8 Congenital heart disease.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 68
 Congenital Heart Disease
Congenital Heart Disease
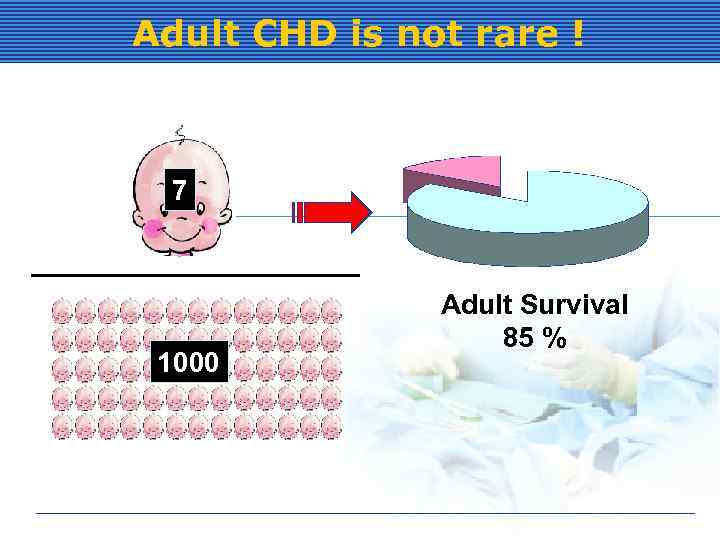 Adult CHD is not rare ! 7 1000 Adult Survival 85 %
Adult CHD is not rare ! 7 1000 Adult Survival 85 %
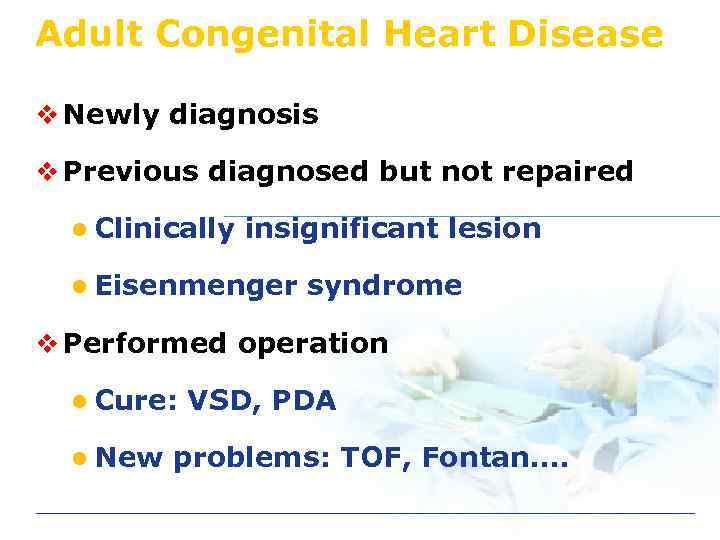 Adult Congenital Heart Disease v Newly diagnosis v Previous diagnosed but not repaired l Clinically insignificant lesion l Eisenmenger syndrome v Performed operation l Cure: l New VSD, PDA problems: TOF, Fontan….
Adult Congenital Heart Disease v Newly diagnosis v Previous diagnosed but not repaired l Clinically insignificant lesion l Eisenmenger syndrome v Performed operation l Cure: l New VSD, PDA problems: TOF, Fontan….
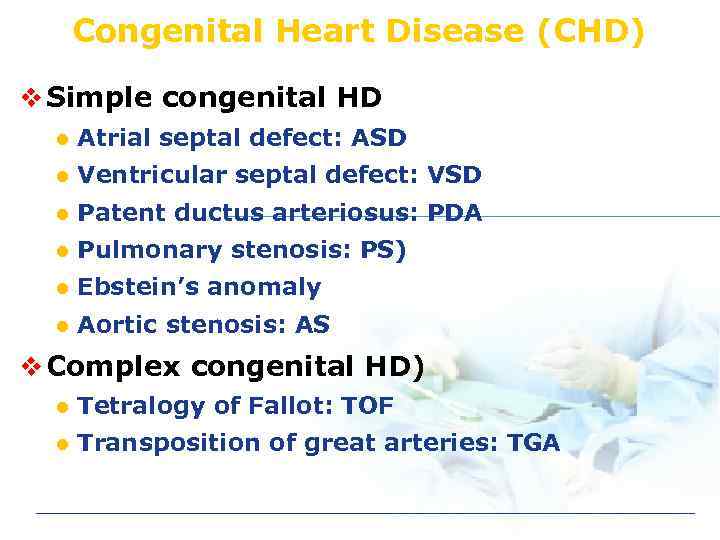 Congenital Heart Disease (CHD) v Simple congenital HD l Atrial septal defect: ASD l Ventricular septal defect: VSD l Patent ductus arteriosus: PDA l Pulmonary stenosis: PS) l Ebstein’s anomaly l Aortic stenosis: AS v Complex congenital HD) l Tetralogy of Fallot: TOF l Transposition of great arteries: TGA
Congenital Heart Disease (CHD) v Simple congenital HD l Atrial septal defect: ASD l Ventricular septal defect: VSD l Patent ductus arteriosus: PDA l Pulmonary stenosis: PS) l Ebstein’s anomaly l Aortic stenosis: AS v Complex congenital HD) l Tetralogy of Fallot: TOF l Transposition of great arteries: TGA
 Clinical Problems in CHD v Heart failure v Infective endocarditis v Pulmonary hypertension (PHT)
