Lect 9 - International Trade.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 12
 International Trade What is International Trade • Exchange of Capital, Goods & Services across international borders • Represents a significant share of gross domestic profit (GDP) for certain countries • International Trade has been in practice since the middle ages (example the silk road connecting mainland china to eastern Europe) • In recent times with the industrialization, globalization & advancement of technology, international trade represents a significant portion of a nation gross domestic product (GDP)
International Trade What is International Trade • Exchange of Capital, Goods & Services across international borders • Represents a significant share of gross domestic profit (GDP) for certain countries • International Trade has been in practice since the middle ages (example the silk road connecting mainland china to eastern Europe) • In recent times with the industrialization, globalization & advancement of technology, international trade represents a significant portion of a nation gross domestic product (GDP)
 International Trade • World Trade Organization (WTO) • Is responsible for global international organization dealing with the rules of trade between nations • Officially commenced on January 1, 1995 under the Marrakech Agreement , replacing the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) • Has 153 members, representing more than 97% of total world trade and 30 observers • WTO's headquarters is at the Centre William Rappard, Geneva Switzerland
International Trade • World Trade Organization (WTO) • Is responsible for global international organization dealing with the rules of trade between nations • Officially commenced on January 1, 1995 under the Marrakech Agreement , replacing the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) • Has 153 members, representing more than 97% of total world trade and 30 observers • WTO's headquarters is at the Centre William Rappard, Geneva Switzerland
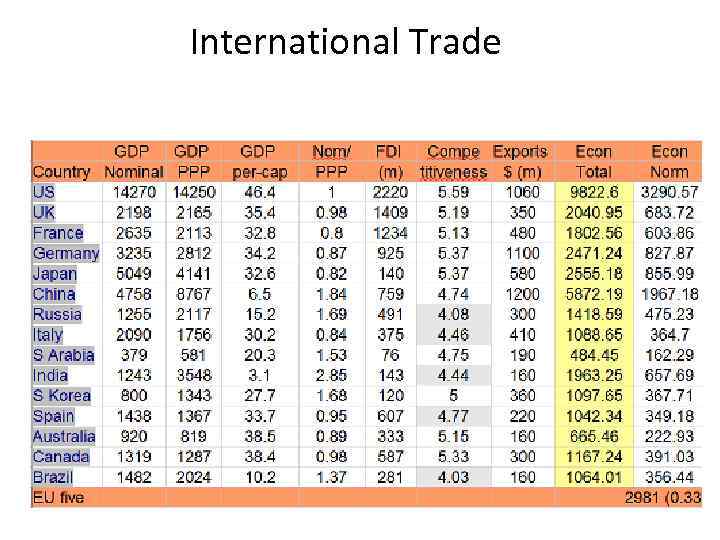 International Trade
International Trade
 International Trade Theories & Models Ricardian model Focuses on comparative advantage and is perhaps the most important concept in international trade theory Ricardian framework predicts that countries will fully specialize instead of producing a broad array of goods The main merit of Ricardian model is that it assumes technology differences between countries. This supports the fact that countries follow their comparative advantage and allows for specialization Example : A country like Singapore with low natural resources will continue to focus on the service based industry as its main contributor to GDP
International Trade Theories & Models Ricardian model Focuses on comparative advantage and is perhaps the most important concept in international trade theory Ricardian framework predicts that countries will fully specialize instead of producing a broad array of goods The main merit of Ricardian model is that it assumes technology differences between countries. This supports the fact that countries follow their comparative advantage and allows for specialization Example : A country like Singapore with low natural resources will continue to focus on the service based industry as its main contributor to GDP
 International Trade Theories & Models Heckscher-Ohlin model Stresses that countries should produce and export goods that require resources (factors) that are abundant and import goods that require resources in short supply Heckscher-Ohlin model was produced as an alternative to the Ricardian model of basic comparative advantage Example : Country with abundant source of crude oil would export oil & import in manufactured goods even though they could also focus on manufacturing based industry for internal needs/comsumption
International Trade Theories & Models Heckscher-Ohlin model Stresses that countries should produce and export goods that require resources (factors) that are abundant and import goods that require resources in short supply Heckscher-Ohlin model was produced as an alternative to the Ricardian model of basic comparative advantage Example : Country with abundant source of crude oil would export oil & import in manufactured goods even though they could also focus on manufacturing based industry for internal needs/comsumption
 Benefits and Threats of International Trade
Benefits and Threats of International Trade
 Benefits of International trade 1. International trade is opening doors to new entrepreneurial opportunity across the globe. – It provides a country's people with a greater choice of goods and services. 2. International trade is an important engine for job creation in many countries. – U. S. Department of Commerce calculates that for every $1 billion increase in exports, 22, 800 jobs are created in the United States.
