L 6 GOAL SETTING 1. Goals 2. How




























d--_fall_2013-decision_making-l6_goal_setting.ppt
- Размер: 716.5 Кб
- Количество слайдов: 29
Описание презентации L 6 GOAL SETTING 1. Goals 2. How по слайдам
 L 6 GOAL SETTING 1. Goals 2. How to set the goals 3. Stages of organizational life cycle
L 6 GOAL SETTING 1. Goals 2. How to set the goals 3. Stages of organizational life cycle
 Goals A goal or objective is a desired result a person or a system envisions, plans and commits to achieve Goal-setting ideally involves establishing specific, measurable, attainable, realistic and time-targeted objectives.
Goals A goal or objective is a desired result a person or a system envisions, plans and commits to achieve Goal-setting ideally involves establishing specific, measurable, attainable, realistic and time-targeted objectives.
 Goals Do students know how to select REALISTIC goals?
Goals Do students know how to select REALISTIC goals?
 Goals • No person would doubt that: • Goals give the sense of direction • Goals motivate • Goals promote efficiency and prevent waste of efforts • Goals sort out between relevant and irrelevant • Goals correct the performance • Goals determine the outcomes / results
Goals • No person would doubt that: • Goals give the sense of direction • Goals motivate • Goals promote efficiency and prevent waste of efforts • Goals sort out between relevant and irrelevant • Goals correct the performance • Goals determine the outcomes / results
 2. HOW TO SET THE GOALS? • It is essential to set the right goals in a right way. • Goal setting is a difficult process !!! • It is a difficult task per se to communicate the goal to employees so that they accept it in a right way BUT before that — someone has to create the GOAL!!! • The special position of the top (or any) manager is to decide what should be the next goal. – How do goals emerge (appear)? – How to make sure the goal is right?
2. HOW TO SET THE GOALS? • It is essential to set the right goals in a right way. • Goal setting is a difficult process !!! • It is a difficult task per se to communicate the goal to employees so that they accept it in a right way BUT before that — someone has to create the GOAL!!! • The special position of the top (or any) manager is to decide what should be the next goal. – How do goals emerge (appear)? – How to make sure the goal is right?
 GARBAGE CAN • GOALS EMERGE FROM GARBAGE • PROCESS IS UNDEFINED • OUTCOMES ARE NOT NECESSARILY MEASUR
GARBAGE CAN • GOALS EMERGE FROM GARBAGE • PROCESS IS UNDEFINED • OUTCOMES ARE NOT NECESSARILY MEASUR
 3. There are some helpful preconditions: • This lecture deals with goal setting for organizations. • Compare to personal goal-setting. • Goals come from your personal likes / dislikes = wants • Goals come from the pressure around to pace up = needs
3. There are some helpful preconditions: • This lecture deals with goal setting for organizations. • Compare to personal goal-setting. • Goals come from your personal likes / dislikes = wants • Goals come from the pressure around to pace up = needs
 ORGANIZATIONS: • WANTS : owners visions, missions, • NEEDS: • Organizational Life cycle theory
ORGANIZATIONS: • WANTS : owners visions, missions, • NEEDS: • Organizational Life cycle theory
 • All organizations, like all living organisms, have a lifecycle and undergo very predictable and repetitive patterns of behavior as they grow and develop • Goals should be congruent with the SWOTs of each cycle
• All organizations, like all living organisms, have a lifecycle and undergo very predictable and repetitive patterns of behavior as they grow and develop • Goals should be congruent with the SWOTs of each cycle
 • At each new stage of development an organization is faced with a unique set of challenges. • How well or poorly management addresses these challenges, and leads a healthy transition from one stage to the next, has a significant impact on the success or failure of their organization.
• At each new stage of development an organization is faced with a unique set of challenges. • How well or poorly management addresses these challenges, and leads a healthy transition from one stage to the next, has a significant impact on the success or failure of their organization.
 Courtship
Courtship
 Courtship • Courtship is the first stage of an organization’s development. At this stage, the company is not yet born. • It exists as a gleam in the Founder(s) eye. The focus of Courtship is necessarily on dreams and possibilities
Courtship • Courtship is the first stage of an organization’s development. At this stage, the company is not yet born. • It exists as a gleam in the Founder(s) eye. The focus of Courtship is necessarily on dreams and possibilities
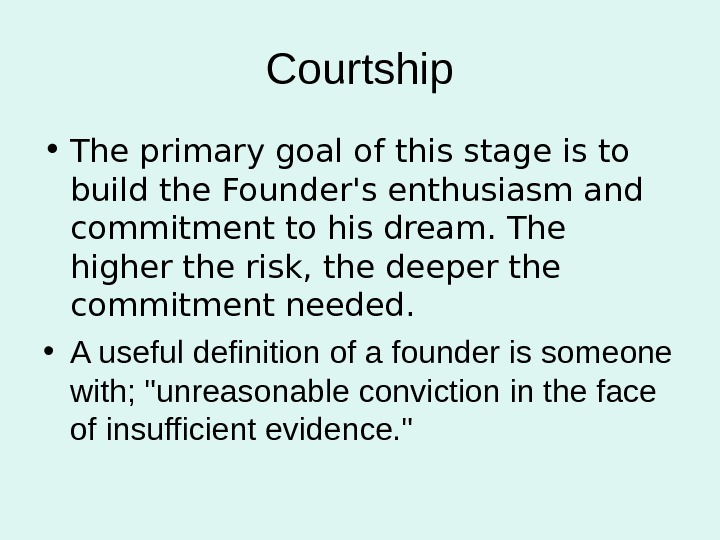
 Courtship • The primary goal of this stage is to build the Founder’s enthusiasm and commitment to his dream. The higher the risk, the deeper the commitment needed. • A useful definition of a founder is someone with; «unreasonable conviction in the face of insufficient evidence. «
Courtship • The primary goal of this stage is to build the Founder’s enthusiasm and commitment to his dream. The higher the risk, the deeper the commitment needed. • A useful definition of a founder is someone with; «unreasonable conviction in the face of insufficient evidence. «
 Problems of Courtship • Over-excitement, possibly unwarranted. • Fuzzy on many details. • Fear, uncertainty and doubts. • Mixed goals. Change the world and make money.
