Asia-regional charachteristic Characteristic of geographical place Asia locate






















29336-asia.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 Asia-regional charachteristic
Asia-regional charachteristic


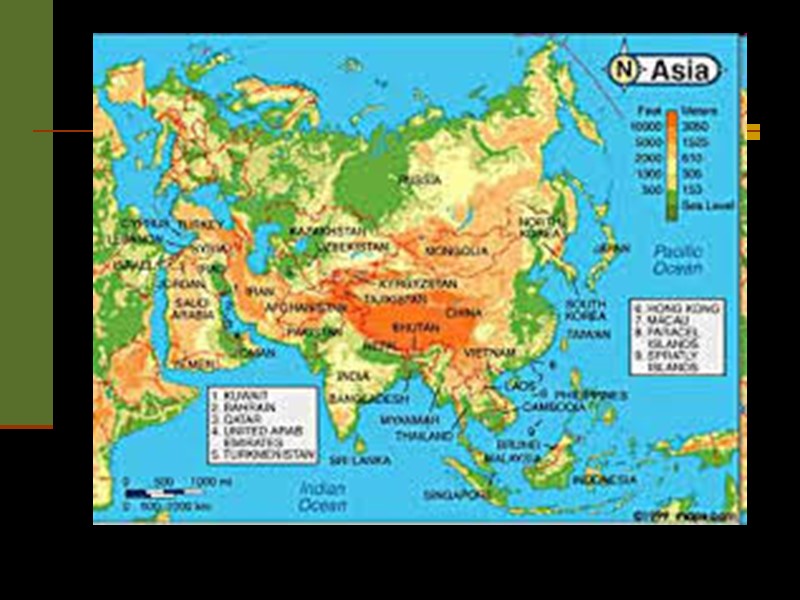
 Characteristic of geographical place Asia locate on South of Eurasia and some adjoin islands on South, East and South-East (Andaman, Nicobar, Maldives, Lakandivskie, Sri Lanka, Japan, Ryukyu Islands, Philippines, Greater and Lesser Sunda, the Moluccas). Asia is the largest of the world’s continents, covering approximately 30 percent of the Earth’s land area. It is also the world’s most populous continent, with roughly 60 percent of the total population. Square - about 43,608,000 km2
Characteristic of geographical place Asia locate on South of Eurasia and some adjoin islands on South, East and South-East (Andaman, Nicobar, Maldives, Lakandivskie, Sri Lanka, Japan, Ryukyu Islands, Philippines, Greater and Lesser Sunda, the Moluccas). Asia is the largest of the world’s continents, covering approximately 30 percent of the Earth’s land area. It is also the world’s most populous continent, with roughly 60 percent of the total population. Square - about 43,608,000 km2
 Physical-geographical division West Asia (Caucasus and Southwest highland); Southwest Asia (Arabian Peninsula and the Levant); South Asia (Indian subcontinent and the island of Sri Lanka); Southeast Asia (Indochina peninsula and the Malay Archipelago); East Asia (Korean peninsula, the islands of Japan, the eastern part of China); Northern Asia (Siberia and north-east of Eurasia); Central Asia (Pamir, Tien Shan, Turan Lowland).
Physical-geographical division West Asia (Caucasus and Southwest highland); Southwest Asia (Arabian Peninsula and the Levant); South Asia (Indian subcontinent and the island of Sri Lanka); Southeast Asia (Indochina peninsula and the Malay Archipelago); East Asia (Korean peninsula, the islands of Japan, the eastern part of China); Northern Asia (Siberia and north-east of Eurasia); Central Asia (Pamir, Tien Shan, Turan Lowland).
