d861b310327dd1f2989f792941e5581e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 72
 ce an orm ing rf Pe Us ion rom at alu ces f Ev ian sts ar Co V ard nd r 7 ta S pte ha C c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
ce an orm ing rf Pe Us ion rom at alu ces f Ev ian sts ar Co V ard nd r 7 ta S pte ha C c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
 Learning Objectives 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Describe the types of standards and how they are established. Describe and illustrate how standards are used in budgeting. Compute and interpret direct materials and direct labor variances. Compute and interpret factory overhead controllable and volume variances. Journalize the entries for recording standards in the accounts and prepare an income statement that includes variances from standard. Describe and provide examples of nonfinancial performance measures.
Learning Objectives 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Describe the types of standards and how they are established. Describe and illustrate how standards are used in budgeting. Compute and interpret direct materials and direct labor variances. Compute and interpret factory overhead controllable and volume variances. Journalize the entries for recording standards in the accounts and prepare an income statement that includes variances from standard. Describe and provide examples of nonfinancial performance measures.
 Lear ning Obje Desc ctive ribe the t ypes of sta how ndar they ds an are e d stab lishe d. 1 c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
Lear ning Obje Desc ctive ribe the t ypes of sta how ndar they ds an are e d stab lishe d. 1 c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
 Standards o Standards are performance goals. Manufacturing companies normally use standard cost for each of the three following product costs: Ø Direct materials Ø Direct labor Ø Factory overhead c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
Standards o Standards are performance goals. Manufacturing companies normally use standard cost for each of the three following product costs: Ø Direct materials Ø Direct labor Ø Factory overhead c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
 Standards o Accounting systems that use standards for product costs are called standard cost systems. o Standard cost systems enable management to determine the following: Ø How much a product should cost (standard cost) Ø How much it does cost (actual cost) c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
Standards o Accounting systems that use standards for product costs are called standard cost systems. o Standard cost systems enable management to determine the following: Ø How much a product should cost (standard cost) Ø How much it does cost (actual cost) c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
 Standard o When actual costs are compared with standard costs, only the exceptions or variances are reported for cost control. This reporting by the principle of exceptions allows management to focus on correcting the cost variances. c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
Standard o When actual costs are compared with standard costs, only the exceptions or variances are reported for cost control. This reporting by the principle of exceptions allows management to focus on correcting the cost variances. c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
 Setting Standards o The standard-setting process normally requires the joint efforts of accountants, engineers, and other management personnel. c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
Setting Standards o The standard-setting process normally requires the joint efforts of accountants, engineers, and other management personnel. c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
 Types of Standards o Unrealistic standards that can be achieved only under perfect operating conditions (such as no idle time, no machine breakdowns, and no materials spoilage) are called ideal standards or theoretical standards. c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
Types of Standards o Unrealistic standards that can be achieved only under perfect operating conditions (such as no idle time, no machine breakdowns, and no materials spoilage) are called ideal standards or theoretical standards. c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
 Types of Standards o Currently attainable standards, sometimes called normal standards, can be attained with reasonable effort. Such standards, which are used by most companies, allow for normal production difficulties and mistakes. c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
Types of Standards o Currently attainable standards, sometimes called normal standards, can be attained with reasonable effort. Such standards, which are used by most companies, allow for normal production difficulties and mistakes. c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
 Reviewing and Revising Standards o Standard costs should be periodically reviewed to ensure that they reflect current operating conditions. Standards should not be revised, however, just because they differ from actual costs. c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
Reviewing and Revising Standards o Standard costs should be periodically reviewed to ensure that they reflect current operating conditions. Standards should not be revised, however, just because they differ from actual costs. c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
 Criticisms of Standard Costs o Standards limit operating improvements by discouraging improvement beyond the standard. o Standards are too difficult to maintain in a dynamic manufacturing environment, resulting in “stale standards. ” o Standards can cause workers to lose sight of the larger objectives of the organization by focusing only on efficiency improvements. c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
Criticisms of Standard Costs o Standards limit operating improvements by discouraging improvement beyond the standard. o Standards are too difficult to maintain in a dynamic manufacturing environment, resulting in “stale standards. ” o Standards can cause workers to lose sight of the larger objectives of the organization by focusing only on efficiency improvements. c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
 Criticisms of Standard Costs o Standards can cause workers to unduly focus on their own operations to the possible harm of other operations that rely on them. c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
Criticisms of Standard Costs o Standards can cause workers to unduly focus on their own operations to the possible harm of other operations that rely on them. c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
