 Human Immune system (HIS)
Human Immune system (HIS)
 Immunology • Immunology is the study of the strategies and mechanisms that the body uses to rid itself of foreign substances
Immunology • Immunology is the study of the strategies and mechanisms that the body uses to rid itself of foreign substances
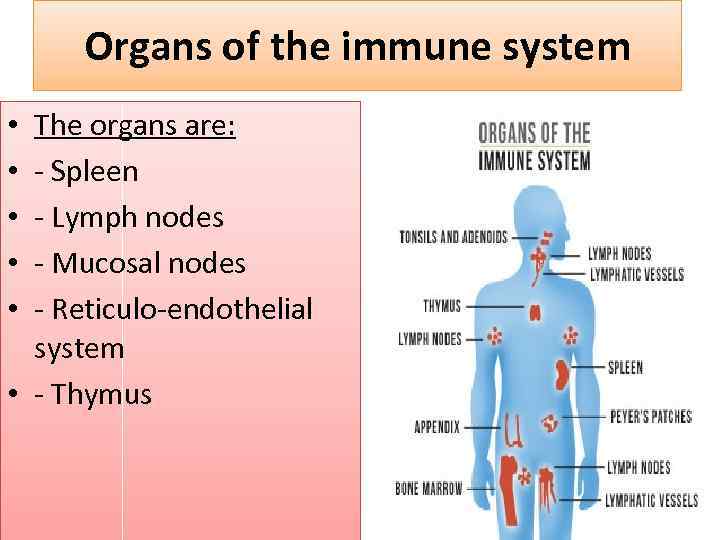 Organs of the immune system The organs are: - Spleen - Lymph nodes - Mucosal nodes - Reticulo-endothelial system • - Thymus • • •
Organs of the immune system The organs are: - Spleen - Lymph nodes - Mucosal nodes - Reticulo-endothelial system • - Thymus • • •
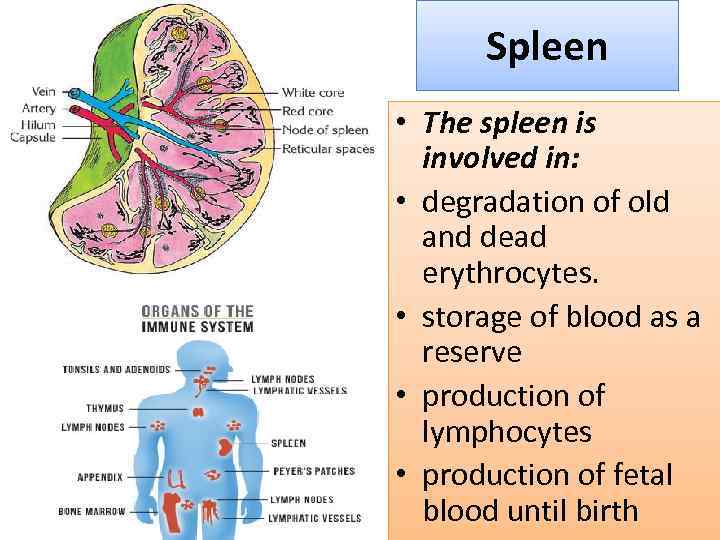 Spleen • The spleen is involved in: • degradation of old and dead erythrocytes. • storage of blood as a reserve • production of lymphocytes • production of fetal blood until birth
Spleen • The spleen is involved in: • degradation of old and dead erythrocytes. • storage of blood as a reserve • production of lymphocytes • production of fetal blood until birth
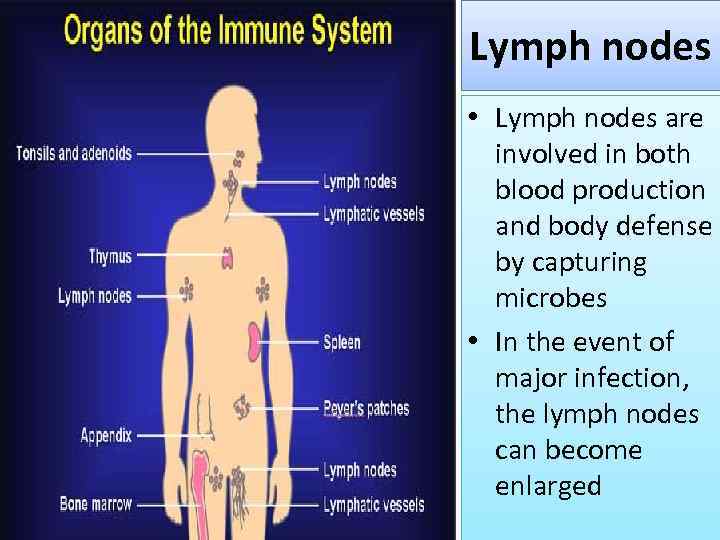 Lymph nodes • Lymph nodes are involved in both blood production and body defense by capturing microbes • In the event of major infection, the lymph nodes can become enlarged
