Anatomy & Physiology of Heart Geu-Ru Hong, MD,










1._heart_anatomy_and_physiology.ppt
- Размер: 4.9 Mегабайта
- Количество слайдов: 44
Описание презентации Anatomy & Physiology of Heart Geu-Ru Hong, MD, по слайдам
 Anatomy & Physiology of Heart Geu-Ru Hong, MD, Ph. D Associate Professor Director of Echocardiography Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea
Anatomy & Physiology of Heart Geu-Ru Hong, MD, Ph. D Associate Professor Director of Echocardiography Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea
 Agenda Day 1: Heart anatomy & Physioligy, Ultrasound physics & Hemodynamic Assessment Day 2: Standard Imaging, Systolic & diastolic function Assessment Day 3: Valvular heart disease & Ischemic heart disease Day 4: Cardiomyopathy & Congenital heart disease Day 5: Pericardial disease, tumor, aortic disease, New technology in echo
Agenda Day 1: Heart anatomy & Physioligy, Ultrasound physics & Hemodynamic Assessment Day 2: Standard Imaging, Systolic & diastolic function Assessment Day 3: Valvular heart disease & Ischemic heart disease Day 4: Cardiomyopathy & Congenital heart disease Day 5: Pericardial disease, tumor, aortic disease, New technology in echo