 Lear ning Obje ctive D stand escribe a and i ards llustr are u ate h sed i ow n bu dget ing. 2 c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
Lear ning Obje ctive D stand escribe a and i ards llustr are u ate h sed i ow n bu dget ing. 2 c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
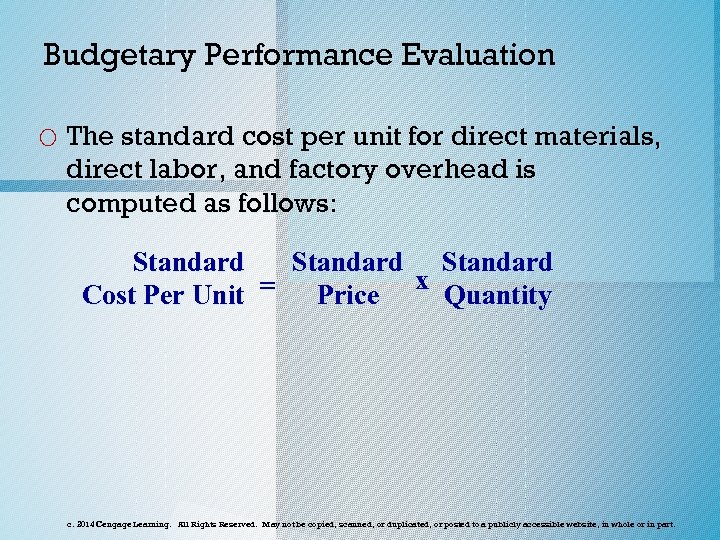 Budgetary Performance Evaluation o The standard cost per unit for direct materials, direct labor, and factory overhead is computed as follows: Standard = Price x Quantity Cost Per Unit c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
Budgetary Performance Evaluation o The standard cost per unit for direct materials, direct labor, and factory overhead is computed as follows: Standard = Price x Quantity Cost Per Unit c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
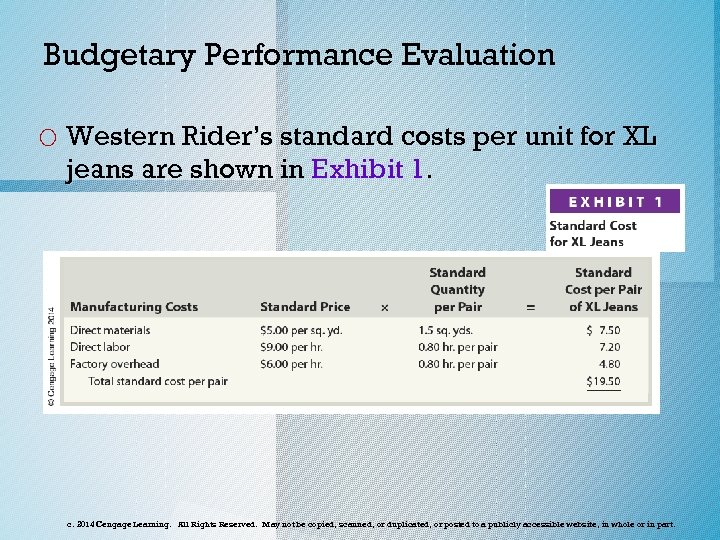 Budgetary Performance Evaluation o Western Rider’s standard costs per unit for XL jeans are shown in Exhibit 1. c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
Budgetary Performance Evaluation o Western Rider’s standard costs per unit for XL jeans are shown in Exhibit 1. c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
 Budget Performance Report o The report that summarizes actual costs, standard costs, and the differences for the units produced is called a budget performance report. c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
Budget Performance Report o The report that summarizes actual costs, standard costs, and the differences for the units produced is called a budget performance report. c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
 Budget Performance Report o The differences between actual and standard costs are called costs variances. o A favorable cost variance occurs when the actual cost is less than the standard cost (at actual volumes). o An unfavorable cost variance occurs when the actual cost exceeds the standard cost. c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
Budget Performance Report o The differences between actual and standard costs are called costs variances. o A favorable cost variance occurs when the actual cost is less than the standard cost (at actual volumes). o An unfavorable cost variance occurs when the actual cost exceeds the standard cost. c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
 BUDGET PERFORMANCE REPORT
BUDGET PERFORMANCE REPORT
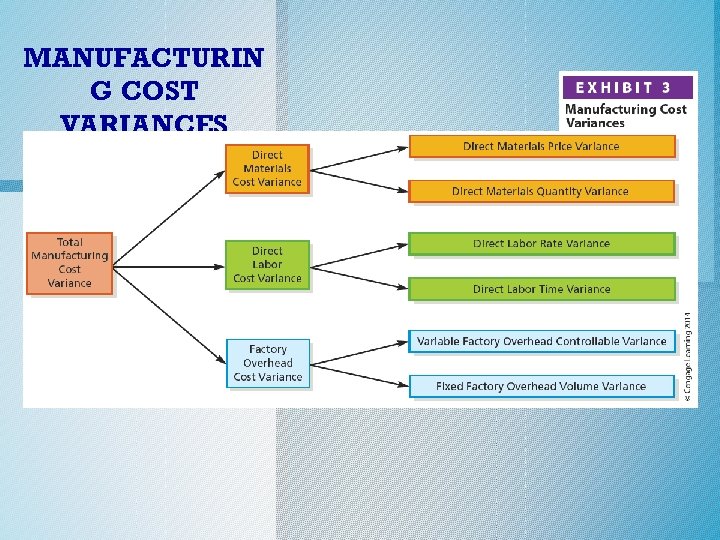
 Manufacturing Cost Variances o The total manufacturing cost variance is the difference between total standard costs and total actual costs for the units produced. o For control purposes, each product cost variance is separated into two additional variances as shown in Exhibit 3 (next slide). c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
Manufacturing Cost Variances o The total manufacturing cost variance is the difference between total standard costs and total actual costs for the units produced. o For control purposes, each product cost variance is separated into two additional variances as shown in Exhibit 3 (next slide). c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
 MANUFACTURIN G COST VARIANCES
MANUFACTURIN G COST VARIANCES
 Manufacturing Cost Variances o The total direct materials variance is separated into a price and quantity variance. o Thus, the actual and standard direct materials costs may differ because of either a price difference (variance) or a quantity difference (variance) or both. c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
Manufacturing Cost Variances o The total direct materials variance is separated into a price and quantity variance. o Thus, the actual and standard direct materials costs may differ because of either a price difference (variance) or a quantity difference (variance) or both. c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
 Manufacturing Cost Variances o Likewise, the total direct labor variance is separated into a rate and a time variance. o Therefore, the actual and standard direct labor costs may differ because of either a rate difference (variance) or a time difference (variance) or both. c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
Manufacturing Cost Variances o Likewise, the total direct labor variance is separated into a rate and a time variance. o Therefore, the actual and standard direct labor costs may differ because of either a rate difference (variance) or a time difference (variance) or both. c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
 Lear ning Obje ctive Com mate rials pute an d int and erpr direc et di t lab rect or va rianc es. 3 c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
Lear ning Obje ctive Com mate rials pute an d int and erpr direc et di t lab rect or va rianc es. 3 c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
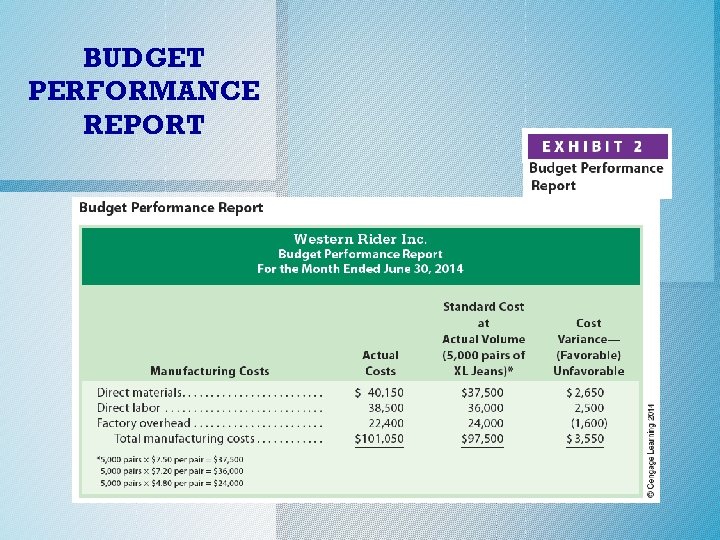
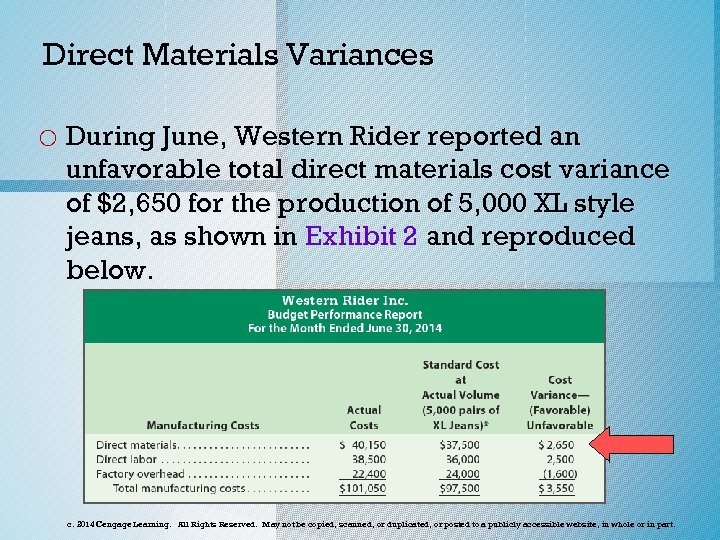 Direct Materials Variances o During June, Western Rider reported an unfavorable total direct materials cost variance of $2, 650 for the production of 5, 000 XL style jeans, as shown in Exhibit 2 and reproduced below. c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
Direct Materials Variances o During June, Western Rider reported an unfavorable total direct materials cost variance of $2, 650 for the production of 5, 000 XL style jeans, as shown in Exhibit 2 and reproduced below. c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
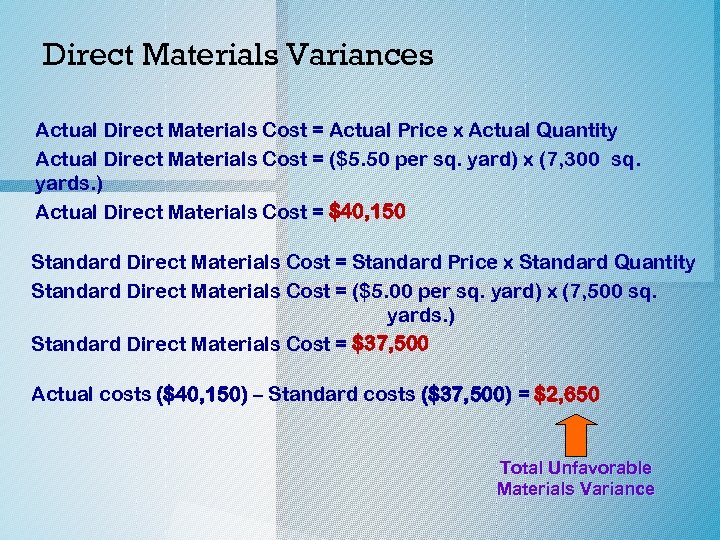 Direct Materials Variances Actual Direct Materials Cost = Actual Price x Actual Quantity Actual Direct Materials Cost = ($5. 50 per sq. yard) x (7, 300 sq. yards. ) Actual Direct Materials Cost = $40, 150 Standard Direct Materials Cost = Standard Price x Standard Quantity Standard Direct Materials Cost = ($5. 00 per sq. yard) x (7, 500 sq. yards. ) Standard Direct Materials Cost = $37, 500 Actual costs ($40, 150) – Standard costs ($37, 500) = $2, 650 Total Unfavorable Materials Variance
Direct Materials Variances Actual Direct Materials Cost = Actual Price x Actual Quantity Actual Direct Materials Cost = ($5. 50 per sq. yard) x (7, 300 sq. yards. ) Actual Direct Materials Cost = $40, 150 Standard Direct Materials Cost = Standard Price x Standard Quantity Standard Direct Materials Cost = ($5. 00 per sq. yard) x (7, 500 sq. yards. ) Standard Direct Materials Cost = $37, 500 Actual costs ($40, 150) – Standard costs ($37, 500) = $2, 650 Total Unfavorable Materials Variance
 Direct Materials Price Variance = (Actual Price – Standard Price) x Actual Quantity Direct Materials Price Variance = ($5. 50 - $5. 00) x 7, 300 sq. yds. Direct Materials Price Variance = $3, 650 Unfavorable direct materials price variance Western Rider paid $0. 50 more per square yard of material than the standard.
