risk management.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28
 End Risk management ©UNCTAD 2000 1
End Risk management ©UNCTAD 2000 1
 End About … Risk Management ©UNCTAD 2000 2
End About … Risk Management ©UNCTAD 2000 2
 End What is Risk Management? Who uses Risk Management? Mouse ‘Click’ to move on to the next slide ©UNCTAD 2000 3
End What is Risk Management? Who uses Risk Management? Mouse ‘Click’ to move on to the next slide ©UNCTAD 2000 3
 End What is Risk Management? Risk management is an analysis of a risk situation, design and substantiation of the administrative decision in the form of the legal certificate directed on minimization of risk. The risk management process can be presented in the form of block diagram. Mouse ‘Click’ to move on to the next slide ©UNCTAD 2000 4
End What is Risk Management? Risk management is an analysis of a risk situation, design and substantiation of the administrative decision in the form of the legal certificate directed on minimization of risk. The risk management process can be presented in the form of block diagram. Mouse ‘Click’ to move on to the next slide ©UNCTAD 2000 4
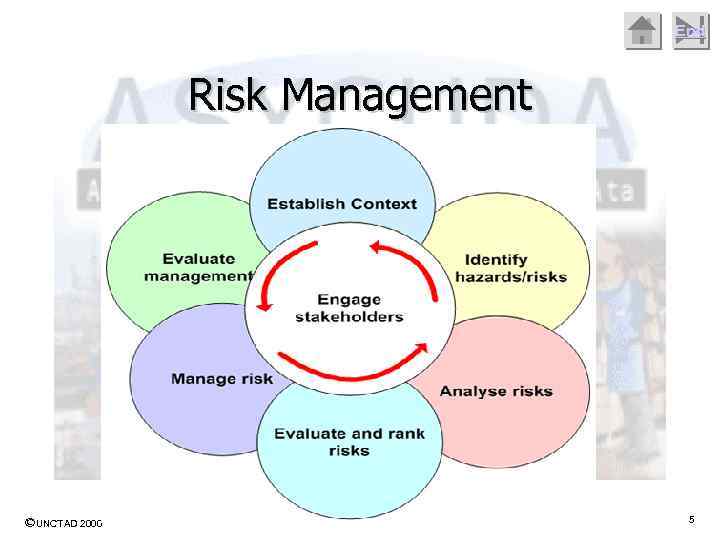 End Risk Management ©UNCTAD 2000 5
End Risk Management ©UNCTAD 2000 5
 End What is Risk Management? Risk Management is the name given to a logical and systematic method of identifying, analysing, treating and monitoring the risks involved in any activity or process. Mouse ‘Click’ to move on to the next slide ©UNCTAD 2000 Next 6
End What is Risk Management? Risk Management is the name given to a logical and systematic method of identifying, analysing, treating and monitoring the risks involved in any activity or process. Mouse ‘Click’ to move on to the next slide ©UNCTAD 2000 Next 6
 End What is Risk Management? Risk Management is a methodology that helps managers make best use of their available resources Mouse ‘Click’ to move on to the next slide ©UNCTAD 2000 Next 7
End What is Risk Management? Risk Management is a methodology that helps managers make best use of their available resources Mouse ‘Click’ to move on to the next slide ©UNCTAD 2000 Next 7
 End Who uses Risk Management? Risk Management practices are widely used in public and the private sectors, covering a wide range of activities or operations. These include: • Finance and Investment • Insurance • Health Care • Public Institutions • Governments ©UNCTAD 2000 8
End Who uses Risk Management? Risk Management practices are widely used in public and the private sectors, covering a wide range of activities or operations. These include: • Finance and Investment • Insurance • Health Care • Public Institutions • Governments ©UNCTAD 2000 8
 End Who uses Risk Management? • Effective Risk Management is a recognized and valued skill. • Educational institutions have formal study courses and award degrees in Risk Management. • The Risk Management process is well established. (International RM process standards. ) ©UNCTAD 2000 9