 Leonardo Da Vinci 1452 -1519 Understanding Heart Disease From Discovery to Application
Leonardo Da Vinci 1452 -1519 Understanding Heart Disease From Discovery to Application
 Edler – cardiologist at the Dept. of Cardiology at the University of Lund. Hertz — graduate in Physics. Borrowed an Ultrasonic Reflectroscope from a Shipyard in Malmo used for testing Metals. May 1953 — Detected moving echoes by the Ultrasound Reflectroscope.
Edler – cardiologist at the Dept. of Cardiology at the University of Lund. Hertz — graduate in Physics. Borrowed an Ultrasonic Reflectroscope from a Shipyard in Malmo used for testing Metals. May 1953 — Detected moving echoes by the Ultrasound Reflectroscope.
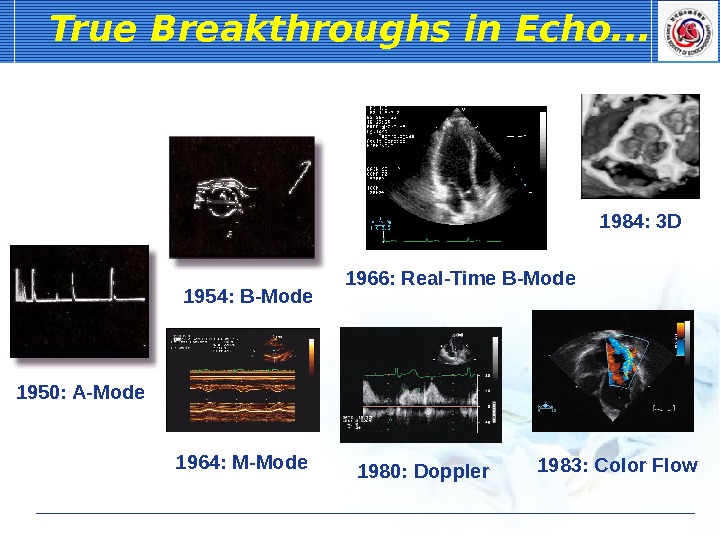
 1966: Real-Time B-Mode. True Breakthroughs in Echo. . . 1950: A-Mode 1954: B-Mode 1964: M-Mode 1984: 3 D 1980: Doppler 1983: Color Flow
1966: Real-Time B-Mode. True Breakthroughs in Echo. . . 1950: A-Mode 1954: B-Mode 1964: M-Mode 1984: 3 D 1980: Doppler 1983: Color Flow
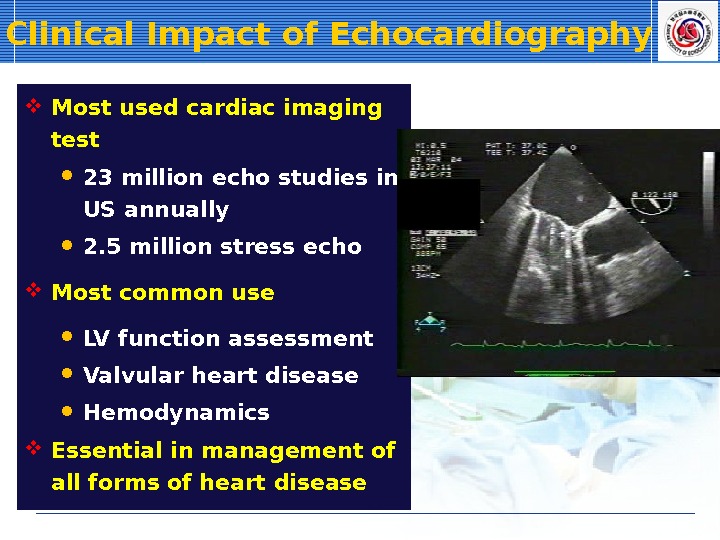
 Clinical Impact of Echocardiography Most used cardiac imaging test 23 million echo studies in US annually 2. 5 million stress echo Most common use LV function assessment Valvular heart disease Hemodynamics Essential in management of all forms of heart disease