Direct Materials Price Variance = (Actual Price – Standard Price) x Actual Quantity Direct Materials Price Variance = ($5. 50 - $5. 00) x 7, 300 sq. yds. Direct Materials Price Variance = $3, 650 Unfavorable direct materials price variance Western Rider paid $0. 50 more per square yard of material than the standard.
 Direct Materials Quantity Variance = (Actual Quantity – Standard Quantity) x Standard Price Direct Materials Quantity Variance = (7, 300 sq. yds. – 7, 500 sq. yds. ) x $5. 00 Direct Materials Quantity Variance = – $1, 000 Western Rider used 200 square yards less than the standard. Favorable direct materials quantity variance
Direct Materials Quantity Variance = (Actual Quantity – Standard Quantity) x Standard Price Direct Materials Quantity Variance = (7, 300 sq. yds. – 7, 500 sq. yds. ) x $5. 00 Direct Materials Quantity Variance = – $1, 000 Western Rider used 200 square yards less than the standard. Favorable direct materials quantity variance
 Direct Materials Variance Relationships o The relationship among the total direct materials cost variance, the direct materials price variance, and the direct materials quantity variance is shown in an animated reproduction of Exhibit 4 in the next slide. c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
Direct Materials Variance Relationships o The relationship among the total direct materials cost variance, the direct materials price variance, and the direct materials quantity variance is shown in an animated reproduction of Exhibit 4 in the next slide. c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
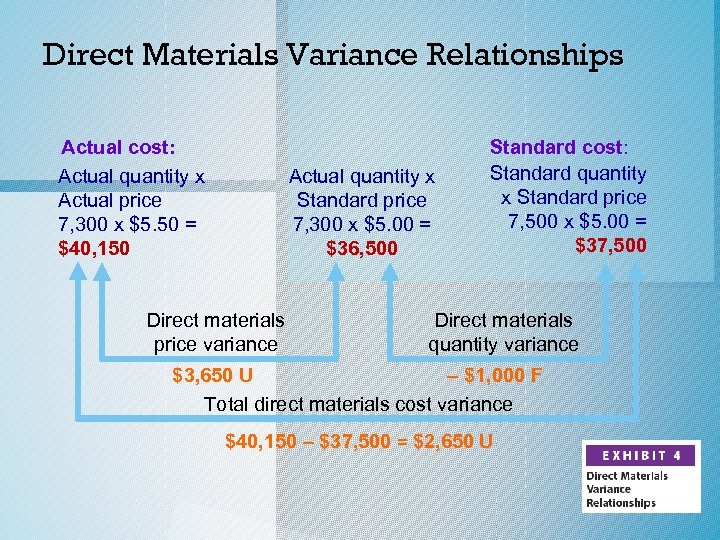 Direct Materials Variance Relationships Actual cost: Actual quantity x Actual price 7, 300 x $5. 50 = $40, 150 Actual quantity x Standard price 7, 300 x $5. 00 = $36, 500 Direct materials price variance Standard cost: Standard quantity x Standard price 7, 500 x $5. 00 = $37, 500 Direct materials quantity variance $3, 650 U – $1, 000 F Total direct materials cost variance $40, 150 – $37, 500 = $2, 650 U
Direct Materials Variance Relationships Actual cost: Actual quantity x Actual price 7, 300 x $5. 50 = $40, 150 Actual quantity x Standard price 7, 300 x $5. 00 = $36, 500 Direct materials price variance Standard cost: Standard quantity x Standard price 7, 500 x $5. 00 = $37, 500 Direct materials quantity variance $3, 650 U – $1, 000 F Total direct materials cost variance $40, 150 – $37, 500 = $2, 650 U
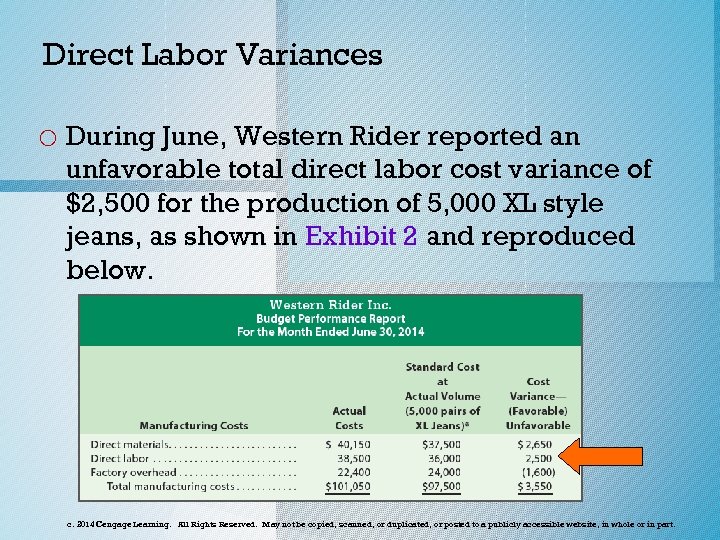 Direct Labor Variances o During June, Western Rider reported an unfavorable total direct labor cost variance of $2, 500 for the production of 5, 000 XL style jeans, as shown in Exhibit 2 and reproduced below. c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
Direct Labor Variances o During June, Western Rider reported an unfavorable total direct labor cost variance of $2, 500 for the production of 5, 000 XL style jeans, as shown in Exhibit 2 and reproduced below. c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
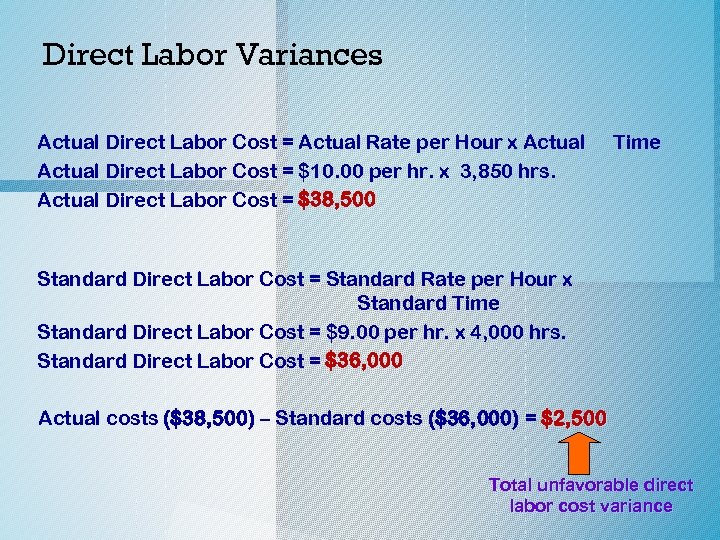 Direct Labor Variances Actual Direct Labor Cost = Actual Rate per Hour x Actual Direct Labor Cost = $10. 00 per hr. x 3, 850 hrs. Actual Direct Labor Cost = $38, 500 Time Standard Direct Labor Cost = Standard Rate per Hour x Standard Time Standard Direct Labor Cost = $9. 00 per hr. x 4, 000 hrs. Standard Direct Labor Cost = $36, 000 Actual costs ($38, 500) – Standard costs ($36, 000) = $2, 500 Total unfavorable direct labor cost variance
Direct Labor Variances Actual Direct Labor Cost = Actual Rate per Hour x Actual Direct Labor Cost = $10. 00 per hr. x 3, 850 hrs. Actual Direct Labor Cost = $38, 500 Time Standard Direct Labor Cost = Standard Rate per Hour x Standard Time Standard Direct Labor Cost = $9. 00 per hr. x 4, 000 hrs. Standard Direct Labor Cost = $36, 000 Actual costs ($38, 500) – Standard costs ($36, 000) = $2, 500 Total unfavorable direct labor cost variance
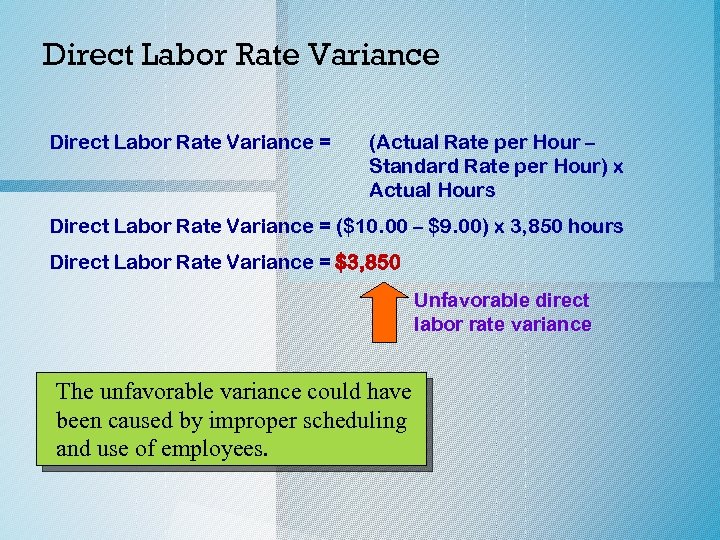 Direct Labor Rate Variance = (Actual Rate per Hour – Standard Rate per Hour) x Actual Hours Direct Labor Rate Variance = ($10. 00 – $9. 00) x 3, 850 hours Direct Labor Rate Variance = $3, 850 Unfavorable direct labor rate variance The unfavorable variance could have been caused by improper scheduling and use of employees.
