9ab2d8394351d0ae4f88ed27db210151.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
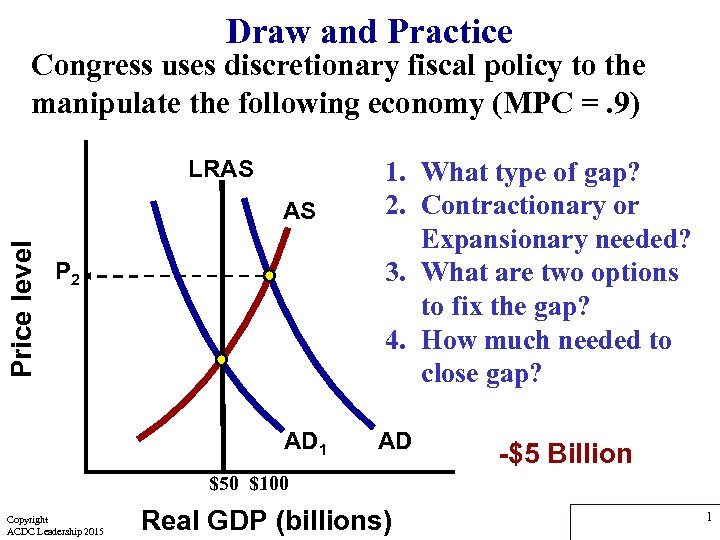 Draw and Practice Congress uses discretionary fiscal policy to the manipulate the following economy (MPC =. 9) LRAS Price level AS P 2 AD 1 1. What type of gap? 2. Contractionary or Expansionary needed? 3. What are two options to fix the gap? 4. How much needed to close gap? AD -$5 Billion $50 $100 Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 Real GDP (billions) 1
Draw and Practice Congress uses discretionary fiscal policy to the manipulate the following economy (MPC =. 9) LRAS Price level AS P 2 AD 1 1. What type of gap? 2. Contractionary or Expansionary needed? 3. What are two options to fix the gap? 4. How much needed to close gap? AD -$5 Billion $50 $100 Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 Real GDP (billions) 1
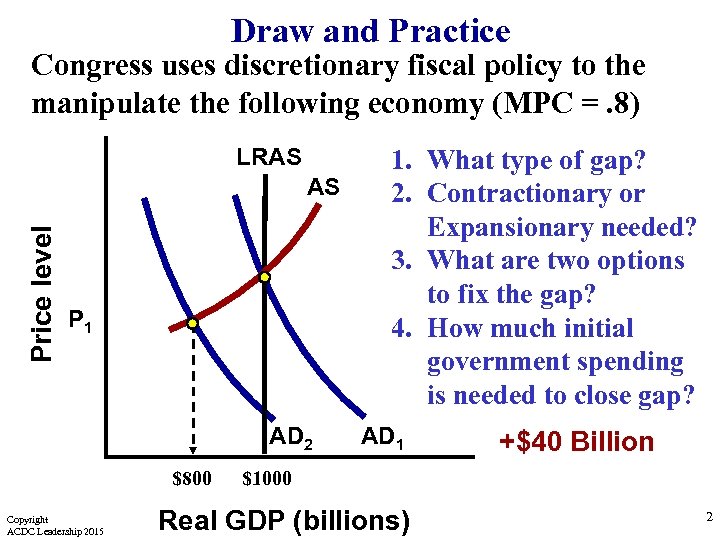 Draw and Practice Congress uses discretionary fiscal policy to the manipulate the following economy (MPC =. 8) LRAS Price level AS P 1 AD 2 $800 Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 1. What type of gap? 2. Contractionary or Expansionary needed? 3. What are two options to fix the gap? 4. How much initial government spending is needed to close gap? AD 1 +$40 Billion $1000 Real GDP (billions) 2
Draw and Practice Congress uses discretionary fiscal policy to the manipulate the following economy (MPC =. 8) LRAS Price level AS P 1 AD 2 $800 Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 1. What type of gap? 2. Contractionary or Expansionary needed? 3. What are two options to fix the gap? 4. How much initial government spending is needed to close gap? AD 1 +$40 Billion $1000 Real GDP (billions) 2
