b9d4b6e6387e05acf07b5f8803ca9ab4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 6 Congress Scott J. Ferrell/ Congressional Quarterly/Getty Images American Government: Roots and Reform, 2014 Election Update , 12 e O'Connor | Sabato | Yanus Copyright © 2016, 2014, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
6 Congress Scott J. Ferrell/ Congressional Quarterly/Getty Images American Government: Roots and Reform, 2014 Election Update , 12 e O'Connor | Sabato | Yanus Copyright © 2016, 2014, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
 Roots & Requirememnts of the U. S. Congress 1. Bicameral legislature 1. House (Art 1 sec 2) 1. Representatives based on population conducted by census every 10 years (Art 1, sec 2, clause 3). 2. Two-year term 3. Members must be 25 & citizen for at least 7 years 2. Senate (Art 1 sec 3) 1. Two from each state 2. Six-year term 3. Members must be 30 & citizens for at least 9 years American Government: Roots and Reform, 2014 Election Update , 12 e O'Connor | Sabato | Yanus Copyright © 2016, 2014, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved 6. 1
Roots & Requirememnts of the U. S. Congress 1. Bicameral legislature 1. House (Art 1 sec 2) 1. Representatives based on population conducted by census every 10 years (Art 1, sec 2, clause 3). 2. Two-year term 3. Members must be 25 & citizen for at least 7 years 2. Senate (Art 1 sec 3) 1. Two from each state 2. Six-year term 3. Members must be 30 & citizens for at least 9 years American Government: Roots and Reform, 2014 Election Update , 12 e O'Connor | Sabato | Yanus Copyright © 2016, 2014, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved 6. 1
 TABLE 6. 1 What are the powers of Congress? American Government: Roots and Reform, 2014 Election Update , 12 e O'Connor | Sabato | Yanus Copyright © 2016, 2014, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved 6. 1
TABLE 6. 1 What are the powers of Congress? American Government: Roots and Reform, 2014 Election Update , 12 e O'Connor | Sabato | Yanus Copyright © 2016, 2014, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved 6. 1
 Key Powers (Art 1 sec 8) ¤ Make laws n Both House and Senate must pass bills. ¤ Raise and spend revenue ¤ Raise an Army ¤ Promote the progress of science ¤ Build post offices and postal roads ¤ Other powers "as necessary and proper" to carry out the functions of Congress American Government: Roots and Reform, 2014 Election Update , 12 e O'Connor | Sabato | Yanus Copyright © 2016, 2014, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved 6. 1
Key Powers (Art 1 sec 8) ¤ Make laws n Both House and Senate must pass bills. ¤ Raise and spend revenue ¤ Raise an Army ¤ Promote the progress of science ¤ Build post offices and postal roads ¤ Other powers "as necessary and proper" to carry out the functions of Congress American Government: Roots and Reform, 2014 Election Update , 12 e O'Connor | Sabato | Yanus Copyright © 2016, 2014, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved 6. 1
 TABLE 6. 2 What are the key differences between the House of Representatives and the Senate? 6. 1 continued on next slide American Government: Roots and Reform, 2014 Election Update , 12 e O'Connor | Sabato | Yanus Copyright © 2016, 2014, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
TABLE 6. 2 What are the key differences between the House of Representatives and the Senate? 6. 1 continued on next slide American Government: Roots and Reform, 2014 Election Update , 12 e O'Connor | Sabato | Yanus Copyright © 2016, 2014, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