Direct Labor Rate Variance = (Actual Rate per Hour – Standard Rate per Hour) x Actual Hours Direct Labor Rate Variance = ($10. 00 – $9. 00) x 3, 850 hours Direct Labor Rate Variance = $3, 850 Unfavorable direct labor rate variance The unfavorable variance could have been caused by improper scheduling and use of employees.
 Direct Labor Time Variance = (Actual Direct Labor Hours Standard Direct Labor Hours) x Standard Rate per Hour Direct Labor Time Variance = (3, 850 hours – 4, 000 direct labor hours) x $9. 00 Direct Labor Time Variance = – $1, 350 If there had been an unfavorable time variance, it might have been caused by a shortage of skilled workers. Favorable direct labor time variance
Direct Labor Time Variance = (Actual Direct Labor Hours Standard Direct Labor Hours) x Standard Rate per Hour Direct Labor Time Variance = (3, 850 hours – 4, 000 direct labor hours) x $9. 00 Direct Labor Time Variance = – $1, 350 If there had been an unfavorable time variance, it might have been caused by a shortage of skilled workers. Favorable direct labor time variance
 DIRECT LABOR VARIANCE RELATIONSHIPS Actual cost: Actual hours x Actual rate 3, 850 x $10 = $38, 500 Actual hours x Standard rate 3, 850 x $9 = $34, 650 Direct labor rate variance Standard cost: Standard hours x Standard rate 4, 000 x $9 = $36, 000 Direct labor time variance $3, 850 U –$1, 350 F Total direct labor cost variance $38, 500 – $36, 000 = $2, 500 U
DIRECT LABOR VARIANCE RELATIONSHIPS Actual cost: Actual hours x Actual rate 3, 850 x $10 = $38, 500 Actual hours x Standard rate 3, 850 x $9 = $34, 650 Direct labor rate variance Standard cost: Standard hours x Standard rate 4, 000 x $9 = $36, 000 Direct labor time variance $3, 850 U –$1, 350 F Total direct labor cost variance $38, 500 – $36, 000 = $2, 500 U
 Lear ning Obje ctive Com pute over and hea ad co ntrol interpret lable facto r and volu y varia me nces. 4 c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
Lear ning Obje ctive Com pute over and hea ad co ntrol interpret lable facto r and volu y varia me nces. 4 c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
 Factory Overhead Variances o Factory overhead costs are more difficult to analyze than direct labor and materials costs. This is because factory overhead costs have fixed and variable cost elements. c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
Factory Overhead Variances o Factory overhead costs are more difficult to analyze than direct labor and materials costs. This is because factory overhead costs have fixed and variable cost elements. c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
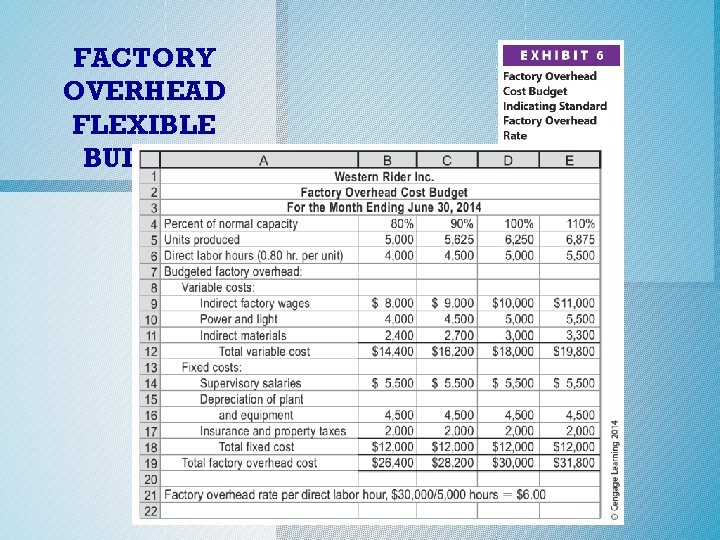 FACTORY OVERHEAD FLEXIBLE BUDGET
FACTORY OVERHEAD FLEXIBLE BUDGET
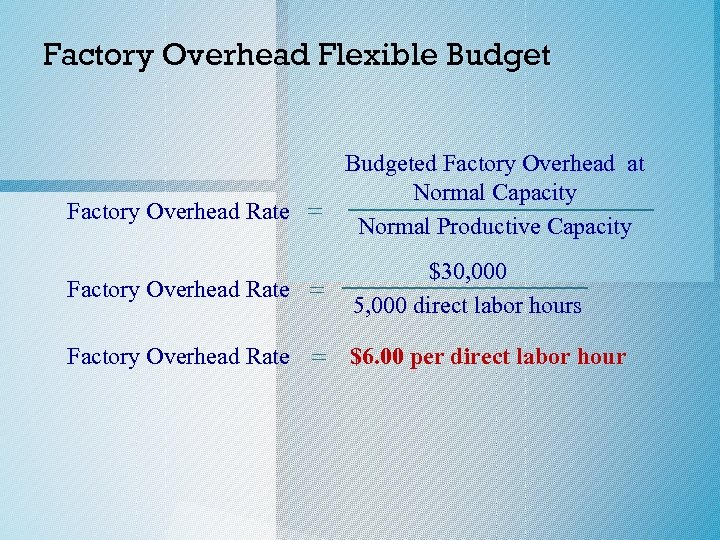 Factory Overhead Flexible Budgeted Factory Overhead at Normal Capacity Factory Overhead Rate = Normal Productive Capacity Factory Overhead Rate = $30, 000 5, 000 direct labor hours Factory Overhead Rate = $6. 00 per direct labor hour
Factory Overhead Flexible Budgeted Factory Overhead at Normal Capacity Factory Overhead Rate = Normal Productive Capacity Factory Overhead Rate = $30, 000 5, 000 direct labor hours Factory Overhead Rate = $6. 00 per direct labor hour
 Factory Overhead Flexible Budgeted Variable Overhead at Normal Capacity Variable Factory Overhead Rate = Normal Productive Capacity Variable Factory Overhead Rate = $18, 000 5, 000 direct labor hours $3. 60 per direct labor hour
Factory Overhead Flexible Budgeted Variable Overhead at Normal Capacity Variable Factory Overhead Rate = Normal Productive Capacity Variable Factory Overhead Rate = $18, 000 5, 000 direct labor hours $3. 60 per direct labor hour
 Factory Overhead Flexible Budget Fixed Factory Overhead Rate = Budgeted Fixed Overhead at Normal Capacity Normal Productive Capacity $12, 000 Fixed Factory Overhead Rate = 5, 000 direct labor hours Fixed Factory Overhead Rate = $2. 40 per direct labor hour
