histology.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 18
 Kazakh National Medical University named after S. Asfendiyarov Казахский Национальный Медицинский Университет имени С. Д. Асфендиярова Histological features of kidney in embryogenesis and in infants Group: GM-047 -1 Prepared by Kenzhebaev A. Almaty 2016
Kazakh National Medical University named after S. Asfendiyarov Казахский Национальный Медицинский Университет имени С. Д. Асфендиярова Histological features of kidney in embryogenesis and in infants Group: GM-047 -1 Prepared by Kenzhebaev A. Almaty 2016
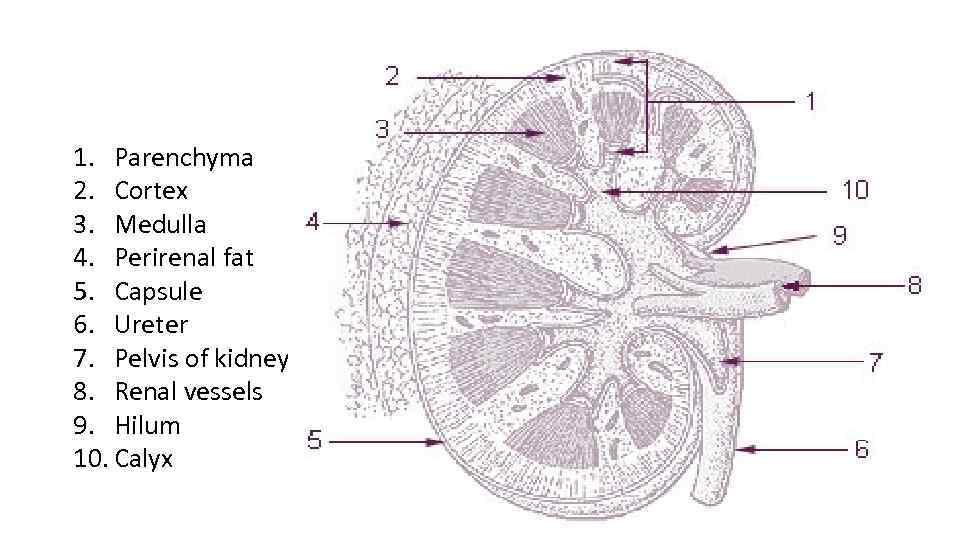 1. Parenchyma 2. Cortex 3. Medulla 4. Perirenal fat 5. Capsule 6. Ureter 7. Pelvis of kidney 8. Renal vessels 9. Hilum 10. Calyx
1. Parenchyma 2. Cortex 3. Medulla 4. Perirenal fat 5. Capsule 6. Ureter 7. Pelvis of kidney 8. Renal vessels 9. Hilum 10. Calyx
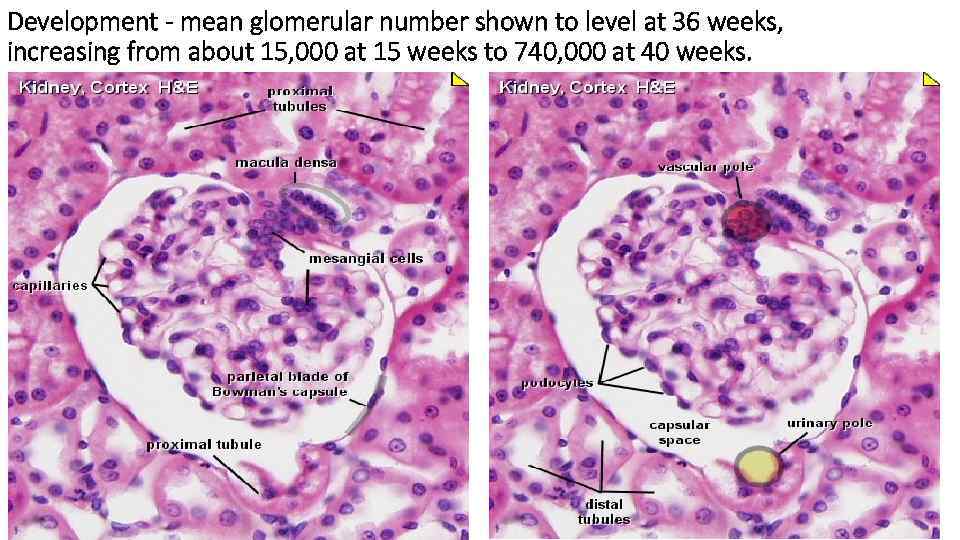 Development - mean glomerular number shown to level at 36 weeks, increasing from about 15, 000 at 15 weeks to 740, 000 at 40 weeks.
