GPI 1 THz = 10 12 Hz


- Размер: 195 Кб
- Количество слайдов: 4
Описание презентации GPI 1 THz = 10 12 Hz по слайдам
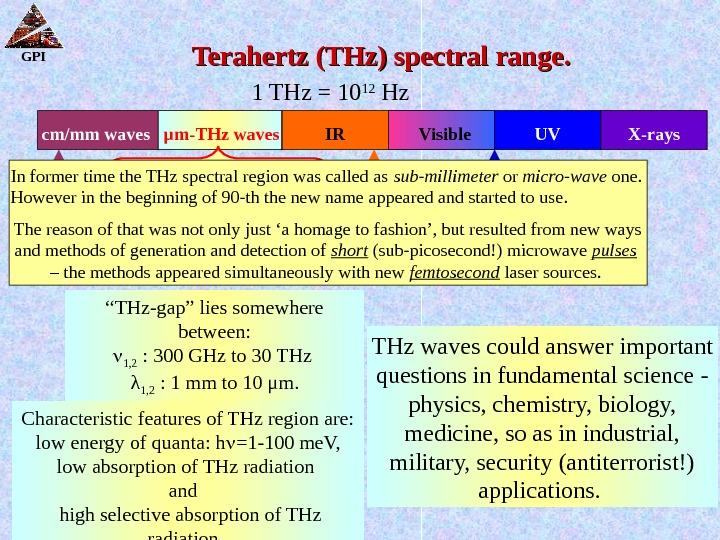
 GPI 1 THz = 10 12 Hz UV X-rays. Visible. IRcm/mm waves µ m-THz waves 1 THz 1010 1212 Hz Hz 300 µµ mm 33. 3 cm -1 -1 4. 13 me. V 1 ps 10 THz 10 13 Hz 30 µ m 333 cm -1 41. 3 me. V 100 fs 0. 1 THz (100 GHz) 10 11 Hz 3 m m 3. 3 cm -1 0. 413 me. V 10 ps 100 THz 10 14 Hz 3 µ m 3333 cm -1 413 me. V 10 fs 1000 THz 10 15 Hz 0. 3 µ m 33333 cm -1 4. 13 e. V 1 fs 0. 01 THz (10 GHz) 10 10 Hz 3 c m 0. 33 cm -1 0. 0413 me. V 100 ps Terahertz (THz) spectral range. “ THz-gap” lies somewhere between: 1, 2 : 300 GHz to 30 THz λ 1, 2 : 1 mm to 10 μ m. 1/ λ 1, 2 : 10 cm -1 to 1000 cm -1 Characteristic features of THz region are: low energy of quanta: h =1 -100 me. V, low absorption of THz radiation and high selective absorption of THz radiation. THz waves could answer important questions in fundamental science — physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, so as in industrial, military, security (antiterrorist!) applications. In former time the THz spectral region was called as sub-millimeter or micro-wave one. However in the beginning of 90 -th the new name appeared and started to use. The reason of that was not only just ‘a homage to fashion’, but resulted from new ways and methods of generation and detection of short (sub-picosecond!) microwave pulses – the methods appeared simultaneously with new femtosecond laser sources.
GPI 1 THz = 10 12 Hz UV X-rays. Visible. IRcm/mm waves µ m-THz waves 1 THz 1010 1212 Hz Hz 300 µµ mm 33. 3 cm -1 -1 4. 13 me. V 1 ps 10 THz 10 13 Hz 30 µ m 333 cm -1 41. 3 me. V 100 fs 0. 1 THz (100 GHz) 10 11 Hz 3 m m 3. 3 cm -1 0. 413 me. V 10 ps 100 THz 10 14 Hz 3 µ m 3333 cm -1 413 me. V 10 fs 1000 THz 10 15 Hz 0. 3 µ m 33333 cm -1 4. 13 e. V 1 fs 0. 01 THz (10 GHz) 10 10 Hz 3 c m 0. 33 cm -1 0. 0413 me. V 100 ps Terahertz (THz) spectral range. “ THz-gap” lies somewhere between: 1, 2 : 300 GHz to 30 THz λ 1, 2 : 1 mm to 10 μ m. 1/ λ 1, 2 : 10 cm -1 to 1000 cm -1 Characteristic features of THz region are: low energy of quanta: h =1 -100 me. V, low absorption of THz radiation and high selective absorption of THz radiation. THz waves could answer important questions in fundamental science — physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, so as in industrial, military, security (antiterrorist!) applications. In former time the THz spectral region was called as sub-millimeter or micro-wave one. However in the beginning of 90 -th the new name appeared and started to use. The reason of that was not only just ‘a homage to fashion’, but resulted from new ways and methods of generation and detection of short (sub-picosecond!) microwave pulses – the methods appeared simultaneously with new femtosecond laser sources.