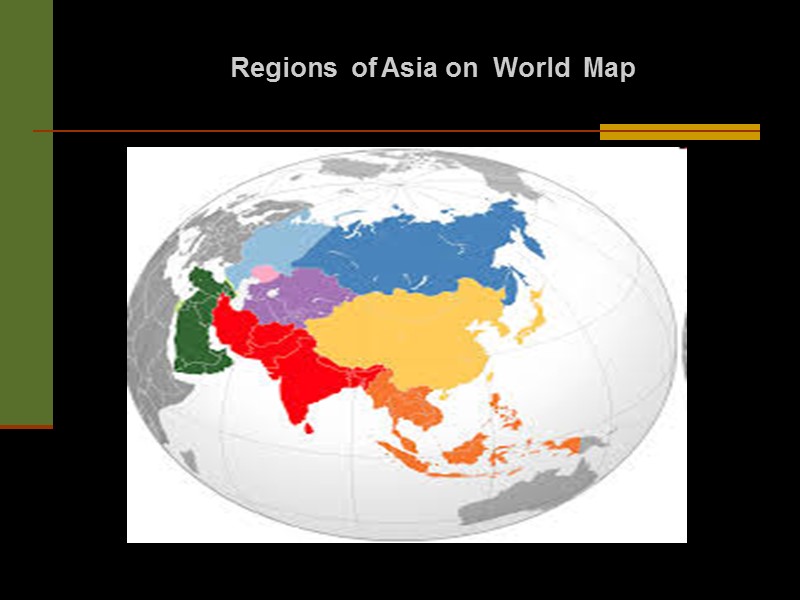
 Regions of Asia on World Map
Regions of Asia on World Map
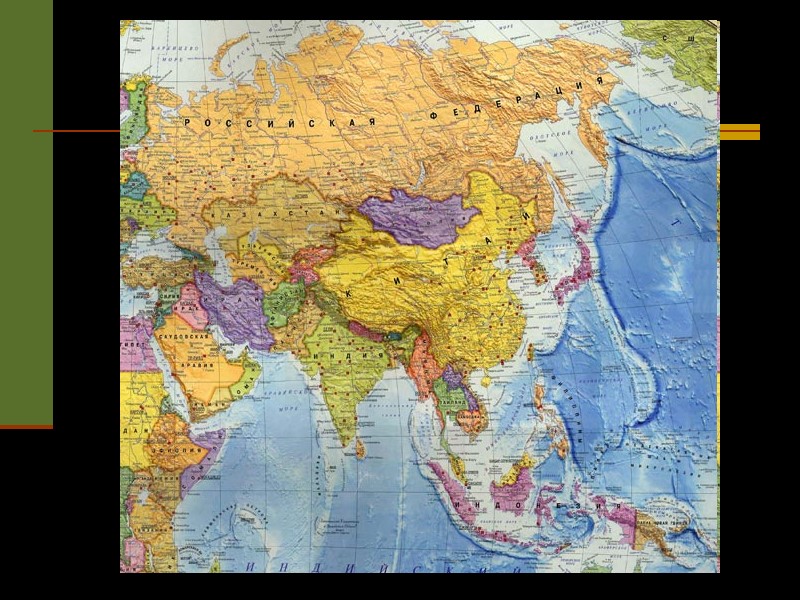
 Political and economical division In Asia locate 49 independent states. Russia, Kazakhstan and Turkey locate a part in Asia, and a part in Europe Asia is on of the big provider of mineral sources and agricultural products. Particularly large role of Asia in production and export of oil, gas, tin, tee, jute and natural rubber..
Political and economical division In Asia locate 49 independent states. Russia, Kazakhstan and Turkey locate a part in Asia, and a part in Europe Asia is on of the big provider of mineral sources and agricultural products. Particularly large role of Asia in production and export of oil, gas, tin, tee, jute and natural rubber..

 Southwest Asia or Western Asia Area 6,255,160 km2 Population 313,428,000 The countries and territories of Western Asia: Armenia, Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Cyprus, Georgia, Iraq, Israel, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Oman, Palestine, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Syria, Turkey, United Arab Emirates, Yemen The region is surrounded by seven major seas; the Aegean Sea, the Black Sea, the Caspian Sea, the Persian Gulf, the Arabian Sea, the Red Sea, and the Mediterranean Sea.
Southwest Asia or Western Asia Area 6,255,160 km2 Population 313,428,000 The countries and territories of Western Asia: Armenia, Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Cyprus, Georgia, Iraq, Israel, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Oman, Palestine, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Syria, Turkey, United Arab Emirates, Yemen The region is surrounded by seven major seas; the Aegean Sea, the Black Sea, the Caspian Sea, the Persian Gulf, the Arabian Sea, the Red Sea, and the Mediterranean Sea.