End Who uses Risk Management? • Effective Risk Management is a recognized and valued skill. • Educational institutions have formal study courses and award degrees in Risk Management. • The Risk Management process is well established. (International RM process standards. ) ©UNCTAD 2000 9
 End Who uses Risk Management? Risk Management is now an integral part of business planning. ©UNCTAD 2000 10
End Who uses Risk Management? Risk Management is now an integral part of business planning. ©UNCTAD 2000 10
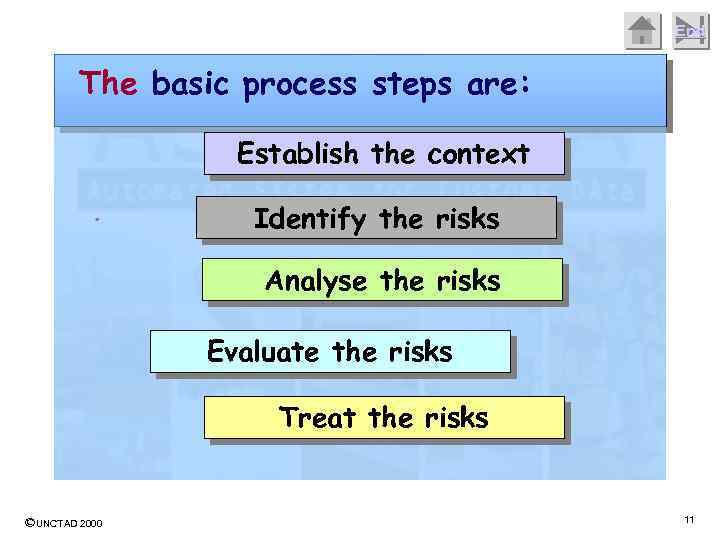 End The basic process steps are: Establish the context. Identify the risks Analyse the risks Evaluate the risks Treat the risks ©UNCTAD 2000 11
End The basic process steps are: Establish the context. Identify the risks Analyse the risks Evaluate the risks Treat the risks ©UNCTAD 2000 11
 End ‘Risk’ is dynamic and subject to constant change, so the process includes continuing: Monitoring and review and Communication & consultation ©UNCTAD 2000 12
End ‘Risk’ is dynamic and subject to constant change, so the process includes continuing: Monitoring and review and Communication & consultation ©UNCTAD 2000 12
 End The Risk Management process: Establish the context The strategic and organizational context in which risk management will take place. For example, the nature of your business, the risks inherent in your business and your priorities. Communicate & consult ©UNCTAD 2000 13
End The Risk Management process: Establish the context The strategic and organizational context in which risk management will take place. For example, the nature of your business, the risks inherent in your business and your priorities. Communicate & consult ©UNCTAD 2000 13
 End The Risk Management process: Identify the risks Defining types of risk, for example, ‘Physical: this could involve personal injuries, environmental and weather conditions and the physical assets of your organization ’. • Identifying the stakeholders, (i. e. , who is involved or affected). • Past events, future developments. Monitor and review Communicate & consult ©UNCTAD 2000 14
End The Risk Management process: Identify the risks Defining types of risk, for example, ‘Physical: this could involve personal injuries, environmental and weather conditions and the physical assets of your organization ’. • Identifying the stakeholders, (i. e. , who is involved or affected). • Past events, future developments. Monitor and review Communicate & consult ©UNCTAD 2000 14
 End The Risk Management process: Analyse the risks How likely is the risk event to happen? (Probability and frequency? ) What would be the impact, cost or consequences of that event occurring? (Economic, political, social? ) Monitor and review Communicate & consult ©UNCTAD 2000 15
End The Risk Management process: Analyse the risks How likely is the risk event to happen? (Probability and frequency? ) What would be the impact, cost or consequences of that event occurring? (Economic, political, social? ) Monitor and review Communicate & consult ©UNCTAD 2000 15
