DIVERSITY OF PLANT FORMS General Botany Classification












diversity_of_plant_forms.ppt
- Размер: 287.5 Кб
- Количество слайдов: 12
Описание презентации DIVERSITY OF PLANT FORMS General Botany Classification по слайдам
 DIVERSITY OF PLANT FORMS General Botany
DIVERSITY OF PLANT FORMS General Botany
 Classification of Plants Artificial classification A. Based on whether or not they can manufacture food out of inorganic nutrients. Autotrophic / independent plant- can produce their own food through photosynthesis. — all green plants Heterotrophic or dependent plant – cannot manufacture their own food i. parasite – nutritionally dependent on other living organism ii. Saprophytes – nutritionally dependent on dead organic matters
Classification of Plants Artificial classification A. Based on whether or not they can manufacture food out of inorganic nutrients. Autotrophic / independent plant- can produce their own food through photosynthesis. — all green plants Heterotrophic or dependent plant – cannot manufacture their own food i. parasite – nutritionally dependent on other living organism ii. Saprophytes – nutritionally dependent on dead organic matters
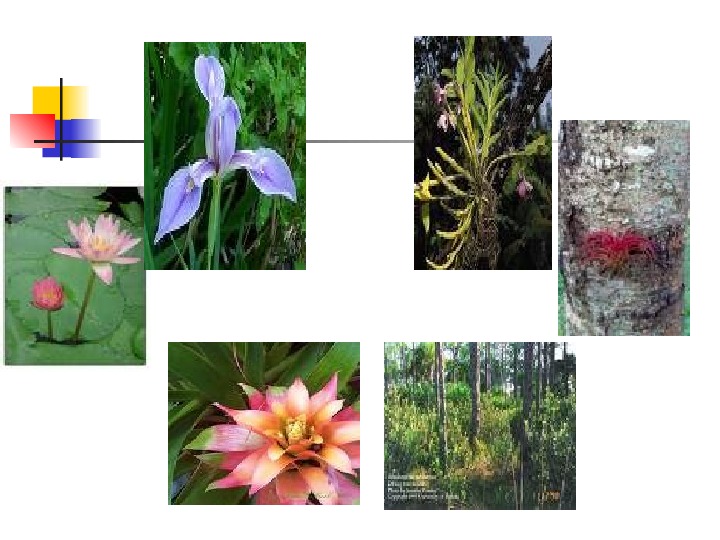
 B. Based on environmental location Aquatic plants — live on water Terrestrial plants — live on land Epiphytes – found above the grounds & attached to plants C. Based on water requirements Xerophytes – live in dry places Mesophytes – require moderate supply of water Hydrophytes – lives in watery or moist places & require abundant supply of water
B. Based on environmental location Aquatic plants — live on water Terrestrial plants — live on land Epiphytes – found above the grounds & attached to plants C. Based on water requirements Xerophytes – live in dry places Mesophytes – require moderate supply of water Hydrophytes – lives in watery or moist places & require abundant supply of water


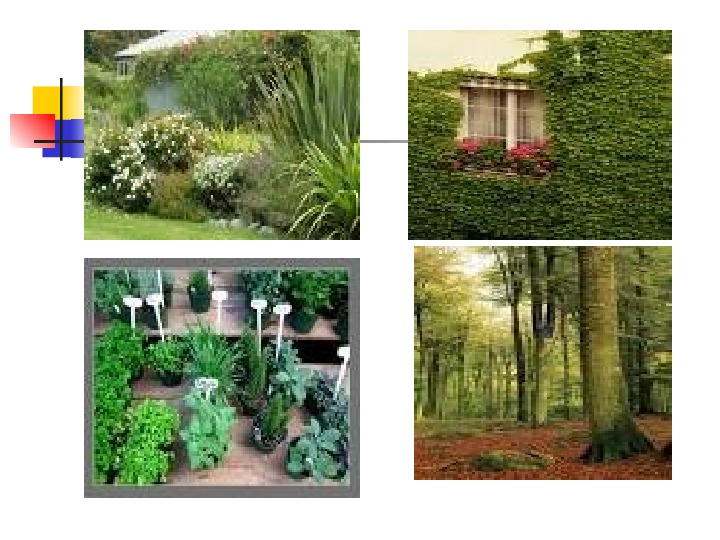
 D. Based on lifespan Annuals – a plant that complete its life cycle during a single growing season & then dies. Biennials – typically herbaceous plants, requires 2 growing seasons. Produce flower & seeds in the 2 nd season. Perennials – a plant that grows for many years, woody or herbaceous. E. Based on appearance or habit Tree – woody w/ single main stem, about 10 ft high Shrub – woody w/ a relatively short main stem w/c gives rise to many branches Herb – soft stemmed w/c is relatively short; short-lived Vine – either creeping along the ground or climb upright.
D. Based on lifespan Annuals – a plant that complete its life cycle during a single growing season & then dies. Biennials – typically herbaceous plants, requires 2 growing seasons. Produce flower & seeds in the 2 nd season. Perennials – a plant that grows for many years, woody or herbaceous. E. Based on appearance or habit Tree – woody w/ single main stem, about 10 ft high Shrub – woody w/ a relatively short main stem w/c gives rise to many branches Herb – soft stemmed w/c is relatively short; short-lived Vine – either creeping along the ground or climb upright.
 annual plant s biennial perennial biennial pl ants biennial perennial p e re nn ia l pl a n ts bi enni al perenni al
annual plant s biennial perennial biennial pl ants biennial perennial p e re nn ia l pl a n ts bi enni al perenni al