Lymph nodes • Lymph nodes are involved in both blood production and body defense by capturing microbes • In the event of major infection, the lymph nodes can become enlarged
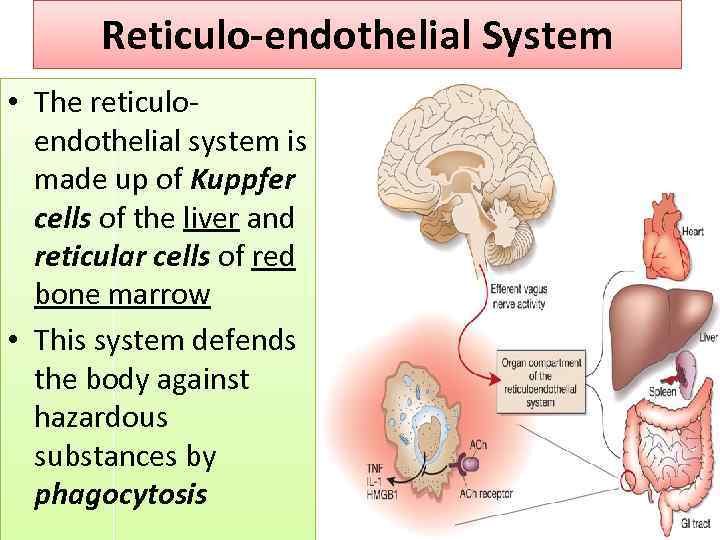 Reticulo-endothelial System • The reticuloendothelial system is made up of Kuppfer cells of the liver and reticular cells of red bone marrow • This system defends the body against hazardous substances by phagocytosis
Reticulo-endothelial System • The reticuloendothelial system is made up of Kuppfer cells of the liver and reticular cells of red bone marrow • This system defends the body against hazardous substances by phagocytosis
 Thymus • Defends the body against infection by producing lymphocytes
Thymus • Defends the body against infection by producing lymphocytes
 Immunity • Immunity is the recognition and removal of molecules foreign to the body
Immunity • Immunity is the recognition and removal of molecules foreign to the body
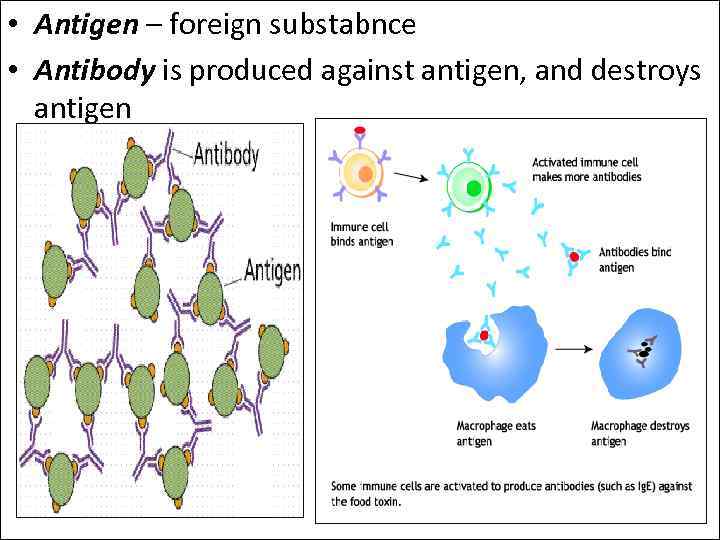 • Antigen – foreign substabnce • Antibody is produced against antigen, and destroys antigen
• Antigen – foreign substabnce • Antibody is produced against antigen, and destroys antigen
