7cfafeb3ce683232488a27a5909f4ed0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 g < Vo. IP / Internet Telephony Peter Gradwell > FBCS www. gradwell. com 01225 800 26 Cheltenham St, Bath, BA 2 3 EX 1
g < Vo. IP / Internet Telephony Peter Gradwell > FBCS www. gradwell. com 01225 800 26 Cheltenham St, Bath, BA 2 3 EX 1
 Gradwell dot com Ltd g < > Founded 1998 whilst an Undergrad Now. . . 30 Staff in Bath rd largest UK Vo. IP Provider for SMEs 3 30, 000 lines on a Vo. IP platform gives us some interesting lessons to explore 2
Gradwell dot com Ltd g < > Founded 1998 whilst an Undergrad Now. . . 30 Staff in Bath rd largest UK Vo. IP Provider for SMEs 3 30, 000 lines on a Vo. IP platform gives us some interesting lessons to explore 2
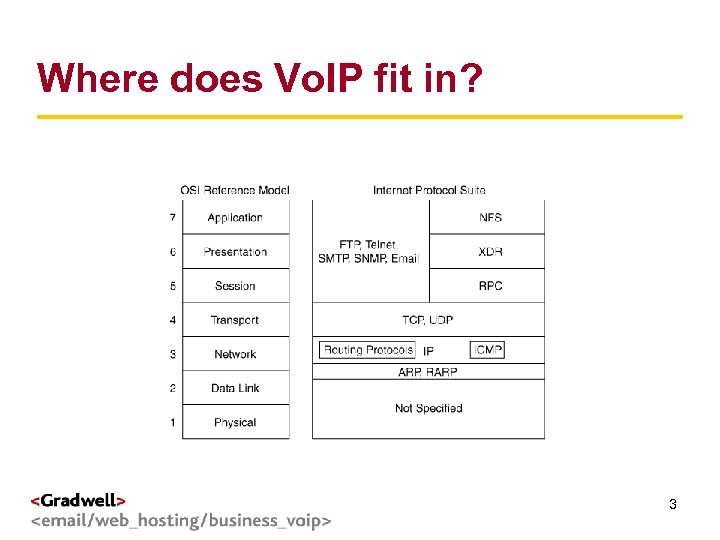 Where does Vo. IP fit in? g < > 3
Where does Vo. IP fit in? g < > 3
 Messaging + Talk g < > 4
Messaging + Talk g < > 4
 Different Types of Vo. IP g < > 5
Different Types of Vo. IP g < > 5
 Voice Protocols > All systems use some kind of application protocol to communicate g < SIP H 323 IAX (Inter Asterisk e. Xchange) Skinny (Cisco Protocol) Audio is transported as RTP 6
Voice Protocols > All systems use some kind of application protocol to communicate g < SIP H 323 IAX (Inter Asterisk e. Xchange) Skinny (Cisco Protocol) Audio is transported as RTP 6
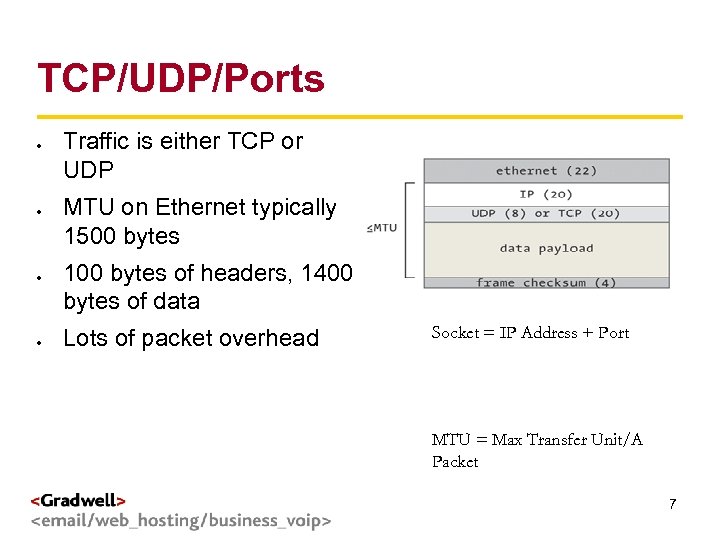 TCP/UDP/Ports Traffic is either TCP or UDP g < > MTU on Ethernet typically 1500 bytes 100 bytes of headers, 1400 bytes of data Lots of packet overhead Socket = IP Address + Port MTU = Max Transfer Unit/A Packet 7