 End In analyzing a risk you are deciding on the relationship between the likelihood of a risk occurring and the consequences of the risk you have identified. You then have to define the level of risk: • Extreme: An extreme risk requires immediate action as the potential could be devastating to the enterprise. • High: A high level of risk requires action, as it has the potential to be damaging to the enterprise. • Moderate: Allocate specific responsibility to a moderate risk and implement monitoring or response procedures. • Low: Manage a low level of risk with routine procedures. ©UNCTAD 2000 16
End In analyzing a risk you are deciding on the relationship between the likelihood of a risk occurring and the consequences of the risk you have identified. You then have to define the level of risk: • Extreme: An extreme risk requires immediate action as the potential could be devastating to the enterprise. • High: A high level of risk requires action, as it has the potential to be damaging to the enterprise. • Moderate: Allocate specific responsibility to a moderate risk and implement monitoring or response procedures. • Low: Manage a low level of risk with routine procedures. ©UNCTAD 2000 16
 End The Risk Management process: Evaluate the risks In this step you are deciding whether a risk is acceptable. Your evaluation will take into account the following: • the importance of the activity you are risk managing and its outcomes • the degree of control you have over the risk Monitor and review Communicate & consult ©UNCTAD 2000 17
End The Risk Management process: Evaluate the risks In this step you are deciding whether a risk is acceptable. Your evaluation will take into account the following: • the importance of the activity you are risk managing and its outcomes • the degree of control you have over the risk Monitor and review Communicate & consult ©UNCTAD 2000 17
 The Risk Management process: End Evaluate the risks • the potential and actual losses which may arise from the risk • the benefits and opportunities presented by the risk Monitor and review Communicate & consult ©UNCTAD 2000 18
The Risk Management process: End Evaluate the risks • the potential and actual losses which may arise from the risk • the benefits and opportunities presented by the risk Monitor and review Communicate & consult ©UNCTAD 2000 18
 End The Risk Management process: Treat the risks Develop and implement a plan with specific counter-measures to address the identified risks. Consider: • Priorities (Strategic and operational) • Resources (human, financial and technical) • Risk acceptance, (i. e. , low risks) ©UNCTAD 2000 19
End The Risk Management process: Treat the risks Develop and implement a plan with specific counter-measures to address the identified risks. Consider: • Priorities (Strategic and operational) • Resources (human, financial and technical) • Risk acceptance, (i. e. , low risks) ©UNCTAD 2000 19
