Current assets. Plan Enterprise current assets: essence, composition





































current_assets.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39
 Current assets
Current assets
 Plan Enterprise current assets: essence, composition and structure. Current assets rationing (normalization). Indicators and ways to improve the efficiency of enterprise current assets.
Plan Enterprise current assets: essence, composition and structure. Current assets rationing (normalization). Indicators and ways to improve the efficiency of enterprise current assets.
 Current assets Current assets – is a fund, directed on enterprise current assets financing, which is used by enterprise for providing continuity of production and sales process.
Current assets Current assets – is a fund, directed on enterprise current assets financing, which is used by enterprise for providing continuity of production and sales process.
 Working capital Working capital – is a complex of production revolving fund and fund turnover.
Working capital Working capital – is a complex of production revolving fund and fund turnover.
 Classification By location and role in production process: working capital in production (revolving fund) working capital in circulation areas (fund turnover) According to the sources of formation: own involved By means of planning or formation: normalized irregular
Classification By location and role in production process: working capital in production (revolving fund) working capital in circulation areas (fund turnover) According to the sources of formation: own involved By means of planning or formation: normalized irregular
 Revolving fund Revolving fund – is work items involved in only one production period for which their full cost is transferred on output value, thus changing their form, size, physical or chemical condition.
Revolving fund Revolving fund – is work items involved in only one production period for which their full cost is transferred on output value, thus changing their form, size, physical or chemical condition.
 Revolving fund Enterprise revolving fund has material and expensive forms. The following elements are included to the composition of revolving fund: inventory; work in progress / process (WIP) and semi finished products of own production; prepaid expenses.
Revolving fund Enterprise revolving fund has material and expensive forms. The following elements are included to the composition of revolving fund: inventory; work in progress / process (WIP) and semi finished products of own production; prepaid expenses.
 Inventory Inventory is the largest value of revolving fund. They include raw materials, basic and auxiliary materials, semi-finished products purchased, fuel and fuel containers, repair parts and components, little value tools, household equipment and other items as well as similar items which are rapidly used.
Inventory Inventory is the largest value of revolving fund. They include raw materials, basic and auxiliary materials, semi-finished products purchased, fuel and fuel containers, repair parts and components, little value tools, household equipment and other items as well as similar items which are rapidly used.
 Work in progress Work in progress— is work items, which processing (recycling) is not completed in a given enterprise manufacturing divisions. They are situated directly in workplace or during transportation from one workplace to another.
Work in progress Work in progress— is work items, which processing (recycling) is not completed in a given enterprise manufacturing divisions. They are situated directly in workplace or during transportation from one workplace to another.
 Prepaid expenses Prepaid expenses represent cash expenses that occur in that period of time, but reimbursed by the cost of production (works, services) in subsequent periods. They include the costs of production preparation, development of new products, rationalization and invention, acquisition of scientific and economic information, periodicals subscription, etc.
Prepaid expenses Prepaid expenses represent cash expenses that occur in that period of time, but reimbursed by the cost of production (works, services) in subsequent periods. They include the costs of production preparation, development of new products, rationalization and invention, acquisition of scientific and economic information, periodicals subscription, etc.
 Structure of production revolving fund Production revolving fund ratio in the opening of individual elements and stages of operation (inventory, work in progress, prepared expenses) describes their production technology (stage) structure. Production revolving fund structure will be different for different branches and enterprises: it depends on length of production cycles, the coefficient of variability, type of production, and labor intensive training to use
Structure of production revolving fund Production revolving fund ratio in the opening of individual elements and stages of operation (inventory, work in progress, prepared expenses) describes their production technology (stage) structure. Production revolving fund structure will be different for different branches and enterprises: it depends on length of production cycles, the coefficient of variability, type of production, and labor intensive training to use
 Fund turnover Fund turnover includes: finished goods, shipped and outstanding goods, money (in cash, accounts in banks) and money in the calculations (accounts receivable).
Fund turnover Fund turnover includes: finished goods, shipped and outstanding goods, money (in cash, accounts in banks) and money in the calculations (accounts receivable).
 Irregular working capital includes: shipped and outstanding goods; money; money in the calculations. All other оборотні засоби are normalized.