Factory Overhead Flexible Budget Fixed Factory Overhead Rate = Budgeted Fixed Overhead at Normal Capacity Normal Productive Capacity $12, 000 Fixed Factory Overhead Rate = 5, 000 direct labor hours Fixed Factory Overhead Rate = $2. 40 per direct labor hour
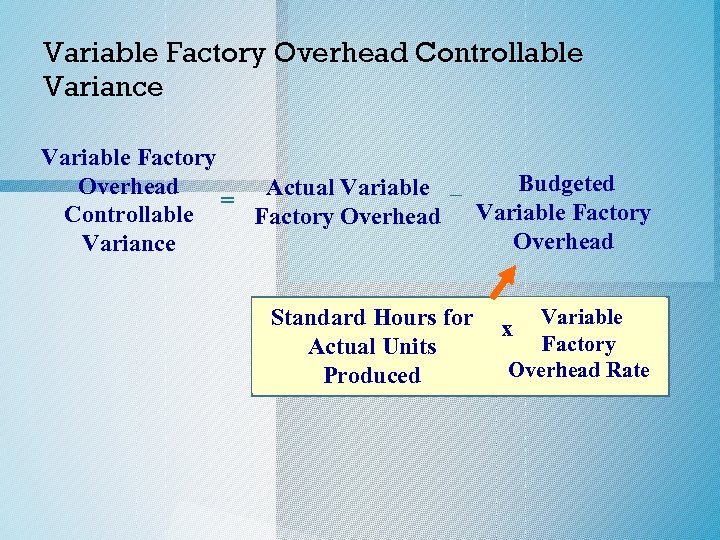 Variable Factory Overhead Controllable Variance Variable Factory Budgeted Overhead Actual Variable – = Controllable Factory Overhead Variance Standard Hours for Actual Units Produced Variable x Factory Overhead Rate
Variable Factory Overhead Controllable Variance Variable Factory Budgeted Overhead Actual Variable – = Controllable Factory Overhead Variance Standard Hours for Actual Units Produced Variable x Factory Overhead Rate
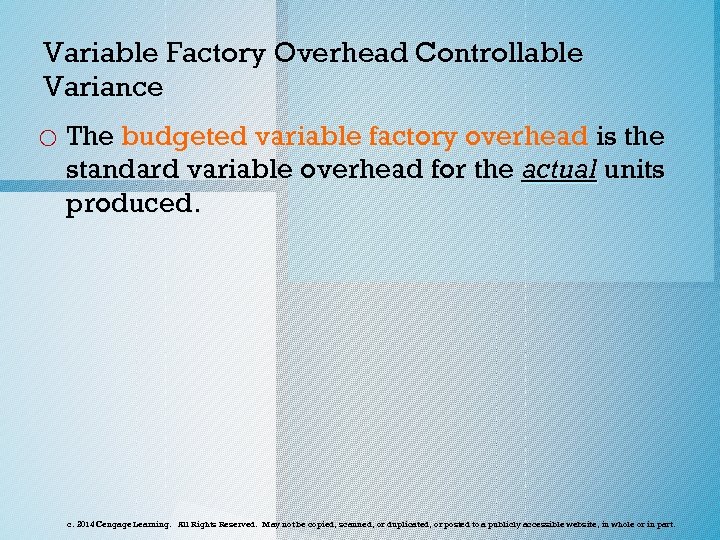 Variable Factory Overhead Controllable Variance o The budgeted variable factory overhead is the standard variable overhead for the actual units produced. c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
Variable Factory Overhead Controllable Variance o The budgeted variable factory overhead is the standard variable overhead for the actual units produced. c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
 Variable Factory Overhead Controllable Variance Variable Factory Budgeted Actual Variable Overhead – = Factory Overhead Variable Factory Controllable Overhead Variance Variable Factory Overhead = Controllable Variance 4, 000 direct labor hours x $3. 60 $10, 400 – $14, 400 – $4, 000 Favorable Variance
Variable Factory Overhead Controllable Variance Variable Factory Budgeted Actual Variable Overhead – = Factory Overhead Variable Factory Controllable Overhead Variance Variable Factory Overhead = Controllable Variance 4, 000 direct labor hours x $3. 60 $10, 400 – $14, 400 – $4, 000 Favorable Variance
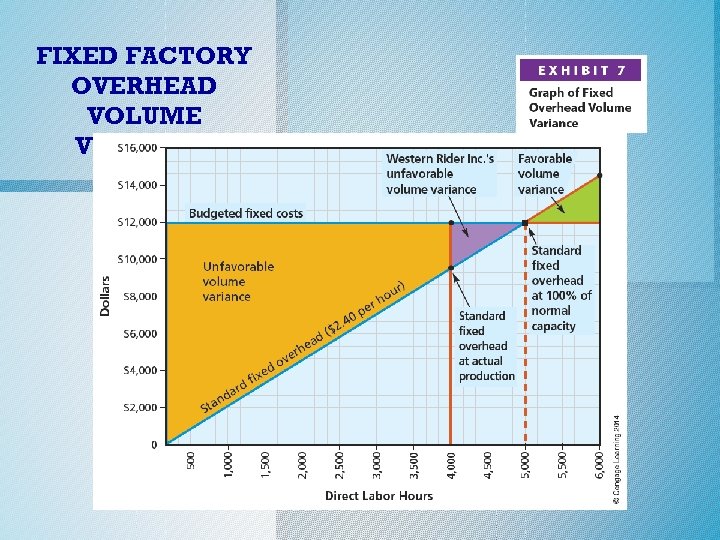
 Fixed Factory Overhead Volume Variance Fixed Factory Overhead Volume = Variance Fixed Factory Overhead = Volume Variance Standard Fixed Hours for – x Factory 100% of Actual Units Overhead Normal Produced Rate Capacity 5, 000 direct 4, 000 direct – x $2. 40 labor hours Fixed Factory Overhead = $2, 400 Unfavorable Variance Volume Variance
Fixed Factory Overhead Volume Variance Fixed Factory Overhead Volume = Variance Fixed Factory Overhead = Volume Variance Standard Fixed Hours for – x Factory 100% of Actual Units Overhead Normal Produced Rate Capacity 5, 000 direct 4, 000 direct – x $2. 40 labor hours Fixed Factory Overhead = $2, 400 Unfavorable Variance Volume Variance
 FIXED FACTORY OVERHEAD VOLUME VARIANCE
FIXED FACTORY OVERHEAD VOLUME VARIANCE
 Fixed Factory Overhead Volume Variance o An unfavorable volume variance may be due to factors such as the following: Ø Failure to maintain an even flow of work Ø Machine breakdowns Ø Work stoppages caused by lack of materials or skilled labor Ø Lack of enough sales orders to keep the factory operating at normal capacity c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
Fixed Factory Overhead Volume Variance o An unfavorable volume variance may be due to factors such as the following: Ø Failure to maintain an even flow of work Ø Machine breakdowns Ø Work stoppages caused by lack of materials or skilled labor Ø Lack of enough sales orders to keep the factory operating at normal capacity c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
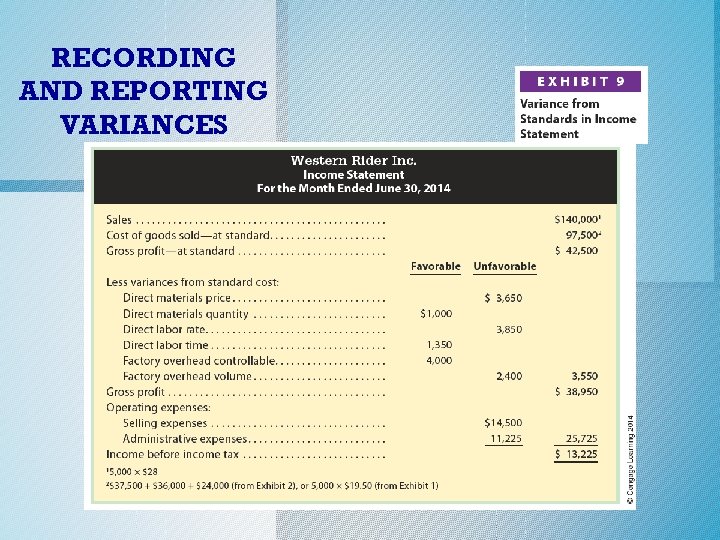
 Reporting Factory Overhead Variances o A factory overhead cost variance report is useful to management in controlling factory overhead costs. o Exhibit 8 (next slide) illustrates this report for Western Rider Inc. for June. c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
