Глава 5. Спектроскопия рассеяния ионов низких энергий





Глава 5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 Глава 5. Спектроскопия рассеяния ионов низких энергий 1. Физические принципы построения метода. 2. Аппаратура. 2. 1. Пучок ионов. 2. 2. Требования к вакуумной системе. 2. 3. Анализатор энергий рассеянных частиц. 2. 4. Детектирование сигнала рассеянных ионов: ВЭУ, каналтрон. 3. Примеры анализа.
Глава 5. Спектроскопия рассеяния ионов низких энергий 1. Физические принципы построения метода. 2. Аппаратура. 2. 1. Пучок ионов. 2. 2. Требования к вакуумной системе. 2. 3. Анализатор энергий рассеянных частиц. 2. 4. Детектирование сигнала рассеянных ионов: ВЭУ, каналтрон. 3. Примеры анализа.
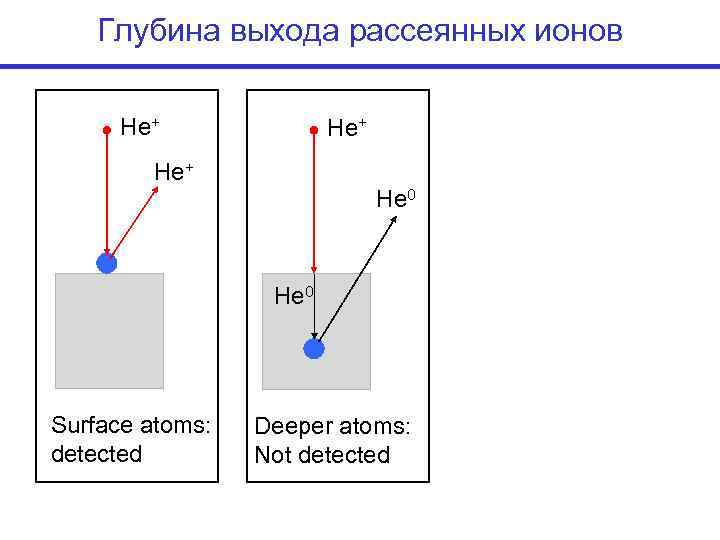
 Глубина выхода рассеянных ионов He+ He 0 Surface atoms: Deeper atoms: detected Not detected
Глубина выхода рассеянных ионов He+ He 0 Surface atoms: Deeper atoms: detected Not detected
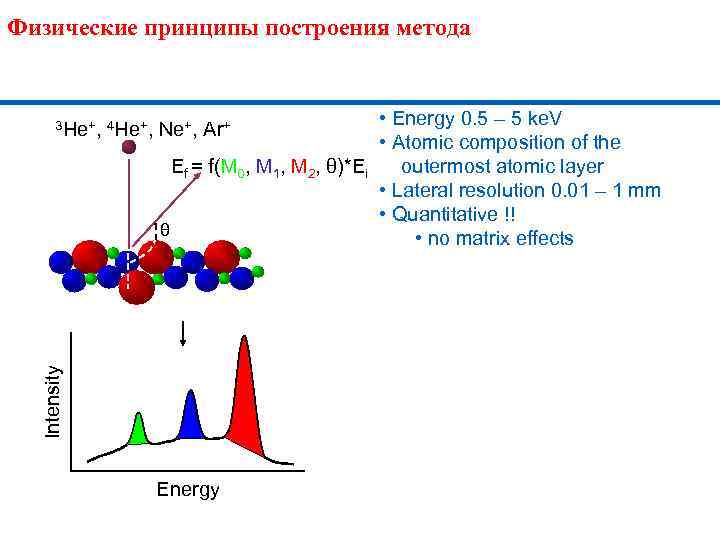
 Физические принципы построения метода 3 He+, 4 He+, • Energy 0. 5 – 5 ke. V Ne+, Ar+ • Atomic composition of the Ef = f(M 0, M 1, M 2, θ)*Ei outermost atomic layer • Lateral resolution 0. 01 – 1 mm • Quantitative !! θ • no matrix effects Intensity Energy