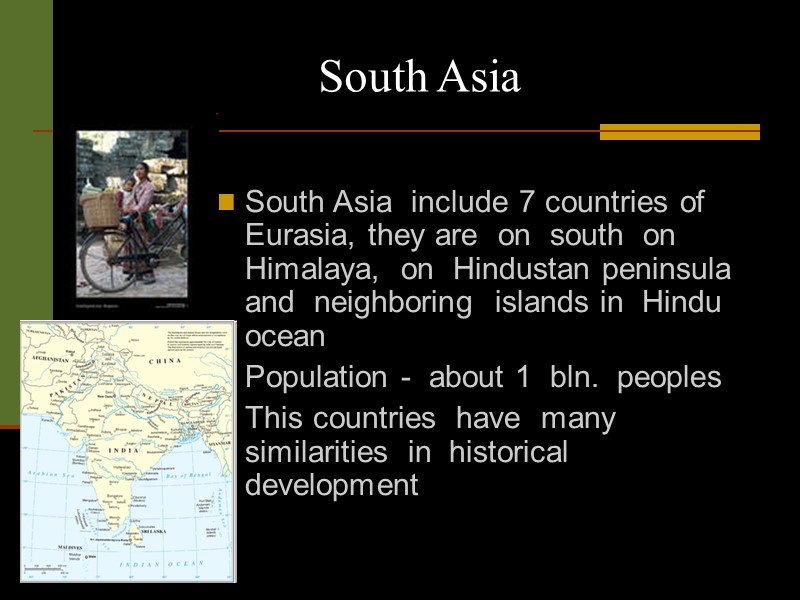
 South Asia South Asia include 7 countries of Eurasia, they are on south on Himalaya, on Hindustan peninsula and neighboring islands in Hindu ocean Population - about 1 bln. peoples This countries have many similarities in historical development
South Asia South Asia include 7 countries of Eurasia, they are on south on Himalaya, on Hindustan peninsula and neighboring islands in Hindu ocean Population - about 1 bln. peoples This countries have many similarities in historical development
 South-East Asia Southeast Asia consists of two geographic regions: Mainland Southeast Asia, also known as Indochina, comprising Cambodia, Laos, Myanmar (Burma), Thailand, Vietnam Maritime Southeast Asia, comprising Brunei, Malaysia, East Timor, Indonesia, Philippines, Christmas Island, and Singapore.
South-East Asia Southeast Asia consists of two geographic regions: Mainland Southeast Asia, also known as Indochina, comprising Cambodia, Laos, Myanmar (Burma), Thailand, Vietnam Maritime Southeast Asia, comprising Brunei, Malaysia, East Timor, Indonesia, Philippines, Christmas Island, and Singapore.
 East Asia Area is 12,000,000 km2 or about 28% of the Asian continent, Population - more than 1.5 billion people Historically, many societies in East Asia have been part of the Chinese cultural sphere, and East Asian vocabulary and scripts are often derived from Classical Chinese and Chinese script. Sometimes Northeast Asia is used to denote Japan and Korea. Region include: China, Japan, Both Korea, Aomyn and Hong Kong
East Asia Area is 12,000,000 km2 or about 28% of the Asian continent, Population - more than 1.5 billion people Historically, many societies in East Asia have been part of the Chinese cultural sphere, and East Asian vocabulary and scripts are often derived from Classical Chinese and Chinese script. Sometimes Northeast Asia is used to denote Japan and Korea. Region include: China, Japan, Both Korea, Aomyn and Hong Kong
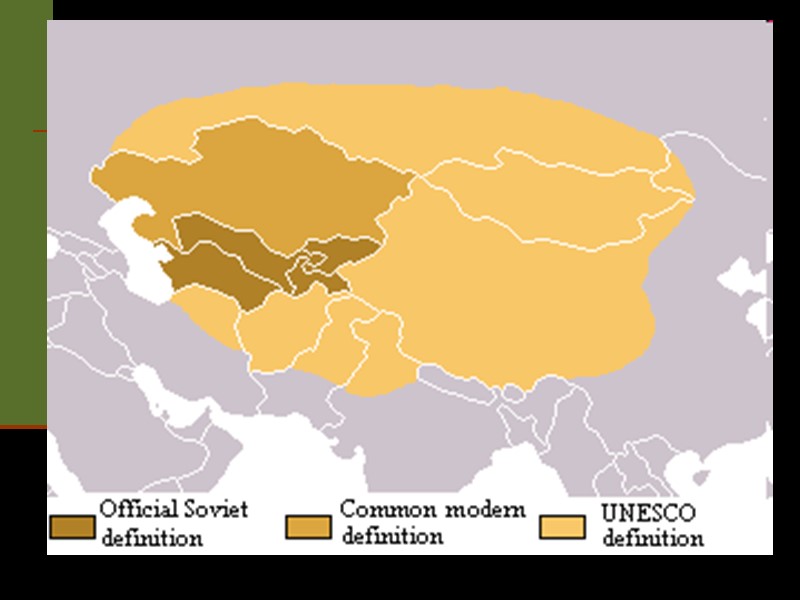
 Central Asia Central Asia is the core region of the Asian continent and stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to China in the east and from Afghanistan in the south to Russia in the north. In modern contexts, all definitions of Central Asia include five republics of the former Soviet Union: Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan Other areas sometimes included are Afghanistan, Mongolia, eastern Iran, and northwestern Pakistan, and sometimes Xinjiang and Tibet in western China, the Kashmir region of northern India and northern Pakistan, and southern Siberia in southern Russia.