TCP/UDP/Ports Traffic is either TCP or UDP g < > MTU on Ethernet typically 1500 bytes 100 bytes of headers, 1400 bytes of data Lots of packet overhead Socket = IP Address + Port MTU = Max Transfer Unit/A Packet 7
 Good book: If you're interested in more details You can read most of it on amazon g < > 8
Good book: If you're interested in more details You can read most of it on amazon g < > 8
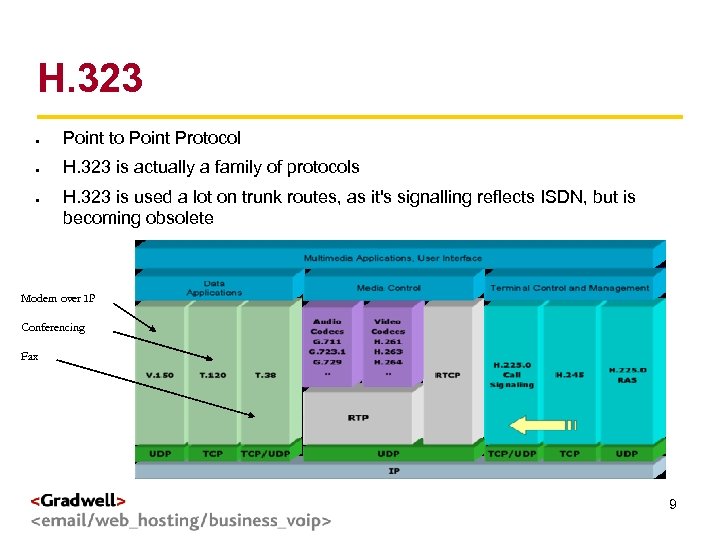 H. 323 Point to Point Protocol H. 323 is actually a family of protocols g < > H. 323 is used a lot on trunk routes, as it's signalling reflects ISDN, but is becoming obsolete Modem over IP Conferencing Fax 9
H. 323 Point to Point Protocol H. 323 is actually a family of protocols g < > H. 323 is used a lot on trunk routes, as it's signalling reflects ISDN, but is becoming obsolete Modem over IP Conferencing Fax 9
 Inter-Asterisk e. Xchange g < Asterisk is a major Open. Source phone system IAX was invented by Mark Spencer/Digium > Single UDP stream – port 4569 Handles the Media inband on the same socket Can support multiple RTP streams Single signalling link Far more bandwidth efficient Also much friendlier for firewalls Pronounced “eeks” 10
Inter-Asterisk e. Xchange g < Asterisk is a major Open. Source phone system IAX was invented by Mark Spencer/Digium > Single UDP stream – port 4569 Handles the Media inband on the same socket Can support multiple RTP streams Single signalling link Far more bandwidth efficient Also much friendlier for firewalls Pronounced “eeks” 10
 Skinny / SCCP g < > Skinny is a lightweight protocol which allows for efficient communication with Cisco Call. Manager Not many other people use it, but there is a big Cisco install base Signalling via TCP, Media via RTP/UDP 11