 Problems With Fiscal Policy Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 3
Problems With Fiscal Policy Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 3
 5 Problems With Fiscal Policy • When there is a recessionary gap what two options does Congress have to fix it? • What’s wrong with combining both? 1. Deficit Spending!!!! • A Budget Deficit is when the government’s expenditures exceeds its revenue. • The National Debt is the accumulation of all the budget deficits over time. • If the Government increases spending without increasing taxes they will increase the annual deficit and the national debt. Most economists agree that budget deficits are a necessary evil because forcing a balanced budget would not allow Congress to stimulate the economy. 4 Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015
5 Problems With Fiscal Policy • When there is a recessionary gap what two options does Congress have to fix it? • What’s wrong with combining both? 1. Deficit Spending!!!! • A Budget Deficit is when the government’s expenditures exceeds its revenue. • The National Debt is the accumulation of all the budget deficits over time. • If the Government increases spending without increasing taxes they will increase the annual deficit and the national debt. Most economists agree that budget deficits are a necessary evil because forcing a balanced budget would not allow Congress to stimulate the economy. 4 Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015
 US National Debt US Debt Clock Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 5
US National Debt US Debt Clock Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 5
 The Onion: Government Stages Coup Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 6
The Onion: Government Stages Coup Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 6
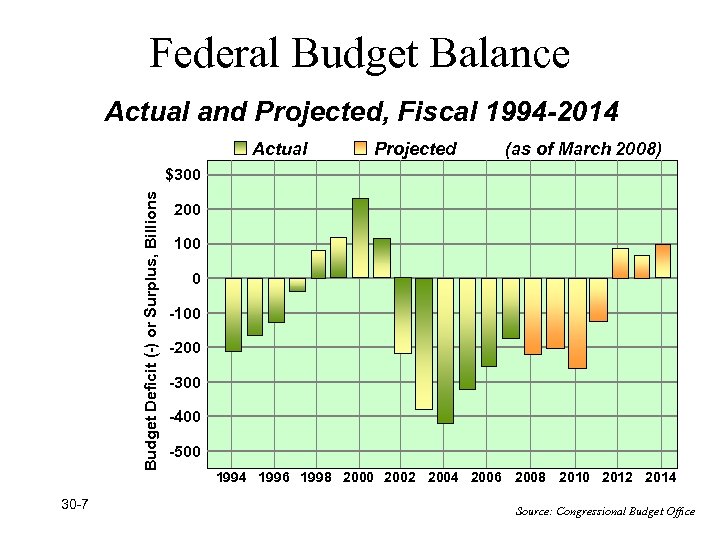 Federal Budget Balance Actual and Projected, Fiscal 1994 -2014 Actual Projected (as of March 2008) Budget Deficit (-) or Surplus, Billions $300 30 -7 200 100 0 -100 -200 -300 -400 -500 1994 1996 1998 2000 2002 2004 2006 2008 2010 2012 2014 Source: Congressional Budget Office
Federal Budget Balance Actual and Projected, Fiscal 1994 -2014 Actual Projected (as of March 2008) Budget Deficit (-) or Surplus, Billions $300 30 -7 200 100 0 -100 -200 -300 -400 -500 1994 1996 1998 2000 2002 2004 2006 2008 2010 2012 2014 Source: Congressional Budget Office
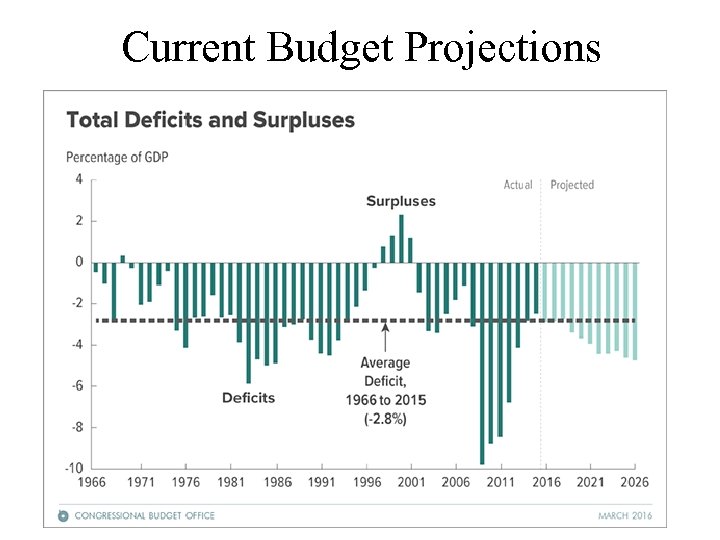 Current Budget Projections
Current Budget Projections
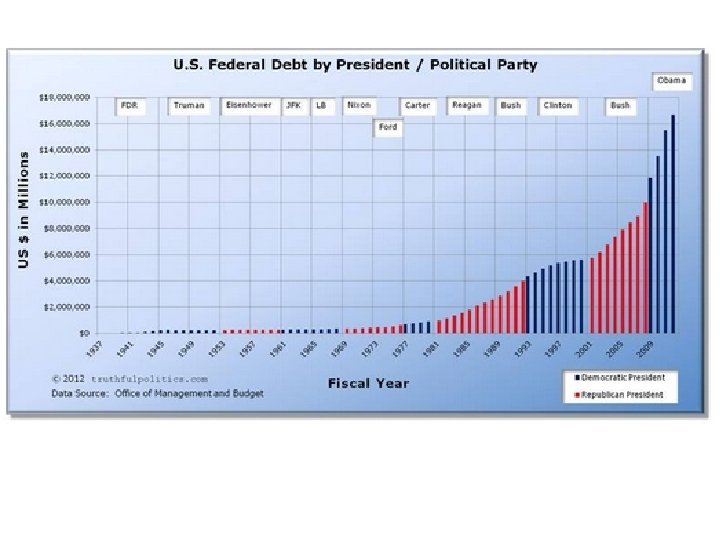
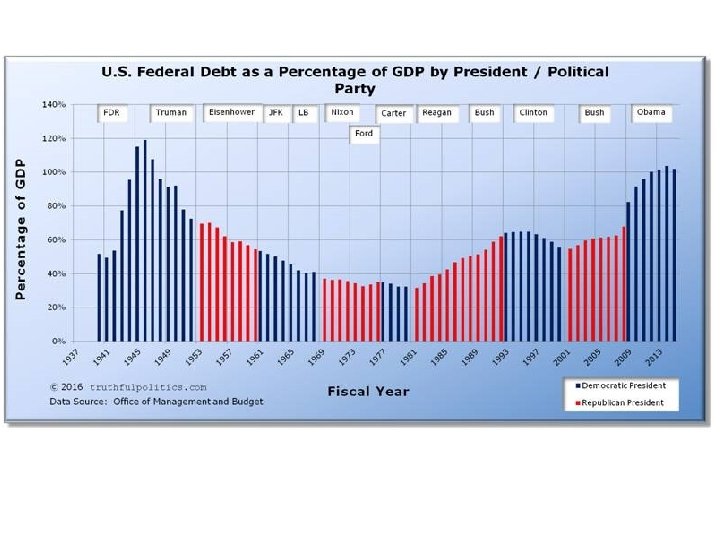
 Who owns the debt? 30 -11
Who owns the debt? 30 -11
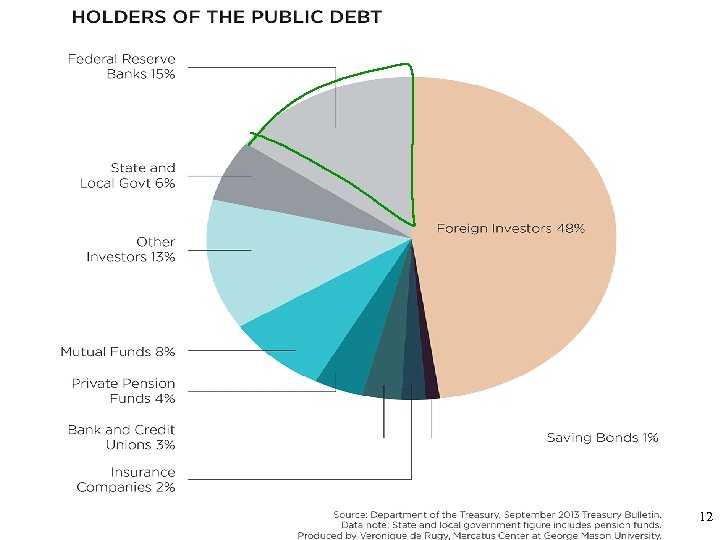 12
12
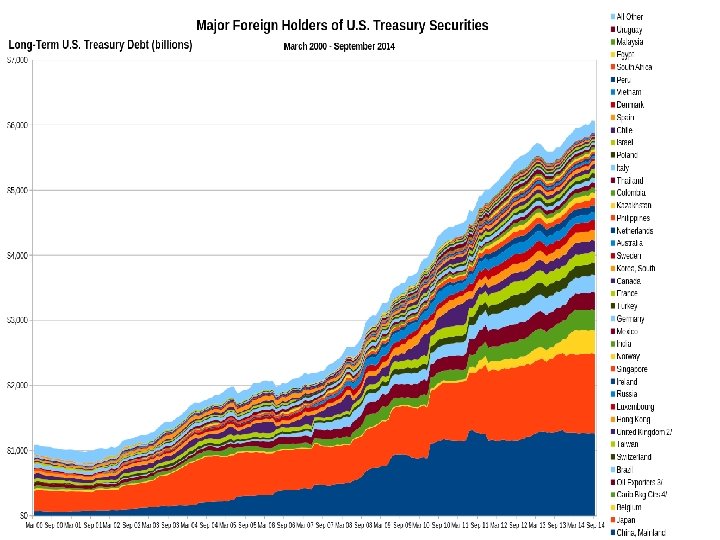
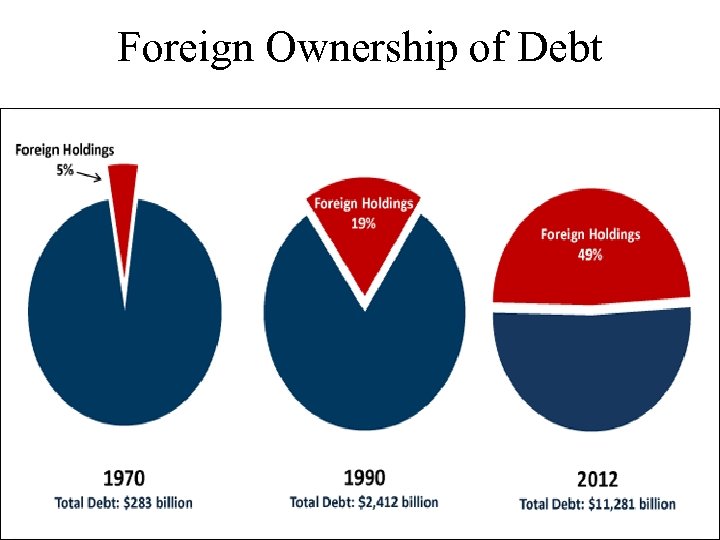 Foreign Ownership of Debt 30 -13
Foreign Ownership of Debt 30 -13
 30 -14
30 -14
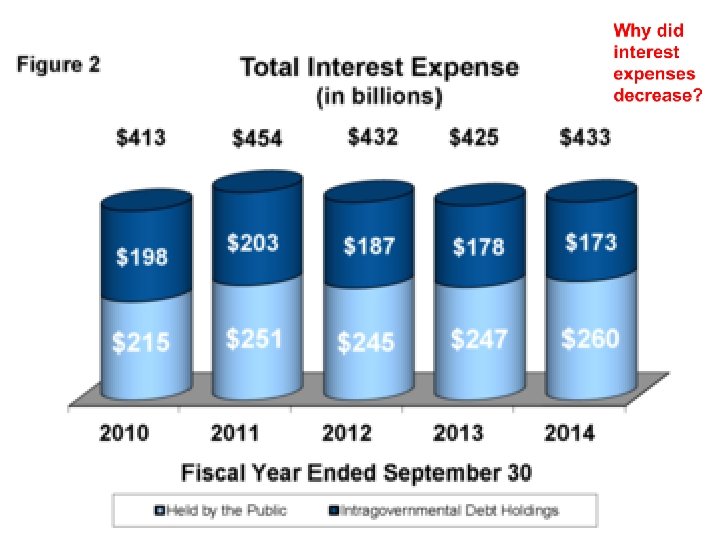 30 -15
30 -15
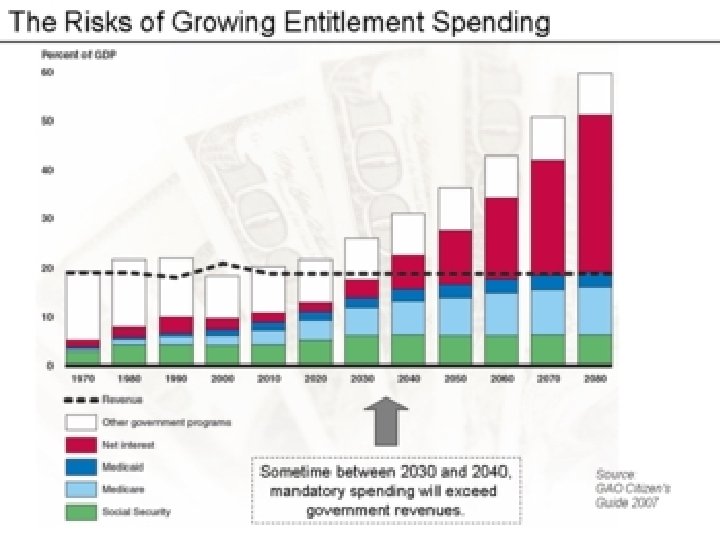 30 -16
30 -16
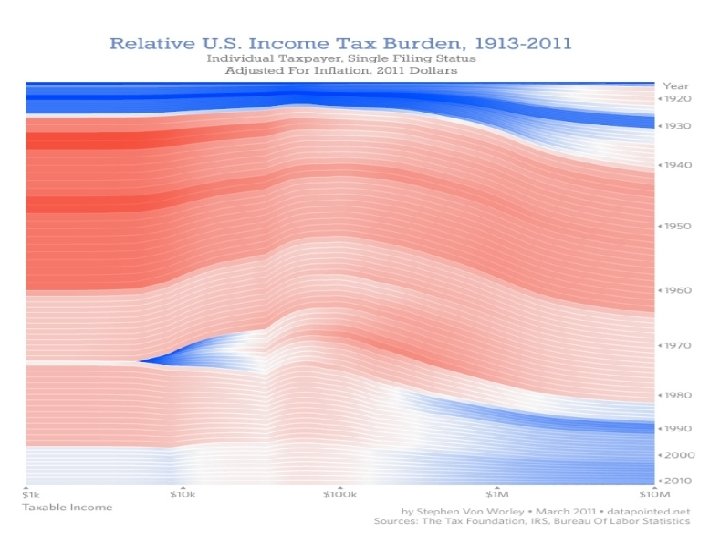 ` 30 -17