Irregular working capital includes: shipped and outstanding goods; money; money in the calculations. All other оборотні засоби are normalized.
 According to the sources of formation Own sources of current assets – are funds, formed while creating an enterprise, and involved – are funds, got as a credit, other types of accounts payable. Revenue – is a main source of current assets growth financing.
According to the sources of formation Own sources of current assets – are funds, formed while creating an enterprise, and involved – are funds, got as a credit, other types of accounts payable. Revenue – is a main source of current assets growth financing.
 Funds, that can be equated to own Special purpose financing Steel liabilities - are involved funds that does not formally belong to an enterprise, but are available to enterprises by acceptable payment system (transitional arrears from salary, payments to insurance funds, budget, etc.)
Funds, that can be equated to own Special purpose financing Steel liabilities - are involved funds that does not formally belong to an enterprise, but are available to enterprises by acceptable payment system (transitional arrears from salary, payments to insurance funds, budget, etc.)
 Normalization Normalization – is a process of determining required size of funds, that are invested in minimum reserves of inventory items to ensure continuous production process.
Normalization Normalization – is a process of determining required size of funds, that are invested in minimum reserves of inventory items to ensure continuous production process.
 Norms of working capital — is their minimal planned size, needed for normal enterprise functioning.
Norms of working capital — is their minimal planned size, needed for normal enterprise functioning.
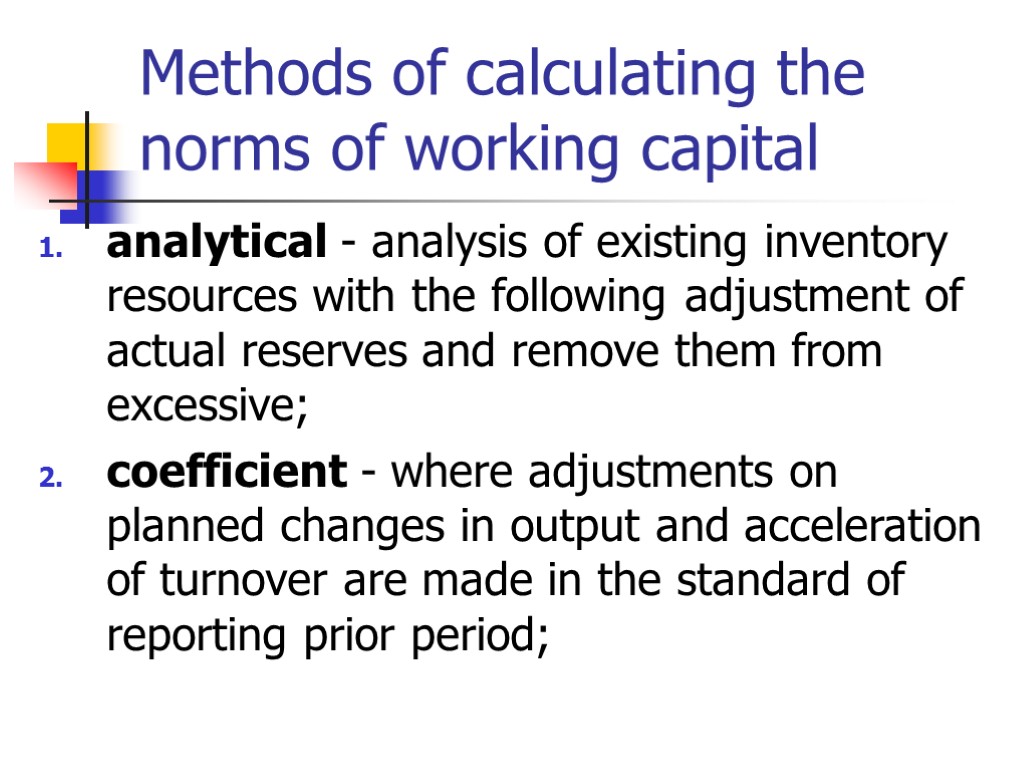
 Methods of calculating the norms of working capital analytical - analysis of existing inventory resources with the following adjustment of actual reserves and remove them from excessive; coefficient - where adjustments on planned changes in output and acceleration of turnover are made in the standard of reporting prior period;