Central Asia Central Asia is the core region of the Asian continent and stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to China in the east and from Afghanistan in the south to Russia in the north. In modern contexts, all definitions of Central Asia include five republics of the former Soviet Union: Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan Other areas sometimes included are Afghanistan, Mongolia, eastern Iran, and northwestern Pakistan, and sometimes Xinjiang and Tibet in western China, the Kashmir region of northern India and northern Pakistan, and southern Siberia in southern Russia.

 Geographical characteristic Big part of Asian countries Большинство стран Азии have a seaside location, providing them access to the seas of the Pacific, Indian and Atlantic Oceans. Mongolia, Afghanistan, Nepal, Bhutan and Laos are located in the interior of the continent and have no outlet to the sea.
Geographical characteristic Big part of Asian countries Большинство стран Азии have a seaside location, providing them access to the seas of the Pacific, Indian and Atlantic Oceans. Mongolia, Afghanistan, Nepal, Bhutan and Laos are located in the interior of the continent and have no outlet to the sea.
 Geographical characteristic Climates range of Asia are from arctic and subarctic in Siberia to tropical in southern India and Southeast Asia. It is moist across southeast sections, and dry across much of the interior. Some of the largest daily temperature ranges on Earth occur in western sections of Asia. The most active place on Earth for tropical cyclone activity lies northeast of the Philippines and south of Japan. The Gobi Desert is in Mongolia and the Arabian Desert stretches across much of the Middle East.
Geographical characteristic Climates range of Asia are from arctic and subarctic in Siberia to tropical in southern India and Southeast Asia. It is moist across southeast sections, and dry across much of the interior. Some of the largest daily temperature ranges on Earth occur in western sections of Asia. The most active place on Earth for tropical cyclone activity lies northeast of the Philippines and south of Japan. The Gobi Desert is in Mongolia and the Arabian Desert stretches across much of the Middle East.
 Demography of Asia The continent covers 29.4% of the Earth's land area and has a population of over 4 billion - accounting for about 56% of the world population. Together, China's and India's populations are estimated to be around 2.5 billion people.
Demography of Asia The continent covers 29.4% of the Earth's land area and has a population of over 4 billion - accounting for about 56% of the world population. Together, China's and India's populations are estimated to be around 2.5 billion people.
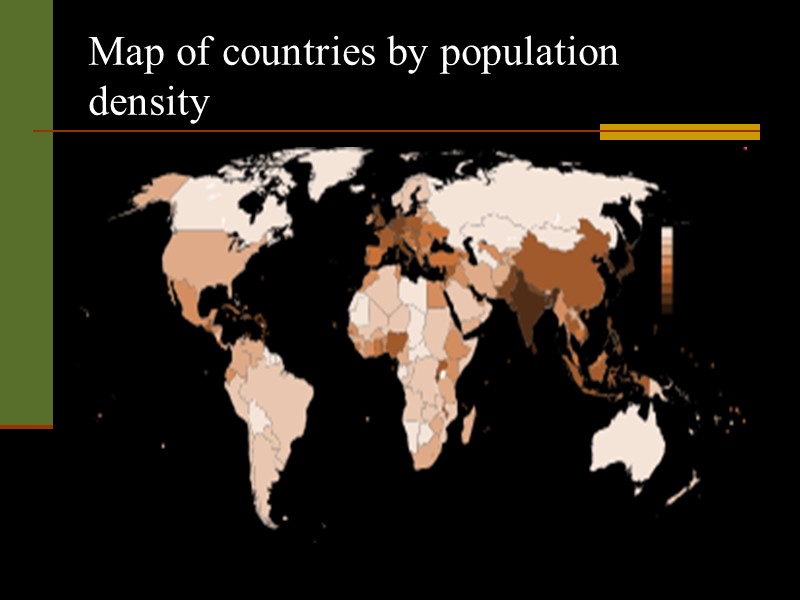
 Map of countries by population density
Map of countries by population density
 Ethnical and religious conposition Asia is home to several language families and many language isolates. For instance, according to Ethnologue, more than 600 languages are spoken in Indonesia, more than 800 languages spoken in India, and more than 100 are spoken in the Philippines. Asia was the birthplace of most of the world's mainstream religions including Islam, Buddhism, Confucianism, Judaism, Hinduism, Christianity, Jainism, Sikhism, Taoism, Zoroastranism, as well as many other beliefs.