 TABLE 6. 2 What are the key differences between the House of Representatives and the Senate? American Government: Roots and Reform, 2014 Election Update , 12 e O'Connor | Sabato | Yanus Copyright © 2016, 2014, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved 6. 1
TABLE 6. 2 What are the key differences between the House of Representatives and the Senate? American Government: Roots and Reform, 2014 Election Update , 12 e O'Connor | Sabato | Yanus Copyright © 2016, 2014, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved 6. 1
 Congressional Demographics 6. 2 ¤ Better educated than general population n Two-thirds of members hold advanced degrees ¤ Wealthier than general population n Senate "Millionaires Club" ¤ Recent increases in minority representation American Government: Roots and Reform, 2014 Election Update , 12 e O'Connor | Sabato | Yanus Copyright © 2016, 2014, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Congressional Demographics 6. 2 ¤ Better educated than general population n Two-thirds of members hold advanced degrees ¤ Wealthier than general population n Senate "Millionaires Club" ¤ Recent increases in minority representation American Government: Roots and Reform, 2014 Election Update , 12 e O'Connor | Sabato | Yanus Copyright © 2016, 2014, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
 Redistricting & Apportionment ¤ Apportionment - 6. 2 When states gain or lose members in the U. S. House following the census n Redistricting - When State Legislatures redraw Federal districts following ¤ Often political in nature n Party in power in state legislatures controls the process ¤ Gerrymandering n Drawing a district to favor a party or candidate n Unconstitutional in the State of Florida American Government: Roots and Reform, 2014 Election Update , 12 e O'Connor | Sabato | Yanus Copyright © 2016, 2014, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Redistricting & Apportionment ¤ Apportionment - 6. 2 When states gain or lose members in the U. S. House following the census n Redistricting - When State Legislatures redraw Federal districts following ¤ Often political in nature n Party in power in state legislatures controls the process ¤ Gerrymandering n Drawing a district to favor a party or candidate n Unconstitutional in the State of Florida American Government: Roots and Reform, 2014 Election Update , 12 e O'Connor | Sabato | Yanus Copyright © 2016, 2014, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
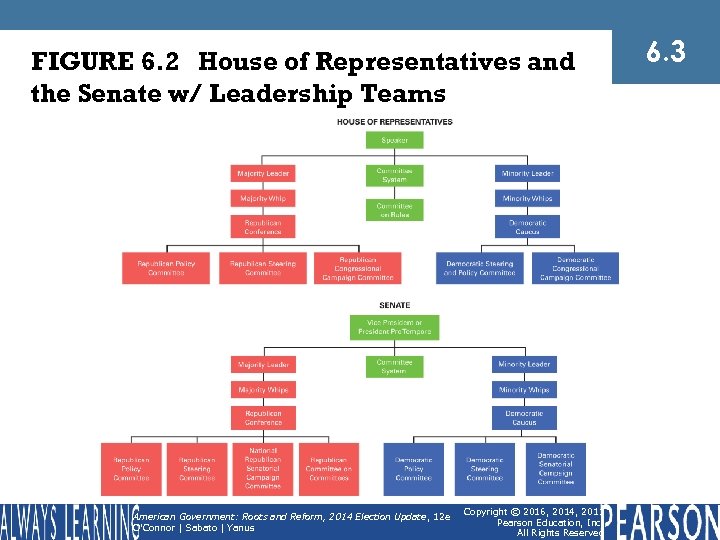 FIGURE 6. 2 House of Representatives and the Senate w/ Leadership Teams American Government: Roots and Reform, 2014 Election Update , 12 e O'Connor | Sabato | Yanus Copyright © 2016, 2014, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved 6. 3
FIGURE 6. 2 House of Representatives and the Senate w/ Leadership Teams American Government: Roots and Reform, 2014 Election Update , 12 e O'Connor | Sabato | Yanus Copyright © 2016, 2014, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved 6. 3