Development - mean glomerular number shown to level at 36 weeks, increasing from about 15, 000 at 15 weeks to 740, 000 at 40 weeks.
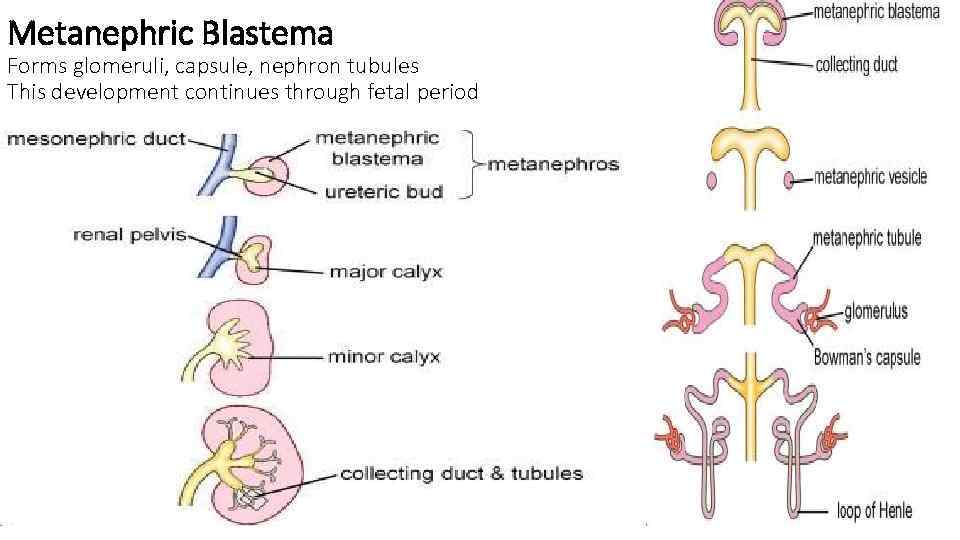 Metanephric Blastema Forms glomeruli, capsule, nephron tubules This development continues through fetal period
Metanephric Blastema Forms glomeruli, capsule, nephron tubules This development continues through fetal period
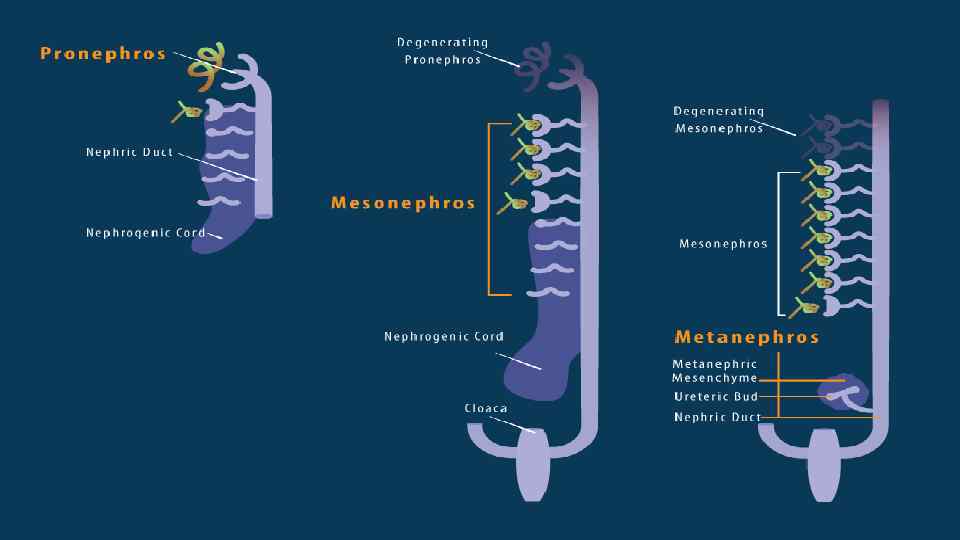
 Nephros Development • Three pairs appearing in sequence within intermediate mesoderm during development. • pronephros • mesonephros • metanephros
Nephros Development • Three pairs appearing in sequence within intermediate mesoderm during development. • pronephros • mesonephros • metanephros
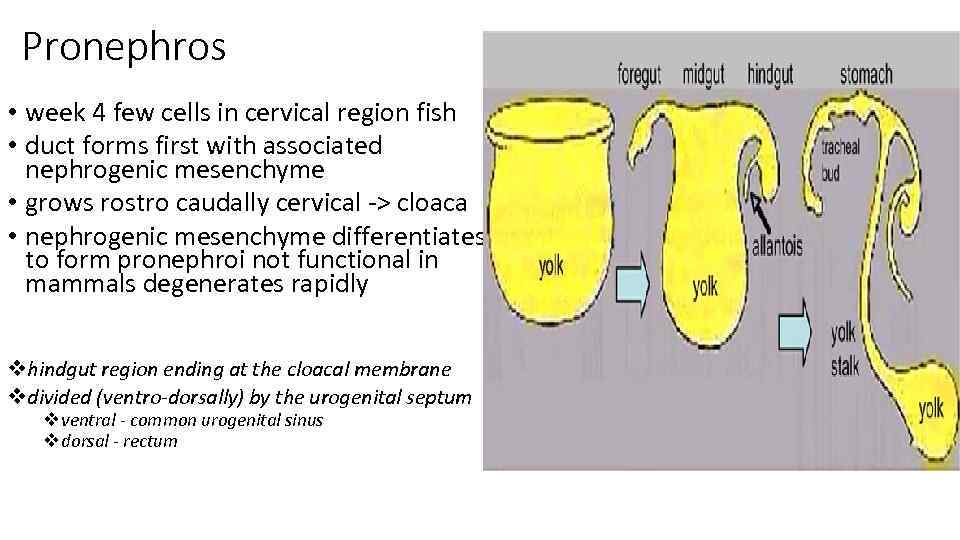 Pronephros • week 4 few cells in cervical region fish • duct forms first with associated nephrogenic mesenchyme • grows rostro caudally cervical -> cloaca • nephrogenic mesenchyme differentiates to form pronephroi not functional in mammals degenerates rapidly vhindgut region ending at the cloacal membrane vdivided (ventro-dorsally) by the urogenital septum v ventral - common urogenital sinus v dorsal - rectum
Pronephros • week 4 few cells in cervical region fish • duct forms first with associated nephrogenic mesenchyme • grows rostro caudally cervical -> cloaca • nephrogenic mesenchyme differentiates to form pronephroi not functional in mammals degenerates rapidly vhindgut region ending at the cloacal membrane vdivided (ventro-dorsally) by the urogenital septum v ventral - common urogenital sinus v dorsal - rectum