Clinical Impact of Echocardiography Most used cardiac imaging test 23 million echo studies in US annually 2. 5 million stress echo Most common use LV function assessment Valvular heart disease Hemodynamics Essential in management of all forms of heart disease
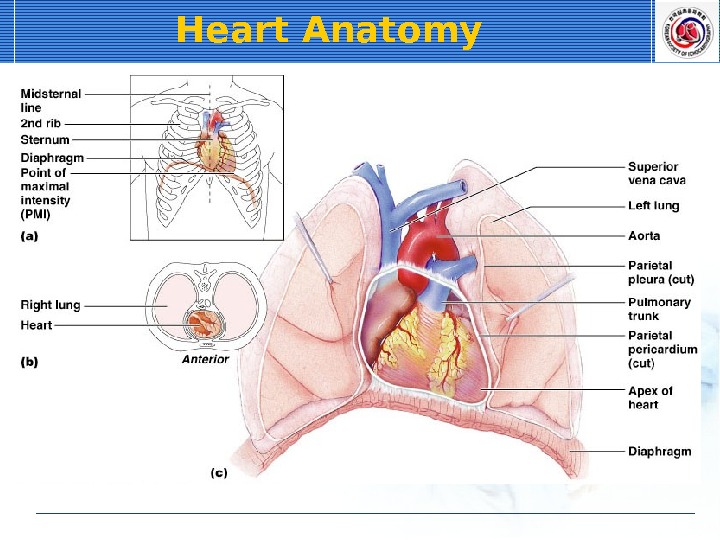
 Heart Anatomy
Heart Anatomy
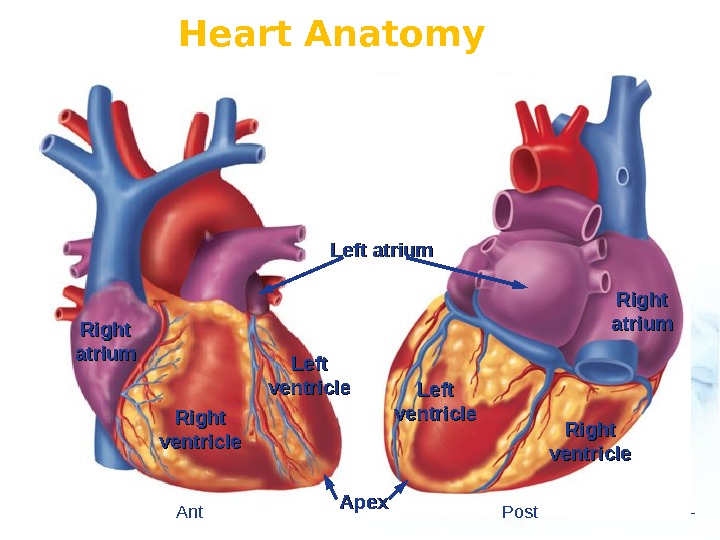
 Heart Anatomy Left ventricle Right ventricle Left atrium Right atriumatrium Right ventricle. Left ventricle Apex Ant Post
Heart Anatomy Left ventricle Right ventricle Left atrium Right atriumatrium Right ventricle. Left ventricle Apex Ant Post
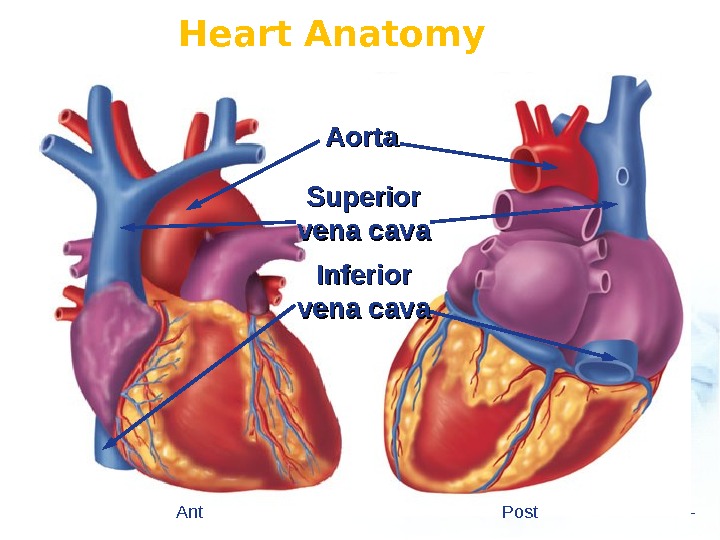
 Heart Anatomy Aorta Superior vena cava Inferior vena cava Ant Post
Heart Anatomy Aorta Superior vena cava Inferior vena cava Ant Post
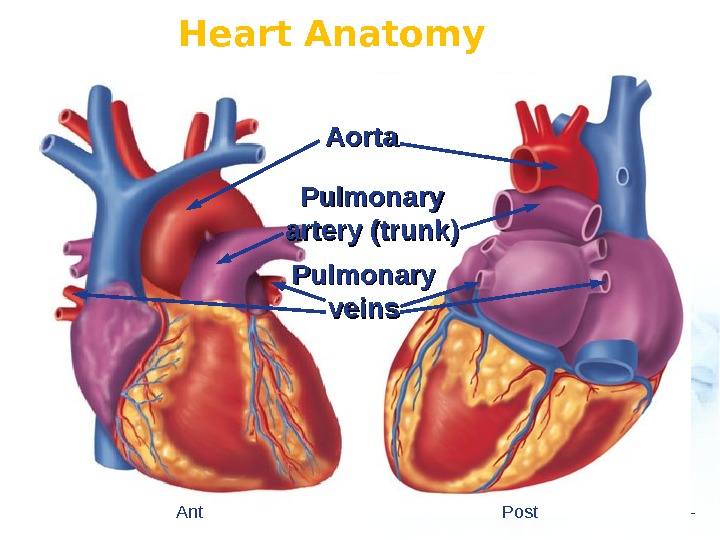
 Heart Anatomy Aorta Pulmonary artery (trunk) Pulmonary veins Ant Post
Heart Anatomy Aorta Pulmonary artery (trunk) Pulmonary veins Ant Post
 Pathway of Blood Through the Heart
Pathway of Blood Through the Heart
 Heart Anatomy Aorta Coronary arteries Cardiac veins Coronary sinus Ant Post