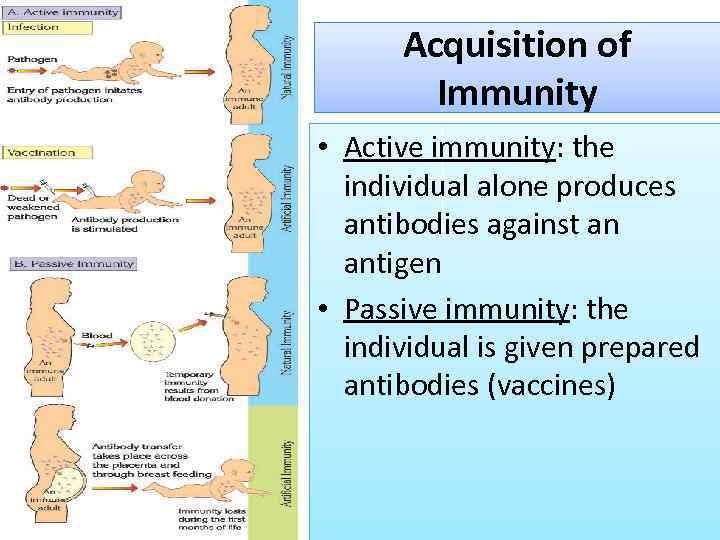 Acquisition of Immunity • Active immunity: the individual alone produces antibodies against an antigen • Passive immunity: the individual is given prepared antibodies (vaccines)
Acquisition of Immunity • Active immunity: the individual alone produces antibodies against an antigen • Passive immunity: the individual is given prepared antibodies (vaccines)
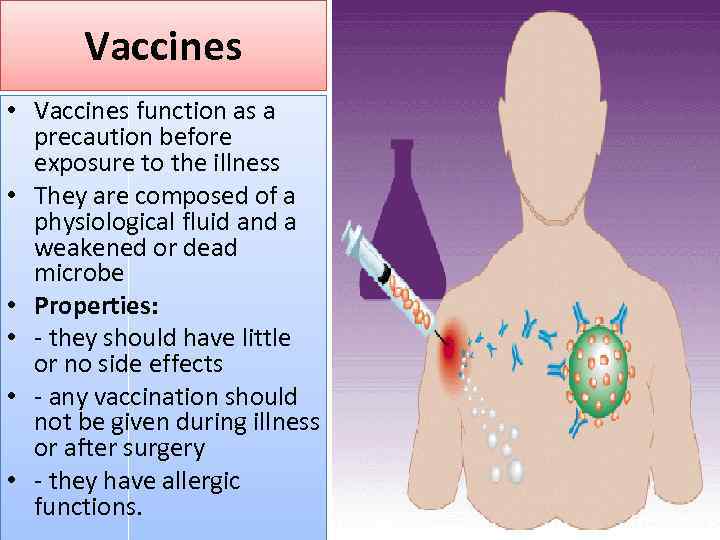 Vaccines • Vaccines function as a precaution before exposure to the illness • They are composed of a physiological fluid and a weakened or dead microbe • Properties: • - they should have little or no side effects • - any vaccination should not be given during illness or after surgery • - they have allergic functions.
Vaccines • Vaccines function as a precaution before exposure to the illness • They are composed of a physiological fluid and a weakened or dead microbe • Properties: • - they should have little or no side effects • - any vaccination should not be given during illness or after surgery • - they have allergic functions.
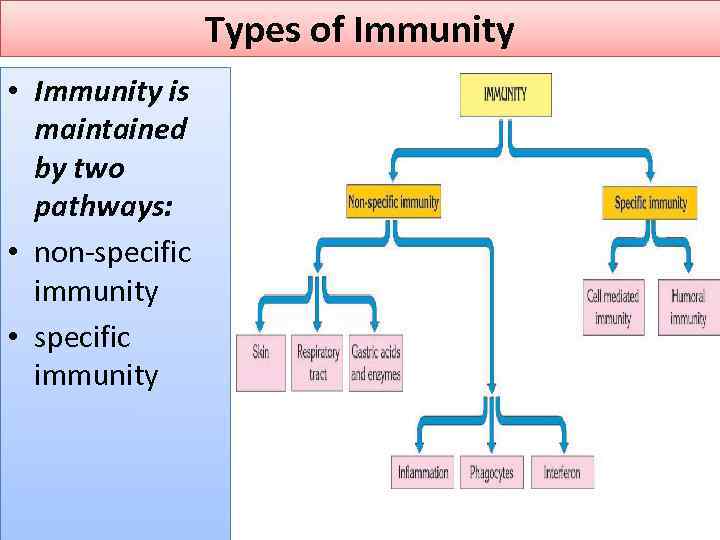 Types of Immunity • Immunity is maintained by two pathways: • non-specific immunity • specific immunity
Types of Immunity • Immunity is maintained by two pathways: • non-specific immunity • specific immunity