Ethnical and religious conposition Asia is home to several language families and many language isolates. For instance, according to Ethnologue, more than 600 languages are spoken in Indonesia, more than 800 languages spoken in India, and more than 100 are spoken in the Philippines. Asia was the birthplace of most of the world's mainstream religions including Islam, Buddhism, Confucianism, Judaism, Hinduism, Christianity, Jainism, Sikhism, Taoism, Zoroastranism, as well as many other beliefs.
 Economic Activities Until the start of the 20th century, subsistence agriculture was the basic economic activity of most of Asia. Most Asian nations have attempted to industrialize and modernize their societies, particularly since World War II. Several nations, especially Japan, South Korea, Taiwan, and Singapore, have succeeded in reaching the industrial and technological level of the major Western nations. The other nations of Asia are dealing, with varying degrees of success, with the many difficult problems of modernization.
Economic Activities Until the start of the 20th century, subsistence agriculture was the basic economic activity of most of Asia. Most Asian nations have attempted to industrialize and modernize their societies, particularly since World War II. Several nations, especially Japan, South Korea, Taiwan, and Singapore, have succeeded in reaching the industrial and technological level of the major Western nations. The other nations of Asia are dealing, with varying degrees of success, with the many difficult problems of modernization.
 Agriculture Agriculture is by far the most important economic activity in Asia. Almost 60 per cent of the continent's working population is engaged in farming. The countries of Asia—led by China and India—produce more than 90 percent of the world's supply of rice. The main wheat-growing areas are northeastern China; Central Asia, especially Kazakhstan; Russia and Turkey and the upper Ganges River valley in India and Pakistan.
Agriculture Agriculture is by far the most important economic activity in Asia. Almost 60 per cent of the continent's working population is engaged in farming. The countries of Asia—led by China and India—produce more than 90 percent of the world's supply of rice. The main wheat-growing areas are northeastern China; Central Asia, especially Kazakhstan; Russia and Turkey and the upper Ganges River valley in India and Pakistan.
 Agriculture In addition to rice, other principal food crops in southern and eastern Asia include millet, sorghum, barley, corn, sweet potatoes and yams, cassava, peanuts, soybeans, and a variety of peas and beans. Export crops include citrus fruit, nuts, dates, figs, and coffee. The most valuable commercial crops are grown primarily in southern and eastern Asia. Among them are rubber and palm nuts in Malaysia, Indonesia, and Thailand; tea in Sri Lanka, India, Indonesia and China; cotton in India, Pakistan, China, Turkey, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan; jute in Bangladesh, China and India; and sugarcane in India, Pakistan, Indonesia, the Philippines, and Thailand. Sericulture (the production of silk by raising silkworms) in Japan, China, India, and North and South Korea accounts for most of the world's raw silk. Much of the world's supply of spices, including pepper, ginger, and cinnamon, comes from Asia.
Agriculture In addition to rice, other principal food crops in southern and eastern Asia include millet, sorghum, barley, corn, sweet potatoes and yams, cassava, peanuts, soybeans, and a variety of peas and beans. Export crops include citrus fruit, nuts, dates, figs, and coffee. The most valuable commercial crops are grown primarily in southern and eastern Asia. Among them are rubber and palm nuts in Malaysia, Indonesia, and Thailand; tea in Sri Lanka, India, Indonesia and China; cotton in India, Pakistan, China, Turkey, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan; jute in Bangladesh, China and India; and sugarcane in India, Pakistan, Indonesia, the Philippines, and Thailand. Sericulture (the production of silk by raising silkworms) in Japan, China, India, and North and South Korea accounts for most of the world's raw silk. Much of the world's supply of spices, including pepper, ginger, and cinnamon, comes from Asia.
 Agriculture Meat is provided by hogs, poultry, sheep, and goats. The great majority of the hogs are raised in China, where they are a chief source of meat. Cattle and water buffalo are raised primarily for milk and for use as draft animals. India has the greatest number of cattle; however, these animals are held sacred by Hindus, so many serve no economic purpose. Sheep, goats, and horses are raised in short-grass regions. Nomadic herders in the semidesert areas of southwestern and central Asia raise goats, sheep, and camels. Yaks, sheep, and goats are kept on the Tibetan Plateau, and reindeer herds on the Siberian tundras.