Skinny / SCCP g < > Skinny is a lightweight protocol which allows for efficient communication with Cisco Call. Manager Not many other people use it, but there is a big Cisco install base Signalling via TCP, Media via RTP/UDP 11
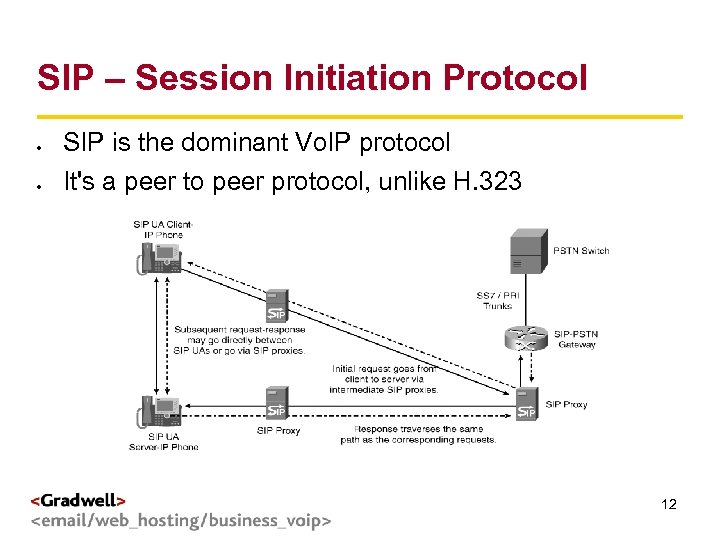 g < SIP – Session Initiation Protocol SIP is the dominant Vo. IP protocol > It's a peer to peer protocol, unlike H. 323 12
g < SIP – Session Initiation Protocol SIP is the dominant Vo. IP protocol > It's a peer to peer protocol, unlike H. 323 12
 SIP Addressing g < > SIP is very similar to Email and HTTP URI Address format: sip: peter@gradwell. com sip: 100@sip. gradwell. net: 5060 sip: 441225800800@sip. gradwell. net 13
SIP Addressing g < > SIP is very similar to Email and HTTP URI Address format: sip: peter@gradwell. com sip: 100@sip. gradwell. net: 5060 sip: 441225800800@sip. gradwell. net 13
 Types of SIP Message g < > INVITE—An INVITE method indicates that the recipient user or service is invited to participate in a session. ACK - An ACK request confirms that the UAC has received the final response to an INVITE request. ACK is used only with INVITE requests. ACK is sent end to end for a 200 OK response. OPTIONS—A UA uses the OPTIONS request to query a UAS about its capabilities BYE—A UA uses BYE to request the termination of a previously established session. CANCEL—The CANCEL request enables UACs and network servers to cancel an in-progress request, such as INVITE. This does not affect completed requests in which the UAS had already sent final responses. REGISTER—A client uses a REGISTER request to register its current location information corresponding to the AOR of the user with SIP servers. 14
