quantitative methods. The main types of mix-methodologies: hall tests, home tests and mystery shopping. Hall-test - method of investigation, when a large group of people (up to 100 -400 people) in a special room is testing a product and/or its elements (packaging, advertisement, etc. ), and then answers questions (fill in the form), relating to the goods. Home-test - similar to the hall-test, with the only difference that the testing of the goods occurs in the home (the home of the Respondent). Use this method when a need long-term testing of the goods. As a rule, product packaging does not contain the names of trademarks and indications of the firm-manufacturer.
Mix-methodologies - mixed methods research, rather successfully combining the advantages of qualitative and quantitative methods. The main types of mix-methodologies: hall tests, home tests and mystery shopping. Hall-test - method of investigation, when a large group of people (up to 100 -400 people) in a special room is testing a product and/or its elements (packaging, advertisement, etc. ), and then answers questions (fill in the form), relating to the goods. Home-test - similar to the hall-test, with the only difference that the testing of the goods occurs in the home (the home of the Respondent). Use this method when a need long-term testing of the goods. As a rule, product packaging does not contain the names of trademarks and indications of the firm-manufacturer.
 Mystery Shopping is a method of research, involving assessment of the level of the service with the help of experts, acting in the role of fake buyers (customers, clients, etc. ). Mystery Shopping allows you to evaluate the work of the personnel from the point of view of the consumer and take timely measures to improve the quality of the service. In addition, Mystery Shopping allows producers of a certain product to evaluate the work of the staff of the retail traders with these goods (availability in the warehouse, presentation, etc. ).
Mystery Shopping is a method of research, involving assessment of the level of the service with the help of experts, acting in the role of fake buyers (customers, clients, etc. ). Mystery Shopping allows you to evaluate the work of the personnel from the point of view of the consumer and take timely measures to improve the quality of the service. In addition, Mystery Shopping allows producers of a certain product to evaluate the work of the staff of the retail traders with these goods (availability in the warehouse, presentation, etc. ).