Физические принципы построения метода 3 He+, 4 He+, • Energy 0. 5 – 5 ke. V Ne+, Ar+ • Atomic composition of the Ef = f(M 0, M 1, M 2, θ)*Ei outermost atomic layer • Lateral resolution 0. 01 – 1 mm • Quantitative !! θ • no matrix effects Intensity Energy
 Схема устройства LEIS
Схема устройства LEIS
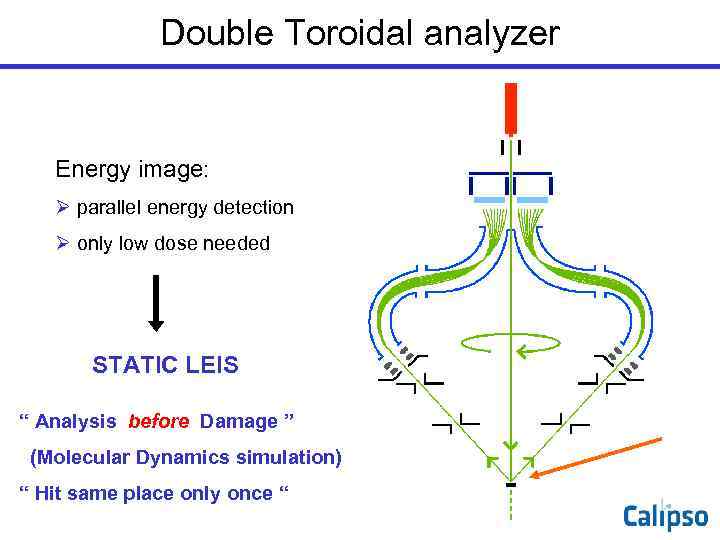
 Double Toroidal analyzer Energy image: Ø parallel energy detection Ø only low dose needed STATIC LEIS “ Analysis before Damage ” (Molecular Dynamics simulation) “ Hit same place only once “
Double Toroidal analyzer Energy image: Ø parallel energy detection Ø only low dose needed STATIC LEIS “ Analysis before Damage ” (Molecular Dynamics simulation) “ Hit same place only once “
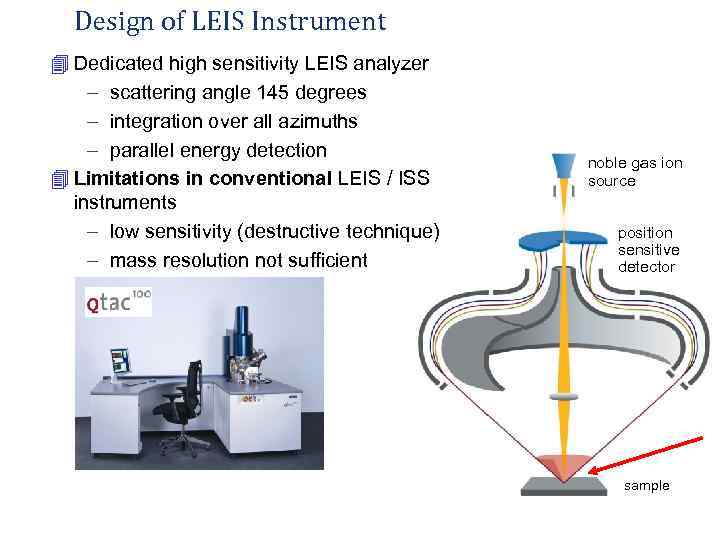
 Design of LEIS Instrument 4 Dedicated high sensitivity LEIS analyzer - scattering angle 145 degrees - integration over all azimuths - parallel energy detection noble gas ion 4 Limitations in conventional LEIS / ISS source instruments - low sensitivity (destructive technique) position sensitive - mass resolution not sufficient detector sample