` 30 -17
 5 Problems with Fiscal Policy 2. Problems of Timing • Recognition Lag- Congress must react to economic indicators before it’s too late • Administrative Lag- Congress takes time to pass legislation • Operational Lag- Spending/planning takes time to organize and execute ( changing taxing is quicker) 3. Politically Motivated Policies • Politicians may use economically inappropriate policies to get reelected. • Ex: A senator promises more welfare and public works programs when there is already an inflationary gap. Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 18
5 Problems with Fiscal Policy 2. Problems of Timing • Recognition Lag- Congress must react to economic indicators before it’s too late • Administrative Lag- Congress takes time to pass legislation • Operational Lag- Spending/planning takes time to organize and execute ( changing taxing is quicker) 3. Politically Motivated Policies • Politicians may use economically inappropriate policies to get reelected. • Ex: A senator promises more welfare and public works programs when there is already an inflationary gap. Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 18
 5 Problems with Fiscal Policy 4. Crowding-Out Effect • In basketball, what is “Boxing Out”? • Government spending might cause unintended effects that weaken the impact of the policy. Example: • The government increases spending but must borrow the money (AD increases) • This increases the price for money (the interest rate). • Interest rates rise so Investment falls. (AD decrease) Another Example: • We have a recessionary gap • Government creates new public library. (AD increases) • Now but consumer spend less on books (AD decreases) The government “crowds out” consumers and/or investors Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 19