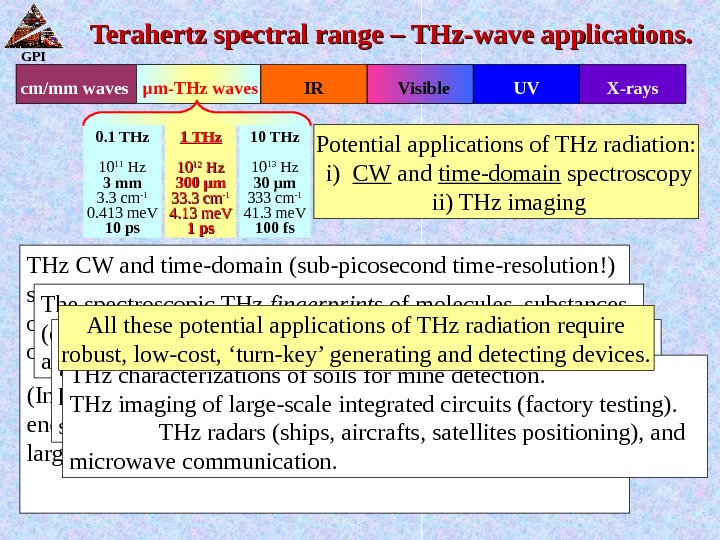
 GPI Terahertz spectral range – THz-wave applications. UV X-rays. Visible. IRcm/mm waves µ m-THz waves 1 THz 1010 1212 Hz Hz 300 µµ mm 33. 3 cm -1 -1 4. 13 me. V 1 ps 10 THz 10 13 Hz 30 µ m 333 cm -1 41. 3 me. V 100 fs 0. 1 THz 10 11 Hz 3 m m 3. 3 cm -1 0. 413 me. V 10 ps THz CW and time-domain (sub-picosecond time-resolution!) spectroscopy techniques apply in studies of solids (dynamics of ‘quasi-particles’, soft modes), liquids (spin-modified ortho- and para- water!), gases, plasmas (dust plasma). (In particular, THz frequencies correspond to relevant energies of molecular rotations and intermolecular modes of large biomolecules in the gas and liquid phase. ) The spectroscopic THz fingerprints of molecules, substances (explosives!) and tissue — allow new approaches in pharmacy and security applications. THz imaging of biomedical tissues and THz computed tomography (due to low absorption of surrounding tissue and high absorption of a tumor along with sub-millimeter space-resolution) THz characterizations of soils for mine detection. THz imaging of large-scale integrated circuits (factory testing). THz radars (ships, aircrafts, satellites positioning), and microwave communication. All these potential applications of THz radiation require robust, low-cost, ‘turn-key’ generating and detecting devices. Potential applications of THz radiation: i) CW and time-domain spectroscopy ii) THz imaging
GPI Terahertz spectral range – THz-wave applications. UV X-rays. Visible. IRcm/mm waves µ m-THz waves 1 THz 1010 1212 Hz Hz 300 µµ mm 33. 3 cm -1 -1 4. 13 me. V 1 ps 10 THz 10 13 Hz 30 µ m 333 cm -1 41. 3 me. V 100 fs 0. 1 THz 10 11 Hz 3 m m 3. 3 cm -1 0. 413 me. V 10 ps THz CW and time-domain (sub-picosecond time-resolution!) spectroscopy techniques apply in studies of solids (dynamics of ‘quasi-particles’, soft modes), liquids (spin-modified ortho- and para- water!), gases, plasmas (dust plasma). (In particular, THz frequencies correspond to relevant energies of molecular rotations and intermolecular modes of large biomolecules in the gas and liquid phase. ) The spectroscopic THz fingerprints of molecules, substances (explosives!) and tissue — allow new approaches in pharmacy and security applications. THz imaging of biomedical tissues and THz computed tomography (due to low absorption of surrounding tissue and high absorption of a tumor along with sub-millimeter space-resolution) THz characterizations of soils for mine detection. THz imaging of large-scale integrated circuits (factory testing). THz radars (ships, aircrafts, satellites positioning), and microwave communication. All these potential applications of THz radiation require robust, low-cost, ‘turn-key’ generating and detecting devices. Potential applications of THz radiation: i) CW and time-domain spectroscopy ii) THz imaging
