Conditionals Учитель английского языка Леонова Елена Васильевна ГОУ















conditionals-presentation.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18
 Conditionals Учитель английского языка Леонова Елена Васильевна ГОУ Школа N 555 «Белогорье» [email protected] Санкт-Петербург
Conditionals Учитель английского языка Леонова Елена Васильевна ГОУ Школа N 555 «Белогорье» [email protected] Санкт-Петербург
 main clause if - clause You won’t understand if you don’t listen carefully. Conditional sentences consist of two parts: if – clause which begins with the word if, and the main clause which shows the result. if – clause main clause If you don’t listen carefully, you won’t understand.
main clause if - clause You won’t understand if you don’t listen carefully. Conditional sentences consist of two parts: if – clause which begins with the word if, and the main clause which shows the result. if – clause main clause If you don’t listen carefully, you won’t understand.
 Type 1 Conditionals If Robert studies hard, he will pass his exam. Which is the if-clause? Which is the main clause? What tense do we use in the if-clause? What tense do we use in the main clause? Is it possible that Robert will pass his exam?
Type 1 Conditionals If Robert studies hard, he will pass his exam. Which is the if-clause? Which is the main clause? What tense do we use in the if-clause? What tense do we use in the main clause? Is it possible that Robert will pass his exam?
 Water turns into ice if the temperature falls bellow 0̊C. Which is the if-clause? Which is the main clause? What tense do we use in the if-clause? What tense do we use in the main clause? Is it true that water turns into ice if the temperature falls bellow 0̊C?
Water turns into ice if the temperature falls bellow 0̊C. Which is the if-clause? Which is the main clause? What tense do we use in the if-clause? What tense do we use in the main clause? Is it true that water turns into ice if the temperature falls bellow 0̊C?
 If you don’t understand, look at the example. Which is the if-clause? Which is the main clause? What tense do we use in the if-clause? What tense do we use in the main clause? What do you notice about the main clause? If he looks at the example, is it possible that he will understand?
If you don’t understand, look at the example. Which is the if-clause? Which is the main clause? What tense do we use in the if-clause? What tense do we use in the main clause? What do you notice about the main clause? If he looks at the example, is it possible that he will understand?
 If you go to New York, you can see the statue of Liberty. Which is the if-clause? Which is the main clause? What tense do we use in the if-clause? What tense do we use in the main clause? What do you notice about the main clause?