Reporting Factory Overhead Variances o A factory overhead cost variance report is useful to management in controlling factory overhead costs. o Exhibit 8 (next slide) illustrates this report for Western Rider Inc. for June. c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
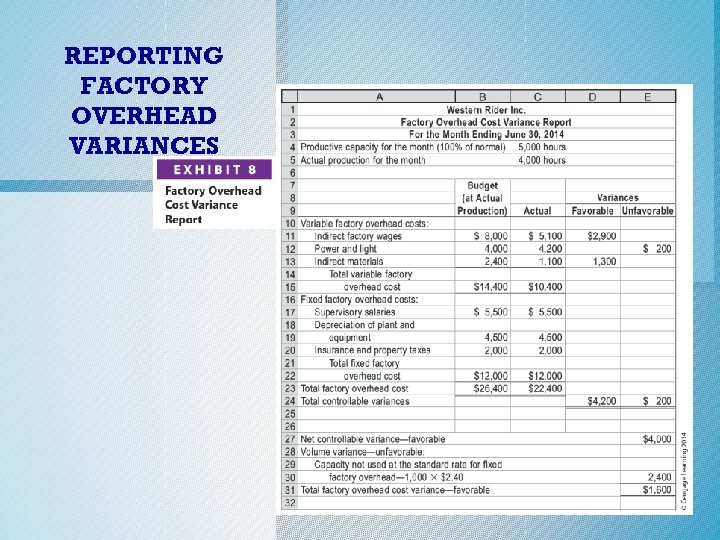 REPORTING FACTORY OVERHEAD VARIANCES
REPORTING FACTORY OVERHEAD VARIANCES
 Factory Overhead Account Applied Factory = Standard Hours for x Total Factory Actual Units Produced Overhead Rate Overhead Applied Factory = Overhead 5, 000 jeans x 0. 80 direct labor hr. per pair of jeans x $6. 00 Applied Factory = 4, 000 direct labor hrs. x $6. 00 = $24, 000 Overhead
Factory Overhead Account Applied Factory = Standard Hours for x Total Factory Actual Units Produced Overhead Rate Overhead Applied Factory = Overhead 5, 000 jeans x 0. 80 direct labor hr. per pair of jeans x $6. 00 Applied Factory = 4, 000 direct labor hrs. x $6. 00 = $24, 000 Overhead
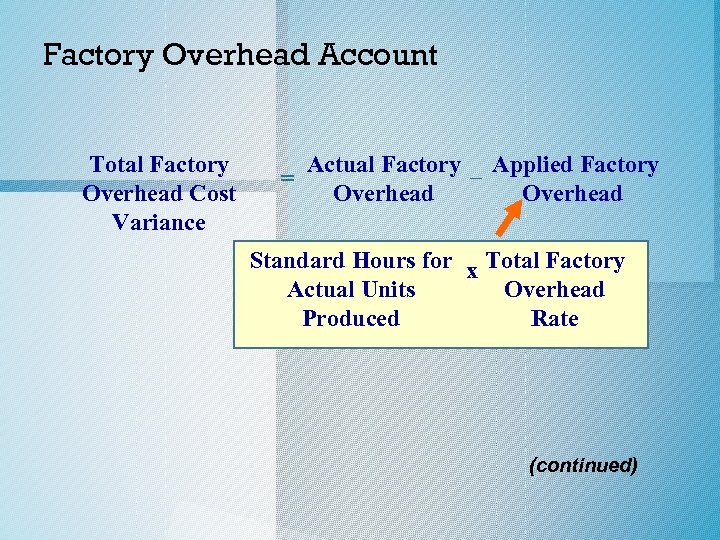 Factory Overhead Account Total Factory Overhead Cost Variance = Actual Factory – Applied Factory Overhead Standard Hours for x Total Factory Actual Units Overhead Produced Rate (continued)
Factory Overhead Account Total Factory Overhead Cost Variance = Actual Factory – Applied Factory Overhead Standard Hours for x Total Factory Actual Units Overhead Produced Rate (continued)
 Factory Overhead Account Total Factory Overhead Cost Variance = Actual Factory – $24, 000 Overhead 5, 000 jeans x 0. 80 direct labor hr. per x $6. 00 pair of jeans (continued)
Factory Overhead Account Total Factory Overhead Cost Variance = Actual Factory – $24, 000 Overhead 5, 000 jeans x 0. 80 direct labor hr. per x $6. 00 pair of jeans (continued)
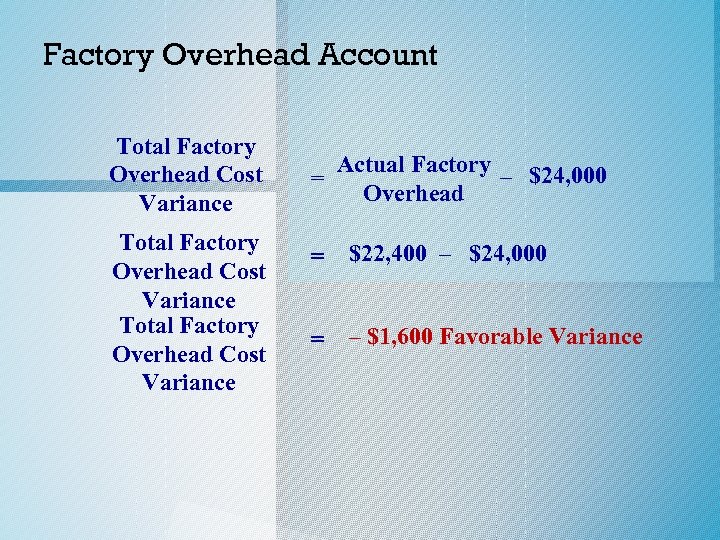 Factory Overhead Account Total Factory Overhead Cost Variance = Actual Factory – $24, 000 Overhead = $22, 400 – $24, 000 = – $1, 600 Favorable Variance
Factory Overhead Account Total Factory Overhead Cost Variance = Actual Factory – $24, 000 Overhead = $22, 400 – $24, 000 = – $1, 600 Favorable Variance
 Factory Overhead Account o Underapplied and overapplied factory overhead account balances represent the following total factory overhead cost variances: Ø Underapplied Factory Overhead = Unfavorable Total Factory Overhead Cost Variance Ø Overapplied Factory Overhead = Favorable Total Factory Overhead Cost Variance c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
Factory Overhead Account o Underapplied and overapplied factory overhead account balances represent the following total factory overhead cost variances: Ø Underapplied Factory Overhead = Unfavorable Total Factory Overhead Cost Variance Ø Overapplied Factory Overhead = Favorable Total Factory Overhead Cost Variance c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
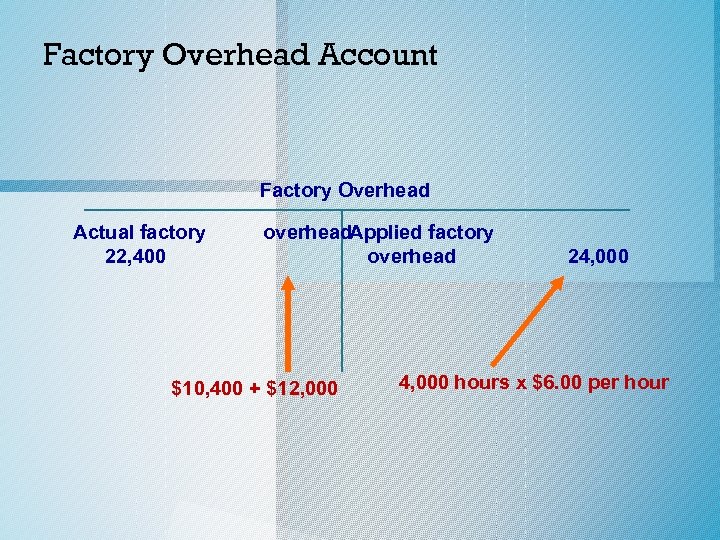 Factory Overhead Account Factory Overhead Actual factory 22, 400 overhead. Applied factory overhead $10, 400 + $12, 000 24, 000 hours x $6. 00 per hour
Factory Overhead Account Factory Overhead Actual factory 22, 400 overhead. Applied factory overhead $10, 400 + $12, 000 24, 000 hours x $6. 00 per hour
 Factory Overhead Account Factory Overhead Actual factory 22, 400 overhead. Applied factory overhead 24, 000 Balance, June 30 Overapplied factory overhead 1, 600
Factory Overhead Account Factory Overhead Actual factory 22, 400 overhead. Applied factory overhead 24, 000 Balance, June 30 Overapplied factory overhead 1, 600
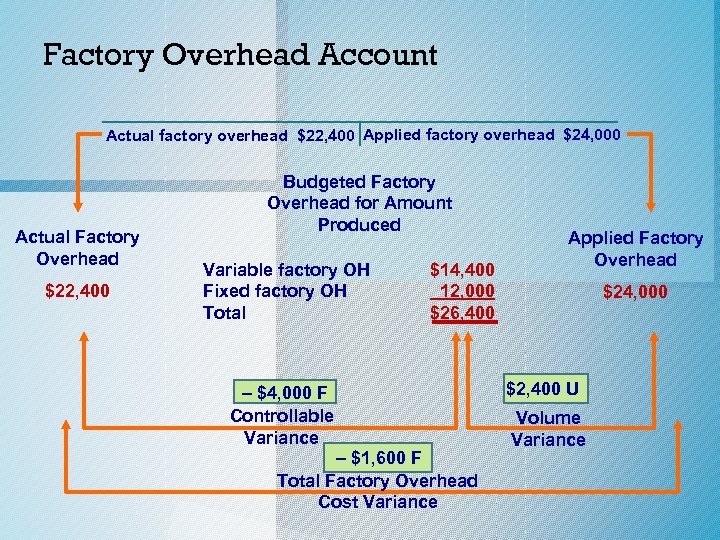 Factory Overhead Account Actual factory overhead $22, 400 Applied factory overhead $24, 000 Actual Factory Overhead $22, 400 Budgeted Factory Overhead for Amount Produced Variable factory OH Fixed factory OH Total $14, 400 12, 000 $26, 400 – $4, 000 F Controllable Variance – $1, 600 F Total Factory Overhead Cost Variance Applied Factory Overhead $24, 000 $2, 400 U Volume Variance