 Mesonephros & • caudal to pronephros • forms by induction from pronephros • pronephric duct now becomes mesonephric duct (also called Wolffian Duct) Metanephros • epithelia bud at end of mesonephric duct uteric bud and associated metanephric mesenchyme • Uteric Bud • induced by metanephric mesenchyme to differentiate • forms collecting tubules, renal pelvis, ureter • metanephric mesenchyme induced by uteric to differentiate forms nephron
Mesonephros & • caudal to pronephros • forms by induction from pronephros • pronephric duct now becomes mesonephric duct (also called Wolffian Duct) Metanephros • epithelia bud at end of mesonephric duct uteric bud and associated metanephric mesenchyme • Uteric Bud • induced by metanephric mesenchyme to differentiate • forms collecting tubules, renal pelvis, ureter • metanephric mesenchyme induced by uteric to differentiate forms nephron
 Nephron development • has four identifiable developmental stages: 1. Vesicle (V) stage (13 -19 weeks, second trimester) 2. S-shaped body (S) stage ( 20 -24 weeks, second trimester) 3. Capillary loop (C) stage (25 -29 weeks, third trimester) 4. Maturation (M) stage (infants aged 1 -6 months, neonatal and postnatal) qnephrogenesis only occurs before birth, though nephron maturation continues postnatally. Mean glomerular number increase from about 15, 000 at 15 weeks to 740, 000 at 40 weeks.