Benefits of International trade 1. International trade is opening doors to new entrepreneurial opportunity across the globe. – It provides a country's people with a greater choice of goods and services. 2. International trade is an important engine for job creation in many countries. – U. S. Department of Commerce calculates that for every $1 billion increase in exports, 22, 800 jobs are created in the United States.
 Cont’d 3. Domestic producers produce more efficiently – Due to their international specialization and the pressure that comes from foreign competition, and consumers enjoy a wider variety of domestic and imported goods at lower prices. 4. More exchange of technical know how – An actively trading country benefits from the new technologies that “spill over” to it from its trading partners, such as through the knowledge embedded in imported production equipments.
Cont’d 3. Domestic producers produce more efficiently – Due to their international specialization and the pressure that comes from foreign competition, and consumers enjoy a wider variety of domestic and imported goods at lower prices. 4. More exchange of technical know how – An actively trading country benefits from the new technologies that “spill over” to it from its trading partners, such as through the knowledge embedded in imported production equipments.
 Cont’d 5. Increases a Business’ sales and profits – Larger platform to offer their goods and services; – Provides firms of all sizes a larger market in which to take full advantage of the rewards of economies of scale; 6. Rapid economic growth – Example: China’s economy grew at an average rate of 10% per year during the period 1990 -2004, the highest growth rate in the world. the resulting increase in business activity drastically reduced poverty
Cont’d 5. Increases a Business’ sales and profits – Larger platform to offer their goods and services; – Provides firms of all sizes a larger market in which to take full advantage of the rewards of economies of scale; 6. Rapid economic growth – Example: China’s economy grew at an average rate of 10% per year during the period 1990 -2004, the highest growth rate in the world. the resulting increase in business activity drastically reduced poverty
 Threats poses by International trade 1. Local industries may be overshadowed by their international competitors – Certain domestic players can be outperformed by financially stronger multi nationals and forced to close down or get merged. 2. Exhaustion of Natural Resources – It means exhaust all a country’s natural resource in due course of time. It encourages an underdeveloped country to export its all raw material very early.
Threats poses by International trade 1. Local industries may be overshadowed by their international competitors – Certain domestic players can be outperformed by financially stronger multi nationals and forced to close down or get merged. 2. Exhaustion of Natural Resources – It means exhaust all a country’s natural resource in due course of time. It encourages an underdeveloped country to export its all raw material very early.
 Cont’d 3. Ideological differences may emerge between nations – Procedures in trade practices. 2. Rich countries may influence political matters in other countries and gain control over weaker nations.
Cont’d 3. Ideological differences may emerge between nations – Procedures in trade practices. 2. Rich countries may influence political matters in other countries and gain control over weaker nations.
 Risks in International trade Risks can be divided into the following: - • Economic- Risk of concession in economic Risk control , Risk of non-acceptance ; • Political- Risk of non- renewal of import and exports licenses , Risks due to war; • Commercial- A buyer's failure pertaining to payment due to financial limitations ; • Other risks- Cultural differences and language barriers.
Risks in International trade Risks can be divided into the following: - • Economic- Risk of concession in economic Risk control , Risk of non-acceptance ; • Political- Risk of non- renewal of import and exports licenses , Risks due to war; • Commercial- A buyer's failure pertaining to payment due to financial limitations ; • Other risks- Cultural differences and language barriers.