Clinical Problems in CHD v Heart failure v Infective endocarditis v Pulmonary hypertension (PHT)
 Echo in congenital disease v Diagnosis v Severity l Prognosis l Decision of treatment - OP v Combined anomaly v Evaluaion of cardiac function
Echo in congenital disease v Diagnosis v Severity l Prognosis l Decision of treatment - OP v Combined anomaly v Evaluaion of cardiac function
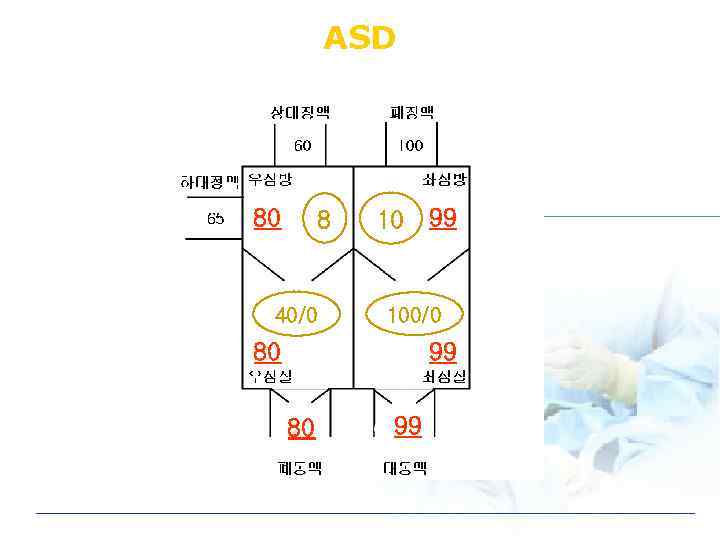 ASD 80 8 40/0 10 99 100/0 80 99
ASD 80 8 40/0 10 99 100/0 80 99
 Diagnosis of ASD v Clinical features l Dyspnea, Cardiomegaly, Atrial fibrillation v Direct findings l Identification l Confirm of shunt: 2 D echo of shunt: Doppler v Indirect findings l Volume overloading of Rt heart - Enlargement of RV, RA, PV l Pulmonary hypertension
Diagnosis of ASD v Clinical features l Dyspnea, Cardiomegaly, Atrial fibrillation v Direct findings l Identification l Confirm of shunt: 2 D echo of shunt: Doppler v Indirect findings l Volume overloading of Rt heart - Enlargement of RV, RA, PV l Pulmonary hypertension
 Echo in ASD v When we suspect ASD? v How we diagnose ASD? v What is type of ASD? v How severe ASD? • Enlargement of RV, RA, PV • Pulmonary hypertension: TR jet velocity • Qp/Qs v Combined congenital anomaly v ASD size
Echo in ASD v When we suspect ASD? v How we diagnose ASD? v What is type of ASD? v How severe ASD? • Enlargement of RV, RA, PV • Pulmonary hypertension: TR jet velocity • Qp/Qs v Combined congenital anomaly v ASD size