Heart Anatomy Aorta Coronary arteries Cardiac veins Coronary sinus Ant Post
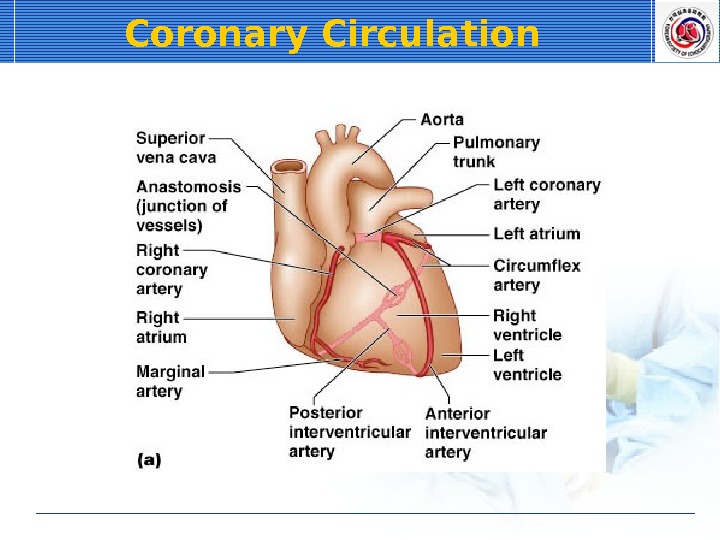
 Coronary Circulation
Coronary Circulation
 Coronary Circulation
Coronary Circulation
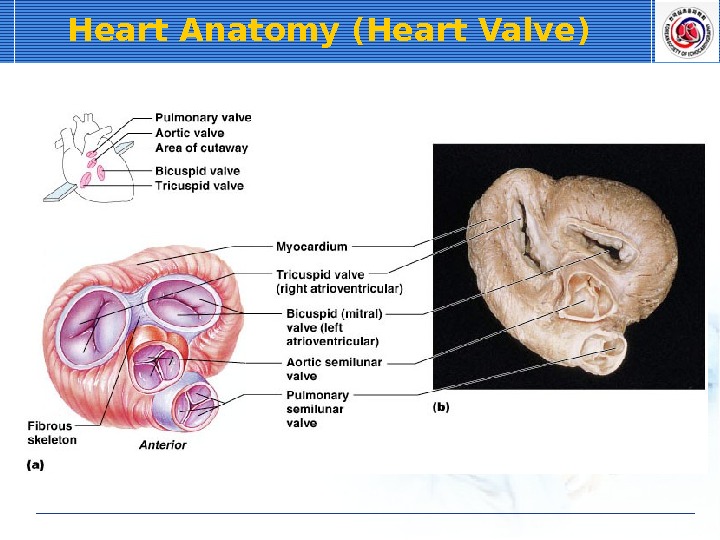
 Heart Anatomy (Heart Valve)
Heart Anatomy (Heart Valve)
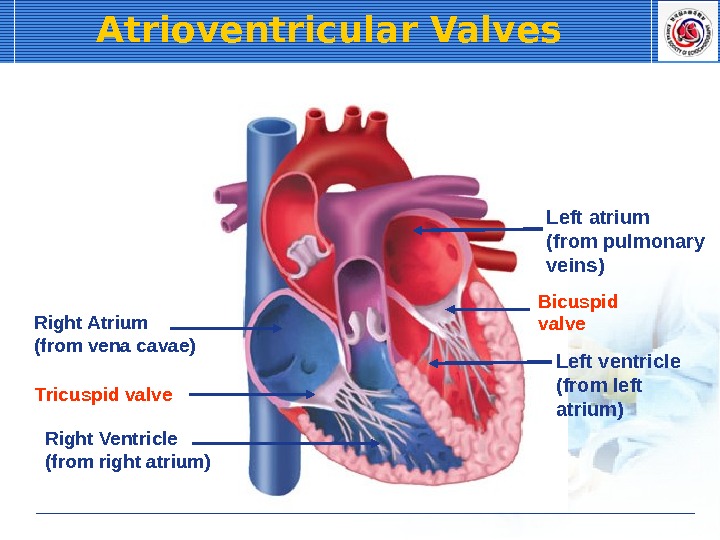
 Atrioventricular Valves Right Atrium (from vena cavae) Right Ventricle (from right atrium) Left atrium (from pulmonary veins) Left ventricle (from left atrium)Tricuspid valve Bicuspid valve
Atrioventricular Valves Right Atrium (from vena cavae) Right Ventricle (from right atrium) Left atrium (from pulmonary veins) Left ventricle (from left atrium)Tricuspid valve Bicuspid valve
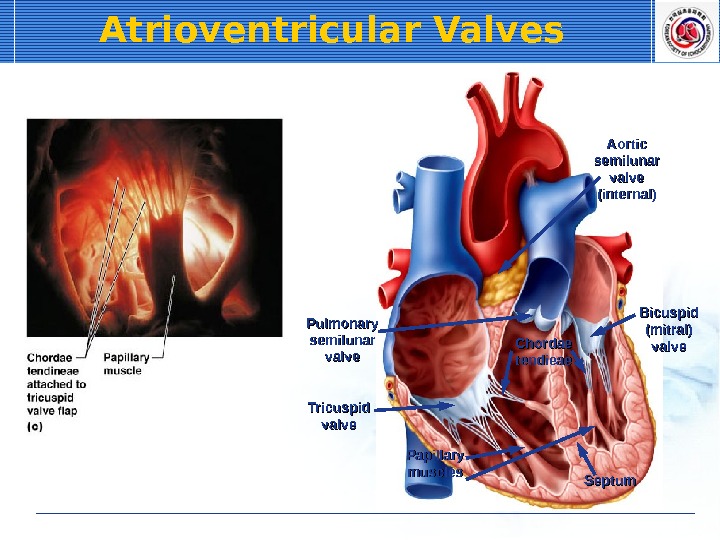
 Atrioventricular Valves Chordae tendieae Tricuspid valve Bicuspid (mitral) valve. Pulmonary semilunar valve Papillary muscles Septum Aortic semilunar valve (internal)
Atrioventricular Valves Chordae tendieae Tricuspid valve Bicuspid (mitral) valve. Pulmonary semilunar valve Papillary muscles Septum Aortic semilunar valve (internal)
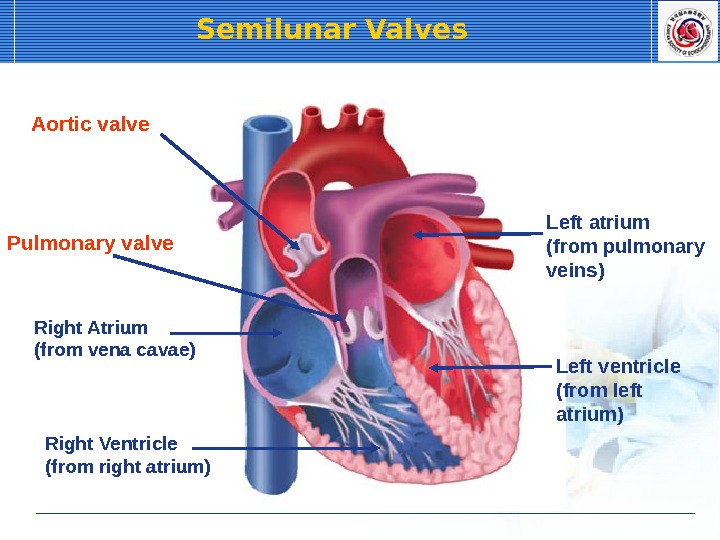