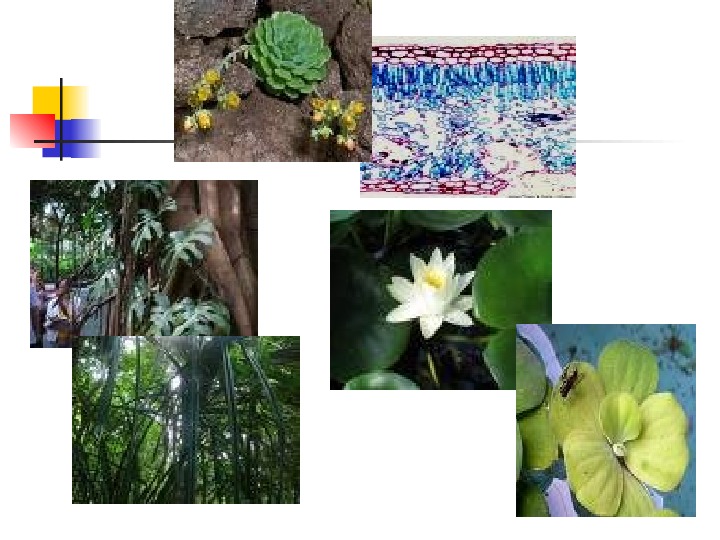
 Natural classification — based on morphological & structural relationships. A. Non-vascular plants –lack conducting tissues (phloem & xylem) a. thallophytes — simplest forms of plants thallus – is their body composed of undifferentiated roots, stem, leaves. Ex: algae, fungi, lichens (alga & fungi) b. bryophytes – mosses, liverworts, & hornworts. — usually found in moist places, rocks, & trees.
Natural classification — based on morphological & structural relationships. A. Non-vascular plants –lack conducting tissues (phloem & xylem) a. thallophytes — simplest forms of plants thallus – is their body composed of undifferentiated roots, stem, leaves. Ex: algae, fungi, lichens (alga & fungi) b. bryophytes – mosses, liverworts, & hornworts. — usually found in moist places, rocks, & trees.
 B. Vascular plants – have conducting tissues a. Pteridophytes – produces spores — ex: ferns b. Gymnosperms – seed bearing plants w/c do not produce flowers. — ex: cycads (pitogo), pine trees, & spruces c. Angiosperms – flowering plants that produce seeds — ex: gumamela, santan, etc.
B. Vascular plants – have conducting tissues a. Pteridophytes – produces spores — ex: ferns b. Gymnosperms – seed bearing plants w/c do not produce flowers. — ex: cycads (pitogo), pine trees, & spruces c. Angiosperms – flowering plants that produce seeds — ex: gumamela, santan, etc.
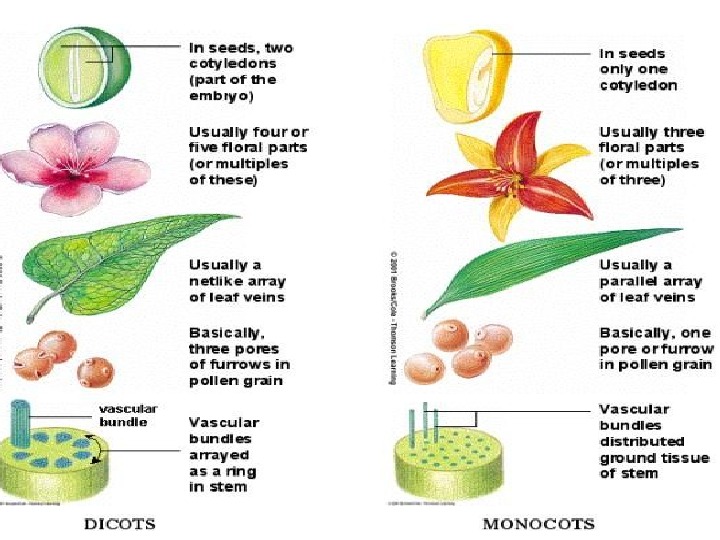
 Angiosperms Monocotyledonae (Monocot) — has one seed leaf or cotyledon Dicotyledonae (Dicot) — contains two seed leaves
Angiosperms Monocotyledonae (Monocot) — has one seed leaf or cotyledon Dicotyledonae (Dicot) — contains two seed leaves