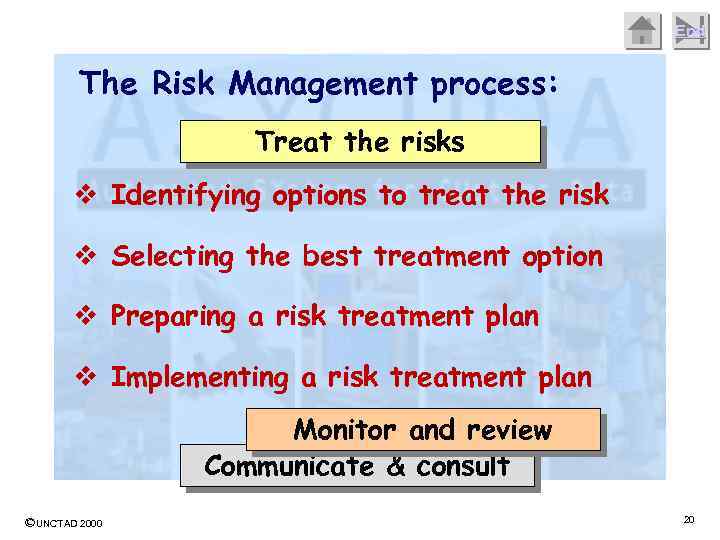 End The Risk Management process: Treat the risks v Identifying options to treat the risk v Selecting the best treatment option v Preparing a risk treatment plan v Implementing a risk treatment plan Monitor and review Communicate & consult ©UNCTAD 2000 20
End The Risk Management process: Treat the risks v Identifying options to treat the risk v Selecting the best treatment option v Preparing a risk treatment plan v Implementing a risk treatment plan Monitor and review Communicate & consult ©UNCTAD 2000 20
 The Risk Management process: End Treat the risks • The options available to manage this risk are to: • Avoid the risk by deciding not to process with the activity or choosing another way to achieve the same outcome. • Control the risk by reducing the likelihood of the risk occurring, the consequences of the risk or both. • Transfer the risk by shifting all or part of the responsibility of the risk to another party who is best able to control it. • Retain the risk after accepting that the risk cannot be avoided, controlled to transferred ©UNCTAD 2000 21
The Risk Management process: End Treat the risks • The options available to manage this risk are to: • Avoid the risk by deciding not to process with the activity or choosing another way to achieve the same outcome. • Control the risk by reducing the likelihood of the risk occurring, the consequences of the risk or both. • Transfer the risk by shifting all or part of the responsibility of the risk to another party who is best able to control it. • Retain the risk after accepting that the risk cannot be avoided, controlled to transferred ©UNCTAD 2000 21
 End The Risk Management process: Monitor and review In identifying, prioritising and treating risks, organisations make assumptions and decisions based on situations that are subject to change, (e. g. , the business environment, trading patterns, or government policies). Risk Management policies and decisions must be regularly reviewed. Communicate & consult ©UNCTAD 2000 22
End The Risk Management process: Monitor and review In identifying, prioritising and treating risks, organisations make assumptions and decisions based on situations that are subject to change, (e. g. , the business environment, trading patterns, or government policies). Risk Management policies and decisions must be regularly reviewed. Communicate & consult ©UNCTAD 2000 22
 End The Risk Management process: Monitor and review Risk Managers must monitor activities and processes to determine the accuracy of planning assumptions and the effectiveness of the measures taken to treat the risk. Methods can include data evaluation, audit, compliance measurement. Communicate & consult ©UNCTAD 2000 23
End The Risk Management process: Monitor and review Risk Managers must monitor activities and processes to determine the accuracy of planning assumptions and the effectiveness of the measures taken to treat the risk. Methods can include data evaluation, audit, compliance measurement. Communicate & consult ©UNCTAD 2000 23