 Right Atrium (from vena cavae) Right Ventricle (from right atrium) Left atrium (from pulmonary veins) Left ventricle (from left atrium)Aortic valve Pulmonary valve Semilunar Valves
Right Atrium (from vena cavae) Right Ventricle (from right atrium) Left atrium (from pulmonary veins) Left ventricle (from left atrium)Aortic valve Pulmonary valve Semilunar Valves
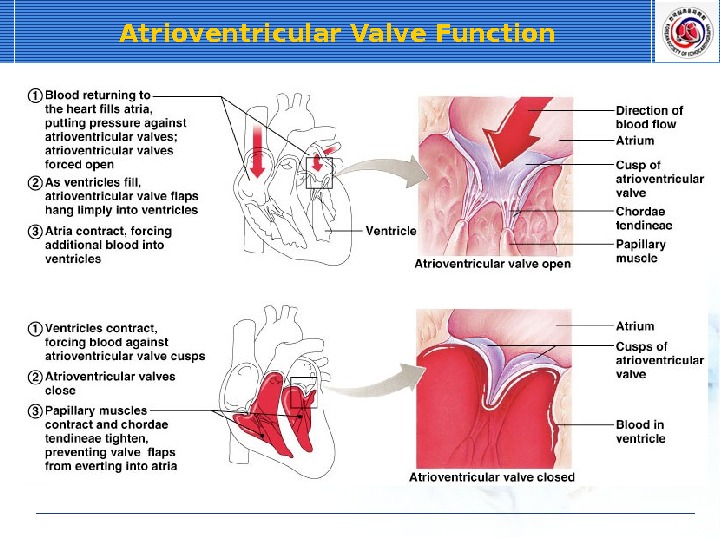
 Atrioventricular Valve Function
Atrioventricular Valve Function
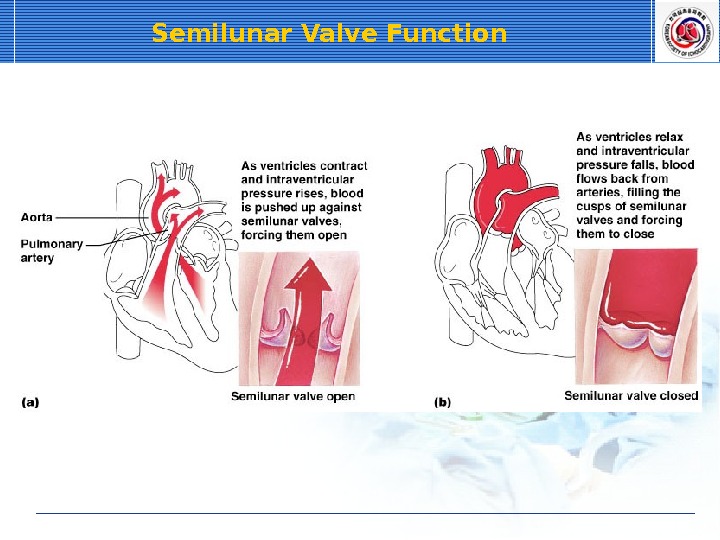
 Semilunar Valve Function
Semilunar Valve Function
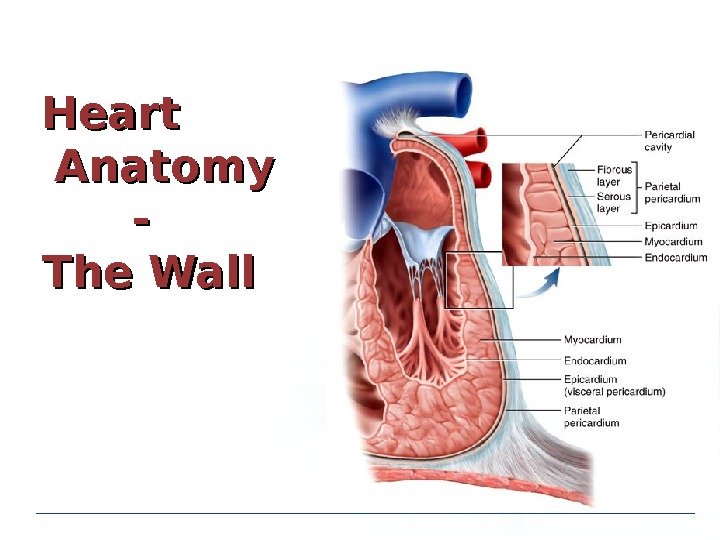
 Heart Anatomy — The Wall
Heart Anatomy — The Wall
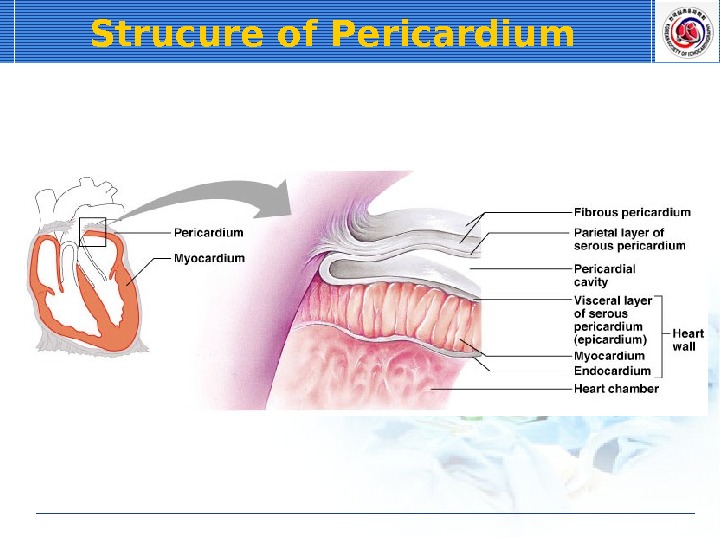
 Strucure of Pericardium
Strucure of Pericardium
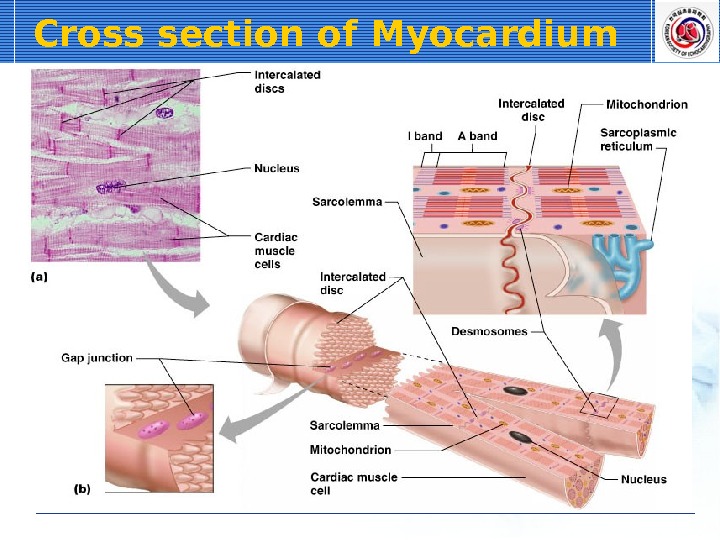
 Cross section of Myocardium
Cross section of Myocardium
 Heart physiology — Hemodynamics — Electrophysiology
Heart physiology — Hemodynamics — Electrophysiology
 Heart physiology Hemodynamics 1 Electrophysiology
Heart physiology Hemodynamics 1 Electrophysiology
 Preload & Afterload
Preload & Afterload
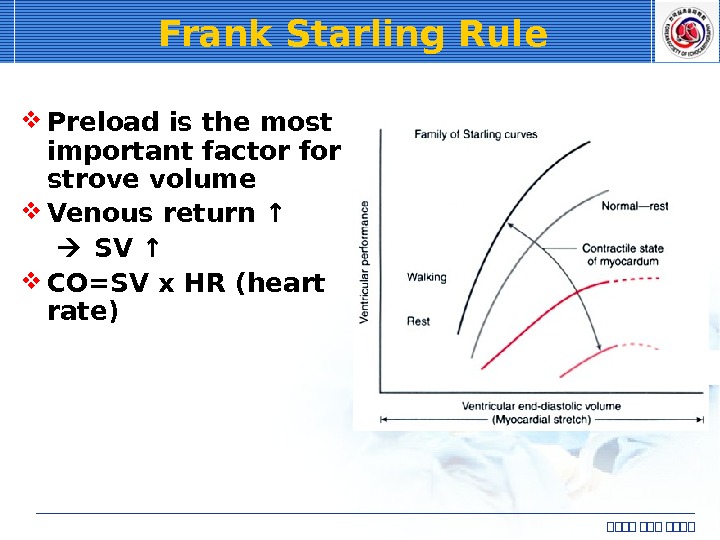
 Frank Starling Rule Preload is the most important factor for strove volume Venous return ↑ SV ↑ CO=SV x HR (heart rate) 심심심심
