 Introducing to OSPF and EIGRP routing protocols Prepared by Ezhov Pavel
Introducing to OSPF and EIGRP routing protocols Prepared by Ezhov Pavel
 Link State & Distance Vector Link state OSPF is an example Each router tells the world about its neighbors All information passed is connectivity related Each node in the network constructs a connectivity map of the network Each node keeps identical link-state database from which routing table is derived More complex than distance vector protocols Distance vector EIGRP is an example (but does not behave like a “pure” DV protocol) Each router tells its neighbors about its world Each node shares its routing table with its neighbors Simpler than link state protocols
Link State & Distance Vector Link state OSPF is an example Each router tells the world about its neighbors All information passed is connectivity related Each node in the network constructs a connectivity map of the network Each node keeps identical link-state database from which routing table is derived More complex than distance vector protocols Distance vector EIGRP is an example (but does not behave like a “pure” DV protocol) Each router tells its neighbors about its world Each node shares its routing table with its neighbors Simpler than link state protocols
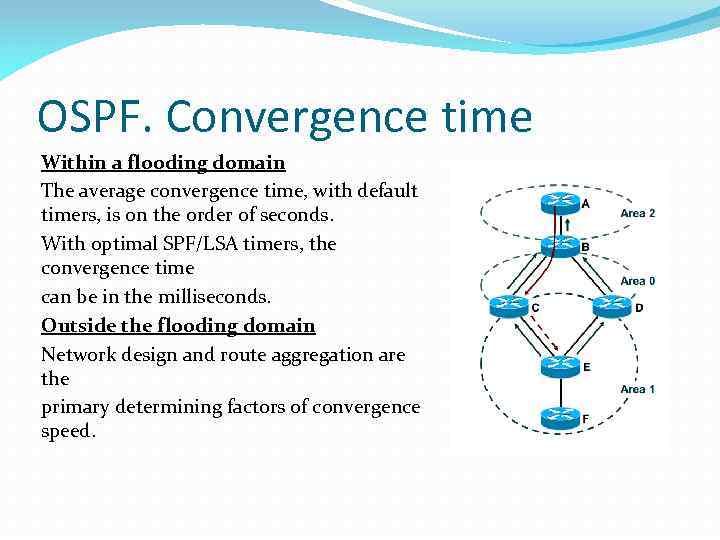 OSPF. Convergence time Within a flooding domain The average convergence time, with default timers, is on the order of seconds. With optimal SPF/LSA timers, the convergence time can be in the milliseconds. Outside the flooding domain Network design and route aggregation are the primary determining factors of convergence speed.
OSPF. Convergence time Within a flooding domain The average convergence time, with default timers, is on the order of seconds. With optimal SPF/LSA timers, the convergence time can be in the milliseconds. Outside the flooding domain Network design and route aggregation are the primary determining factors of convergence speed.
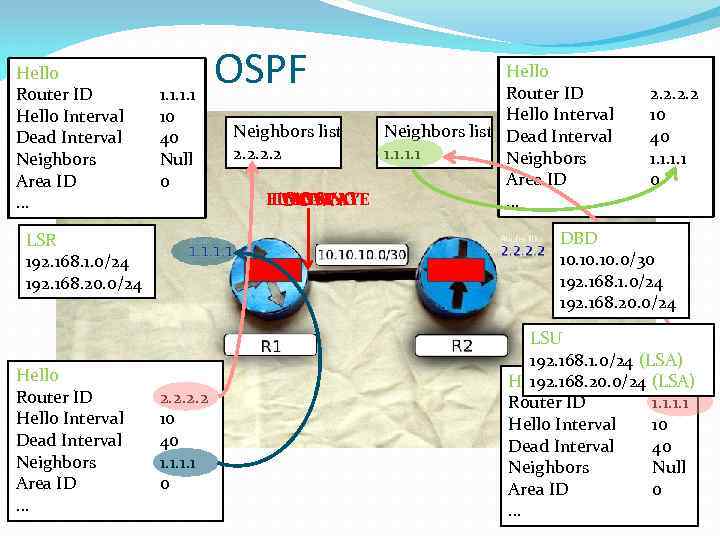 Hello Router ID Hello Interval Dead Interval Neighbors Area ID … 1. 1 10 40 Null 0 Hello Router ID Hello Interval Neighbors list Dead Interval 2. 2 1. 1 Neighbors Area ID FULL STATE TWO-WAY LOADING INIT DOWN … 2. 2 10 40 1. 1 0 DBD 10. 10. 0/30 192. 168. 1. 0/24 192. 168. 20. 0/24 LSR 192. 168. 1. 0/24 192. 168. 20. 0/24 Hello Router ID Hello Interval Dead Interval Neighbors Area ID … OSPF 2. 2 10 40 1. 1 0 LSU 192. 168. 1. 0/24 (LSA) Hello 192. 168. 20. 0/24 (LSA) Router ID 1. 1 Hello Interval 10 Dead Interval 40 Neighbors Null Area ID 0 …
Hello Router ID Hello Interval Dead Interval Neighbors Area ID … 1. 1 10 40 Null 0 Hello Router ID Hello Interval Neighbors list Dead Interval 2. 2 1. 1 Neighbors Area ID FULL STATE TWO-WAY LOADING INIT DOWN … 2. 2 10 40 1. 1 0 DBD 10. 10. 0/30 192. 168. 1. 0/24 192. 168. 20. 0/24 LSR 192. 168. 1. 0/24 192. 168. 20. 0/24 Hello Router ID Hello Interval Dead Interval Neighbors Area ID … OSPF 2. 2 10 40 1. 1 0 LSU 192. 168. 1. 0/24 (LSA) Hello 192. 168. 20. 0/24 (LSA) Router ID 1. 1 Hello Interval 10 Dead Interval 40 Neighbors Null Area ID 0 …
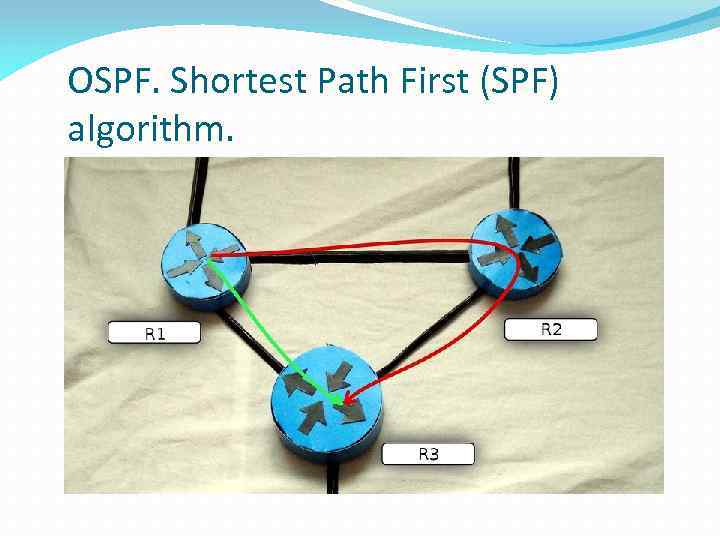 OSPF. Shortest Path First (SPF) algorithm.