Agriculture Meat is provided by hogs, poultry, sheep, and goats. The great majority of the hogs are raised in China, where they are a chief source of meat. Cattle and water buffalo are raised primarily for milk and for use as draft animals. India has the greatest number of cattle; however, these animals are held sacred by Hindus, so many serve no economic purpose. Sheep, goats, and horses are raised in short-grass regions. Nomadic herders in the semidesert areas of southwestern and central Asia raise goats, sheep, and camels. Yaks, sheep, and goats are kept on the Tibetan Plateau, and reindeer herds on the Siberian tundras.
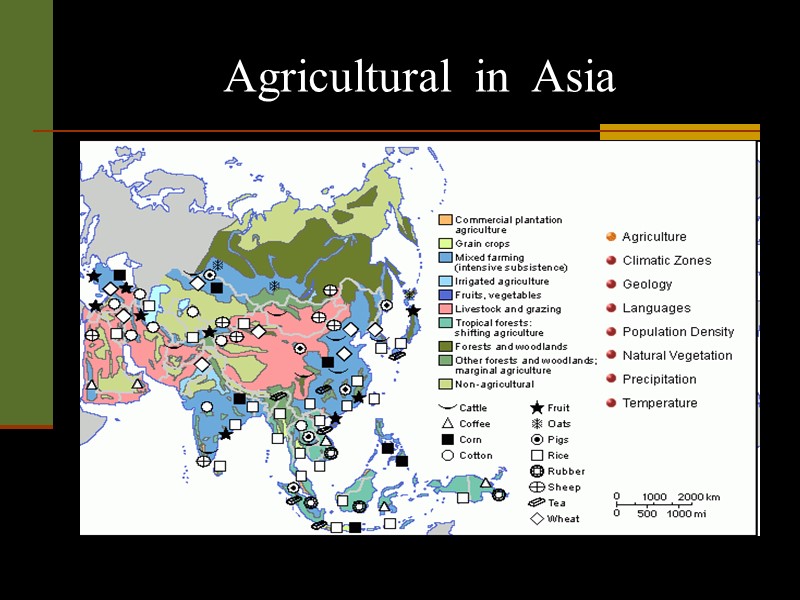
 Agricultural in Asia
Agricultural in Asia
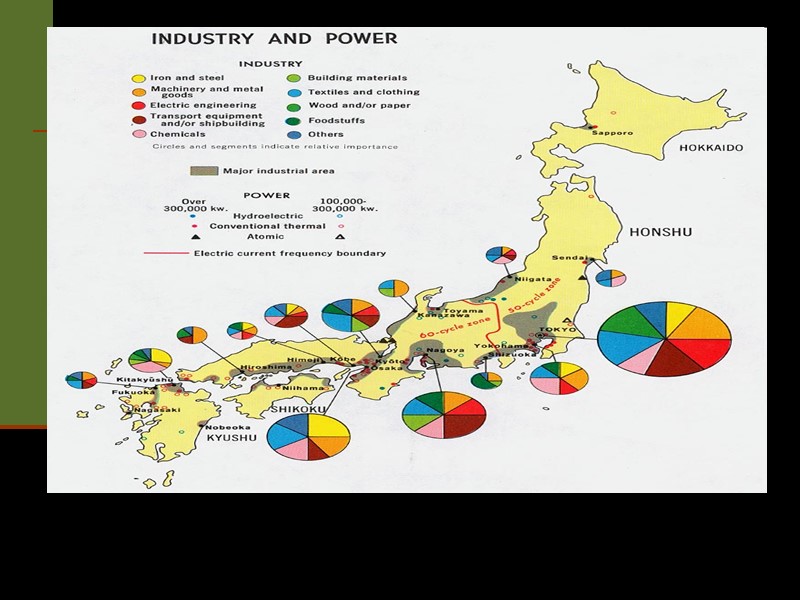
 Japan is one of Asia's leading manufacturing nation. It is a serious producer of iron and steel, transportation equipment, photographic equipment, and electronic goods. Japan is the only major Asian nation to have a predominantly urban population employed mainly in manufacturing and commerce. Both mainland China and India have attempted large-scale industrialization since roughly the mid-20th century. Manufacturing is also a significant and growing part of the economies of Indonesia, Iran, Pakistan, the Philippines, Thailand, Turkey, and Vietnam. They produce mostly consumer goods for their large home markets and, increasingly, for export. Manufacturing
Japan is one of Asia's leading manufacturing nation. It is a serious producer of iron and steel, transportation equipment, photographic equipment, and electronic goods. Japan is the only major Asian nation to have a predominantly urban population employed mainly in manufacturing and commerce. Both mainland China and India have attempted large-scale industrialization since roughly the mid-20th century. Manufacturing is also a significant and growing part of the economies of Indonesia, Iran, Pakistan, the Philippines, Thailand, Turkey, and Vietnam. They produce mostly consumer goods for their large home markets and, increasingly, for export. Manufacturing

 In Singapore and Hong Kong, export-oriented manufacturing is coupled with shipping, international banking, and other commerce. In parts of Asia there is little manufacturing except for the processing of a few natural resources, usually for export. Examples are manufacturing of inexpensive jute and cotton textiles in Bangladesh and the refining of petroleum in Kuwait. Light industries play an important role in the economies of such countries as Indonesia, Malaysia, and Thailand. Many Southeast Asian countries manufacture textiles, footwear, personal electronic products, and other consumer goods. Manufacturing
In Singapore and Hong Kong, export-oriented manufacturing is coupled with shipping, international banking, and other commerce. In parts of Asia there is little manufacturing except for the processing of a few natural resources, usually for export. Examples are manufacturing of inexpensive jute and cotton textiles in Bangladesh and the refining of petroleum in Kuwait. Light industries play an important role in the economies of such countries as Indonesia, Malaysia, and Thailand. Many Southeast Asian countries manufacture textiles, footwear, personal electronic products, and other consumer goods. Manufacturing