Frank Starling Rule Preload is the most important factor for strove volume Venous return ↑ SV ↑ CO=SV x HR (heart rate) 심심심심
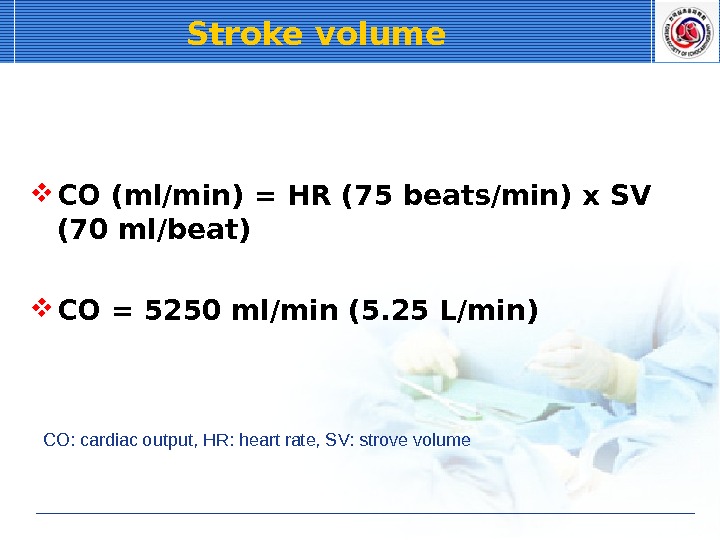
 Stroke volume CO (ml/min) = HR (75 beats/min) x SV (70 ml/beat) CO = 5250 ml/min (5. 25 L/min) CO: cardiac output, HR: heart rate, SV: strove volume
Stroke volume CO (ml/min) = HR (75 beats/min) x SV (70 ml/beat) CO = 5250 ml/min (5. 25 L/min) CO: cardiac output, HR: heart rate, SV: strove volume
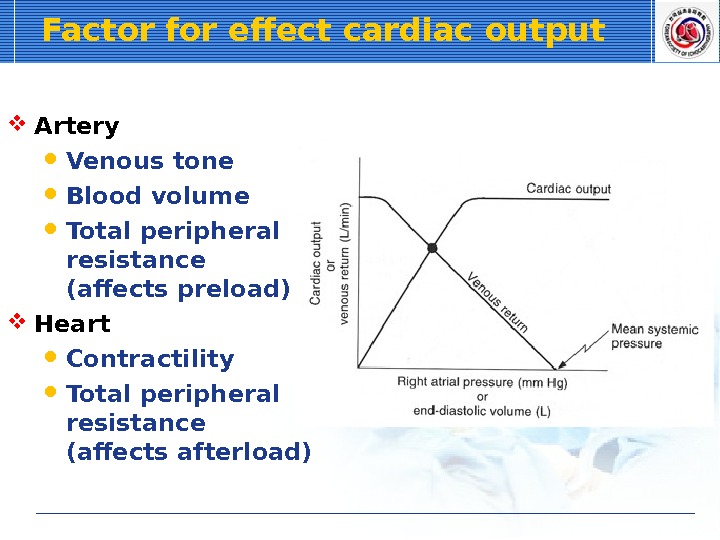
 Factor for effect cardiac output Artery Venous tone Blood volume Total peripheral resistance (affects preload) Heart Contractility Total peripheral resistance (affects afterload)
Factor for effect cardiac output Artery Venous tone Blood volume Total peripheral resistance (affects preload) Heart Contractility Total peripheral resistance (affects afterload)
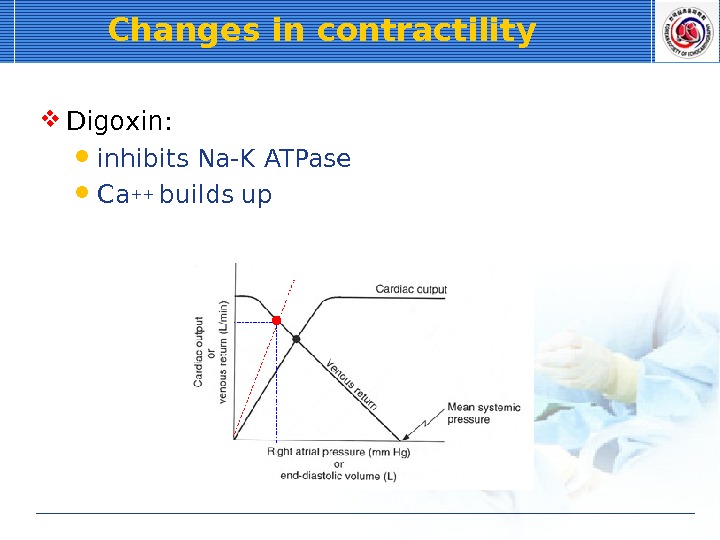
 Changes in contractility Digoxin: inhibits Na-K ATPase Ca++ builds up
Changes in contractility Digoxin: inhibits Na-K ATPase Ca++ builds up
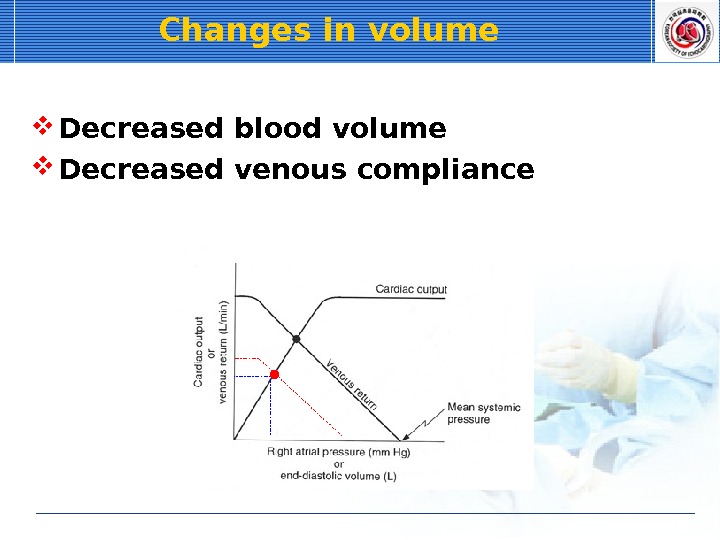
 Changes in volume Decreased blood volume Decreased venous compliance
Changes in volume Decreased blood volume Decreased venous compliance
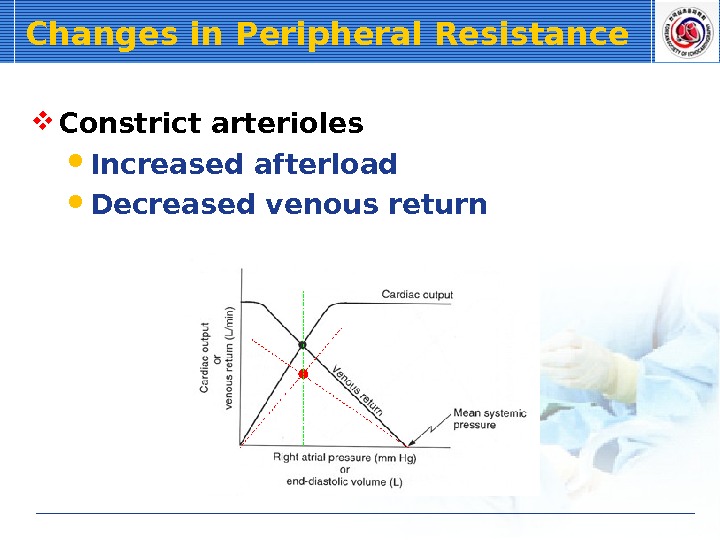