Methods of calculating the norms of working capital analytical - analysis of existing inventory resources with the following adjustment of actual reserves and remove them from excessive; coefficient - where adjustments on planned changes in output and acceleration of turnover are made in the standard of reporting prior period;
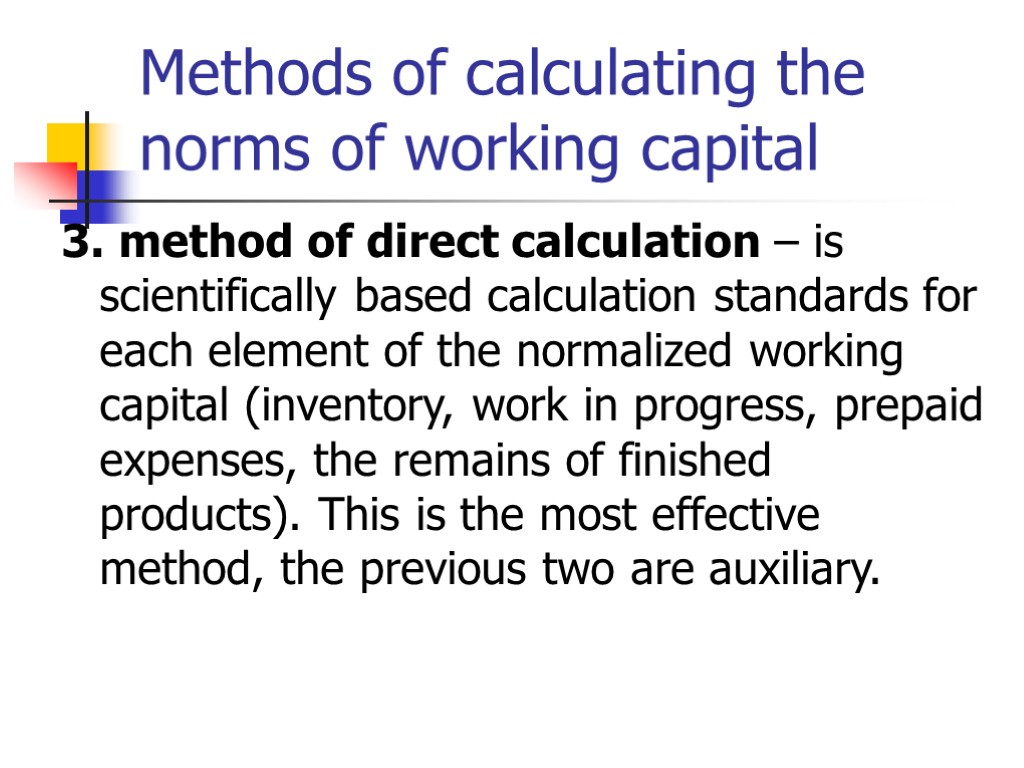
 Methods of calculating the norms of working capital 3. method of direct calculation – is scientifically based calculation standards for each element of the normalized working capital (inventory, work in progress, prepaid expenses, the remains of finished products). This is the most effective method, the previous two are auxiliary.
Methods of calculating the norms of working capital 3. method of direct calculation – is scientifically based calculation standards for each element of the normalized working capital (inventory, work in progress, prepaid expenses, the remains of finished products). This is the most effective method, the previous two are auxiliary.
 While setting the rates of working capital it is necessary to consider dependence of norms on the following factors: duration of the production cycle of goods manufacturing; conditions of supply (supply interval duration, size of the parties that are supplied); remoteness from suppliers to consumers; transportation speed, type and continuity of transport work; time of materials preparation for their running into production; periodicity of materials running into production; sales conditions; systems and forms of payments, speed of documents circulation, possibility of factoring use.
While setting the rates of working capital it is necessary to consider dependence of norms on the following factors: duration of the production cycle of goods manufacturing; conditions of supply (supply interval duration, size of the parties that are supplied); remoteness from suppliers to consumers; transportation speed, type and continuity of transport work; time of materials preparation for their running into production; periodicity of materials running into production; sales conditions; systems and forms of payments, speed of documents circulation, possibility of factoring use.
 The following elements of working capital are standardized: inventory; work in progress; prepaid expenses; finished goods.
The following elements of working capital are standardized: inventory; work in progress; prepaid expenses; finished goods.