Design of LEIS Instrument 4 Dedicated high sensitivity LEIS analyzer - scattering angle 145 degrees - integration over all azimuths - parallel energy detection noble gas ion 4 Limitations in conventional LEIS / ISS source instruments - low sensitivity (destructive technique) position sensitive - mass resolution not sufficient detector sample
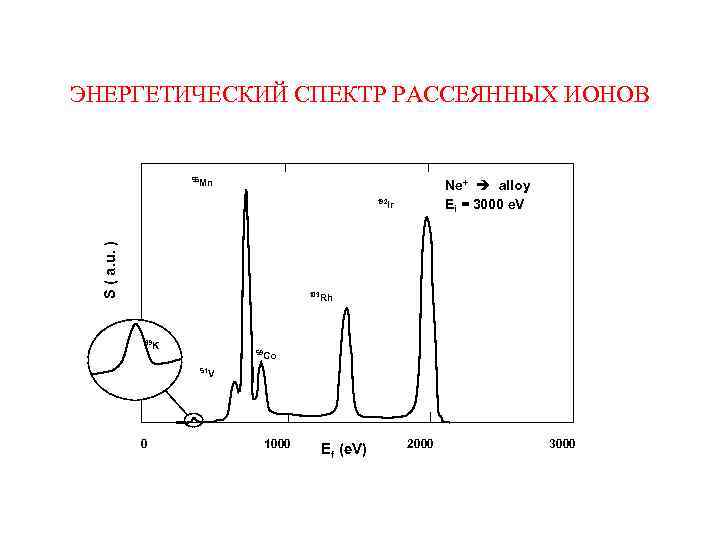
 ЭНЕРГЕТИЧЕСКИЙ СПЕКТР РАССЕЯННЫХ ИОНОВ 55 Mn Ne+ alloy 192 Ir Ei = 3000 e. V Energy spectrum of an alloy S ( a. u. ) 103 Rh 39 K 59 Co 51 V 0 1000 Ef (e. V) 2000 3000
ЭНЕРГЕТИЧЕСКИЙ СПЕКТР РАССЕЯННЫХ ИОНОВ 55 Mn Ne+ alloy 192 Ir Ei = 3000 e. V Energy spectrum of an alloy S ( a. u. ) 103 Rh 39 K 59 Co 51 V 0 1000 Ef (e. V) 2000 3000
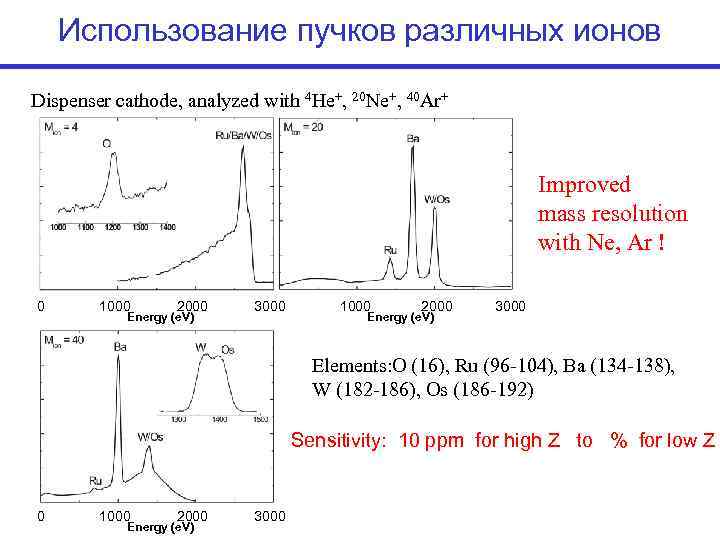
 Использование пучков различных ионов Dispenser cathode, analyzed with 4 He+, 20 Ne+, 40 Ar+ Improved mass resolution with Ne, Ar ! 0 1000 2000 3000 Energy (e. V) Elements: O (16), Ru (96 -104), Ba (134 -138), W (182 -186), Os (186 -192) Sensitivity: 10 ppm for high Z to % for low Z 0 1000 2000 3000 Energy (e. V)