 Mining Fossil fuels are Asia's most important mineral products. Southwestern Asia, especially the area around the Persian Gulf, produces about one-fourth of the world's yearly output of petroleum, nearly all of it for export. Malaysia and Indonesia are also important exporters of petroleum. In many cases, natural gas is produced along with petroleum. Asia's major coal fields are in the Karaganda, in Kazakhstan; the northeastern part of China; and the northeastern area of India. Iron ore is found in significant quantities in northern Kazakhstan; near the major Chinese and Indian coal-producing areas; and in west-central India. Asia is the primary source of much of the world's tin and graphite. Gold, nickel, and platinum and related metals are found in Siberia and precious gems—rubies and sapphires—in Sri Lanka and Burma. Among the many other minerals produced are tungsten, lead, manganese, copper, and bauxite, as well as phosphates and numerous other nonmetallic minerals. China exports large amounts of antimony and tungsten. Manganese and mica from China and India and chromite mined in Turkey and the Philippines are exported to many parts of the world.
Mining Fossil fuels are Asia's most important mineral products. Southwestern Asia, especially the area around the Persian Gulf, produces about one-fourth of the world's yearly output of petroleum, nearly all of it for export. Malaysia and Indonesia are also important exporters of petroleum. In many cases, natural gas is produced along with petroleum. Asia's major coal fields are in the Karaganda, in Kazakhstan; the northeastern part of China; and the northeastern area of India. Iron ore is found in significant quantities in northern Kazakhstan; near the major Chinese and Indian coal-producing areas; and in west-central India. Asia is the primary source of much of the world's tin and graphite. Gold, nickel, and platinum and related metals are found in Siberia and precious gems—rubies and sapphires—in Sri Lanka and Burma. Among the many other minerals produced are tungsten, lead, manganese, copper, and bauxite, as well as phosphates and numerous other nonmetallic minerals. China exports large amounts of antimony and tungsten. Manganese and mica from China and India and chromite mined in Turkey and the Philippines are exported to many parts of the world.
 Tourism Tourism and a related industry, handicrafts, have great economic importance in many parts of Asia, as tourists buy handicrafts made by Asians. The tourist industry is especially active in South, Southeast, and East Asia. A great variety of handicraft items, usually made in small shops for sale in local markets, are produced throughout Asia. Some, including certain textiles, rugs, porcelains, and brassware, are of high quality and find markets throughout the world.
Tourism Tourism and a related industry, handicrafts, have great economic importance in many parts of Asia, as tourists buy handicrafts made by Asians. The tourist industry is especially active in South, Southeast, and East Asia. A great variety of handicraft items, usually made in small shops for sale in local markets, are produced throughout Asia. Some, including certain textiles, rugs, porcelains, and brassware, are of high quality and find markets throughout the world.
 Fishing, and Forestry Fishing is an important activity in Asia. Most of the catch is used for human food; relatively little is processed for livestock feed, fertilizer, or industrial use. The people of southern and eastern Asia depend on fish and shellfish for a large part of the protein in their diet. The major fishing nations of Asia include Japan, China, India, Indonesia, Thailand and South Korea. Asiatic Russia's catch is also important. The richest fisheries in Asian waters are in the western Pacific, especially in northern waters; the eastern Indian Ocean; and the South China Sea. Inland waters are also important. Tropical Asia produces fine hardwoods and veneer woods. In other parts of Asia, including China and India, wood is used mainly as a fuel.