Factory Overhead Account Actual factory overhead $22, 400 Applied factory overhead $24, 000 Actual Factory Overhead $22, 400 Budgeted Factory Overhead for Amount Produced Variable factory OH Fixed factory OH Total $14, 400 12, 000 $26, 400 – $4, 000 F Controllable Variance – $1, 600 F Total Factory Overhead Cost Variance Applied Factory Overhead $24, 000 $2, 400 U Volume Variance
 Lear ning Obje Journ ctive alize stand the entri i dard prep s in t es for rec a h inclu re an in o com e accoun rding des v ts an arian e state d men ces f t rom stand that ard. 5 c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
Lear ning Obje Journ ctive alize stand the entri i dard prep s in t es for rec a h inclu re an in o com e accoun rding des v ts an arian e state d men ces f t rom stand that ard. 5 c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
 Recording and Reporting Variances o Standard costs may be used as a management tool to control costs separately from the accounts in the general ledger. However, many companies include both standard costs and variances, in addition to actual costs, in their accounts. c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
Recording and Reporting Variances o Standard costs may be used as a management tool to control costs separately from the accounts in the general ledger. However, many companies include both standard costs and variances, in addition to actual costs, in their accounts. c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
 Recording and Reporting Variances o Western Rider Inc. purchased, on account, the 7, 300 square yards of blue denim at $5. 50 per square yard. The standard price is $5. 00 per square yard. The entry to record the purchase and the unfavorable direct materials price variance is as follows: c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
Recording and Reporting Variances o Western Rider Inc. purchased, on account, the 7, 300 square yards of blue denim at $5. 50 per square yard. The standard price is $5. 00 per square yard. The entry to record the purchase and the unfavorable direct materials price variance is as follows: c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
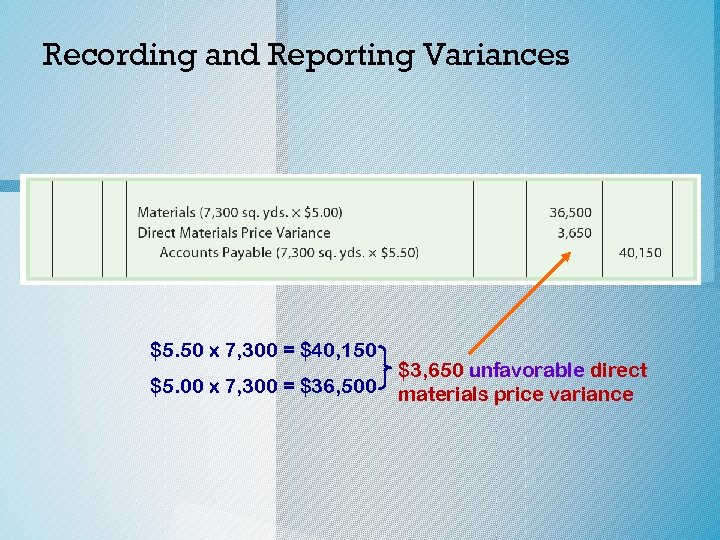 Recording and Reporting Variances $5. 50 x 7, 300 = $40, 150 $5. 00 x 7, 300 = $36, 500 $3, 650 unfavorable direct materials price variance
Recording and Reporting Variances $5. 50 x 7, 300 = $40, 150 $5. 00 x 7, 300 = $36, 500 $3, 650 unfavorable direct materials price variance
 Recording and Reporting Variances 1. Western Rider Inc. used 7, 300 square yards of blue denim to produce 5, 000 pairs of XL jeans. The standard quantity of denim for the 5, 000 jeans produced is 7, 500 square yards. The entry to record the materials used is as follows:
Recording and Reporting Variances 1. Western Rider Inc. used 7, 300 square yards of blue denim to produce 5, 000 pairs of XL jeans. The standard quantity of denim for the 5, 000 jeans produced is 7, 500 square yards. The entry to record the materials used is as follows:
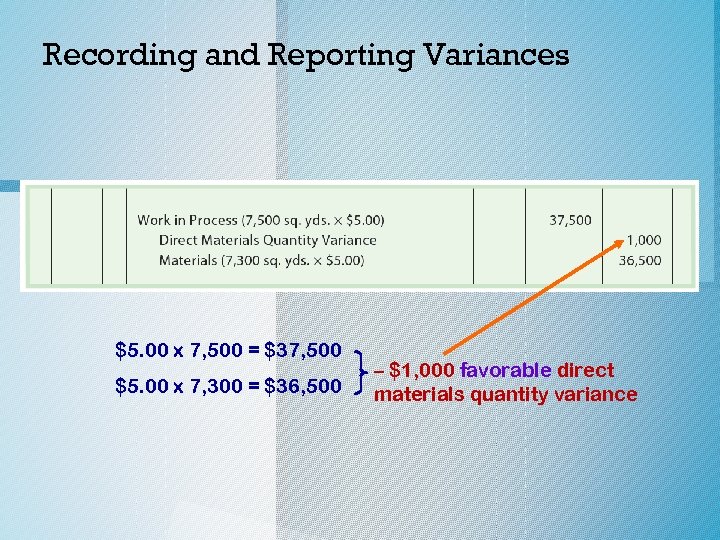 Recording and Reporting Variances $5. 00 x 7, 500 = $37, 500 $5. 00 x 7, 300 = $36, 500 – $1, 000 favorable direct materials quantity variance
Recording and Reporting Variances $5. 00 x 7, 500 = $37, 500 $5. 00 x 7, 300 = $36, 500 – $1, 000 favorable direct materials quantity variance
 Recording and Reporting Variances o Two journal entries are usually required for the purchase and use of direct materials because they are rarely the same amount. o Direct labor can be recorded in a single entry because “what you buy is what you use. ” o The diagram on the next slide is from Exhibit 5 where direct labor variances were illustrated. c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