Использование пучков различных ионов Dispenser cathode, analyzed with 4 He+, 20 Ne+, 40 Ar+ Improved mass resolution with Ne, Ar ! 0 1000 2000 3000 Energy (e. V) Elements: O (16), Ru (96 -104), Ba (134 -138), W (182 -186), Os (186 -192) Sensitivity: 10 ppm for high Z to % for low Z 0 1000 2000 3000 Energy (e. V)
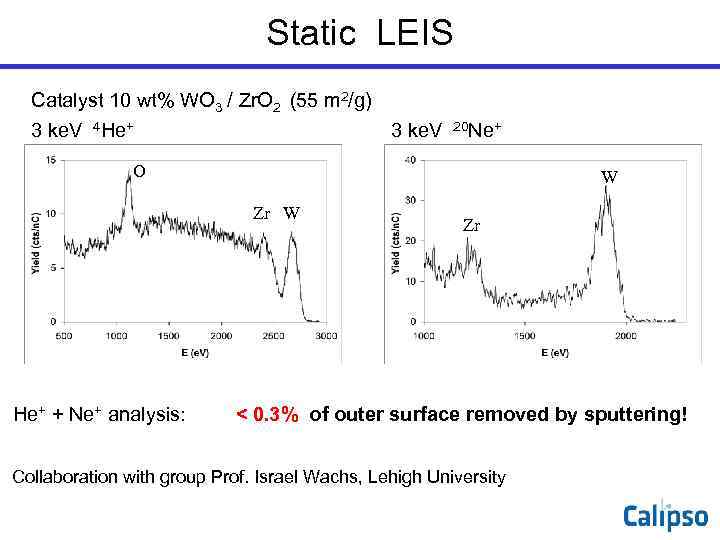
 Static LEIS Catalyst 10 wt% WO 3 / Zr. O 2 (55 m 2/g) 3 ke. V 4 He+ 3 ke. V 20 Ne+ O W Zr He+ + Ne+ analysis: < 0. 3% of outer surface removed by sputtering! Collaboration with group Prof. Israel Wachs, Lehigh University
Static LEIS Catalyst 10 wt% WO 3 / Zr. O 2 (55 m 2/g) 3 ke. V 4 He+ 3 ke. V 20 Ne+ O W Zr He+ + Ne+ analysis: < 0. 3% of outer surface removed by sputtering! Collaboration with group Prof. Israel Wachs, Lehigh University
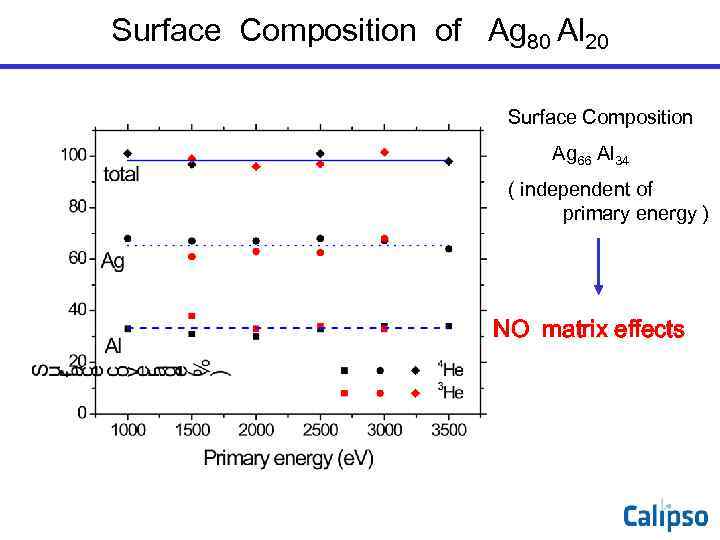
 Surface Composition of Ag 80 Al 20 Surface Composition Ag 66 Al 34 ( independent of primary energy ) NO matrix effects
Surface Composition of Ag 80 Al 20 Surface Composition Ag 66 Al 34 ( independent of primary energy ) NO matrix effects
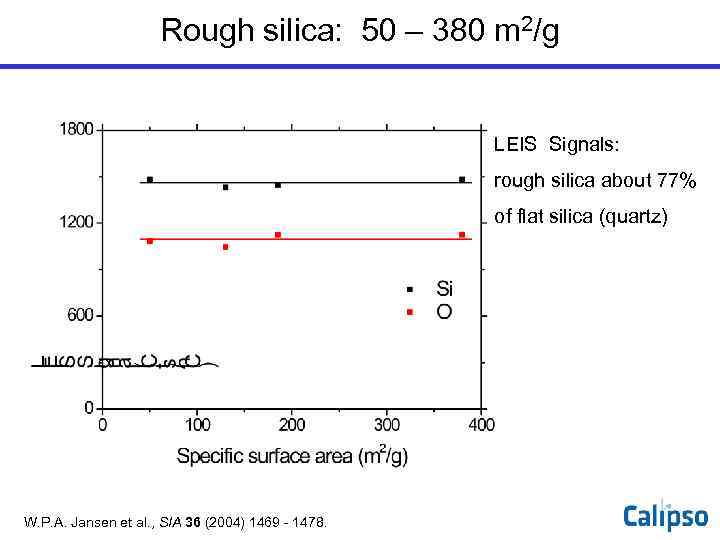
 Rough silica: 50 – 380 m 2/g LEIS Signals: rough silica about 77% of flat silica (quartz) W. P. A. Jansen et al. , SIA 36 (2004) 1469 - 1478.