Nephron development • has four identifiable developmental stages: 1. Vesicle (V) stage (13 -19 weeks, second trimester) 2. S-shaped body (S) stage ( 20 -24 weeks, second trimester) 3. Capillary loop (C) stage (25 -29 weeks, third trimester) 4. Maturation (M) stage (infants aged 1 -6 months, neonatal and postnatal) qnephrogenesis only occurs before birth, though nephron maturation continues postnatally. Mean glomerular number increase from about 15, 000 at 15 weeks to 740, 000 at 40 weeks.
 Nephron Development • Disorganised mesenchymal cells become a highly organised epithelial tubule • Condensation - groups of about 100 cells condense tightly together to form a distinct mass • Epithelialisation - condensed cells lose their mesenchymal character and gain epithelial • At end of this period formed a small epithelial cyst complete with a basement membrane, cell-cell junctions and a defined cellular apicobasal polarity.
Nephron Development • Disorganised mesenchymal cells become a highly organised epithelial tubule • Condensation - groups of about 100 cells condense tightly together to form a distinct mass • Epithelialisation - condensed cells lose their mesenchymal character and gain epithelial • At end of this period formed a small epithelial cyst complete with a basement membrane, cell-cell junctions and a defined cellular apicobasal polarity.
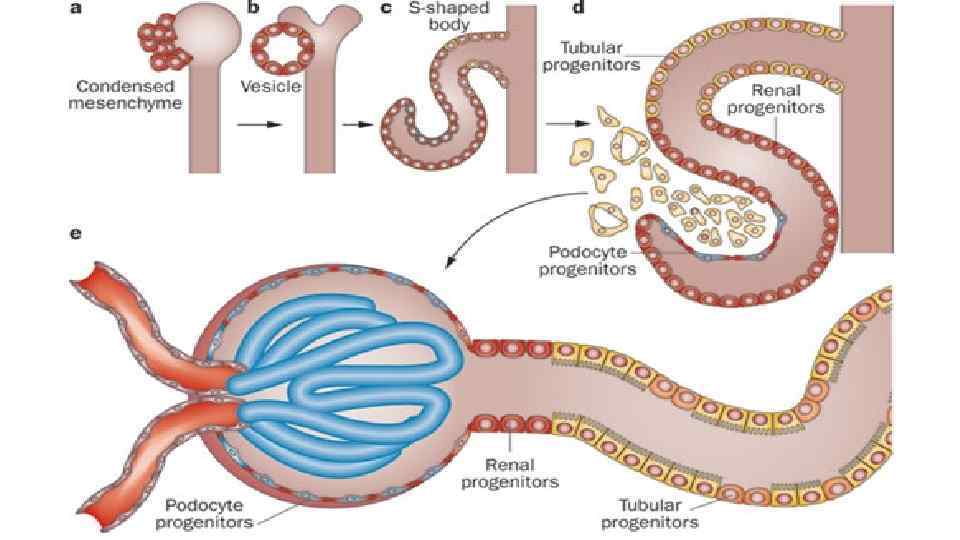
 Early Morphogenesis • cyst invaginates twice to form a comma • then a S-shaped body one invagination site later becomes the glomerular cleft • At about this time blood vessel progenitors invade cleft to begin construction of vascular component of glomerulus • Tubule maturation specialised transporting segments of nephron differentiate complex of convoluted tubules is created