Types of SIP Message g < > INVITE—An INVITE method indicates that the recipient user or service is invited to participate in a session. ACK - An ACK request confirms that the UAC has received the final response to an INVITE request. ACK is used only with INVITE requests. ACK is sent end to end for a 200 OK response. OPTIONS—A UA uses the OPTIONS request to query a UAS about its capabilities BYE—A UA uses BYE to request the termination of a previously established session. CANCEL—The CANCEL request enables UACs and network servers to cancel an in-progress request, such as INVITE. This does not affect completed requests in which the UAS had already sent final responses. REGISTER—A client uses a REGISTER request to register its current location information corresponding to the AOR of the user with SIP servers. 14
 SIP Registration g < > Phone registers periodically to tell the SIP server where it is 15
SIP Registration g < > Phone registers periodically to tell the SIP server where it is 15
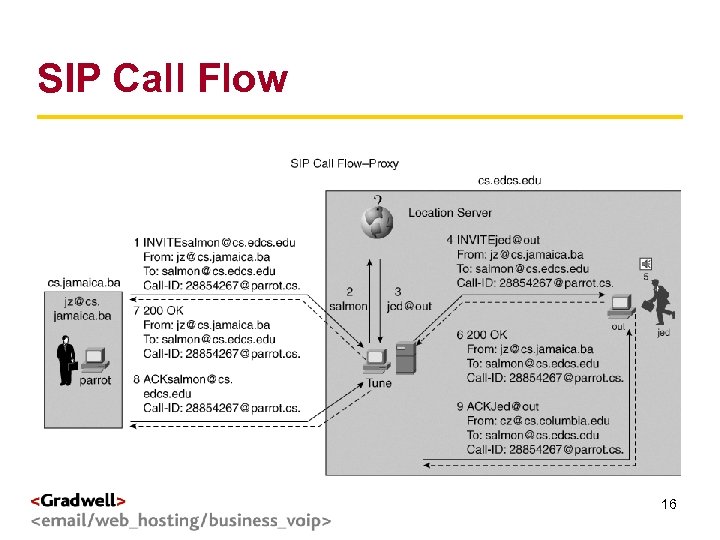 SIP Call Flow g < > 16
SIP Call Flow g < > 16
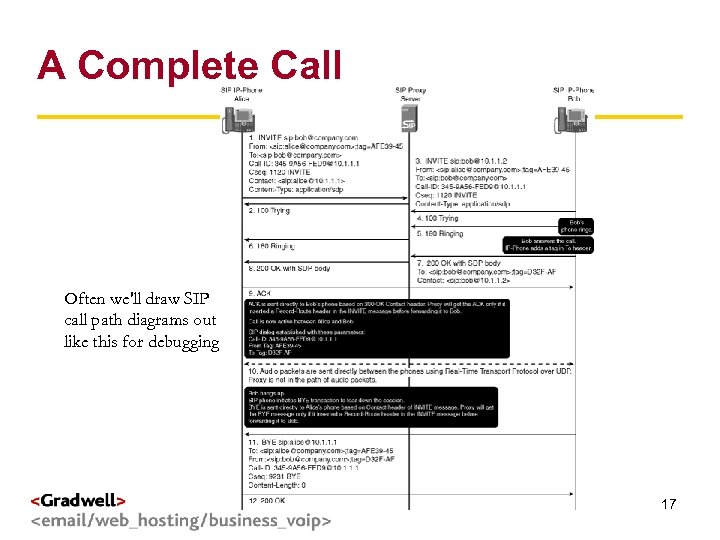 A Complete Call g < > Often we'll draw SIP call path diagrams out like this for debugging 17
A Complete Call g < > Often we'll draw SIP call path diagrams out like this for debugging 17
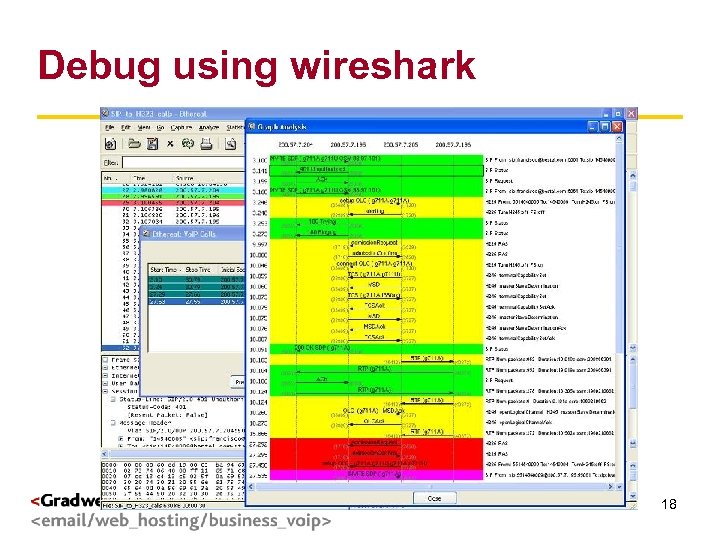 Debug using wireshark g < > 18
Debug using wireshark g < > 18
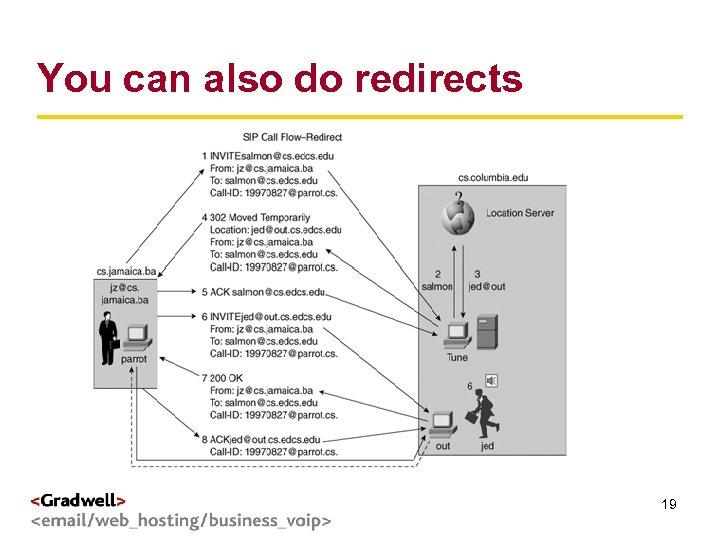 g < You can also do redirects > 19
g < You can also do redirects > 19
 SIP – Just for signalling Register – Hello Invite – Ringing ACK – Please hold OK – Connecting you caller BYE – Nice to talk to you g < > But no sound! 20