Rough silica: 50 – 380 m 2/g LEIS Signals: rough silica about 77% of flat silica (quartz) W. P. A. Jansen et al. , SIA 36 (2004) 1469 - 1478.
 3 ke. V 4 He+ → Multi-1
3 ke. V 4 He+ → Multi-1
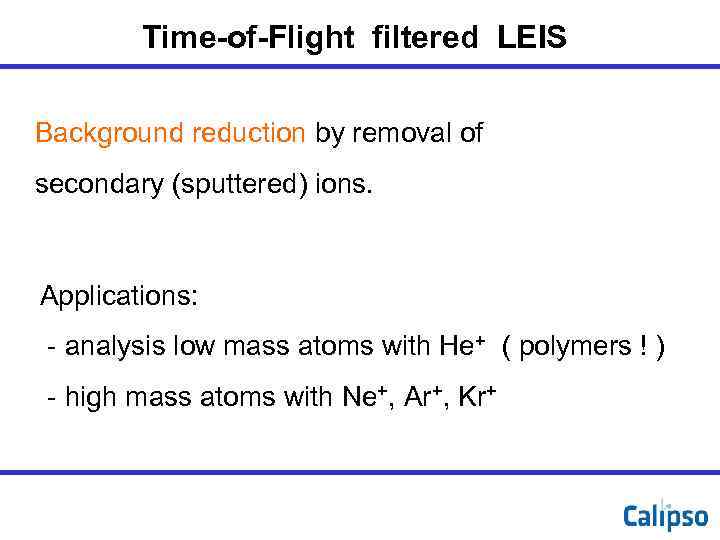
 Time-of-Flight filtered LEIS Background reduction by removal of secondary (sputtered) ions. Applications: - analysis low mass atoms with He+ ( polymers ! ) - high mass atoms with Ne+, Ar+, Kr+
Time-of-Flight filtered LEIS Background reduction by removal of secondary (sputtered) ions. Applications: - analysis low mass atoms with He+ ( polymers ! ) - high mass atoms with Ne+, Ar+, Kr+
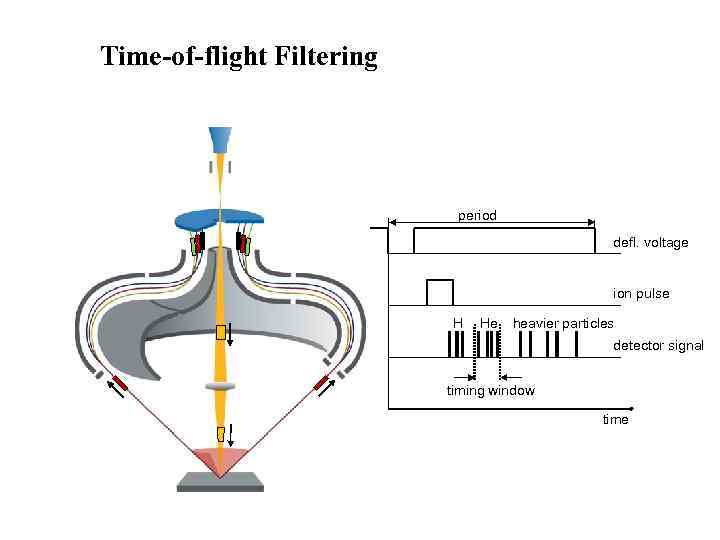
 Time-of-flight Filtering period defl. voltage ion pulse H He heavier particles detector signal timing window time
Time-of-flight Filtering period defl. voltage ion pulse H He heavier particles detector signal timing window time
 5 ke. V 20 Ne+ → Multi-1 LEIS + To. F filter
5 ke. V 20 Ne+ → Multi-1 LEIS + To. F filter
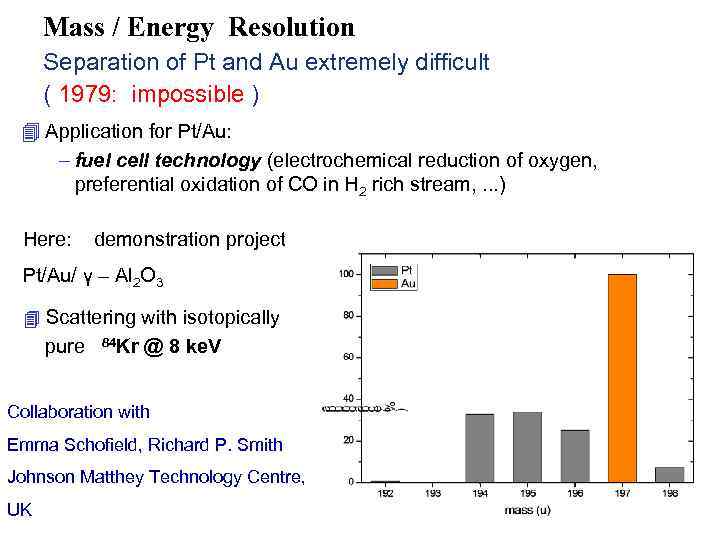
 Mass / Energy Resolution Separation of Pt and Au extremely difficult ( 1979: impossible ) 4 Application for Pt/Au: – fuel cell technology (electrochemical reduction of oxygen, preferential oxidation of CO in H 2 rich stream, . . . ) Here: demonstration project Pt/Au/ γ – Al 2 O 3 4 Scattering with isotopically pure 84 Kr @ 8 ke. V Collaboration with Emma Schofield, Richard P. Smith Johnson Matthey Technology Centre, UK