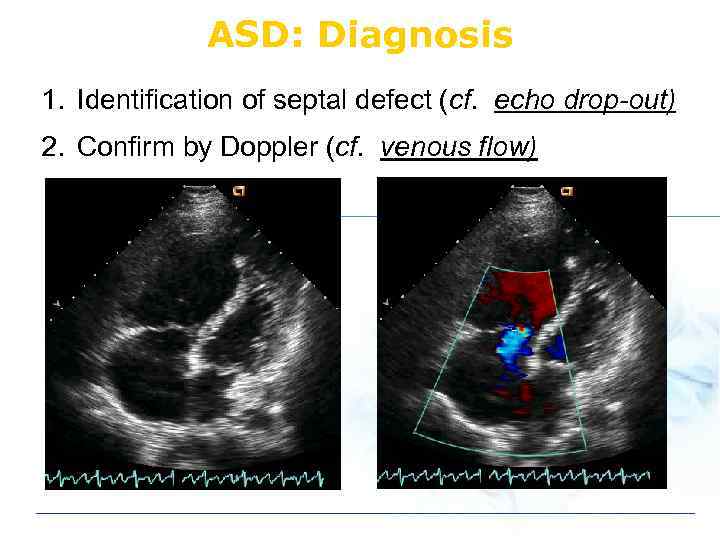 ASD: Diagnosis 1. Identification of septal defect (cf. echo drop-out) 2. Confirm by Doppler (cf. venous flow)
ASD: Diagnosis 1. Identification of septal defect (cf. echo drop-out) 2. Confirm by Doppler (cf. venous flow)
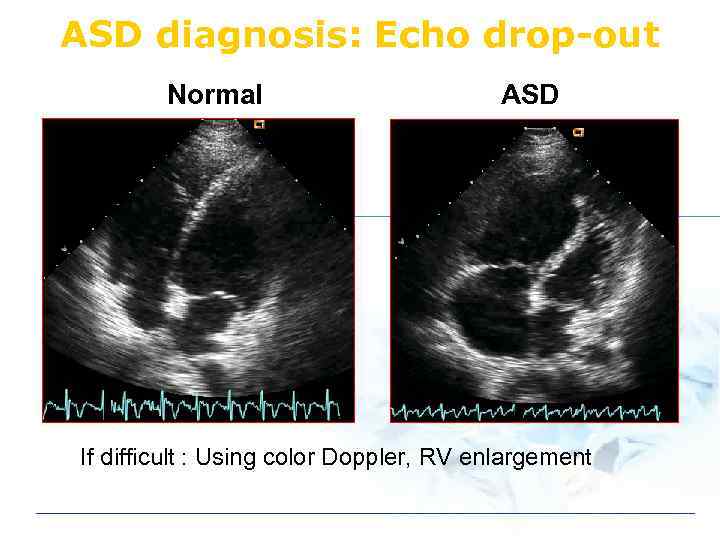 ASD diagnosis: Echo drop-out Normal ASD If difficult : Using color Doppler, RV enlargement
ASD diagnosis: Echo drop-out Normal ASD If difficult : Using color Doppler, RV enlargement
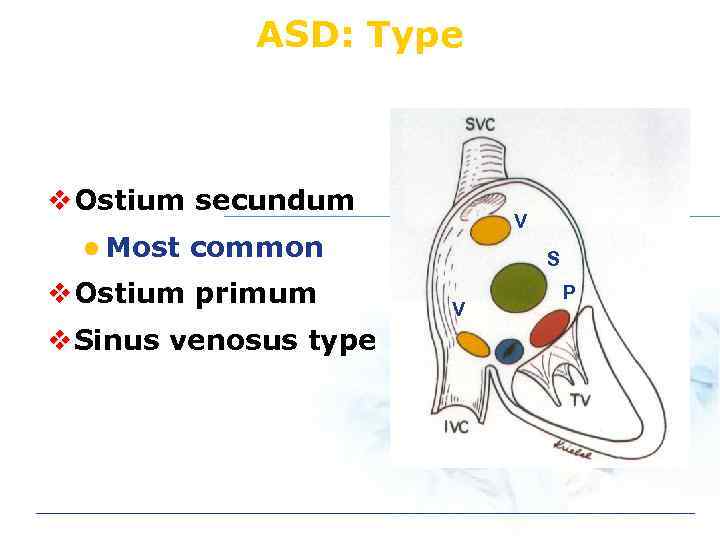 ASD: Type v Ostium secundum l Most V common v Ostium primum v Sinus venosus type S V P
ASD: Type v Ostium secundum l Most V common v Ostium primum v Sinus venosus type S V P
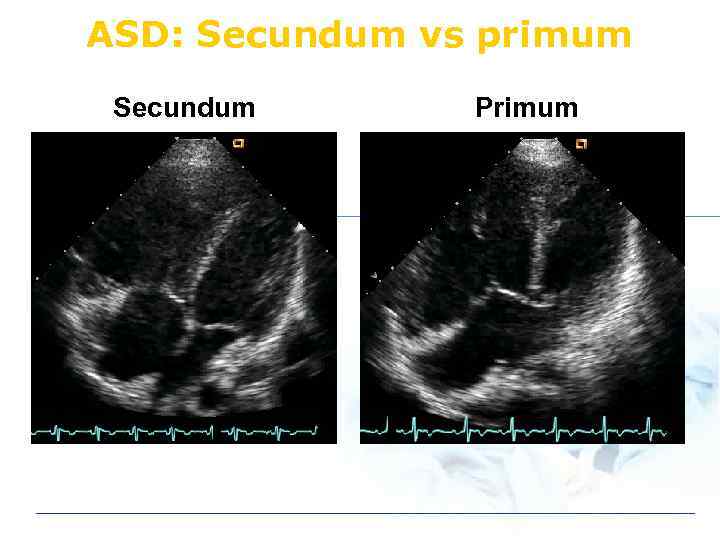 ASD: Secundum vs primum Secundum Primum
ASD: Secundum vs primum Secundum Primum
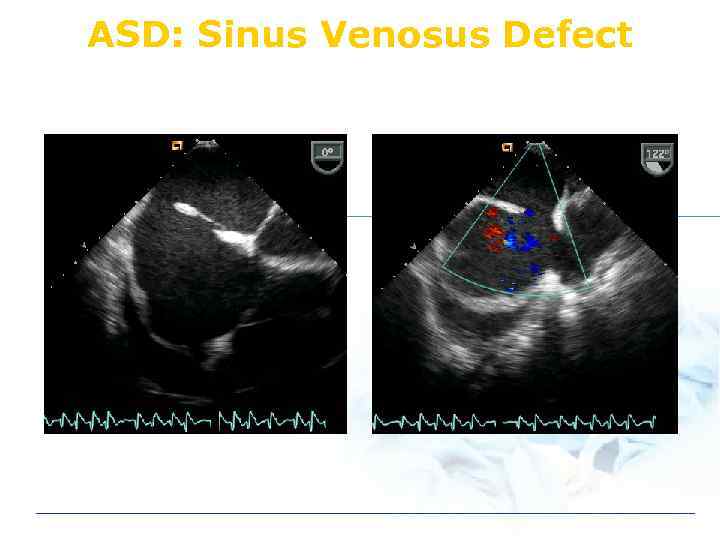 ASD: Sinus Venosus Defect
ASD: Sinus Venosus Defect
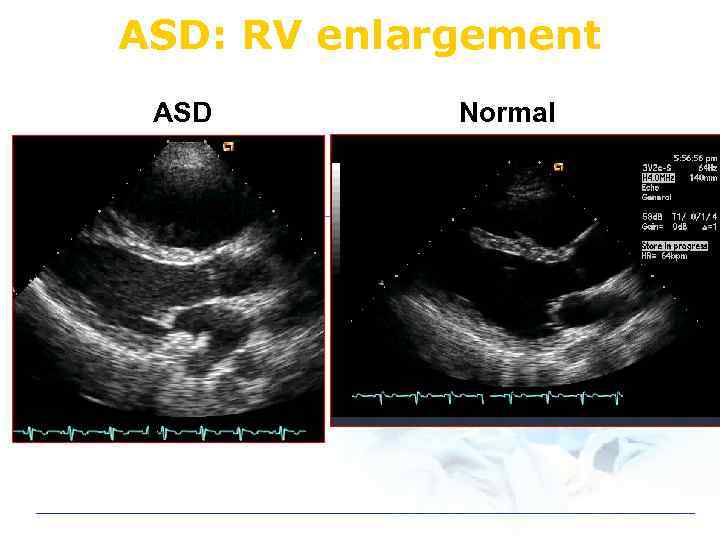 ASD: RV enlargement ASD Normal
ASD: RV enlargement ASD Normal
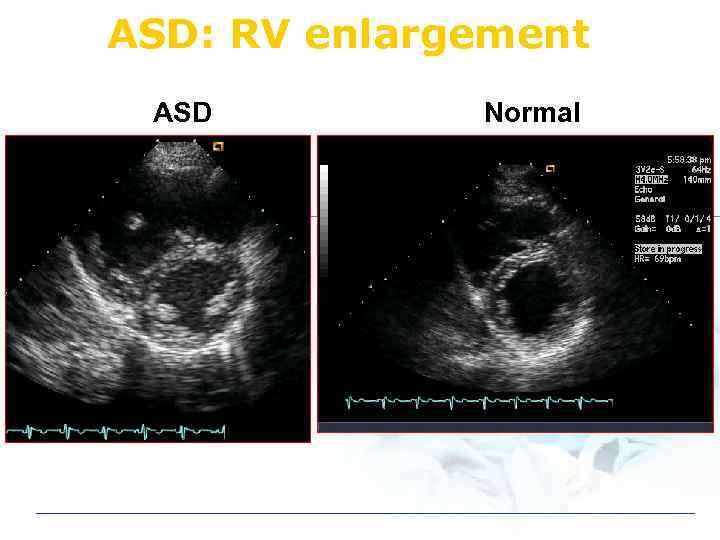 ASD: RV enlargement ASD Normal
ASD: RV enlargement ASD Normal
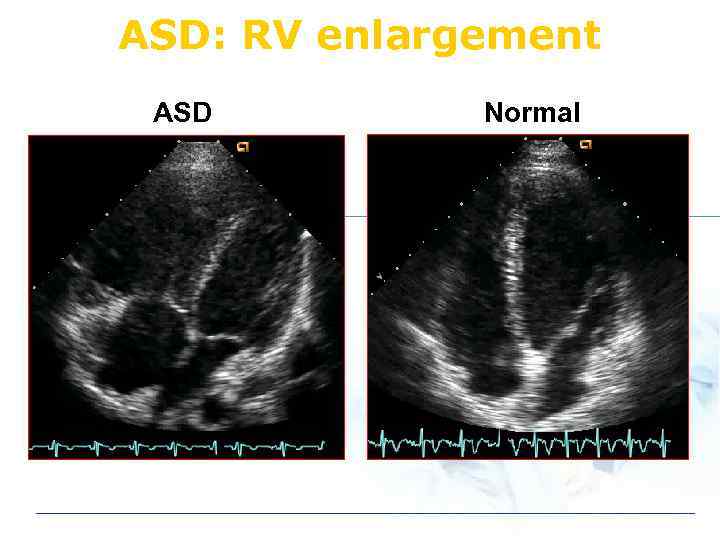 ASD: RV enlargement ASD Normal
ASD: RV enlargement ASD Normal
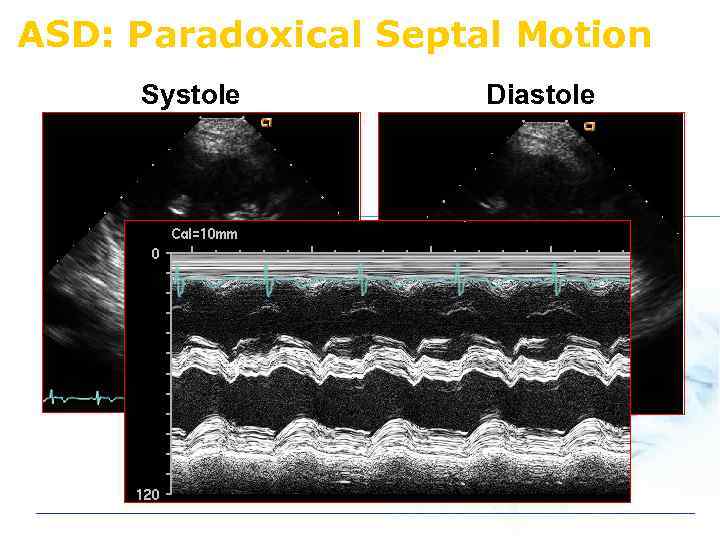 ASD: Paradoxical Septal Motion Systole Diastole
ASD: Paradoxical Septal Motion Systole Diastole
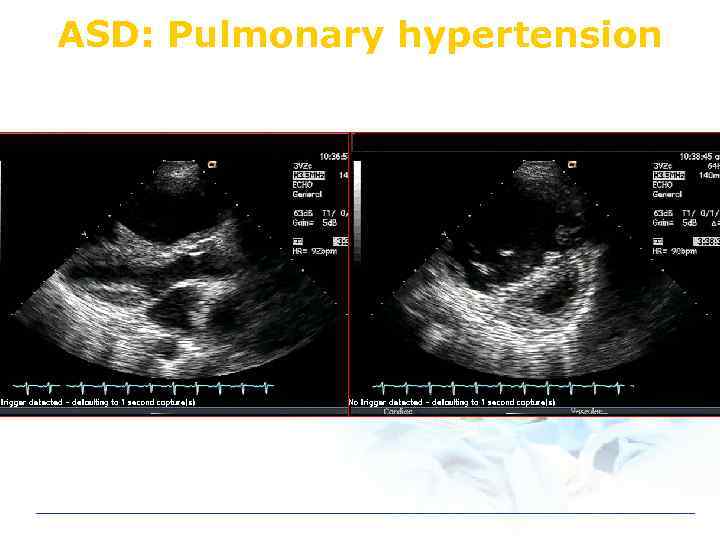 ASD: Pulmonary hypertension
ASD: Pulmonary hypertension
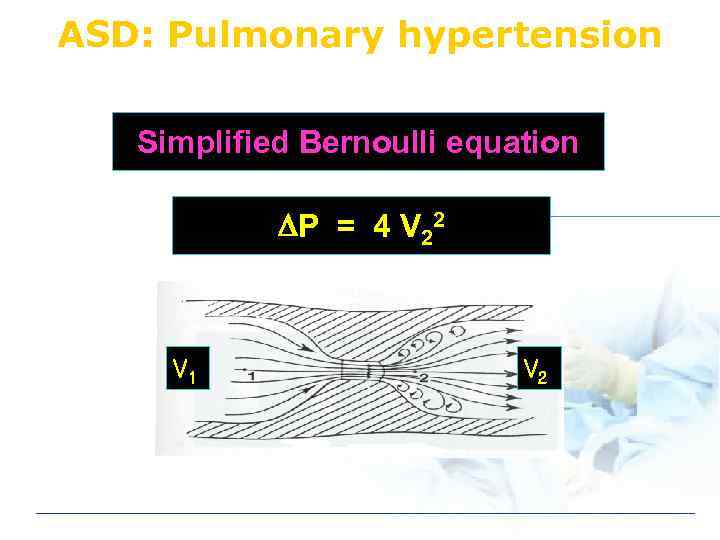 ASD: Pulmonary hypertension Simplified Bernoulli equation P = 4 V 22 V 1 V 2