SIP – Just for signalling Register – Hello Invite – Ringing ACK – Please hold OK – Connecting you caller BYE – Nice to talk to you g < > But no sound! 20
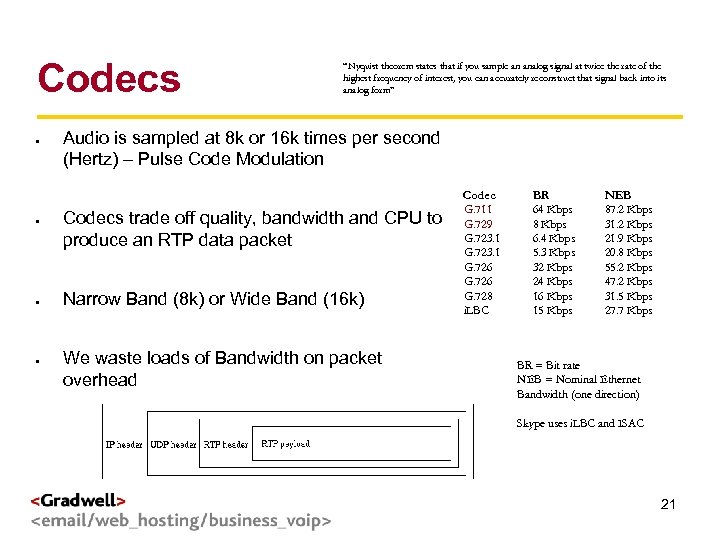 Codecs g < Audio is sampled at 8 k or 16 k times per second (Hertz) – Pulse Code Modulation Codec > “Nyquist theorem states that if you sample an analog signal at twice the rate of the highest frequency of interest, you can accurately reconstruct that signal back into its analog form” Codecs trade off quality, bandwidth and CPU to produce an RTP data packet Narrow Band (8 k) or Wide Band (16 k) We waste loads of Bandwidth on packet overhead G. 711 G. 729 G. 723. 1 G. 726 G. 728 i. LBC BR 64 Kbps 8 Kbps 6. 4 Kbps 5. 3 Kbps 32 Kbps 24 Kbps 16 Kbps 15 Kbps NEB 87. 2 Kbps 31. 2 Kbps 21. 9 Kbps 20. 8 Kbps 55. 2 Kbps 47. 2 Kbps 31. 5 Kbps 27. 7 Kbps BR = Bit rate NEB = Nominal Ethernet Bandwidth (one direction) Skype uses i. LBC and ISAC 21
Codecs g < Audio is sampled at 8 k or 16 k times per second (Hertz) – Pulse Code Modulation Codec > “Nyquist theorem states that if you sample an analog signal at twice the rate of the highest frequency of interest, you can accurately reconstruct that signal back into its analog form” Codecs trade off quality, bandwidth and CPU to produce an RTP data packet Narrow Band (8 k) or Wide Band (16 k) We waste loads of Bandwidth on packet overhead G. 711 G. 729 G. 723. 1 G. 726 G. 728 i. LBC BR 64 Kbps 8 Kbps 6. 4 Kbps 5. 3 Kbps 32 Kbps 24 Kbps 16 Kbps 15 Kbps NEB 87. 2 Kbps 31. 2 Kbps 21. 9 Kbps 20. 8 Kbps 55. 2 Kbps 47. 2 Kbps 31. 5 Kbps 27. 7 Kbps BR = Bit rate NEB = Nominal Ethernet Bandwidth (one direction) Skype uses i. LBC and ISAC 21
 RTP > RTP is used to send packets and reassemble them g < Time stamp Sequence Payload type What if? They arrive out of order - Jitter Or not at all? - Packet Loss 22