 Norm of working capital in inventory is determined by multiplication the value of daily materials consumption to its norm in days
Norm of working capital in inventory is determined by multiplication the value of daily materials consumption to its norm in days
 Norm of working capital in inventory Qр - річний обсяг виробництва, шт.; Д - кількість календарних днів у плановому періоді, дн; qн - норма витрати матеріалу на 1 виріб, кг/вироб; Ц - ціна матеріалу, грн. Тп - проміжок між 2 постачаннями, дн.; Тстрах – страховий запас, дн.
Norm of working capital in inventory Qр - річний обсяг виробництва, шт.; Д - кількість календарних днів у плановому періоді, дн; qн - норма витрати матеріалу на 1 виріб, кг/вироб; Ц - ціна матеріалу, грн. Тп - проміжок між 2 постачаннями, дн.; Тстрах – страховий запас, дн.
 Types of stock transport, preparatory (technology), current, reserve.
Types of stock transport, preparatory (technology), current, reserve.
 Transport stock Transport stock (normally does not exceed two days) after the payment period to suppliers account before goods arrival at enterprise warehouse.
Transport stock Transport stock (normally does not exceed two days) after the payment period to suppliers account before goods arrival at enterprise warehouse.
 Preparatory stock Preparatory stock – time required for receiving, storing and preparation for productive use of resources. Is determined by calculation or by actual time of the reporting period, adjusted to changing conditions, (mechanization of goods handling, improvement of control methods, etc.).
Preparatory stock Preparatory stock – time required for receiving, storing and preparation for productive use of resources. Is determined by calculation or by actual time of the reporting period, adjusted to changing conditions, (mechanization of goods handling, improvement of control methods, etc.).
 Current stock Current stock – is the main type of reserve that is required to ensure uninterrupted production in the period between two ordinary deliveries. The value of this stock is calculated within the middle half of the interval between the supply of certain resources (for example, if contract between consumer and supplier is for a month, then every stock must provide 15 days of work).
Current stock Current stock – is the main type of reserve that is required to ensure uninterrupted production in the period between two ordinary deliveries. The value of this stock is calculated within the middle half of the interval between the supply of certain resources (for example, if contract between consumer and supplier is for a month, then every stock must provide 15 days of work).
 Reserve (insurance) stock Reserve (insurance) stock – is determined by the average deviation from an actual date of delivery marked in contract or by the period necessary for immediate ordering and delivery of materials from producer to consumer.
Reserve (insurance) stock Reserve (insurance) stock – is determined by the average deviation from an actual date of delivery marked in contract or by the period necessary for immediate ordering and delivery of materials from producer to consumer.
 Norms of working capital for work in progress Qр - річний обсяг виробництва, шт; Д - кількість календарних днів у плановому періоді, дн; Сп - повна собівартість даного виробу, грн. Кн.в. - коефіцієнт наростання витрат; Тц - тривалість виробничого циклу виготовлення виробів, дн;
Norms of working capital for work in progress Qр - річний обсяг виробництва, шт; Д - кількість календарних днів у плановому періоді, дн; Сп - повна собівартість даного виробу, грн. Кн.в. - коефіцієнт наростання витрат; Тц - тривалість виробничого циклу виготовлення виробів, дн;
 Growth factor cost де См – матеріальні витрати у собівартості, грн.; Сп – повна собівартість даного виробу, грн.
Growth factor cost де См – матеріальні витрати у собівартості, грн.; Сп – повна собівартість даного виробу, грн.
 Norms of working capital in prepaid expenses НБП = РБН + РП - РВ де РБН — сума засобів, вкладених у витрати майбутніх періодів, на початок планового року; Рп — витрати на даний плановий період по кошторису; Рв — витрати, що включаються в собівартість продукції планового періоду по кошторису витрат на виробництво.
Norms of working capital in prepaid expenses НБП = РБН + РП - РВ де РБН — сума засобів, вкладених у витрати майбутніх періодів, на початок планового року; Рп — витрати на даний плановий період по кошторису; Рв — витрати, що включаються в собівартість продукції планового періоду по кошторису витрат на виробництво.
 Norms for finished goods Нгот - норма наявності готової продукції, дн.
Norms for finished goods Нгот - норма наявності готової продукції, дн.