Problems of Courtship • Over-excitement, possibly unwarranted. • Fuzzy on many details. • Fear, uncertainty and doubts. • Mixed goals. Change the world and make money.
 Infancy
Infancy
 Infancy • Infancy begins the moment financial risk has been undertaken and the Founder quits her paying job, signs the loan documents or promises 40% of the company to outside investors • Performance in Infant organizations is inconsistent.
Infancy • Infancy begins the moment financial risk has been undertaken and the Founder quits her paying job, signs the loan documents or promises 40% of the company to outside investors • Performance in Infant organizations is inconsistent.
 Infancy • Like a real baby, Infant organizations need two things to survive: – 1) periodic infusion of milk (operating capital), – 2) the unconditional love of their parents (Founder(s). • Infant companies need more sales, more production, more improvements, more effort and more focus. Everyone in an infant company must be action-oriented
Infancy • Like a real baby, Infant organizations need two things to survive: – 1) periodic infusion of milk (operating capital), – 2) the unconditional love of their parents (Founder(s). • Infant companies need more sales, more production, more improvements, more effort and more focus. Everyone in an infant company must be action-oriented
 GO-GO
GO-GO
 GO-GO • A Go-Go organization is a company that has a successful product or service, rapidly growing sales and strong cash flow. The company is not only surviving, it’s flourishing. • Go-Go companies are like babies that have just learned to walk. They can move quickly and everything looks interesting
GO-GO • A Go-Go organization is a company that has a successful product or service, rapidly growing sales and strong cash flow. The company is not only surviving, it’s flourishing. • Go-Go companies are like babies that have just learned to walk. They can move quickly and everything looks interesting
 GO-GO • Sales Drive the Ship. The Go-Go company is sales driven and has an insatiable appetite for growth. More is better. • It reacts rather than proacts to opportunities. In the rush to close the deal, agreements are sometimes signed before the company really understands if it can do the work.
GO-GO • Sales Drive the Ship. The Go-Go company is sales driven and has an insatiable appetite for growth. More is better. • It reacts rather than proacts to opportunities. In the rush to close the deal, agreements are sometimes signed before the company really understands if it can do the work.
 ADOLESCEN
ADOLESCEN
 ADOLESCENCE • During the Adolescent stage, the company is reborn. This second birth is an emotional time where the company must find a life apart from that provided by its Founder. • This critical transition is much like the rebirth a teenager goes through to establish independence from their parents.
ADOLESCENCE • During the Adolescent stage, the company is reborn. This second birth is an emotional time where the company must find a life apart from that provided by its Founder. • This critical transition is much like the rebirth a teenager goes through to establish independence from their parents.
 ADOLESCENCE • Why is the transition from Go-Go to Adolescence so difficult? There are three principal challenges: 1. Decentralization of authority. 2. Change in leadership from entrepreneurship to professional management. 3. Goal displacement.
ADOLESCENCE • Why is the transition from Go-Go to Adolescence so difficult? There are three principal challenges: 1. Decentralization of authority. 2. Change in leadership from entrepreneurship to professional management. 3. Goal displacement.
 PRIM
PRIM
 PRIME • Prime is the optimal position on the lifecycle, where the organization finally achieves a balance between control and flexibility. • The organization is guided by the vision of its reason for being. There is a clear purpose and people know what they will do, and will not do, «they walk their talk». • Stretch goals are set, aligned and consistently achieved
PRIME • Prime is the optimal position on the lifecycle, where the organization finally achieves a balance between control and flexibility. • The organization is guided by the vision of its reason for being. There is a clear purpose and people know what they will do, and will not do, «they walk their talk». • Stretch goals are set, aligned and consistently achieved
 STABL
STABL
 STABLE • Stable is positioned at the top of the Lifecycle curve, but it is not the place to be. That position is Prime, where organizational vitality is at its maximum. Companies that are in the Stable phase have started to lose their vitality and are aging. When an organization first begins to age, the symptoms won’t show up on its financial reports. In fact, the opposite is true. Stable companies are often cash rich and have strong financial statements
STABLE • Stable is positioned at the top of the Lifecycle curve, but it is not the place to be. That position is Prime, where organizational vitality is at its maximum. Companies that are in the Stable phase have started to lose their vitality and are aging. When an organization first begins to age, the symptoms won’t show up on its financial reports. In fact, the opposite is true. Stable companies are often cash rich and have strong financial statements
 STABLE • The leaders of Stable companies are starting to feel content and somewhat complacent. This attitude has been developing for some time. The company is strong, but it is starting to lose flexibility. • The rocket is slowing down and starting to change direction and head down the lifecycle curve.
STABLE • The leaders of Stable companies are starting to feel content and somewhat complacent. This attitude has been developing for some time. The company is strong, but it is starting to lose flexibility. • The rocket is slowing down and starting to change direction and head down the lifecycle curve.
 DECLIN
DECLIN