Recording and Reporting Variances o Two journal entries are usually required for the purchase and use of direct materials because they are rarely the same amount. o Direct labor can be recorded in a single entry because “what you buy is what you use. ” o The diagram on the next slide is from Exhibit 5 where direct labor variances were illustrated. c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
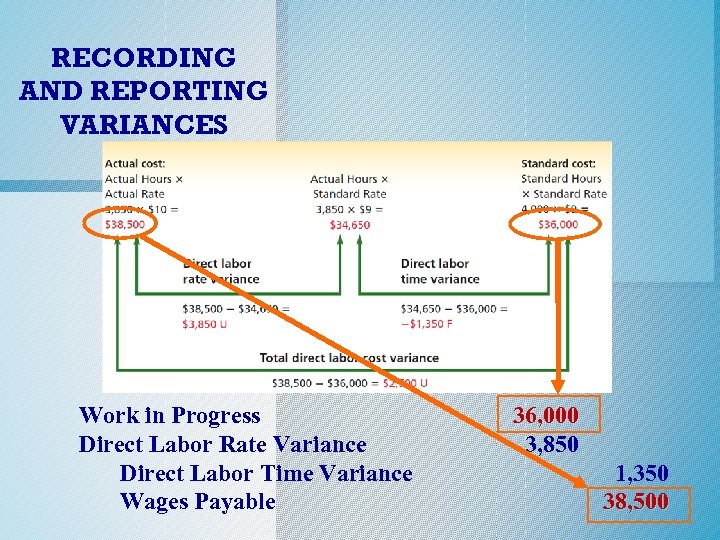 RECORDING AND REPORTING VARIANCES Work in Progress Direct Labor Rate Variance Direct Labor Time Variance Wages Payable 36, 000 3, 850 1, 350 38, 500
RECORDING AND REPORTING VARIANCES Work in Progress Direct Labor Rate Variance Direct Labor Time Variance Wages Payable 36, 000 3, 850 1, 350 38, 500
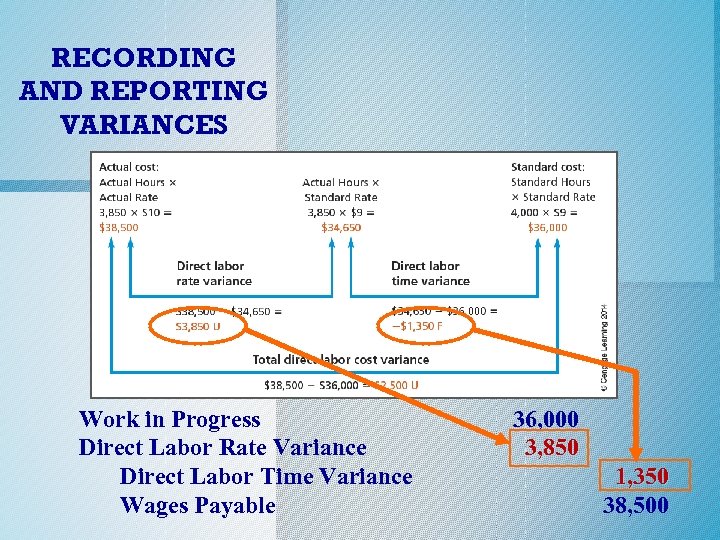 RECORDING AND REPORTING VARIANCES Work in Progress Direct Labor Rate Variance Direct Labor Time Variance Wages Payable 36, 000 3, 850 1, 350 38, 500
RECORDING AND REPORTING VARIANCES Work in Progress Direct Labor Rate Variance Direct Labor Time Variance Wages Payable 36, 000 3, 850 1, 350 38, 500
 RECORDING AND REPORTING VARIANCES
RECORDING AND REPORTING VARIANCES
 Lear ning Obje Desc ctive ribe nonf inan and pro c cial p vide e erfor man xamples ce m easu of res. 6 c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
Lear ning Obje Desc ctive ribe nonf inan and pro c cial p vide e erfor man xamples ce m easu of res. 6 c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
 Nonfinancial Performance Measures o A nonfinancial performance measure expresses performance in a measure other than dollars. c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
Nonfinancial Performance Measures o A nonfinancial performance measure expresses performance in a measure other than dollars. c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
 Nonfinancial Performance Measures o Inventory turnover o Percent on-time delivery o Elapsed time between a customer order and product delivery o Customer preference rankings compared to competitors o Response time to a service call o Time to develop new products o Employee satisfaction o Number of customer complaints c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
Nonfinancial Performance Measures o Inventory turnover o Percent on-time delivery o Elapsed time between a customer order and product delivery o Customer preference rankings compared to competitors o Response time to a service call o Time to develop new products o Employee satisfaction o Number of customer complaints c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
 Nonfinancial Performance Measures o Nonfinancial measures can be linked to either the inputs or outputs of an activity or process. o A process is a sequence of activities linked together for performing a particular task. c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
Nonfinancial Performance Measures o Nonfinancial measures can be linked to either the inputs or outputs of an activity or process. o A process is a sequence of activities linked together for performing a particular task. c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
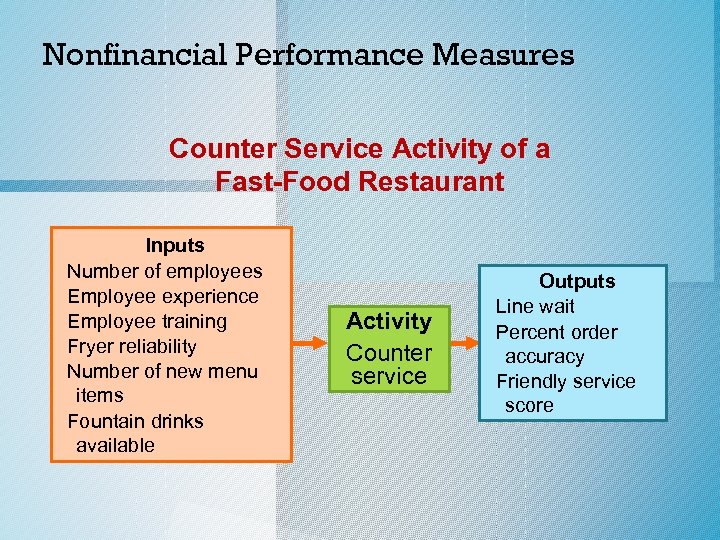 Nonfinancial Performance Measures Counter Service Activity of a Fast-Food Restaurant Inputs Number of employees Employee experience Employee training Fryer reliability Number of new menu items Fountain drinks available Activity Counter service Outputs Line wait Percent order accuracy Friendly service score
Nonfinancial Performance Measures Counter Service Activity of a Fast-Food Restaurant Inputs Number of employees Employee experience Employee training Fryer reliability Number of new menu items Fountain drinks available Activity Counter service Outputs Line wait Percent order accuracy Friendly service score
 ce an orm ing rf Pe Us ion rom at alu ces f Ev ian sts ar Co V ard nd nd ta S e. E Th c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
ce an orm ing rf Pe Us ion rom at alu ces f Ev ian sts ar Co V ard nd nd ta S e. E Th c. 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.