If you go to New York, you can see the statue of Liberty. Which is the if-clause? Which is the main clause? What tense do we use in the if-clause? What tense do we use in the main clause? What do you notice about the main clause?
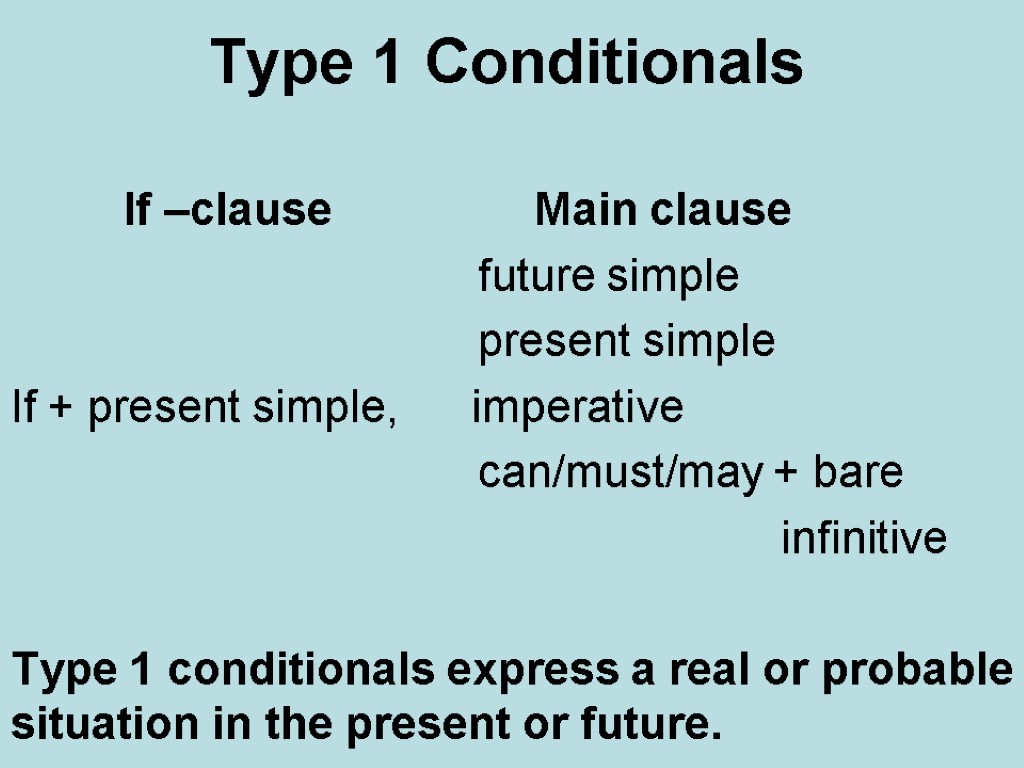
 Type 1 Conditionals If –clause Main clause future simple present simple If + present simple, imperative can/must/may + bare infinitive Type 1 conditionals express a real or probable situation in the present or future.
Type 1 Conditionals If –clause Main clause future simple present simple If + present simple, imperative can/must/may + bare infinitive Type 1 conditionals express a real or probable situation in the present or future.
 If you don’t leave early, you’ll miss the bus. Unless you leave early, you’ll miss the bus. Is there any difference in meaning between these two sentences? What do you notice about the verb form that follows ‘unless’? We can use unless + affirmative verb instead of if… not in the if-clause.
If you don’t leave early, you’ll miss the bus. Unless you leave early, you’ll miss the bus. Is there any difference in meaning between these two sentences? What do you notice about the verb form that follows ‘unless’? We can use unless + affirmative verb instead of if… not in the if-clause.
 Make correct type 1 conditionals about Robert. pass exams get degree find a job earn some money buy a car travel round Europe see lots of new places
Make correct type 1 conditionals about Robert. pass exams get degree find a job earn some money buy a car travel round Europe see lots of new places
 Look at the pictures and the prompts and make sentences, as in the example. If you go to London you can see Big Ben. Rome/ the Colosseum New York/the Empire State Building Paris/the Eiffel Tower Egypt/the Pyramids Sydney/the Sydney Opera House Venice/some gondolas Hawaii/some palm trees
Look at the pictures and the prompts and make sentences, as in the example. If you go to London you can see Big Ben. Rome/ the Colosseum New York/the Empire State Building Paris/the Eiffel Tower Egypt/the Pyramids Sydney/the Sydney Opera House Venice/some gondolas Hawaii/some palm trees
 Type 2 Conditionals If I had a lot of money, I would buy a big house and I’d go on a cruise round the world. Which is the if-clause? Which is the main clause? What tense do we use in the if-clause? What do you notice about the main clause? Has she got a lot of money now? Is this situation real in the present?
Type 2 Conditionals If I had a lot of money, I would buy a big house and I’d go on a cruise round the world. Which is the if-clause? Which is the main clause? What tense do we use in the if-clause? What do you notice about the main clause? Has she got a lot of money now? Is this situation real in the present?