Fishing, and Forestry Fishing is an important activity in Asia. Most of the catch is used for human food; relatively little is processed for livestock feed, fertilizer, or industrial use. The people of southern and eastern Asia depend on fish and shellfish for a large part of the protein in their diet. The major fishing nations of Asia include Japan, China, India, Indonesia, Thailand and South Korea. Asiatic Russia's catch is also important. The richest fisheries in Asian waters are in the western Pacific, especially in northern waters; the eastern Indian Ocean; and the South China Sea. Inland waters are also important. Tropical Asia produces fine hardwoods and veneer woods. In other parts of Asia, including China and India, wood is used mainly as a fuel.
 Transportation Railways are the chief means of long-distance transportation throughout much of Asia. The Colonial rulers built a large network of railroads during the late 19th century, when they used trains to carry raw materials from inland areas to coastal cities and ports. The most heavily used systems are in China, India, and Japan. The colonial rulers also built up Asia's highway system between inland areas and coastal cities. Since the end of colonial rule, an increasing emphasis has been placed on road construction throughout Asia. In general, roads linking large cities and those in and around urban areas form the only extensive networks. Roads have been built into the frontiers of western China, primarily for military purposes. Many kinds of vehicles transport people and goods in Asian cities, such as automobiles, buses, motor scooters, and trucks. Motor vehicles are less common in rural Asia, though buses travel along the rural roads. Huge areas of Asia are remote from roads and railways. The subarctic and arctic regions can be traveled by river during warmer weather. Cold-weather transportation is limited to dogsleds and special arctic vehicles. Some areas in the tropical forests can be reached only by riverboats or rafts. The great mountain chains are also barriers to travel. Air travel has opened up many parts of Asia to the movement of people and cargo. Airlines link most large Asian cities with one another and with other parts of the world. Most of Asia's larger cities and important remote localities have airports. The barriers to land travel and the convenience of water travel contributed to the concentration of population and trade on Asia's southern and eastern seacoasts. There, great cities—Tokyo, Shanghai, Hong Kong, Singapore, Kolkata (Calcutta), and many others—serve as entrance and exit points for much of Asia's goods and travelers. Rivers rank among the chief transportation routes of rural Asia. The people use barges, canoe-like vessels, junks, sampans, and other small boats for travel and to transport goods. Oceangoing vessels carry much cargo to and from Asia's ports. These huge modern ships tower above the small, old-fashioned sampans and other boats that dockworkers use while loading and unloading them.
Transportation Railways are the chief means of long-distance transportation throughout much of Asia. The Colonial rulers built a large network of railroads during the late 19th century, when they used trains to carry raw materials from inland areas to coastal cities and ports. The most heavily used systems are in China, India, and Japan. The colonial rulers also built up Asia's highway system between inland areas and coastal cities. Since the end of colonial rule, an increasing emphasis has been placed on road construction throughout Asia. In general, roads linking large cities and those in and around urban areas form the only extensive networks. Roads have been built into the frontiers of western China, primarily for military purposes. Many kinds of vehicles transport people and goods in Asian cities, such as automobiles, buses, motor scooters, and trucks. Motor vehicles are less common in rural Asia, though buses travel along the rural roads. Huge areas of Asia are remote from roads and railways. The subarctic and arctic regions can be traveled by river during warmer weather. Cold-weather transportation is limited to dogsleds and special arctic vehicles. Some areas in the tropical forests can be reached only by riverboats or rafts. The great mountain chains are also barriers to travel. Air travel has opened up many parts of Asia to the movement of people and cargo. Airlines link most large Asian cities with one another and with other parts of the world. Most of Asia's larger cities and important remote localities have airports. The barriers to land travel and the convenience of water travel contributed to the concentration of population and trade on Asia's southern and eastern seacoasts. There, great cities—Tokyo, Shanghai, Hong Kong, Singapore, Kolkata (Calcutta), and many others—serve as entrance and exit points for much of Asia's goods and travelers. Rivers rank among the chief transportation routes of rural Asia. The people use barges, canoe-like vessels, junks, sampans, and other small boats for travel and to transport goods. Oceangoing vessels carry much cargo to and from Asia's ports. These huge modern ships tower above the small, old-fashioned sampans and other boats that dockworkers use while loading and unloading them.