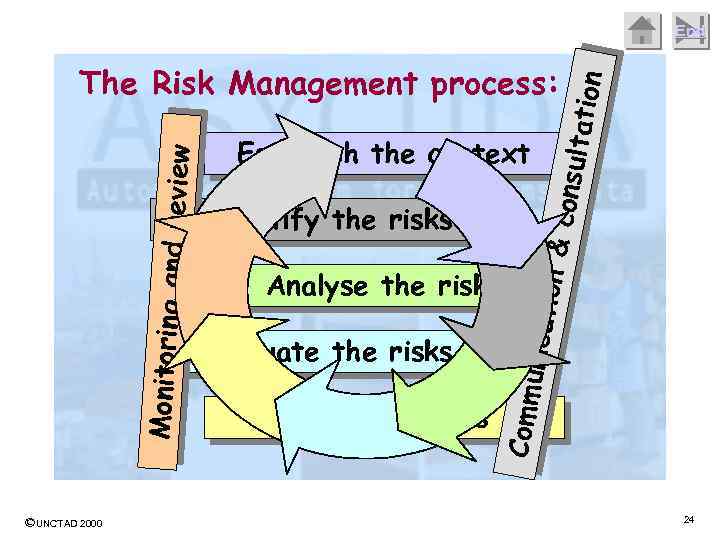 End ©UNCTAD 2000 ion & consul tation Establish the context Identify the risks Evaluate the risks Treat the risks unicat Analyse the risks Comm Monitoring and review The Risk Management process: 24
End ©UNCTAD 2000 ion & consul tation Establish the context Identify the risks Evaluate the risks Treat the risks unicat Analyse the risks Comm Monitoring and review The Risk Management process: 24
 End Resources http: //www. riskmanagement. qld. gov. au http: //www. ourcommunity. com. au/insurance_main. jsp http: //www. ozco. gov. au/arts_resources/ot her/risk_management_and_insurance_fo r_arts_enterprises/files/2131/risk_manage ment%202004. pdf ©UNCTAD 2000 25
End Resources http: //www. riskmanagement. qld. gov. au http: //www. ourcommunity. com. au/insurance_main. jsp http: //www. ozco. gov. au/arts_resources/ot her/risk_management_and_insurance_fo r_arts_enterprises/files/2131/risk_manage ment%202004. pdf ©UNCTAD 2000 25
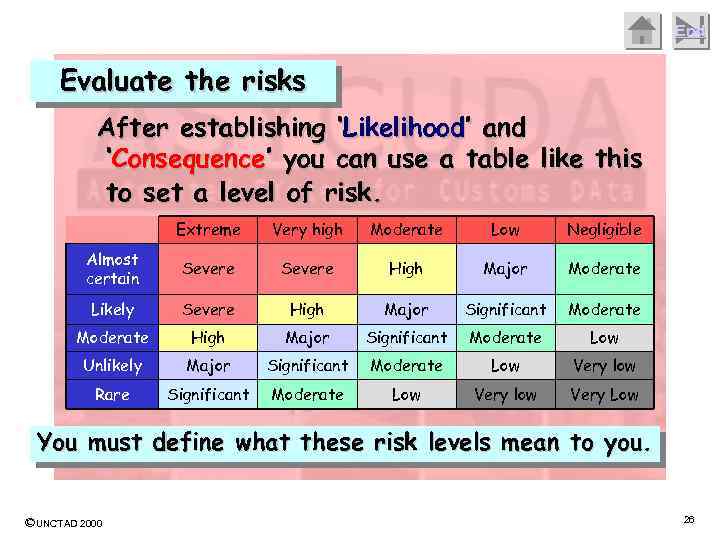 End Evaluate the risks After establishing ‘Likelihood’ and ‘Consequence’ you can use a table like this to set a level of risk. Extreme Very high Moderate Low Negligible Almost certain Severe High Major Moderate Likely Severe High Major Significant Moderate Low Unlikely Major Significant Moderate Low Very low Rare Significant Moderate Low Very low Very Low You must define what these risk levels mean to you. ©UNCTAD 2000 26
End Evaluate the risks After establishing ‘Likelihood’ and ‘Consequence’ you can use a table like this to set a level of risk. Extreme Very high Moderate Low Negligible Almost certain Severe High Major Moderate Likely Severe High Major Significant Moderate Low Unlikely Major Significant Moderate Low Very low Rare Significant Moderate Low Very low Very Low You must define what these risk levels mean to you. ©UNCTAD 2000 26
 End Treating the risks Low and very low level risks can normally be accepted, subject to on-going monitoring. All other risks are included in the management plan. The plan catalogues the risks, the level of risk, and describes a treatment. The treatment is the action proposed, (and perhaps the resources allocated). Next ©UNCTAD 2000 27
End Treating the risks Low and very low level risks can normally be accepted, subject to on-going monitoring. All other risks are included in the management plan. The plan catalogues the risks, the level of risk, and describes a treatment. The treatment is the action proposed, (and perhaps the resources allocated). Next ©UNCTAD 2000 27
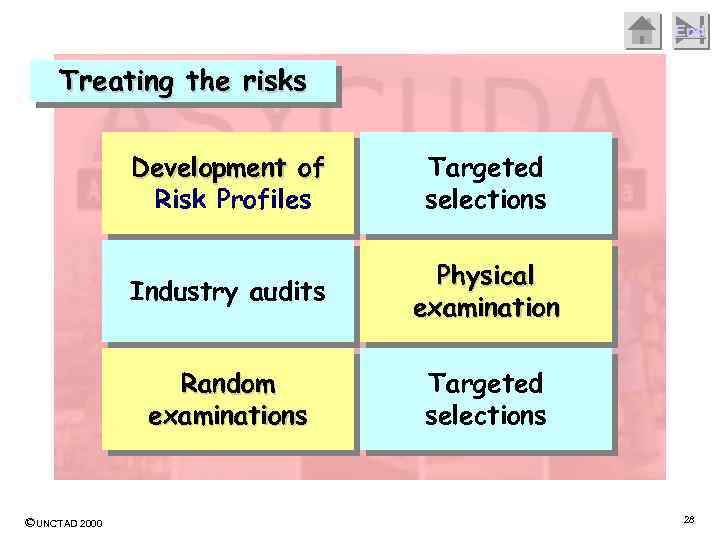 End Treating the risks Development of Risk Profiles Industry audits Physical examination Random examinations ©UNCTAD 2000 Targeted selections 28
End Treating the risks Development of Risk Profiles Industry audits Physical examination Random examinations ©UNCTAD 2000 Targeted selections 28