Early Morphogenesis • cyst invaginates twice to form a comma • then a S-shaped body one invagination site later becomes the glomerular cleft • At about this time blood vessel progenitors invade cleft to begin construction of vascular component of glomerulus • Tubule maturation specialised transporting segments of nephron differentiate complex of convoluted tubules is created
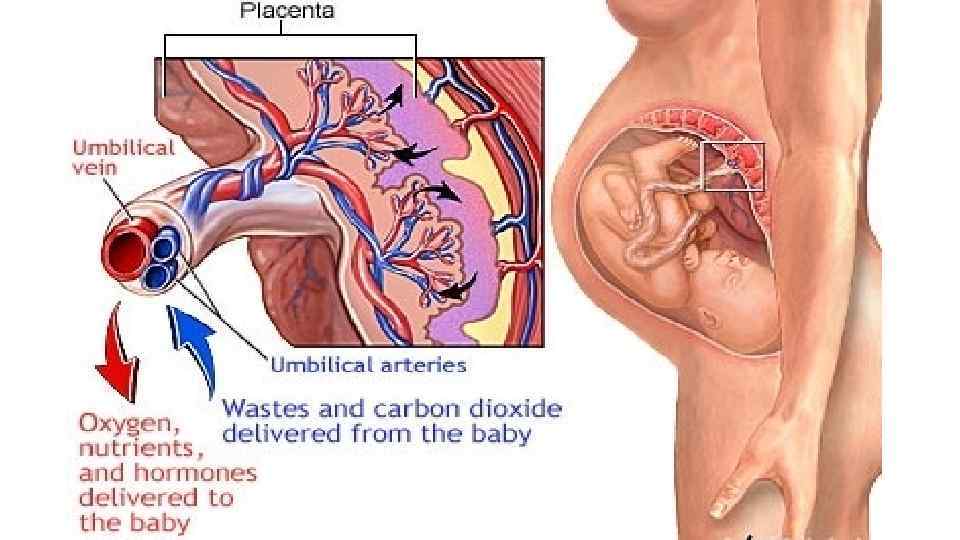
 Features of infants kidneys • Low velocity of Glomerular filtration: • 3 month – 25 ml/min • Adult – 120 -130 ml/min • High excretion of bicarbonates, aminoacids, phosphates with urine • Intensive reabsorption of Na+ in infants • In 1 y. o. increases 3 x • volume of urine: • Infants – 10 -50 ml • 1 y. o. – 50 -100 ml • 2 y. o. – about 200 ml.
Features of infants kidneys • Low velocity of Glomerular filtration: • 3 month – 25 ml/min • Adult – 120 -130 ml/min • High excretion of bicarbonates, aminoacids, phosphates with urine • Intensive reabsorption of Na+ in infants • In 1 y. o. increases 3 x • volume of urine: • Infants – 10 -50 ml • 1 y. o. – 50 -100 ml • 2 y. o. – about 200 ml.
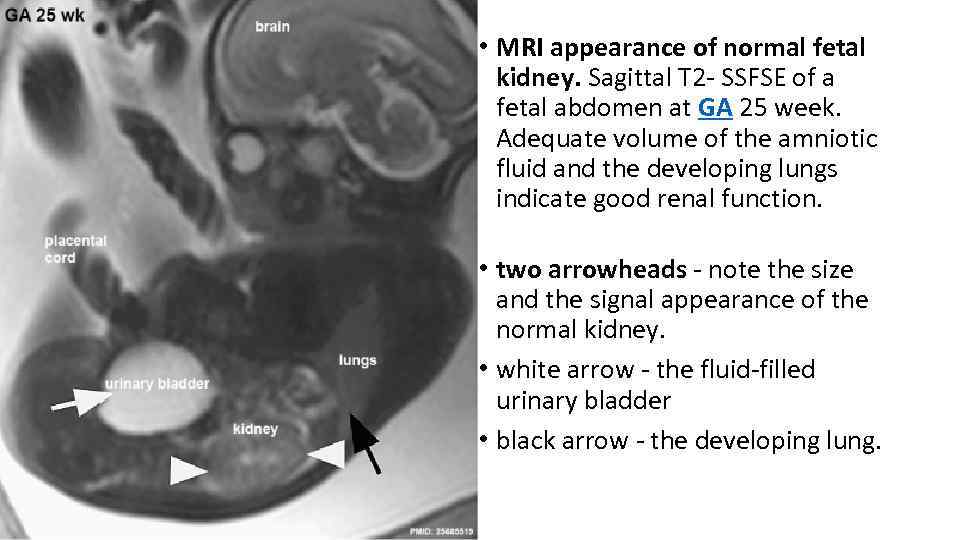 • MRI appearance of normal fetal kidney. Sagittal T 2 - SSFSE of a fetal abdomen at GA 25 week. Adequate volume of the amniotic fluid and the developing lungs indicate good renal function. • two arrowheads - note the size and the signal appearance of the normal kidney. • white arrow - the fluid-filled urinary bladder • black arrow - the developing lung.