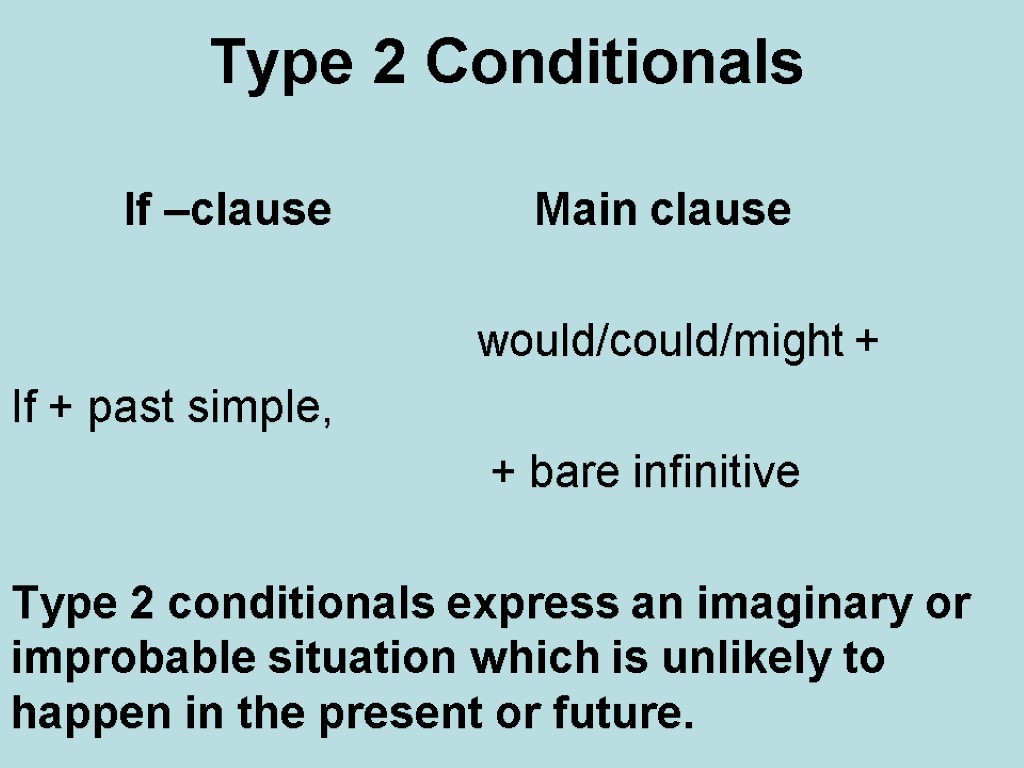
 Type 2 Conditionals If –clause Main clause would/could/might + If + past simple, + bare infinitive Type 2 conditionals express an imaginary or improbable situation which is unlikely to happen in the present or future.
Type 2 Conditionals If –clause Main clause would/could/might + If + past simple, + bare infinitive Type 2 conditionals express an imaginary or improbable situation which is unlikely to happen in the present or future.
 If Sarah was/were here, I’d invite her to my party. We can use ‘were’ instead of ‘was’ for all persons. A: ‘I haven’t got any money.’ B: ‘If I were you, I’d get a job.’ We can use ‘If I were you, I would…’ when we want to give advice. What would you do, if you had a lot of money?
If Sarah was/were here, I’d invite her to my party. We can use ‘were’ instead of ‘was’ for all persons. A: ‘I haven’t got any money.’ B: ‘If I were you, I’d get a job.’ We can use ‘If I were you, I would…’ when we want to give advice. What would you do, if you had a lot of money?
 What advice would you give to your friend who has a sore throat? drink something hot take some medicine not talk not go out not eat any ice-cream go to the doctor
What advice would you give to your friend who has a sore throat? drink something hot take some medicine not talk not go out not eat any ice-cream go to the doctor
 Look at the pictures and the prompts and ask and answer , as in the example. -Shall I paint the fence red or green? -If I were you, I’d paint it red. order a salad/a sandwich have some coffee/orange juice buy a dog/a goldfish go to Japan/France take up golf/baseball
Look at the pictures and the prompts and ask and answer , as in the example. -Shall I paint the fence red or green? -If I were you, I’d paint it red. order a salad/a sandwich have some coffee/orange juice buy a dog/a goldfish go to Japan/France take up golf/baseball
 Type 3 Conditionals This is Jack. He missed the bus yesterday, so he was late for work. If Jack hadn’t missed the bus, he wouldn’t have been late for work yesterday. Which is the if-clause? Which is the main clause? What tense do we use in the if-clause? What do you notice about the main clause? Did Jack miss the bus? Was he late for work?