RTP > RTP is used to send packets and reassemble them g < Time stamp Sequence Payload type What if? They arrive out of order - Jitter Or not at all? - Packet Loss 22
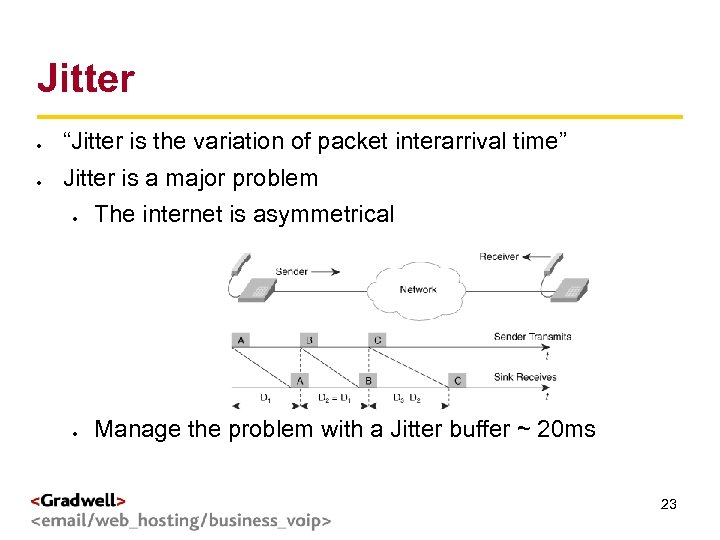 Jitter g < > “Jitter is the variation of packet interarrival time” Jitter is a major problem The internet is asymmetrical Manage the problem with a Jitter buffer ~ 20 ms 23
Jitter g < > “Jitter is the variation of packet interarrival time” Jitter is a major problem The internet is asymmetrical Manage the problem with a Jitter buffer ~ 20 ms 23
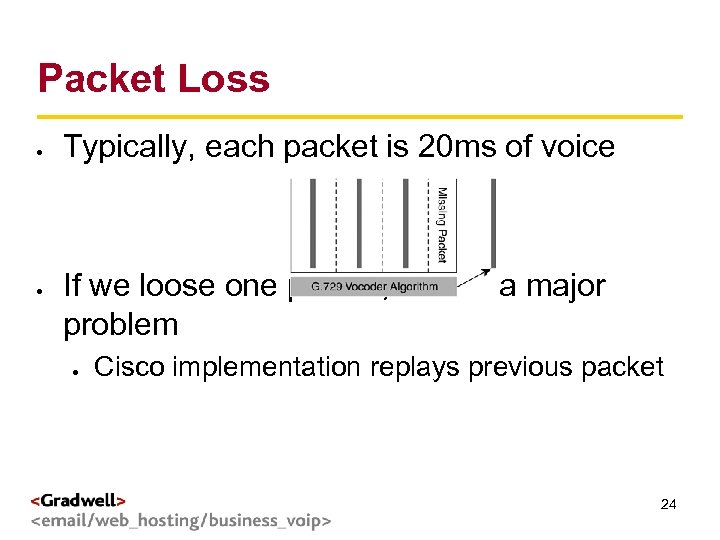 Packet Loss g < > Typically, each packet is 20 ms of voice If we loose one packet, it's not a major problem Cisco implementation replays previous packet 24
Packet Loss g < > Typically, each packet is 20 ms of voice If we loose one packet, it's not a major problem Cisco implementation replays previous packet 24
 Quality of Service g < > Qo. S is needed if a network link is congested Routers need to enforce traffic prioritisation across their links How do they decide? Trust the user? - Diff. Serv, Expedited Forwarding and Low Delay bits in IP header Trust the network – all traffic on port X or from IP address Y is special 25
Quality of Service g < > Qo. S is needed if a network link is congested Routers need to enforce traffic prioritisation across their links How do they decide? Trust the user? - Diff. Serv, Expedited Forwarding and Low Delay bits in IP header Trust the network – all traffic on port X or from IP address Y is special 25
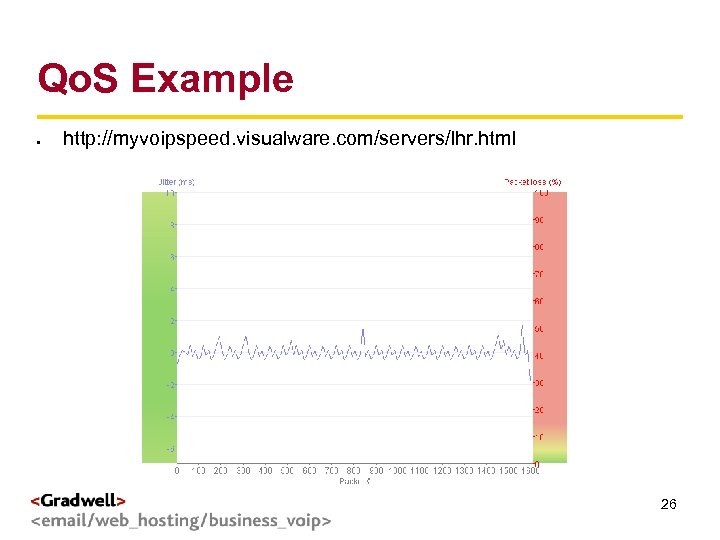 Qo. S Example g < http: //myvoipspeed. visualware. com/servers/lhr. html > 26