• MRI appearance of normal fetal kidney. Sagittal T 2 - SSFSE of a fetal abdomen at GA 25 week. Adequate volume of the amniotic fluid and the developing lungs indicate good renal function. • two arrowheads - note the size and the signal appearance of the normal kidney. • white arrow - the fluid-filled urinary bladder • black arrow - the developing lung.
 References • J R Nyengaard, T F Bendtsen Glomerular number and size in relation to age, kidney weight, and body surface in normal man. Anat. Rec. : 1992, 232(2); 194 -201 Pub. Med 1546799 • M F Schreuder, J Nauta Prenatal programming of nephron number and blood pressure. Kidney Int. : 2007, 72(3); 265 -8 Pub. Med 17495859 • Osman Sulak, Gülnur Ozgüner, Mehmet Ali Malas Size and location of the kidneys during the fetal period. Surg Radiol Anat: 2011, 33(5); 381 -8 Pub. Med 21110022 • Weibin Zhou, Rudrick C Boucher, Frank Bollig, Christoph Englert, Friedhelm Hildebrandt Characterization of mesonephric development and regeneration using transgenic zebrafish. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. : 2010, 299(5); F 1040 -7 Pub. Med 20810610 • Textbooks • The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology (8 th Edition) by Keith L. Moore and T. V. N Persaud - Moore & Persaud Chapter 13 p 303 -346 • Larsen’s Human Embryology by GC. Schoenwolf, SB. Bleyl, PR. Brauer and PH. Francis-West - Chapter 10 p 261 -306 • Before We Are Born (5 th ed. ) Moore and Persaud Chapter 14 p 289 -326 • Essentials of Human Embryology, Larson Chapter 10 p 173 -205 • Human Embryology, Fitzgerald and Fitzgerald Chapter 21 -22 p 134 -152
References • J R Nyengaard, T F Bendtsen Glomerular number and size in relation to age, kidney weight, and body surface in normal man. Anat. Rec. : 1992, 232(2); 194 -201 Pub. Med 1546799 • M F Schreuder, J Nauta Prenatal programming of nephron number and blood pressure. Kidney Int. : 2007, 72(3); 265 -8 Pub. Med 17495859 • Osman Sulak, Gülnur Ozgüner, Mehmet Ali Malas Size and location of the kidneys during the fetal period. Surg Radiol Anat: 2011, 33(5); 381 -8 Pub. Med 21110022 • Weibin Zhou, Rudrick C Boucher, Frank Bollig, Christoph Englert, Friedhelm Hildebrandt Characterization of mesonephric development and regeneration using transgenic zebrafish. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. : 2010, 299(5); F 1040 -7 Pub. Med 20810610 • Textbooks • The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology (8 th Edition) by Keith L. Moore and T. V. N Persaud - Moore & Persaud Chapter 13 p 303 -346 • Larsen’s Human Embryology by GC. Schoenwolf, SB. Bleyl, PR. Brauer and PH. Francis-West - Chapter 10 p 261 -306 • Before We Are Born (5 th ed. ) Moore and Persaud Chapter 14 p 289 -326 • Essentials of Human Embryology, Larson Chapter 10 p 173 -205 • Human Embryology, Fitzgerald and Fitzgerald Chapter 21 -22 p 134 -152