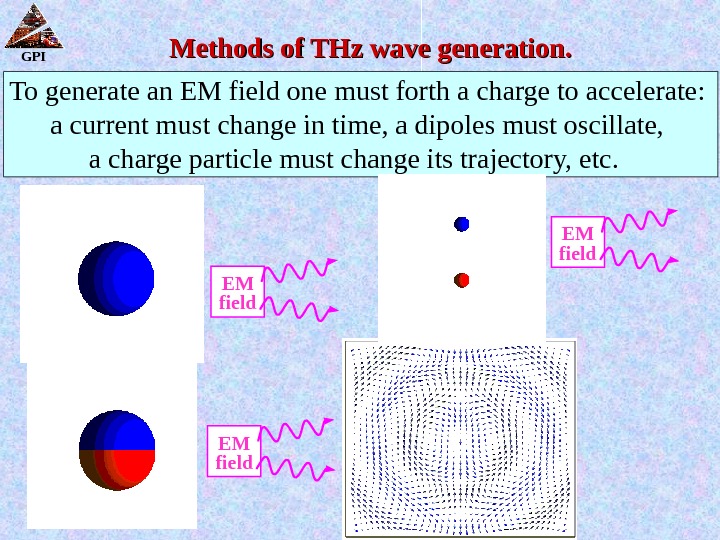
 GPI Methods of THz wave generation. To generate an EM field one must forth a charge to accelerate: a current must change in time, a dipoles must oscillate, a charge particle must change its trajectory, etc. EM field
GPI Methods of THz wave generation. To generate an EM field one must forth a charge to accelerate: a current must change in time, a dipoles must oscillate, a charge particle must change its trajectory, etc. EM field
 GPI Methods of THz wave generation. A variety of methods and techniques for generation and detection of THz radiation were developed. There are two major groups of the generation techniques: i) based on implementation of ‘photoconducting antennas’- Hertzian dipoles, dipole antenna arrays, biased photoconductors, transmission lines with incorporated photoconductors (Auston’s switchers, 1975 !), unbiased photoconductors ( photo-Dember effect), reverse-biased p-i-n structures, etc. ii) based on optical difference frequency mixing in nonlinear optical media (crystals, plasma) — optical rectification (M. Bass 1962 !), THz-wave parametric laser oscillators, electro-optic Cherenkov radiation, etc. Also, THz radiation is generated by: Terahertz quantum cascade lasers; Terahertz FEL (free electron laser) sources; CW THz generators based on backward-wave tubes.
GPI Methods of THz wave generation. A variety of methods and techniques for generation and detection of THz radiation were developed. There are two major groups of the generation techniques: i) based on implementation of ‘photoconducting antennas’- Hertzian dipoles, dipole antenna arrays, biased photoconductors, transmission lines with incorporated photoconductors (Auston’s switchers, 1975 !), unbiased photoconductors ( photo-Dember effect), reverse-biased p-i-n structures, etc. ii) based on optical difference frequency mixing in nonlinear optical media (crystals, plasma) — optical rectification (M. Bass 1962 !), THz-wave parametric laser oscillators, electro-optic Cherenkov radiation, etc. Also, THz radiation is generated by: Terahertz quantum cascade lasers; Terahertz FEL (free electron laser) sources; CW THz generators based on backward-wave tubes.