ASD: Pulmonary hypertension Simplified Bernoulli equation P = 4 V 22 V 1 V 2
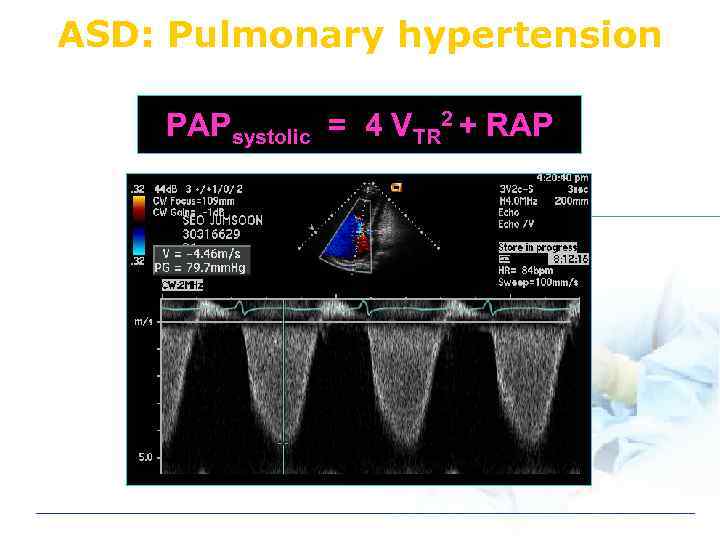 ASD: Pulmonary hypertension PAPsystolic = 4 VTR 2 + RAP
ASD: Pulmonary hypertension PAPsystolic = 4 VTR 2 + RAP
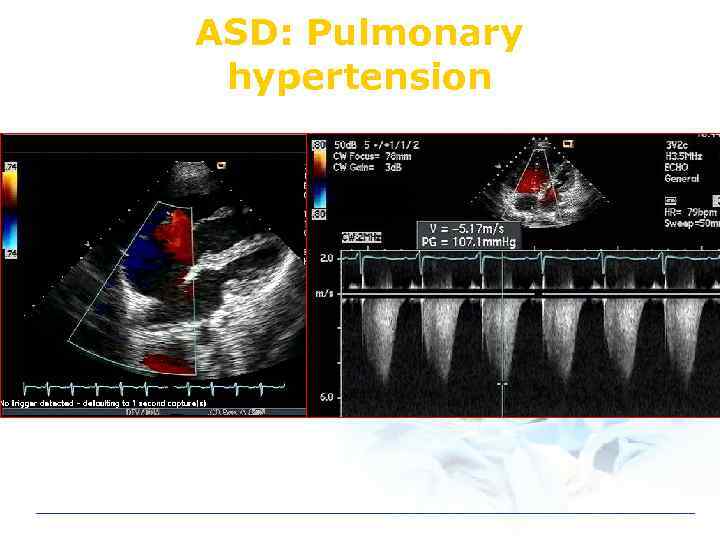 ASD: Pulmonary hypertension
ASD: Pulmonary hypertension
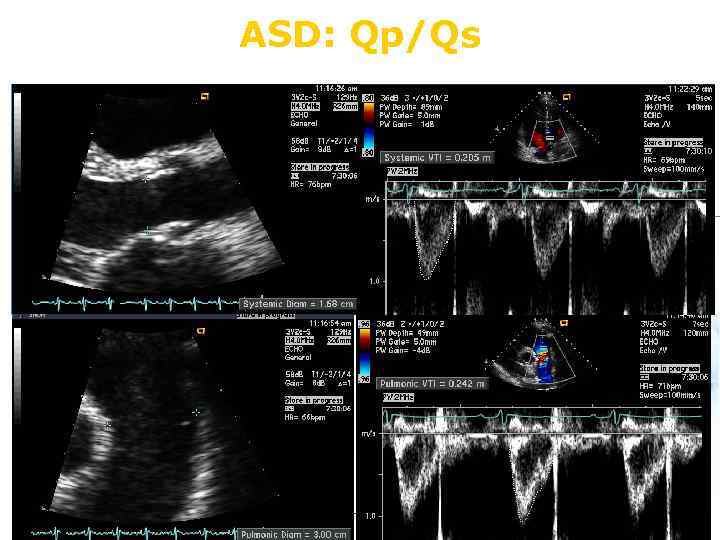 ASD: Qp/Qs
ASD: Qp/Qs
 ASD: Combined anomaly v. Secundum ASD l mitral valve prolapse v. Primum ASD l cleft mitral valve v. Sinus venosus defect l anomalous return pulmonary venous
ASD: Combined anomaly v. Secundum ASD l mitral valve prolapse v. Primum ASD l cleft mitral valve v. Sinus venosus defect l anomalous return pulmonary venous
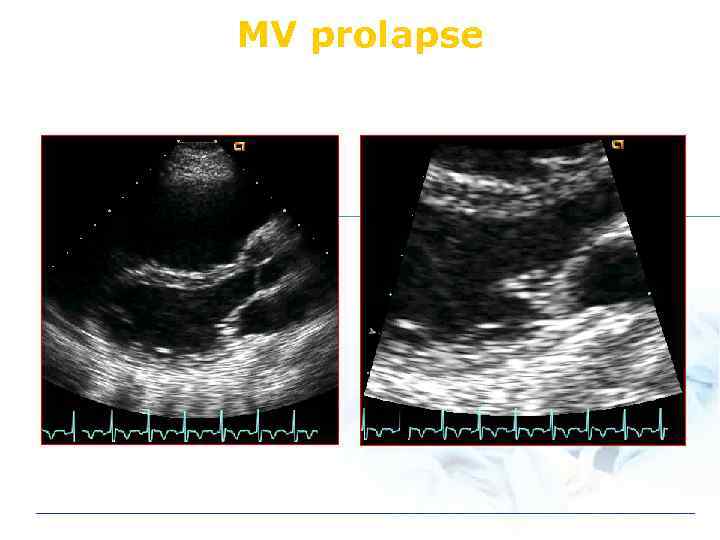 MV prolapse
MV prolapse
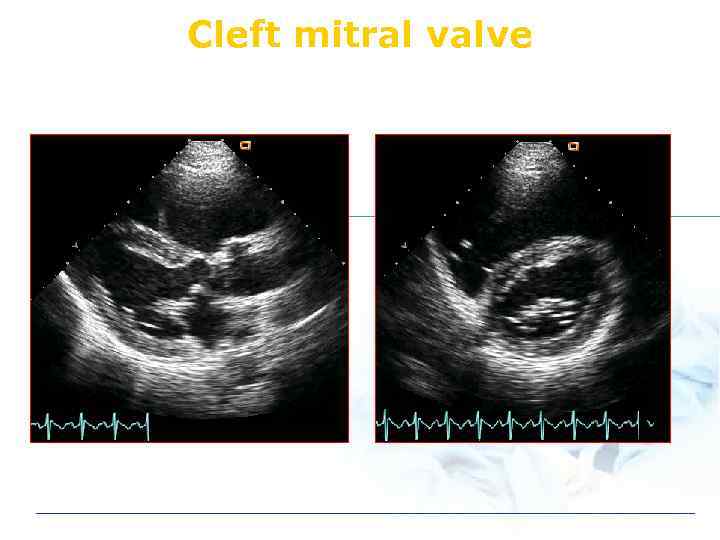 Cleft mitral valve
Cleft mitral valve
 ASD: Treatment v Medical treatment l Endocarditis prophylaxis: not recommended v Surgical treatment l Indication: l Device Qp/Qs 2. 0 closure: secundum ASD l Contraindication Severe pulmonary hypertension
ASD: Treatment v Medical treatment l Endocarditis prophylaxis: not recommended v Surgical treatment l Indication: l Device Qp/Qs 2. 0 closure: secundum ASD l Contraindication Severe pulmonary hypertension
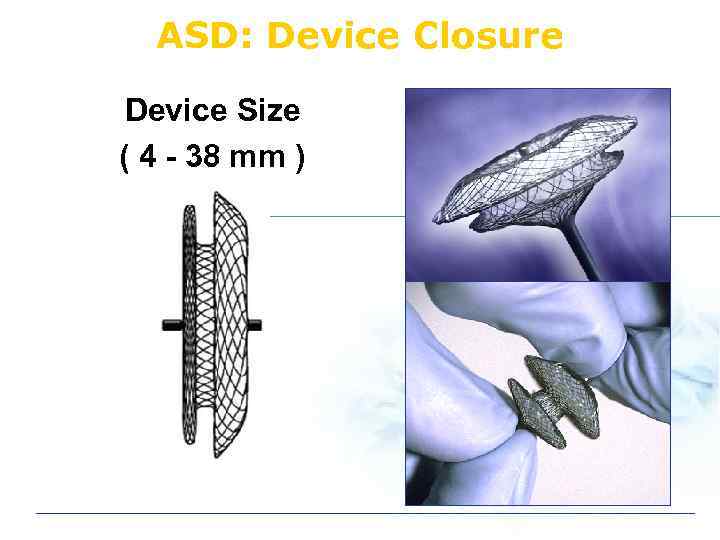 ASD: Device Closure Device Size ( 4 - 38 mm )
ASD: Device Closure Device Size ( 4 - 38 mm )
 Case: 45/Male, Dyspnea
Case: 45/Male, Dyspnea
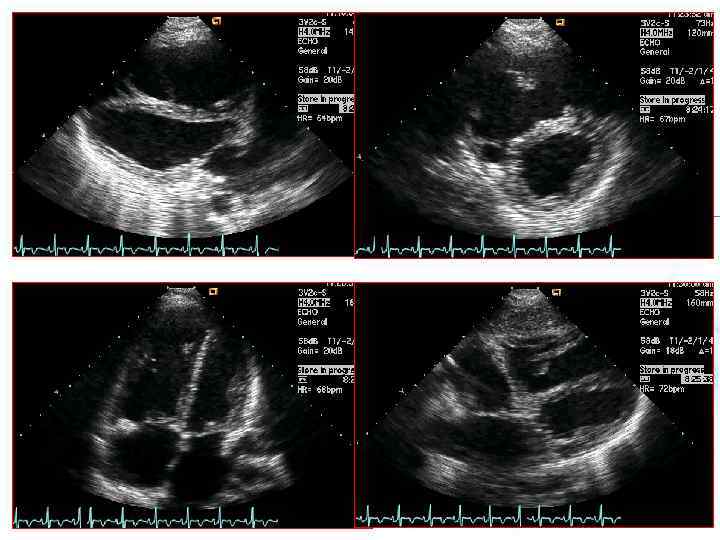