5 Problems with Fiscal Policy 4. Crowding-Out Effect • In basketball, what is “Boxing Out”? • Government spending might cause unintended effects that weaken the impact of the policy. Example: • The government increases spending but must borrow the money (AD increases) • This increases the price for money (the interest rate). • Interest rates rise so Investment falls. (AD decrease) Another Example: • We have a recessionary gap • Government creates new public library. (AD increases) • Now but consumer spend less on books (AD decreases) The government “crowds out” consumers and/or investors Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 19
 5 Problems with Fiscal Policy 5. Net Export Effect International trade reduces the effectiveness of fiscal policies. • • • Example: We have a recessionary gap so the government spends to increase AD. The increase in AD causes an increase in price level and interest rates. U. S. goods are now more expensive and the US dollar appreciates… Foreign countries buy less. (Exports fall) Net Exports (Exports-Imports) falls, decreasing AD. Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 20
5 Problems with Fiscal Policy 5. Net Export Effect International trade reduces the effectiveness of fiscal policies. • • • Example: We have a recessionary gap so the government spends to increase AD. The increase in AD causes an increase in price level and interest rates. U. S. goods are now more expensive and the US dollar appreciates… Foreign countries buy less. (Exports fall) Net Exports (Exports-Imports) falls, decreasing AD. Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 20
 List the 25 Concepts we have covered 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Aggregate Demand Real Balance Effect Interest Rate Effect Foreign Trade Effect Shifters of AD (C, I, G, X) 6. Aggregate Supply 7. Shifter of AS (R. A. P. ) 8. Short Run AS 9. Long Run AS 10. Two Types of Inflation 11. Ratchet Effect 12. Classic vs. Keynesian 13. Three Ranges of AS 14. Fiscal Policy 15. Discretionary vs. Non. Discretionary 16. Expansionary Policy 17. Contractionary Policy 18. The Car Analogy 19. Multiplier Effect 20. Calculating the Spending Multiplier 21. MPC and MPS 22. Deficit Spending 23. Timing Problems 24. Crowding-Out Effect 25. Net Exports Effect 21
List the 25 Concepts we have covered 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Aggregate Demand Real Balance Effect Interest Rate Effect Foreign Trade Effect Shifters of AD (C, I, G, X) 6. Aggregate Supply 7. Shifter of AS (R. A. P. ) 8. Short Run AS 9. Long Run AS 10. Two Types of Inflation 11. Ratchet Effect 12. Classic vs. Keynesian 13. Three Ranges of AS 14. Fiscal Policy 15. Discretionary vs. Non. Discretionary 16. Expansionary Policy 17. Contractionary Policy 18. The Car Analogy 19. Multiplier Effect 20. Calculating the Spending Multiplier 21. MPC and MPS 22. Deficit Spending 23. Timing Problems 24. Crowding-Out Effect 25. Net Exports Effect 21


