 Hepatitis C Execute: Kiyamov A. Spilnik T.
Hepatitis C Execute: Kiyamov A. Spilnik T.
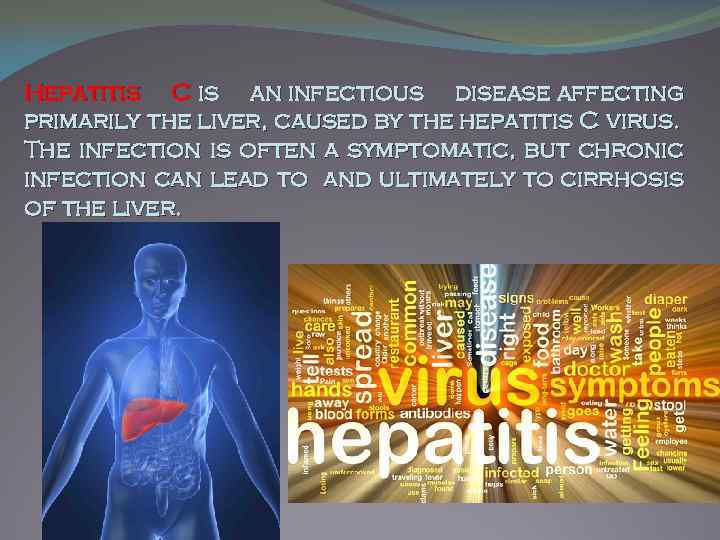 Hepatitis C is an infectious disease affecting primarily the liver, caused by the hepatitis C virus. The infection is often a symptomatic, but chronic infection can lead to and ultimately to cirrhosis of the liver.
Hepatitis C is an infectious disease affecting primarily the liver, caused by the hepatitis C virus. The infection is often a symptomatic, but chronic infection can lead to and ultimately to cirrhosis of the liver.
 Hepatitis is spread by blood-to-blood contact. It associated with intravenous drug use, bad sterilized medical equipment. Around 130– 170 million people in world are infected with hepatitis C. No vaccine against hepatitis C is currently.
Hepatitis is spread by blood-to-blood contact. It associated with intravenous drug use, bad sterilized medical equipment. Around 130– 170 million people in world are infected with hepatitis C. No vaccine against hepatitis C is currently.
 Signs and symptoms Acute infection Hepatitis C infection causes acute symptoms in 15% of cases. Symptoms are generally mild and vague, including a decreased appetite, fatigue, nausea, muscle or joint pains, and weight loss.
Signs and symptoms Acute infection Hepatitis C infection causes acute symptoms in 15% of cases. Symptoms are generally mild and vague, including a decreased appetite, fatigue, nausea, muscle or joint pains, and weight loss.
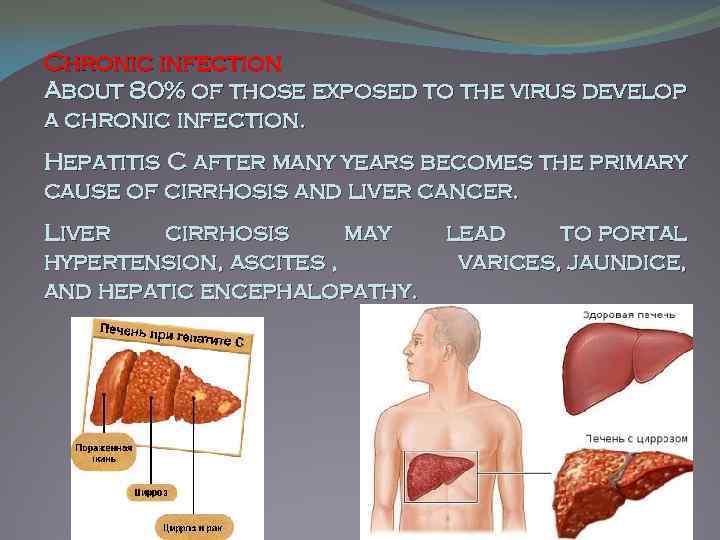 Chronic infection About 80% of those exposed to the virus develop a chronic infection. Hepatitis C after many years becomes the primary cause of cirrhosis and liver cancer. Liver cirrhosis may hypertension, ascites , and hepatic encephalopathy. lead to portal varices, jaundice,
Chronic infection About 80% of those exposed to the virus develop a chronic infection. Hepatitis C after many years becomes the primary cause of cirrhosis and liver cancer. Liver cirrhosis may hypertension, ascites , and hepatic encephalopathy. lead to portal varices, jaundice,
 Transmission The primary methods of transmission in the developed world is intravenous drug use, while in the developing world the main methods are blood transfusions and unsafe medical procedures. The cause of transmission remains unknown in 20% of cases.