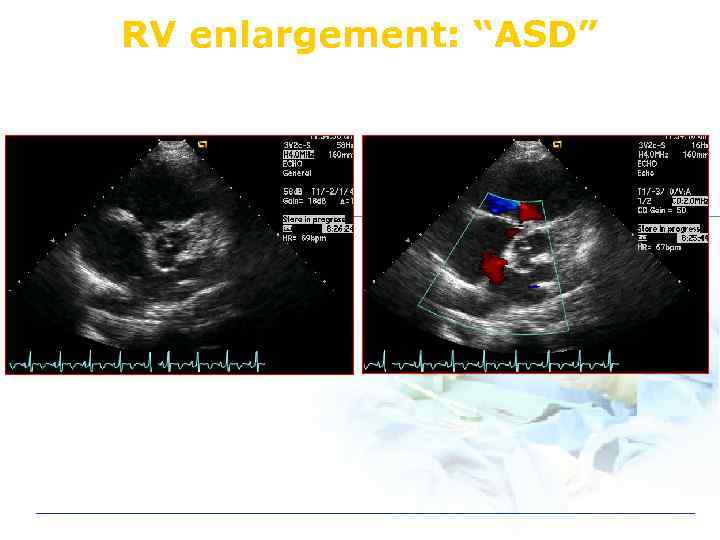 RV enlargement: “ASD”
RV enlargement: “ASD”
 Echo in ASD v Unknown origin RV & RA enlargement v TEE in sinus venosus defect
Echo in ASD v Unknown origin RV & RA enlargement v TEE in sinus venosus defect
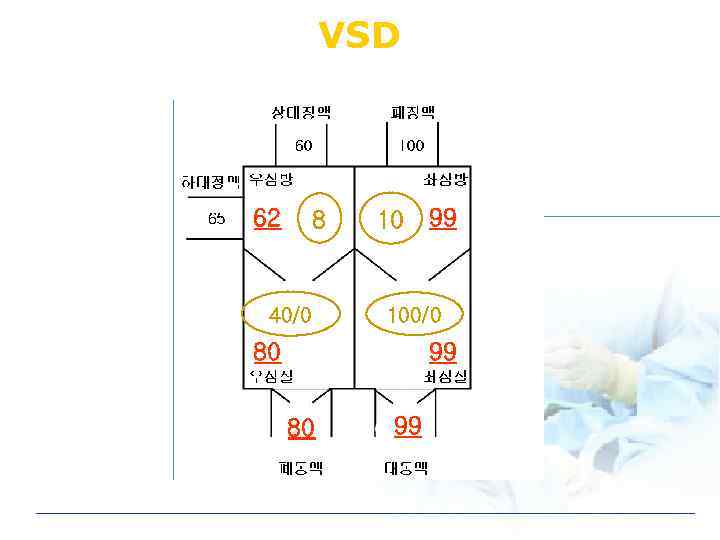 VSD 62 8 40/0 10 99 100/0 80 99
VSD 62 8 40/0 10 99 100/0 80 99
 Echo diagnosis of VSD v Clinical features l Pansystolic murmur v Direct findings l Identify septal defect l Confirm Lt to Rt shunt v Indirect findings l Rt heart volume overloadng - Enlargement of RV l Pulmonary hypertension
Echo diagnosis of VSD v Clinical features l Pansystolic murmur v Direct findings l Identify septal defect l Confirm Lt to Rt shunt v Indirect findings l Rt heart volume overloadng - Enlargement of RV l Pulmonary hypertension
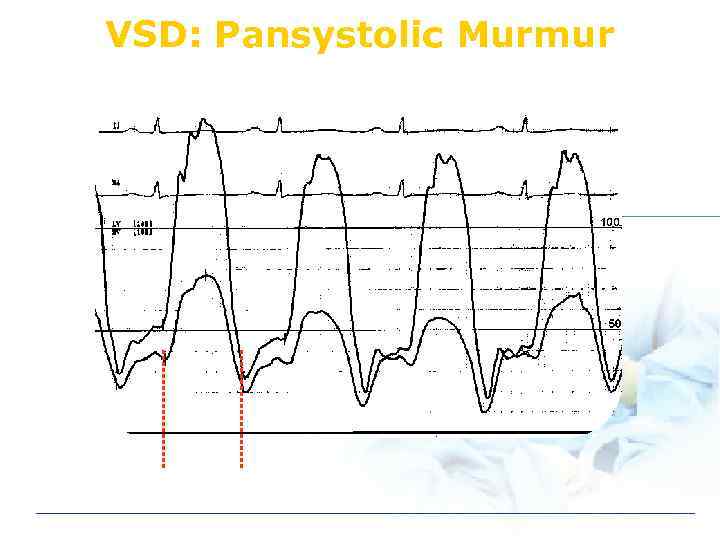 VSD: Pansystolic Murmur
VSD: Pansystolic Murmur
 Echo in VSD v When we suspect VSD? v Diagnosis of VSD? v What type of VSD? v How severe VSD? l RV size & function l Pulmonary hypertension: TR jet vs VSD jet l Qp/Qs v Combined anomaly: AV prolapse, AR
Echo in VSD v When we suspect VSD? v Diagnosis of VSD? v What type of VSD? v How severe VSD? l RV size & function l Pulmonary hypertension: TR jet vs VSD jet l Qp/Qs v Combined anomaly: AV prolapse, AR
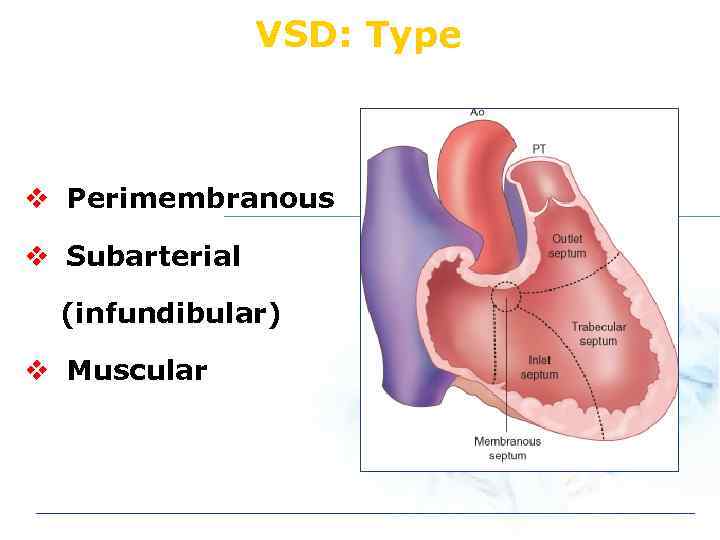 VSD: Type v Perimembranous v Subarterial (infundibular) v Muscular
VSD: Type v Perimembranous v Subarterial (infundibular) v Muscular