 Changes in Peripheral Resistance Constrict arterioles Increased afterload Decreased venous return
Changes in Peripheral Resistance Constrict arterioles Increased afterload Decreased venous return
 Pressure-Volume Loop Factors Preload Afterload Contractility Normal
Pressure-Volume Loop Factors Preload Afterload Contractility Normal
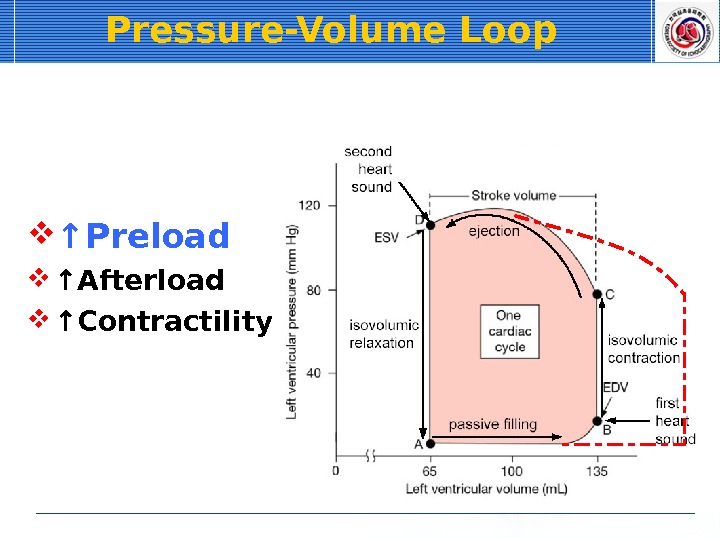
 Pressure-Volume Loop ↑ Preload ↑ Afterload ↑ Contractility
Pressure-Volume Loop ↑ Preload ↑ Afterload ↑ Contractility
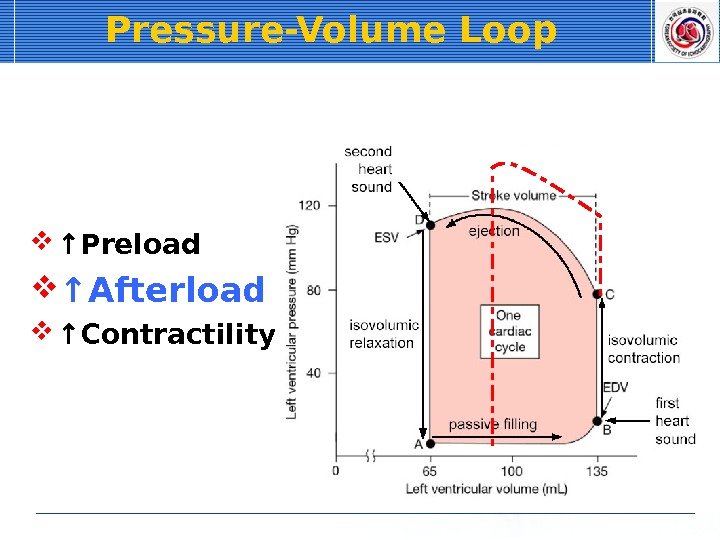
 Pressure-Volume Loop ↑ Preload ↑ Afterload ↑ Contractility
Pressure-Volume Loop ↑ Preload ↑ Afterload ↑ Contractility
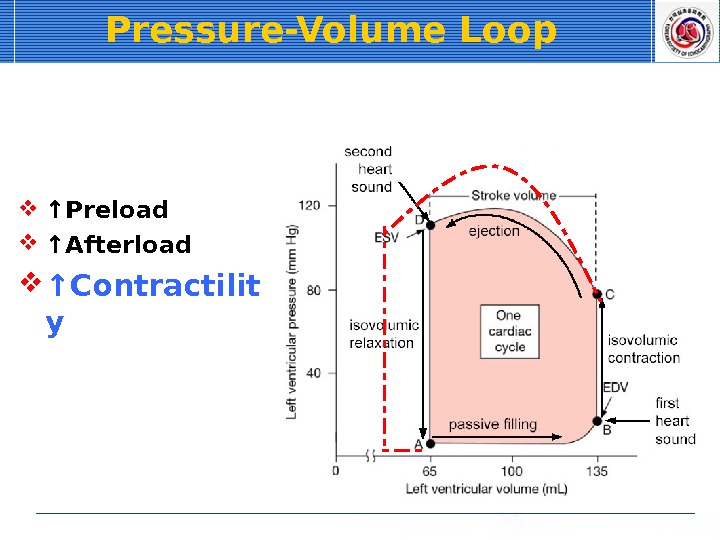
 Pressure-Volume Loop ↑ Preload ↑ Afterload ↑ Contractilit y
Pressure-Volume Loop ↑ Preload ↑ Afterload ↑ Contractilit y
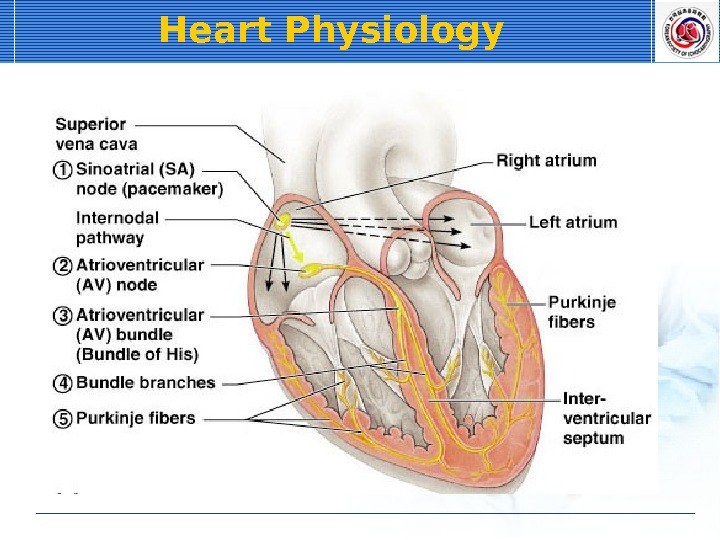
 Heart Physiology
Heart Physiology
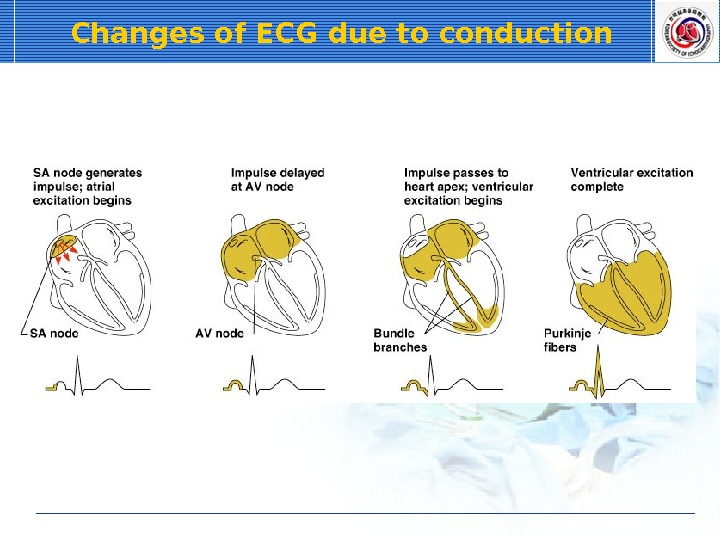
 Changes of ECG due to conduction
Changes of ECG due to conduction
 Cardiac Cycle Cardiac cycle Systole – contraction of heart muscle Diastole – relaxation of heart muscle
Cardiac Cycle Cardiac cycle Systole – contraction of heart muscle Diastole – relaxation of heart muscle