 Effectiveness of working capital use turnover ratio load factor duration of one turnover profitability
Effectiveness of working capital use turnover ratio load factor duration of one turnover profitability
 Turnover ratio Turnover ratio (quantity of turnovers) – is determined by dividing cost of sales over a period on average balance of current assets over the same period. Коб=Qр/Sоз Qр – обсяг реалізації продукції у вартісних одиницях Sоз – середньорічний залишок оборотних засобів
Turnover ratio Turnover ratio (quantity of turnovers) – is determined by dividing cost of sales over a period on average balance of current assets over the same period. Коб=Qр/Sоз Qр – обсяг реалізації продукції у вартісних одиницях Sоз – середньорічний залишок оборотних засобів
 Load factor Load factor – shows how much working capital account for each currency of sales, this is figure turned to turnover ratio. Кз=1/Коб
Load factor Load factor – shows how much working capital account for each currency of sales, this is figure turned to turnover ratio. Кз=1/Коб
 Duration of one turnover Duration of one turnover in days (speed of turnover) – correlation of days in related period (quarter – 90, year - 360) and turnover ratio for the same time. То=Т/Коб Т – кількість днів в періоді Quantity of days in month – 30, quarter - 90, year – 360.
Duration of one turnover Duration of one turnover in days (speed of turnover) – correlation of days in related period (quarter – 90, year - 360) and turnover ratio for the same time. То=Т/Коб Т – кількість днів в періоді Quantity of days in month – 30, quarter - 90, year – 360.
 Profitability Profitability – ratio of enterprise profits to its working capital.
Profitability Profitability – ratio of enterprise profits to its working capital.
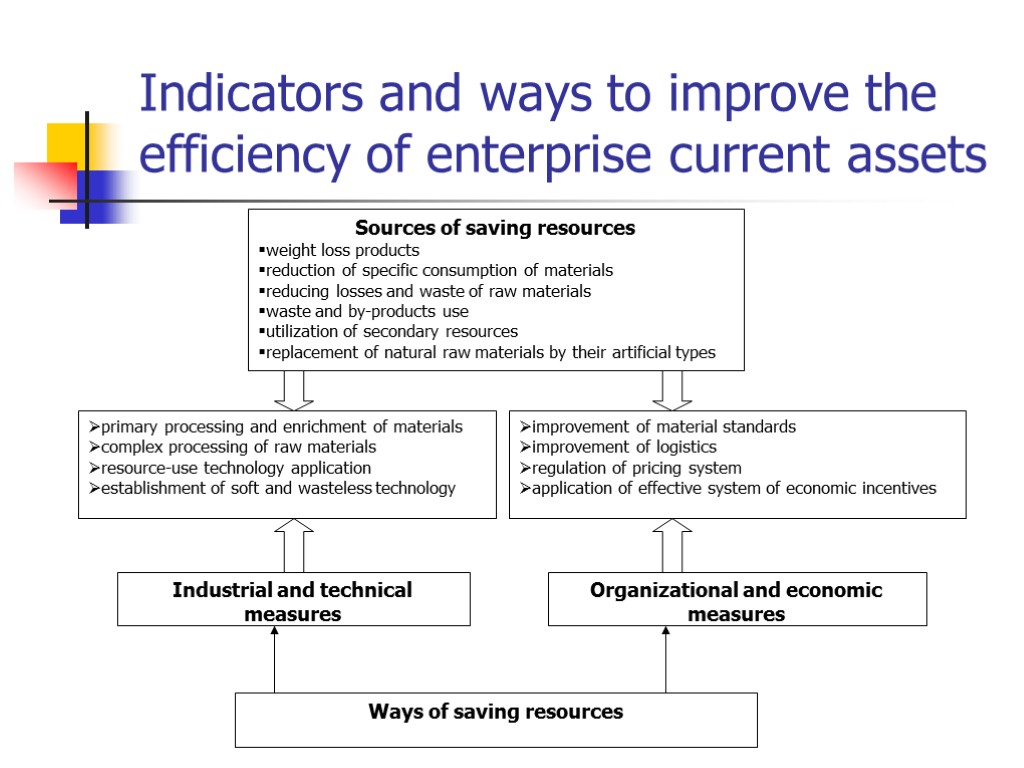
 Indicators and ways to improve the efficiency of enterprise current assets
Indicators and ways to improve the efficiency of enterprise current assets