Transmission The primary methods of transmission in the developed world is intravenous drug use, while in the developing world the main methods are blood transfusions and unsafe medical procedures. The cause of transmission remains unknown in 20% of cases.
 Intravenous drug use Prevalences of hepatitis C in the intravenous drug user population of between 60% and 80%.
Intravenous drug use Prevalences of hepatitis C in the intravenous drug user population of between 60% and 80%.
 Healthcare exposure Blood transfusion, transfusion of blood products, or organ transplantation without HCV screening, reuse of needles and syringes, multiple-use medication vials, infusion bags, and bad sterilized surgical equipment carry significant risks of infection.
Healthcare exposure Blood transfusion, transfusion of blood products, or organ transplantation without HCV screening, reuse of needles and syringes, multiple-use medication vials, infusion bags, and bad sterilized surgical equipment carry significant risks of infection.
 Body piercings Tattooing or piercings is associated with increased risk of hepatitis C. This can be due to improperly sterilized equipment or contamination of the dyes.
Body piercings Tattooing or piercings is associated with increased risk of hepatitis C. This can be due to improperly sterilized equipment or contamination of the dyes.
 Personal care items such as razors, toothbrushes, and manicuring or pedicuring things can be contaminated with blood. Hepatits is not spread through casual contact, such as hugging, kissing ang e. g.
Personal care items such as razors, toothbrushes, and manicuring or pedicuring things can be contaminated with blood. Hepatits is not spread through casual contact, such as hugging, kissing ang e. g.
 Vertical transmission of hepatitis C from an infected mother to her child occurs in less than 10% of pregnancies. There are no measures that alter this risk.
Vertical transmission of hepatitis C from an infected mother to her child occurs in less than 10% of pregnancies. There are no measures that alter this risk.
 Diagnosis There a number of diagnostic tests for hepatitis C including Liver biopsies are used to determine the degree of liver damage present There a blood tests that try to determine the degree of hepatic fibrosis.
Diagnosis There a number of diagnostic tests for hepatitis C including Liver biopsies are used to determine the degree of liver damage present There a blood tests that try to determine the degree of hepatic fibrosis.
 Treatment HCV induces chronic infection in 50 – 80% of infected persons. In rare cases, infection can clear without treatment. Those with chronic hepatitis C are advised to avoid alcohol and medications toxic to the liver, and to be vaccinated for hepatitis A and hepatitis B. here about one hundred medications in development for hepatitis C.
Treatment HCV induces chronic infection in 50 – 80% of infected persons. In rare cases, infection can clear without treatment. Those with chronic hepatitis C are advised to avoid alcohol and medications toxic to the liver, and to be vaccinated for hepatitis A and hepatitis B. here about one hundred medications in development for hepatitis C.
 Epidemiology It is estimated that 130– 170 million people, or ~3% of the world's population, are living with chronic hepatitis C. About 3– 4 million people are infected per year, and more than 350, 000 people die yearly from hepatitis C. World Hepatitis Day, held on July 28, is coordinated by the World Hepatitis Alliance.
Epidemiology It is estimated that 130– 170 million people, or ~3% of the world's population, are living with chronic hepatitis C. About 3– 4 million people are infected per year, and more than 350, 000 people die yearly from hepatitis C. World Hepatitis Day, held on July 28, is coordinated by the World Hepatitis Alliance.
 Спасибо за вниман ие!
Спасибо за вниман ие!