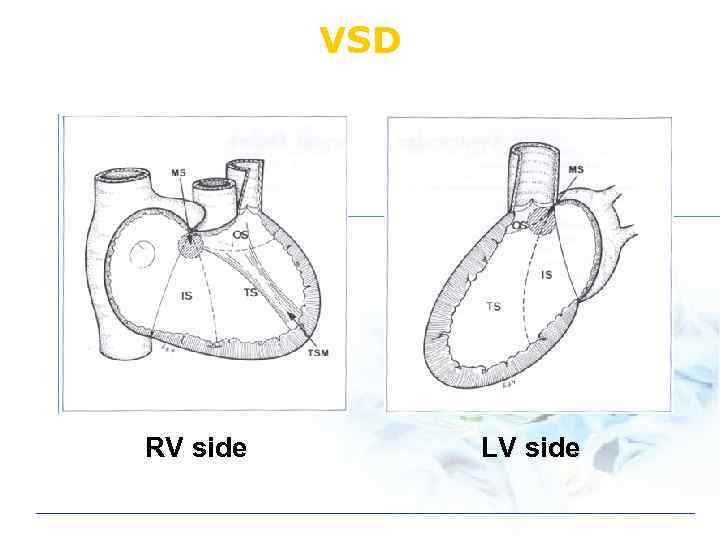 VSD RV side LV side
VSD RV side LV side
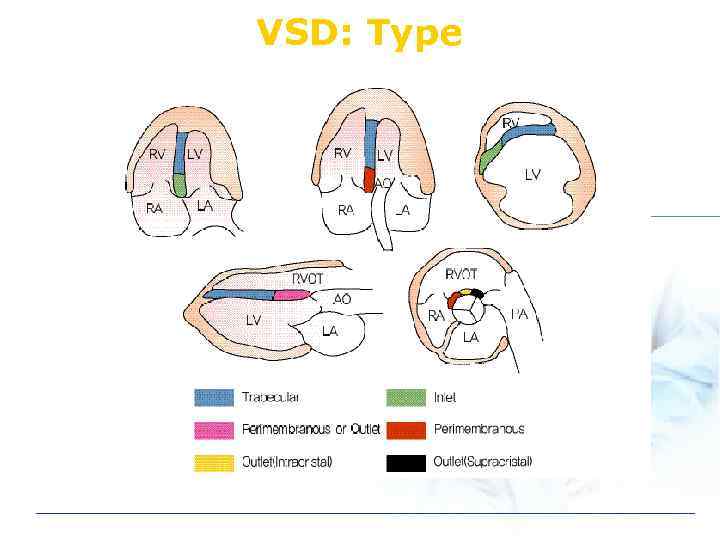 VSD: Type
VSD: Type
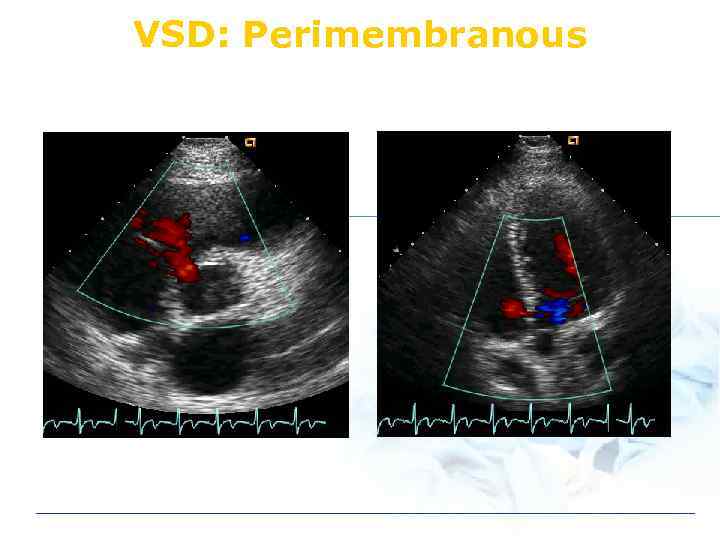 VSD: Perimembranous
VSD: Perimembranous
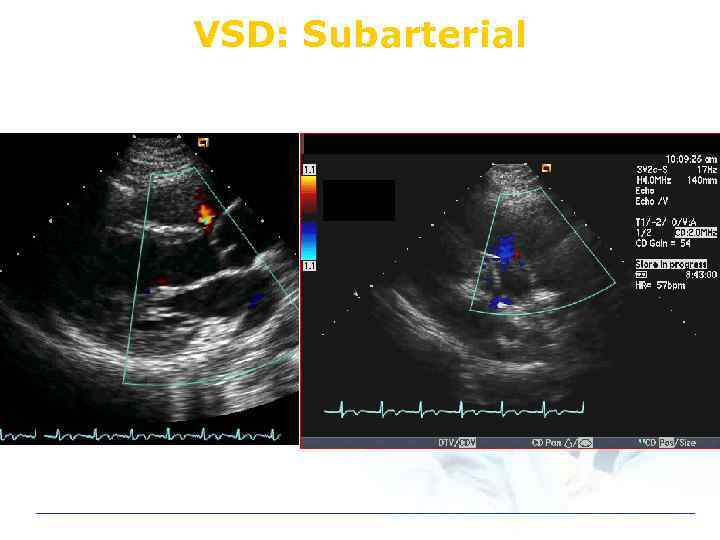 VSD: Subarterial
VSD: Subarterial
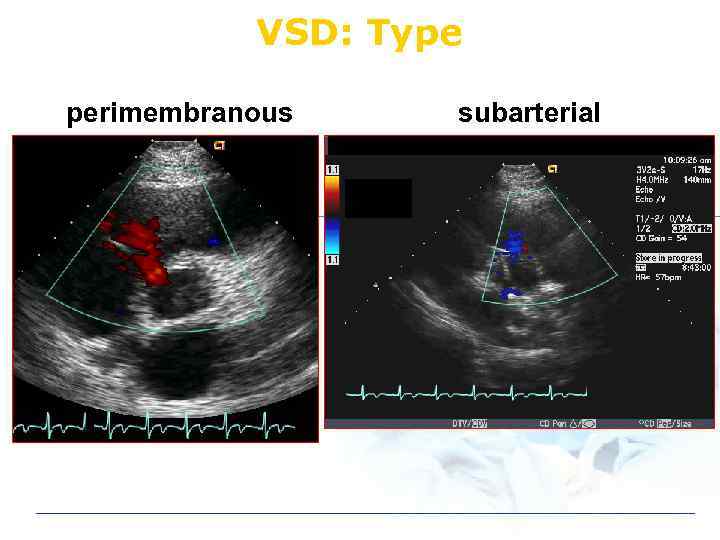 VSD: Type perimembranous subarterial
VSD: Type perimembranous subarterial
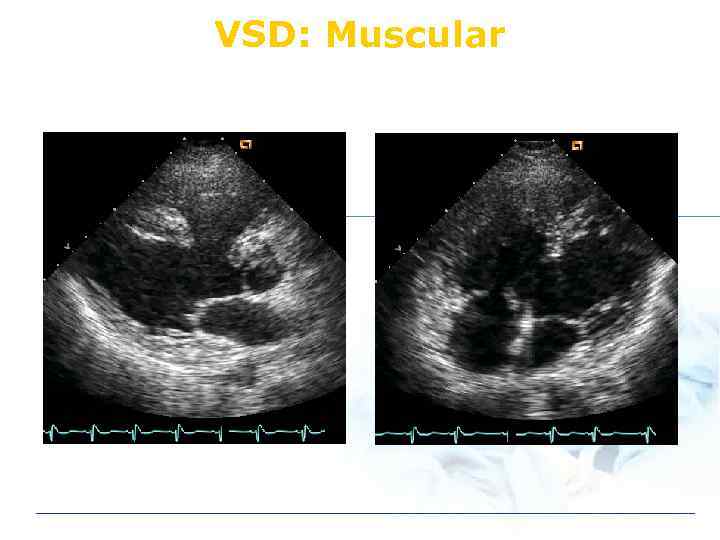 VSD: Muscular
VSD: Muscular
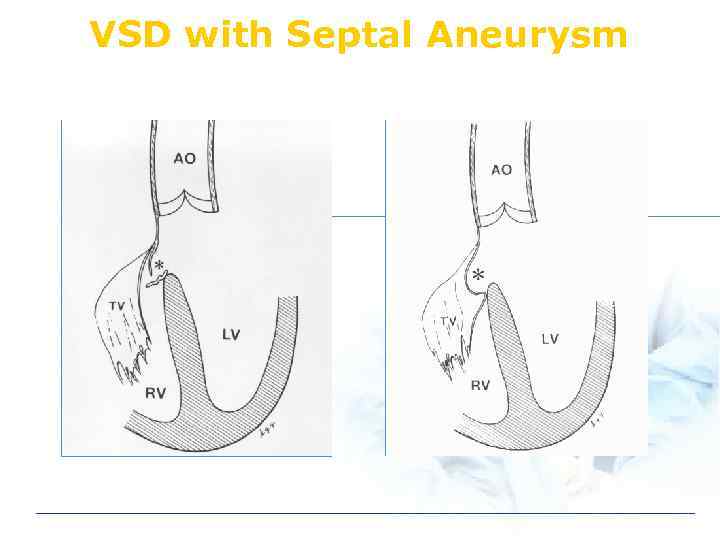 VSD with Septal Aneurysm
VSD with Septal Aneurysm
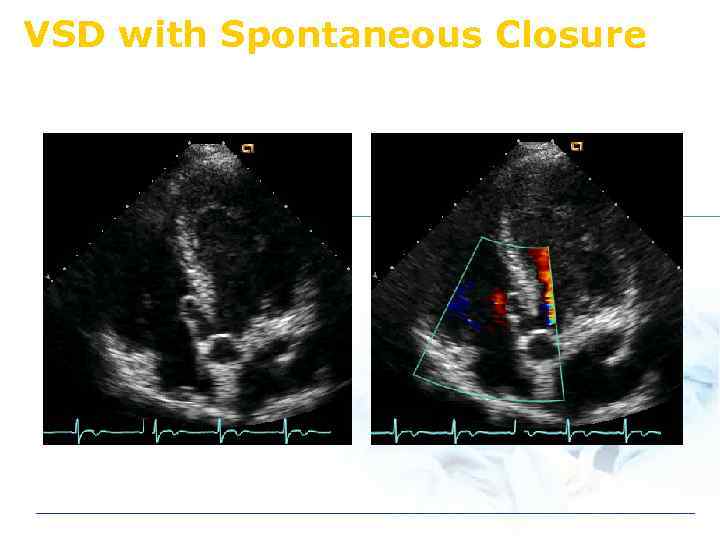 VSD with Spontaneous Closure
VSD with Spontaneous Closure
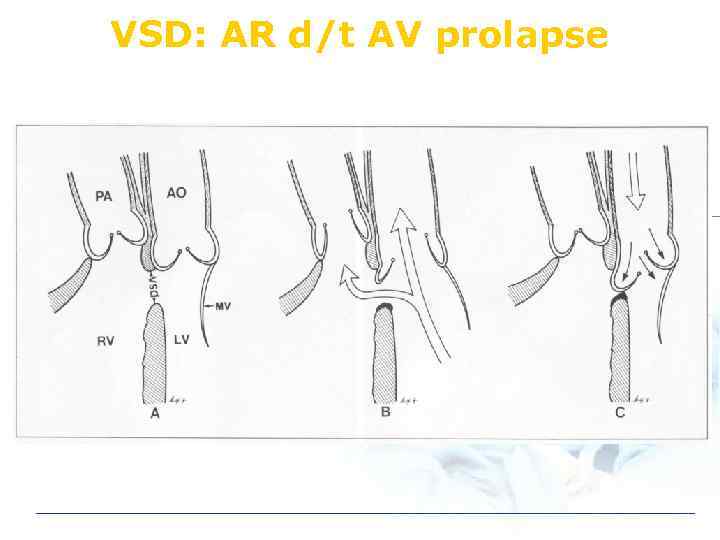 VSD: AR d/t AV prolapse
VSD: AR d/t AV prolapse
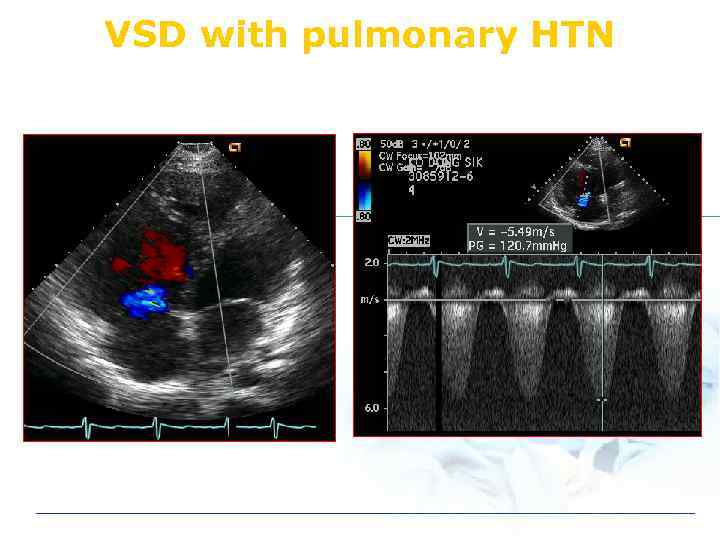 VSD with pulmonary HTN
VSD with pulmonary HTN
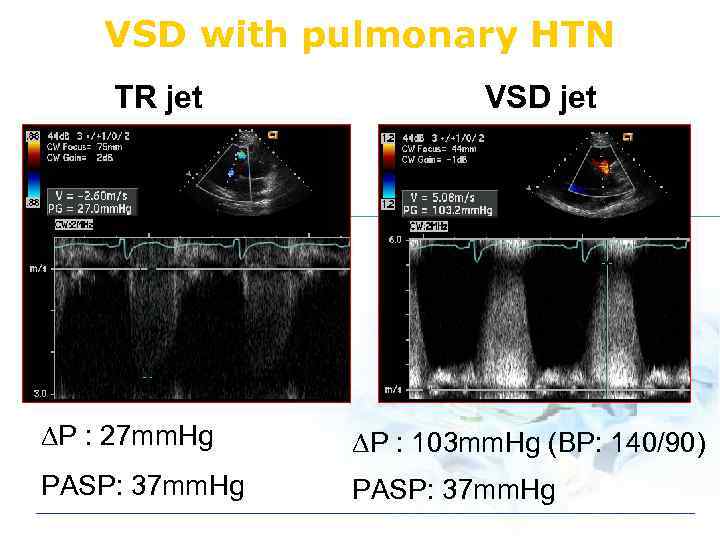 VSD with pulmonary HTN TR jet VSD jet DP : 27 mm. Hg DP : 103 mm. Hg (BP: 140/90) PASP: 37 mm. Hg
VSD with pulmonary HTN TR jet VSD jet DP : 27 mm. Hg DP : 103 mm. Hg (BP: 140/90) PASP: 37 mm. Hg
 VSD: Treatment v Medical treatment l Endocarditis prophylaxis: not recommended v Surgical treatment l Indication: l Device Qp/Qs 1. 5 ~ 2. 0 closure l Contraindication Severe pulmonary hypertension
VSD: Treatment v Medical treatment l Endocarditis prophylaxis: not recommended v Surgical treatment l Indication: l Device Qp/Qs 1. 5 ~ 2. 0 closure l Contraindication Severe pulmonary hypertension
 Patent Ductus Arterosus(PDA)