OSPF. Shortest Path First (SPF) algorithm.
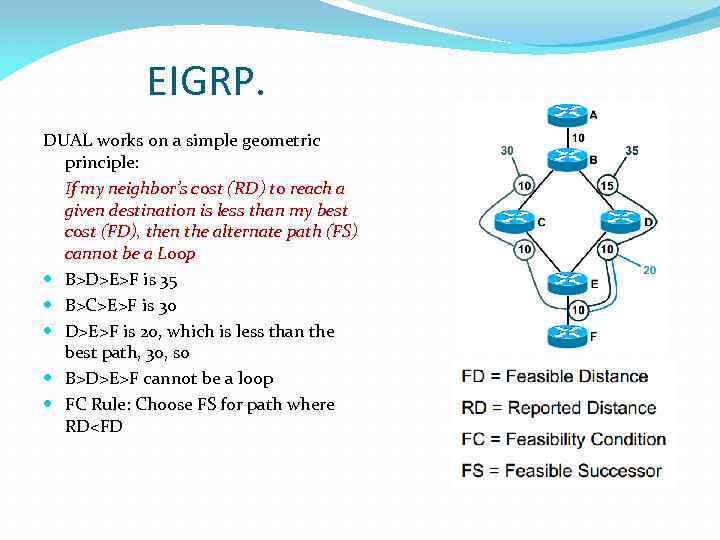 EIGRP. DUAL works on a simple geometric principle: If my neighbor’s cost (RD) to reach a given destination is less than my best cost (FD), then the alternate path (FS) cannot be a Loop B>D>E>F is 35 B>C>E>F is 30 D>E>F is 20, which is less than the best path, 30, so B>D>E>F cannot be a loop FC Rule: Choose FS for path where RD
EIGRP. DUAL works on a simple geometric principle: If my neighbor’s cost (RD) to reach a given destination is less than my best cost (FD), then the alternate path (FS) cannot be a Loop B>D>E>F is 35 B>C>E>F is 30 D>E>F is 20, which is less than the best path, 30, so B>D>E>F cannot be a loop FC Rule: Choose FS for path where RD
 EIGRP. with feasible successors, convergence time is Convergence time. For paths in the milliseconds The existence of feasible successors is dependent on the network design For paths without feasible successors, convergence time is dependent on the number of routers that have to handle and reply to the query Query range is dependent on network design Good design is the key to fast convergence in an EIGRP network
EIGRP. with feasible successors, convergence time is Convergence time. For paths in the milliseconds The existence of feasible successors is dependent on the network design For paths without feasible successors, convergence time is dependent on the number of routers that have to handle and reply to the query Query range is dependent on network design Good design is the key to fast convergence in an EIGRP network
 Summary EIGRP sends hop-by-hop queries only when Feasible Successor cannot be found OSPF regularly syncs LSA database and floods network with topology change EIGRP can be more efficient by minimizing routing information exchanged It’s possible to converge in under one second using either protocol, with the right network design More aggregation tends towards better performance for EIGRP uses metric based on bandwidth and delay OSPF uses interface cost (inversely proportional to bandwidth) EIGRP may provide more flexibility in selecting best path EIGRP forms adjacencies and exchanges routing updates with neighbors OSPF forms adjacencies with DR/BDR OSPF can be more efficient than EIGRP for large meshed networks
Summary EIGRP sends hop-by-hop queries only when Feasible Successor cannot be found OSPF regularly syncs LSA database and floods network with topology change EIGRP can be more efficient by minimizing routing information exchanged It’s possible to converge in under one second using either protocol, with the right network design More aggregation tends towards better performance for EIGRP uses metric based on bandwidth and delay OSPF uses interface cost (inversely proportional to bandwidth) EIGRP may provide more flexibility in selecting best path EIGRP forms adjacencies and exchanges routing updates with neighbors OSPF forms adjacencies with DR/BDR OSPF can be more efficient than EIGRP for large meshed networks
 Thank you for listening to my presentation
Thank you for listening to my presentation