Type 3 Conditionals This is Jack. He missed the bus yesterday, so he was late for work. If Jack hadn’t missed the bus, he wouldn’t have been late for work yesterday. Which is the if-clause? Which is the main clause? What tense do we use in the if-clause? What do you notice about the main clause? Did Jack miss the bus? Was he late for work?
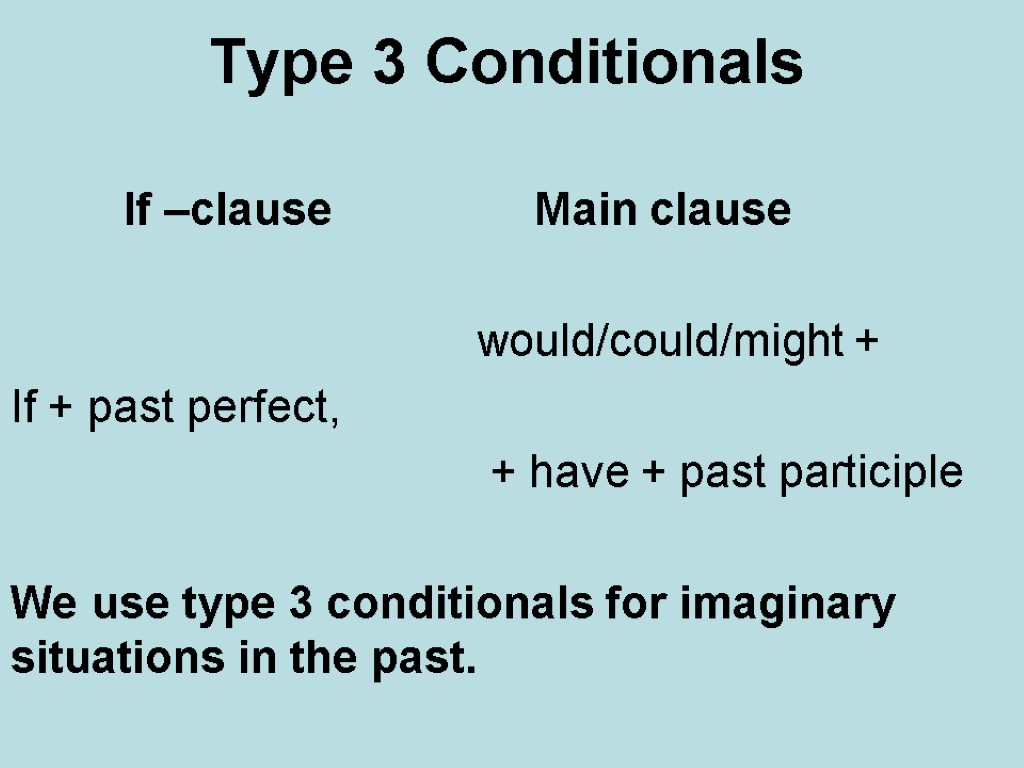
 Type 3 Conditionals If –clause Main clause would/could/might + If + past perfect, + have + past participle We use type 3 conditionals for imaginary situations in the past.
Type 3 Conditionals If –clause Main clause would/could/might + If + past perfect, + have + past participle We use type 3 conditionals for imaginary situations in the past.
 Richard Brooks was very upset yesterday because he missed an important meeting. Look at the prompts and make sentences, as in the example. If the airline hadn’t been on strike, his flight wouldn’t have been delayed. If his flight hadn’t been delayed, … the airline / not be / on strike→ his flight / not be / delayed→ he / arrive / in New York / on time→ he / attend / the meeting→ he / sign / the contract→ his boss / be pleased with him→ she / give / him a promotion
Richard Brooks was very upset yesterday because he missed an important meeting. Look at the prompts and make sentences, as in the example. If the airline hadn’t been on strike, his flight wouldn’t have been delayed. If his flight hadn’t been delayed, … the airline / not be / on strike→ his flight / not be / delayed→ he / arrive / in New York / on time→ he / attend / the meeting→ he / sign / the contract→ his boss / be pleased with him→ she / give / him a promotion