Qo. S Example g < http: //myvoipspeed. visualware. com/servers/lhr. html > 26
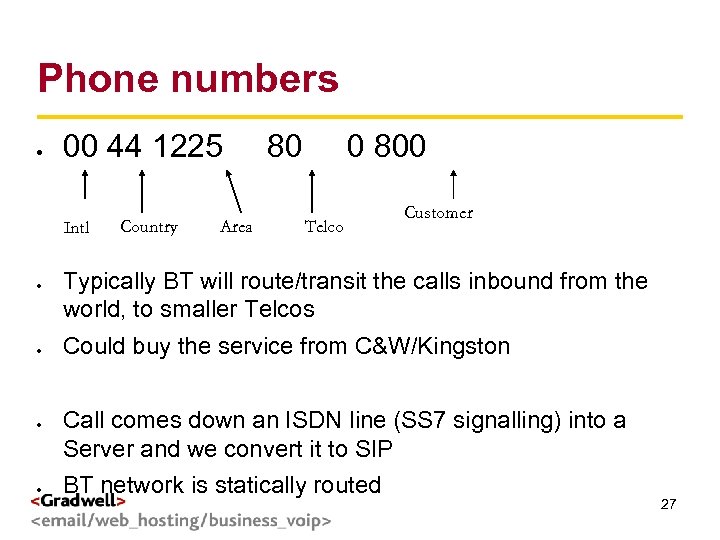 00 44 1225 Intl Country Area 80 g < Phone numbers 0 800 Telco > Customer Typically BT will route/transit the calls inbound from the world, to smaller Telcos Could buy the service from C&W/Kingston Call comes down an ISDN line (SS 7 signalling) into a Server and we convert it to SIP BT network is statically routed 27
00 44 1225 Intl Country Area 80 g < Phone numbers 0 800 Telco > Customer Typically BT will route/transit the calls inbound from the world, to smaller Telcos Could buy the service from C&W/Kingston Call comes down an ISDN line (SS 7 signalling) into a Server and we convert it to SIP BT network is statically routed 27
 ENUM > Phone numbers as domain names My Vo. IP server can now decide how to route the call 01225 800 810 becomes g < 0. 1. 8. 0. 0. 8. 5. 2. 2. 1. 4. 4. e 164. arpa. When I look this up I find TEL: 079700 NNNNN SIP: 1000200@sip. gradwell. net 28
ENUM > Phone numbers as domain names My Vo. IP server can now decide how to route the call 01225 800 810 becomes g < 0. 1. 8. 0. 0. 8. 5. 2. 2. 1. 4. 4. e 164. arpa. When I look this up I find TEL: 079700 NNNNN SIP: 1000200@sip. gradwell. net 28
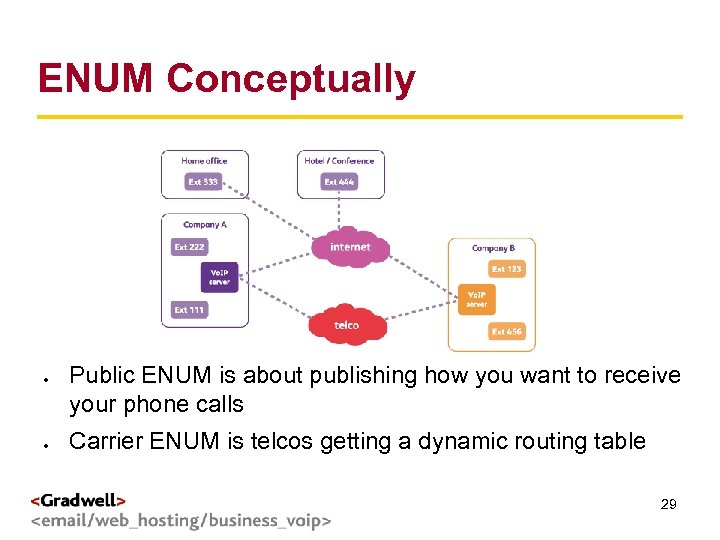 ENUM Conceptually g < > Public ENUM is about publishing how you want to receive your phone calls Carrier ENUM is telcos getting a dynamic routing table 29
ENUM Conceptually g < > Public ENUM is about publishing how you want to receive your phone calls Carrier ENUM is telcos getting a dynamic routing table 29