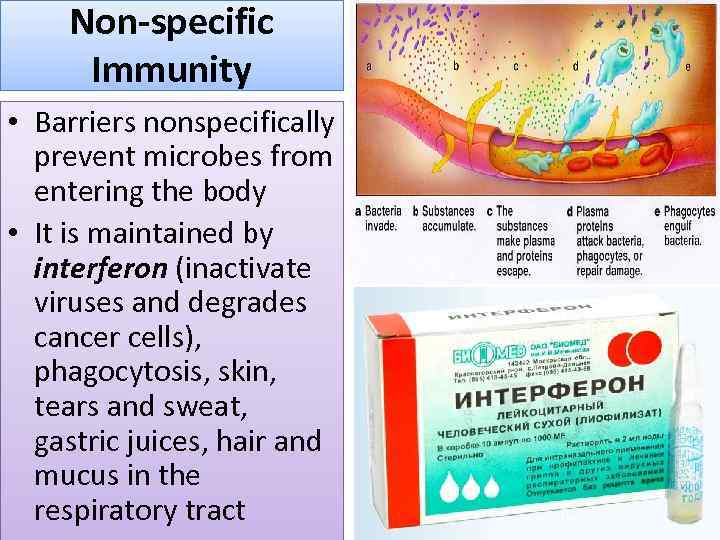 Non-specific Immunity • Barriers nonspecifically prevent microbes from entering the body • It is maintained by interferon (inactivate viruses and degrades cancer cells), phagocytosis, skin, tears and sweat, gastric juices, hair and mucus in the respiratory tract
Non-specific Immunity • Barriers nonspecifically prevent microbes from entering the body • It is maintained by interferon (inactivate viruses and degrades cancer cells), phagocytosis, skin, tears and sweat, gastric juices, hair and mucus in the respiratory tract
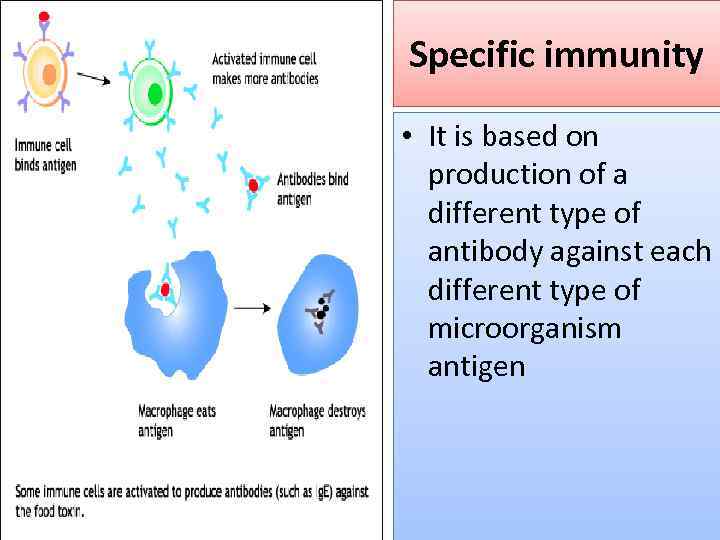 Specific immunity • It is based on production of a different type of antibody against each different type of microorganism antigen
Specific immunity • It is based on production of a different type of antibody against each different type of microorganism antigen
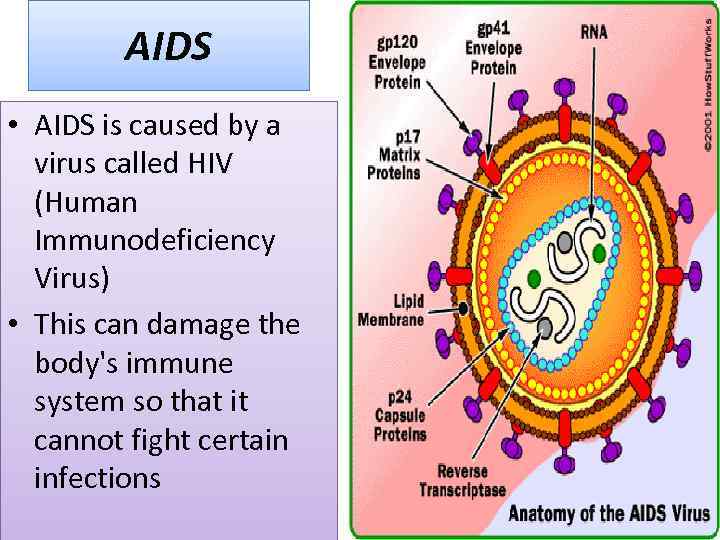 AIDS • AIDS is caused by a virus called HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) • This can damage the body's immune system so that it cannot fight certain infections
AIDS • AIDS is caused by a virus called HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) • This can damage the body's immune system so that it cannot fight certain infections