Patent Ductus Arterosus(PDA)
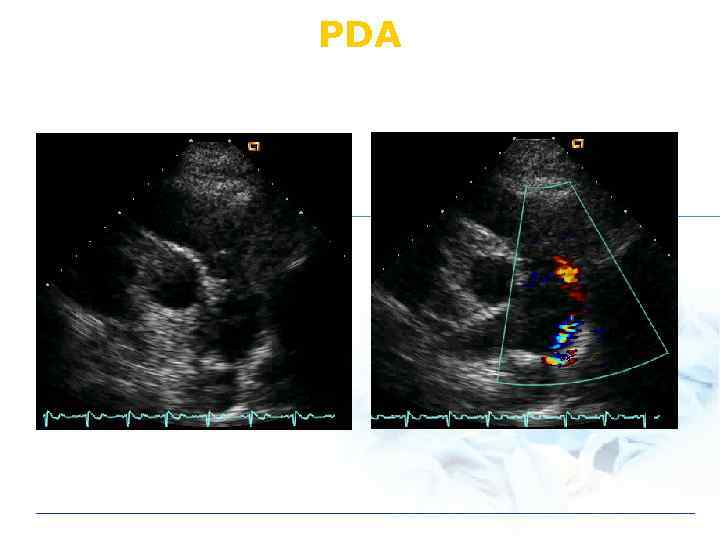 PDA
PDA
 PDA: Physical Findings v Continuous M v Wide pulse pressure v Differential cyanosis l Rt to Lt shunt
PDA: Physical Findings v Continuous M v Wide pulse pressure v Differential cyanosis l Rt to Lt shunt
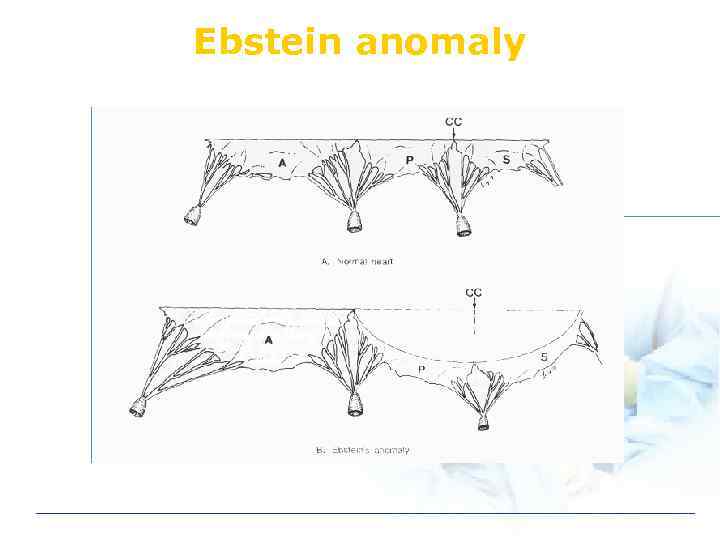 Ebstein anomaly
Ebstein anomaly
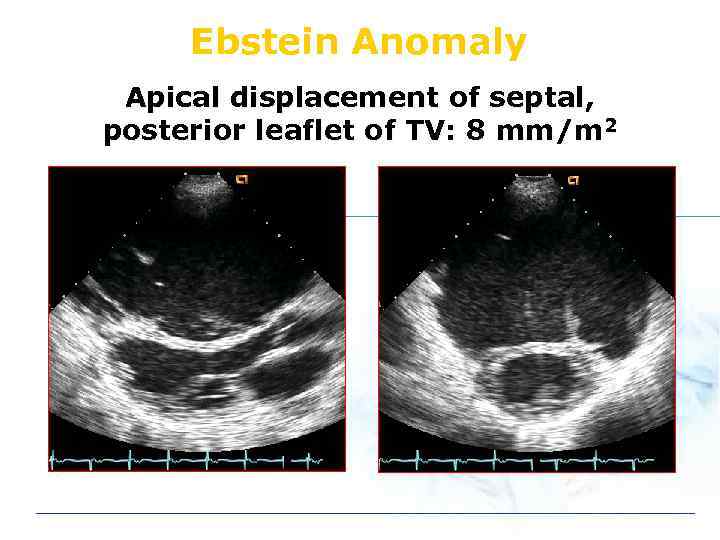 Ebstein Anomaly Apical displacement of septal, posterior leaflet of TV: 8 mm/m 2
Ebstein Anomaly Apical displacement of septal, posterior leaflet of TV: 8 mm/m 2
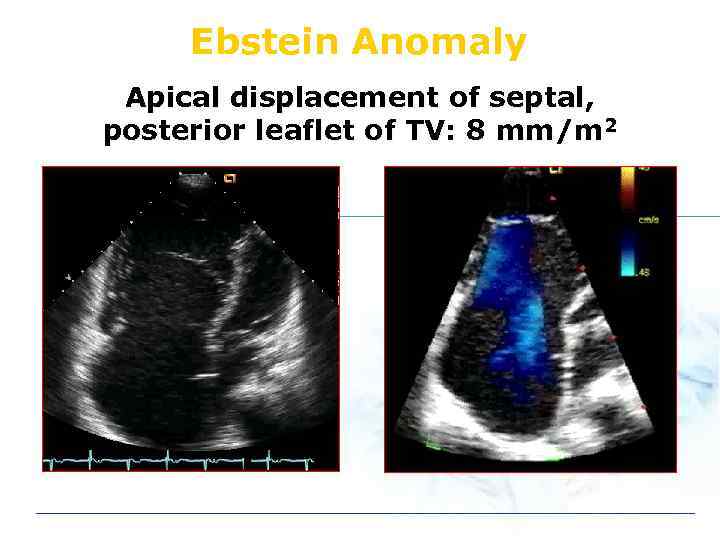 Ebstein Anomaly Apical displacement of septal, posterior leaflet of TV: 8 mm/m 2
Ebstein Anomaly Apical displacement of septal, posterior leaflet of TV: 8 mm/m 2
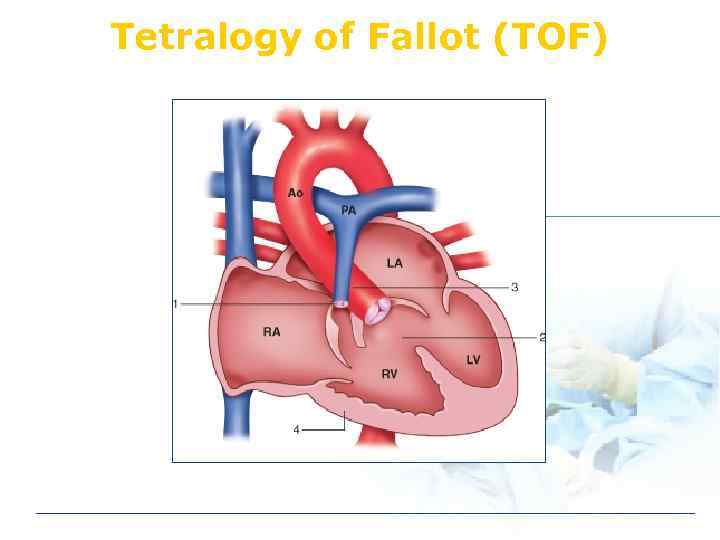 Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF)
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF)
 TOF v Ventricular septal defect v Pulmonic stenosis v Rt ventricular hypertrophy v Overriding of aorta
TOF v Ventricular septal defect v Pulmonic stenosis v Rt ventricular hypertrophy v Overriding of aorta
 TOF
TOF
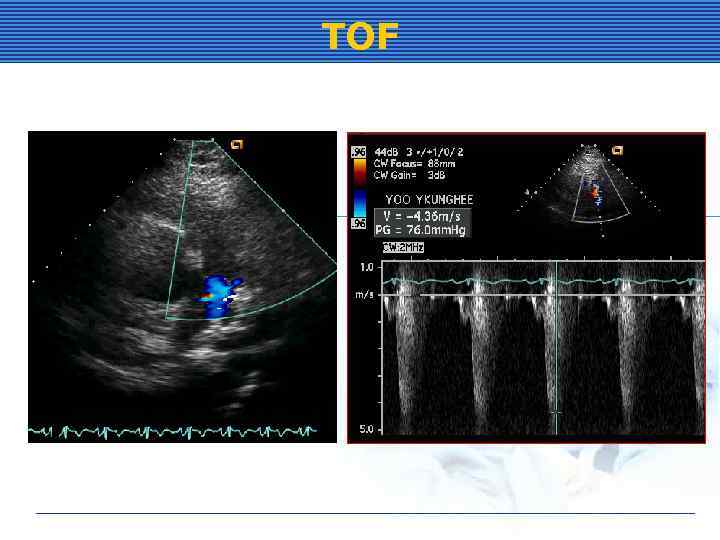 TOF
TOF
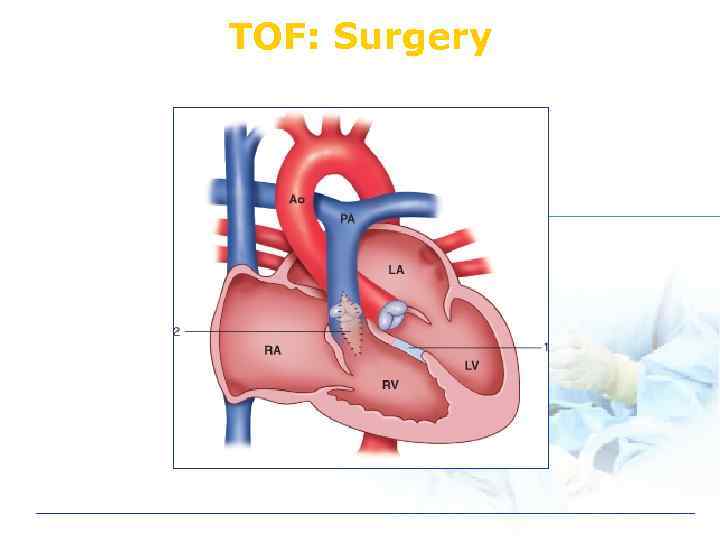 TOF: Surgery
TOF: Surgery
 Clinical Problems in CHD v. Heart failure v. Infective endocarditis v. Pulmonary hypertension (PHT) l Eisenmenger syndrome
Clinical Problems in CHD v. Heart failure v. Infective endocarditis v. Pulmonary hypertension (PHT) l Eisenmenger syndrome