Mass / Energy Resolution Separation of Pt and Au extremely difficult ( 1979: impossible ) 4 Application for Pt/Au: – fuel cell technology (electrochemical reduction of oxygen, preferential oxidation of CO in H 2 rich stream, . . . ) Here: demonstration project Pt/Au/ γ – Al 2 O 3 4 Scattering with isotopically pure 84 Kr @ 8 ke. V Collaboration with Emma Schofield, Richard P. Smith Johnson Matthey Technology Centre, UK
 Mass / Energy Resolution Separation of Pt and Au possible with 8 ke. V 84 Kr+ Peaks scaled to same height
Mass / Energy Resolution Separation of Pt and Au possible with 8 ke. V 84 Kr+ Peaks scaled to same height
 In – Depth profiling Two possibilities: 1. Static LEIS (analogous to RBS, MEIS, but better depth resolution ! ) 2. Static LEIS + sputter depth profiling
In – Depth profiling Two possibilities: 1. Static LEIS (analogous to RBS, MEIS, but better depth resolution ! ) 2. Static LEIS + sputter depth profiling
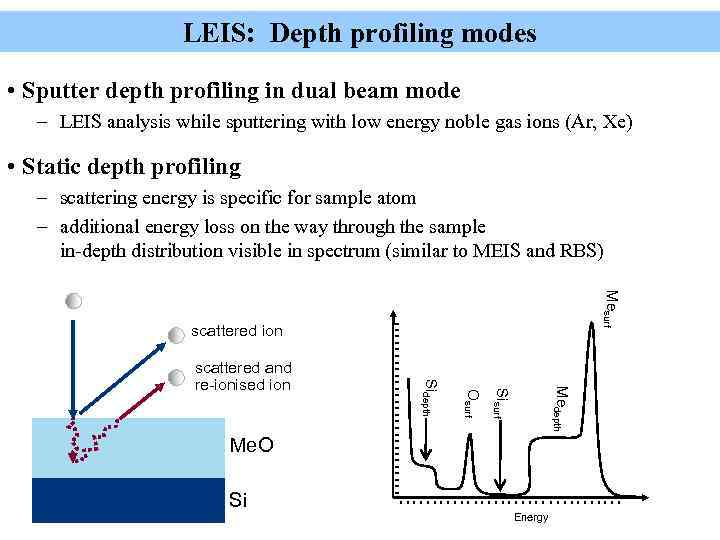
 LEIS: Depth profiling modes • Sputter depth profiling in dual beam mode – LEIS analysis while sputtering with low energy noble gas ions (Ar, Xe) • Static depth profiling – scattering energy is specific for sample atom – additional energy loss on the way through the sample in-depth distribution visible in spectrum (similar to MEIS and RBS) Mesurf scattered ion scattered and re-ionised ion Sidepth Medepth Sisurf Osurf Me. O Si Energy