 SRV Records g < > Can you dial sip: peter@gradwell. com Yes – just do a lookup for the ENUM Records on gradwell. com and make a call to “peter”. Peter = 1000200 30
SRV Records g < > Can you dial sip: peter@gradwell. com Yes – just do a lookup for the ENUM Records on gradwell. com and make a call to “peter”. Peter = 1000200 30
 Lets make a test call g < http: //www. vaxvoip. com/Web. Demo/Softphone. A/Softphone. HTM login: 2443800 password: Jup 5 jojo sip proxy: newsip. gradwell. net Outbound proxy: natproxy. gradwell. net: 5082 Display name: “test” Then call your mobile – cli should be 02031372331 Now dial inbound, everyones phone should ring! > This demo uses an Active. X control, so only works on windows 31
Lets make a test call g < http: //www. vaxvoip. com/Web. Demo/Softphone. A/Softphone. HTM login: 2443800 password: Jup 5 jojo sip proxy: newsip. gradwell. net Outbound proxy: natproxy. gradwell. net: 5082 Display name: “test” Then call your mobile – cli should be 02031372331 Now dial inbound, everyones phone should ring! > This demo uses an Active. X control, so only works on windows 31
 Conclusions SIP – Signalling, RTP – Audio g < > But SIP isn't the only game in town RTP is dependent on Network Quality Routing information can be stored in ENUM 32
Conclusions SIP – Signalling, RTP – Audio g < > But SIP isn't the only game in town RTP is dependent on Network Quality Routing information can be stored in ENUM 32
 Useful Resources www. trixbox. org www. asterisk. org Great Vo. IP wiki www. nominet. org. uk/enum > www. voip-info. org g < Good Enum Primer Cisco Book 33
Useful Resources www. trixbox. org www. asterisk. org Great Vo. IP wiki www. nominet. org. uk/enum > www. voip-info. org g < Good Enum Primer Cisco Book 33