 Eisenmenger Syndrome v 1897: Vicktor Eisenmenger l 32 yo woman with dyspnea, cyanosis l Hemoptysis l Autopsy: Large VSD v 1958: Paul Wood l “Eisenmenger Syndrome”
Eisenmenger Syndrome v 1897: Vicktor Eisenmenger l 32 yo woman with dyspnea, cyanosis l Hemoptysis l Autopsy: Large VSD v 1958: Paul Wood l “Eisenmenger Syndrome”
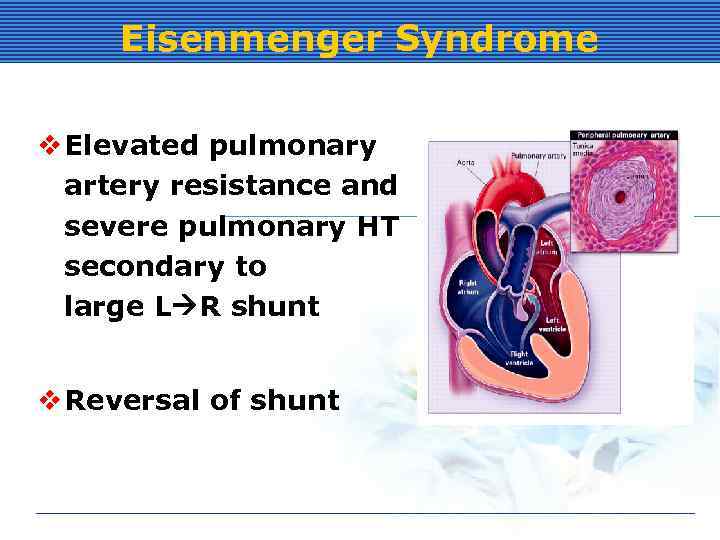 Eisenmenger Syndrome v Elevated pulmonary artery resistance and severe pulmonary HT secondary to large L R shunt v Reversal of shunt
Eisenmenger Syndrome v Elevated pulmonary artery resistance and severe pulmonary HT secondary to large L R shunt v Reversal of shunt
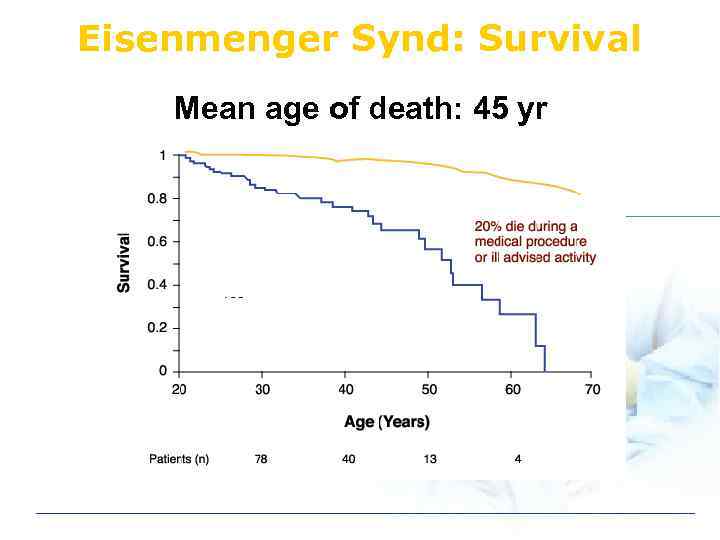 Eisenmenger Synd: Survival Mean age of death: 45 yr
Eisenmenger Synd: Survival Mean age of death: 45 yr
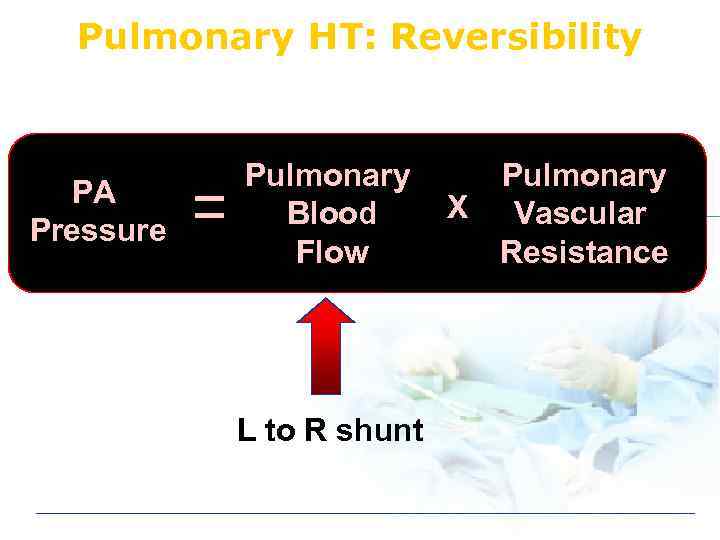 Pulmonary HT: Reversibility PA Pressure Pulmonary Blood Flow L to R shunt X Pulmonary Vascular Resistance
Pulmonary HT: Reversibility PA Pressure Pulmonary Blood Flow L to R shunt X Pulmonary Vascular Resistance
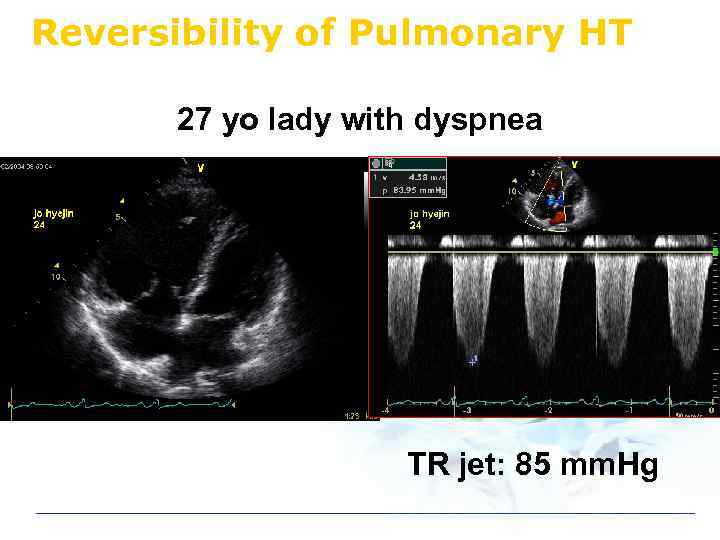 Reversibility of Pulmonary HT 27 yo lady with dyspnea TR jet: 85 mm. Hg
Reversibility of Pulmonary HT 27 yo lady with dyspnea TR jet: 85 mm. Hg
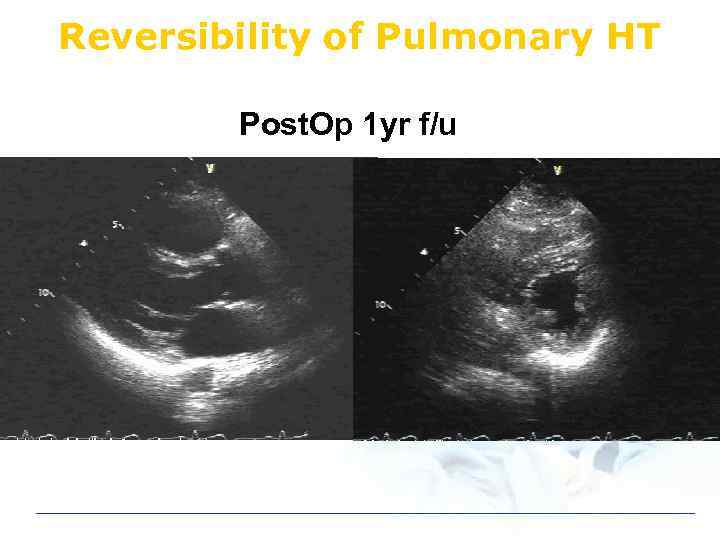 Reversibility of Pulmonary HT Post. Op 1 yr f/u
Reversibility of Pulmonary HT Post. Op 1 yr f/u
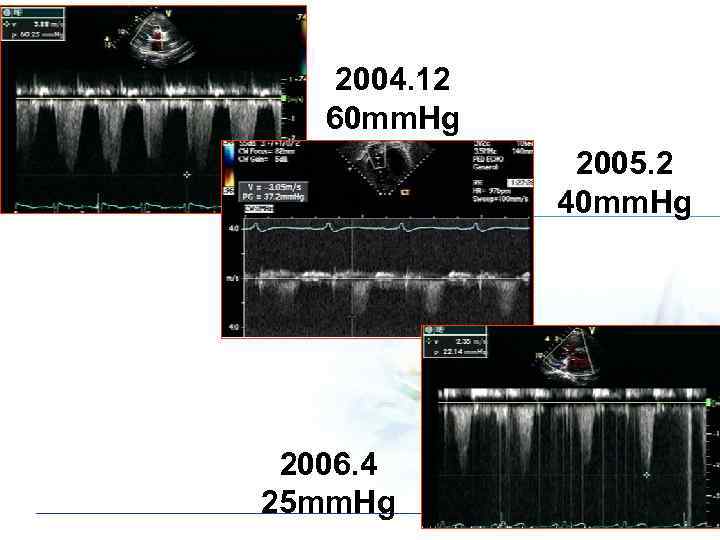 2004. 12 60 mm. Hg 2005. 2 40 mm. Hg 2006. 4 25 mm. Hg
2004. 12 60 mm. Hg 2005. 2 40 mm. Hg 2006. 4 25 mm. Hg