LEIS: Depth profiling modes • Sputter depth profiling in dual beam mode – LEIS analysis while sputtering with low energy noble gas ions (Ar, Xe) • Static depth profiling – scattering energy is specific for sample atom – additional energy loss on the way through the sample in-depth distribution visible in spectrum (similar to MEIS and RBS) Mesurf scattered ion scattered and re-ionised ion Sidepth Medepth Sisurf Osurf Me. O Si Energy
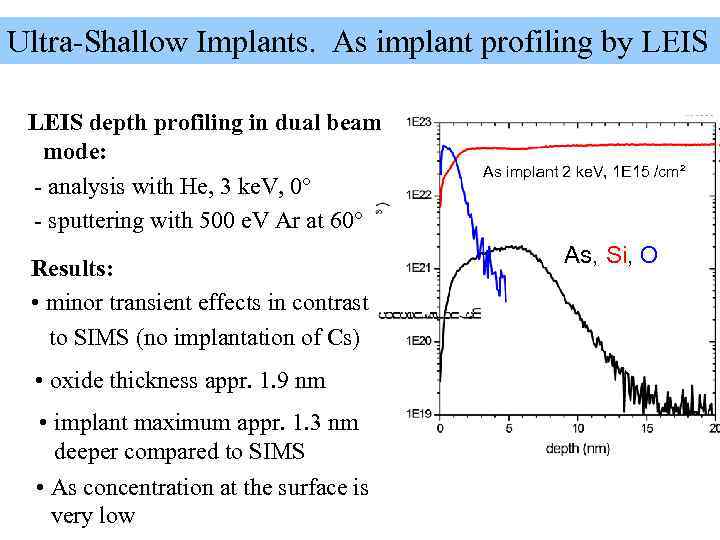
 Ultra-Shallow Implants. As implant profiling by LEIS depth profiling in dual beam mode: As implant 2 ke. V, 1 E 15 /cm² - analysis with He, 3 ke. V, 0° - sputtering with 500 e. V Ar at 60° As, Si, O Results: • minor transient effects in contrast to SIMS (no implantation of Cs) • oxide thickness appr. 1. 9 nm • implant maximum appr. 1. 3 nm deeper compared to SIMS • As concentration at the surface is very low
Ultra-Shallow Implants. As implant profiling by LEIS depth profiling in dual beam mode: As implant 2 ke. V, 1 E 15 /cm² - analysis with He, 3 ke. V, 0° - sputtering with 500 e. V Ar at 60° As, Si, O Results: • minor transient effects in contrast to SIMS (no implantation of Cs) • oxide thickness appr. 1. 9 nm • implant maximum appr. 1. 3 nm deeper compared to SIMS • As concentration at the surface is very low