 Phases of the Cardiac Cycle Atria relax Rising ventricular pressure results in closing of AV valves Isovolumetric contraction phase Ventricular ejection phase opens semilunar valves
Phases of the Cardiac Cycle Atria relax Rising ventricular pressure results in closing of AV valves Isovolumetric contraction phase Ventricular ejection phase opens semilunar valves
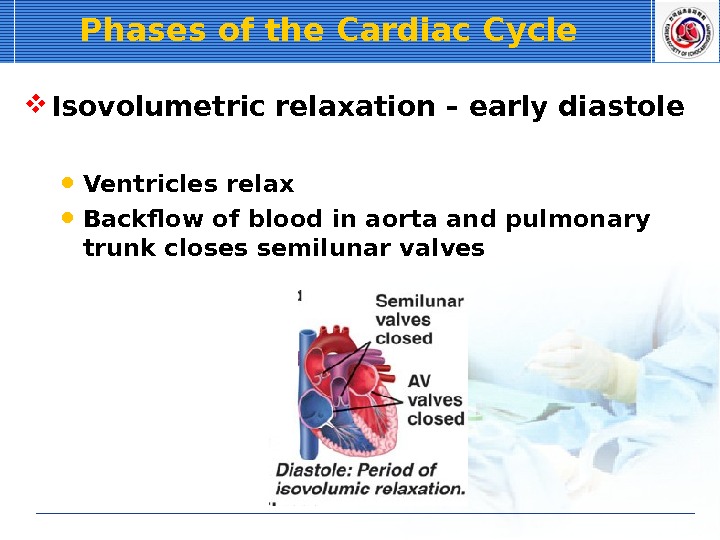
 Phases of the Cardiac Cycle Isovolumetric relaxation – early diastole Ventricles relax Backflow of blood in aorta and pulmonary trunk closes semilunar valves
Phases of the Cardiac Cycle Isovolumetric relaxation – early diastole Ventricles relax Backflow of blood in aorta and pulmonary trunk closes semilunar valves
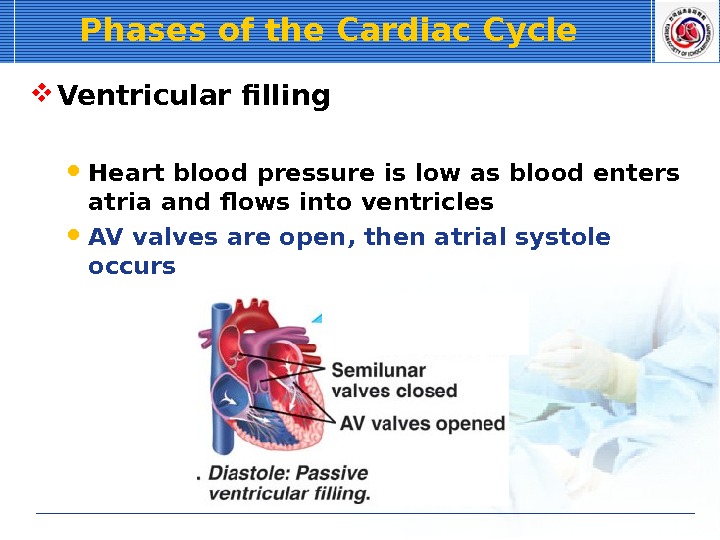
 Phases of the Cardiac Cycle Ventricular filling Heart blood pressure is low as blood enters atria and flows into ventricles AV valves are open, then atrial systole occurs
Phases of the Cardiac Cycle Ventricular filling Heart blood pressure is low as blood enters atria and flows into ventricles AV valves are open, then atrial systole occurs
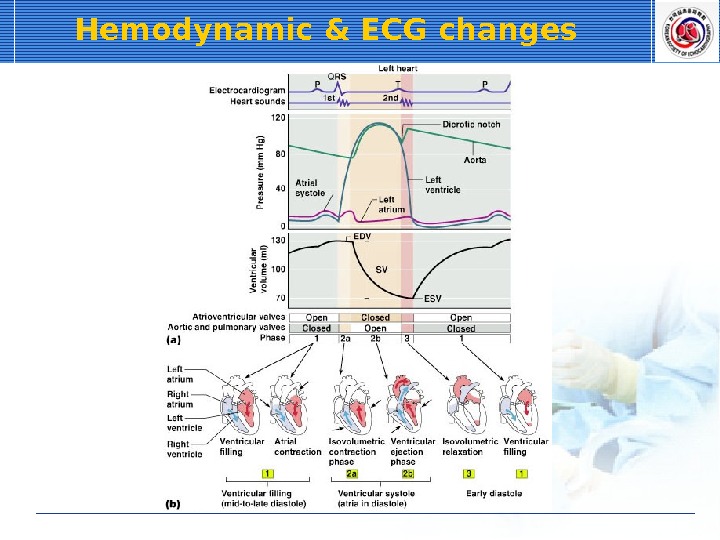
 Hemodynamic & ECG changes
Hemodynamic & ECG changes