 The Committee System 6. 3 1. Types of committees 1. Standing committees – are those to which bills are referred for consideration. Continue from one Congress to the next 2. Joint committees – Standing committee that includes members from both houses 3. Conference committees – special joint committees created to reconcile differences in House & Senate version of a bill 4. Select (or special) committees – temporary committees appointed for specific purposes 2. Committee chairs – authorized to select all subcommittee chairs, call meetings, can kill bills through scheduling, have large staffs & receive favors from lobbyists American Government: Roots and Reform, 2014 Election Update , 12 e O'Connor | Sabato | Yanus Copyright © 2016, 2014, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
The Committee System 6. 3 1. Types of committees 1. Standing committees – are those to which bills are referred for consideration. Continue from one Congress to the next 2. Joint committees – Standing committee that includes members from both houses 3. Conference committees – special joint committees created to reconcile differences in House & Senate version of a bill 4. Select (or special) committees – temporary committees appointed for specific purposes 2. Committee chairs – authorized to select all subcommittee chairs, call meetings, can kill bills through scheduling, have large staffs & receive favors from lobbyists American Government: Roots and Reform, 2014 Election Update , 12 e O'Connor | Sabato | Yanus Copyright © 2016, 2014, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
 TABLE 6. 5 What were the committees of the 113 th Congress? American Government: Roots and Reform, 2014 Election Update , 12 e O'Connor | Sabato | Yanus Copyright © 2016, 2014, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved 6. 3
TABLE 6. 5 What were the committees of the 113 th Congress? American Government: Roots and Reform, 2014 Election Update , 12 e O'Connor | Sabato | Yanus Copyright © 2016, 2014, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved 6. 3
 TABLE 6. 5 What were the committees of the 113 th Congress? American Government: Roots and Reform, 2014 Election Update , 12 e O'Connor | Sabato | Yanus Copyright © 2016, 2014, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved 6. 3
TABLE 6. 5 What were the committees of the 113 th Congress? American Government: Roots and Reform, 2014 Election Update , 12 e O'Connor | Sabato | Yanus Copyright © 2016, 2014, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved 6. 3
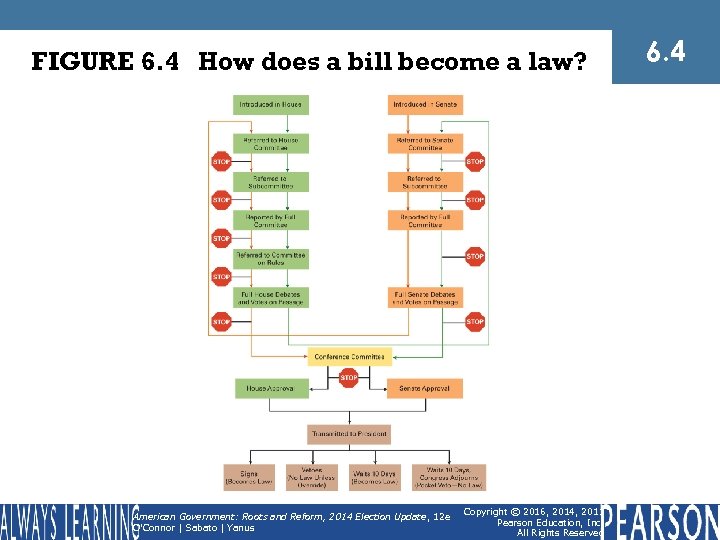 FIGURE 6. 4 How does a bill become a law? American Government: Roots and Reform, 2014 Election Update , 12 e O'Connor | Sabato | Yanus Copyright © 2016, 2014, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved 6. 4
FIGURE 6. 4 How does a bill become a law? American Government: Roots and Reform, 2014 Election Update , 12 e O'Connor | Sabato | Yanus Copyright © 2016, 2014, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved 6. 4
 3 Functions of Congress 6. 4 ¤ Law-making, Budgetary & Oversight ¤ Law-making ¤ Budgetary n First Monday in February (process begins) – October 1 st (fiscal year begins) n Congressional Budget Act (1974) Establishes levels of spending & limits debate ¤ Oversight n Congressional review – allows Congress to overrule regulations for federal agencies n Confirmation of presidential appointees n Impeachment American Government: Roots and Reform, 2014 Election Update , 12 e O'Connor | Sabato | Yanus Copyright © 2016, 2014, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
3 Functions of Congress 6. 4 ¤ Law-making, Budgetary & Oversight ¤ Law-making ¤ Budgetary n First Monday in February (process begins) – October 1 st (fiscal year begins) n Congressional Budget Act (1974) Establishes levels of spending & limits debate ¤ Oversight n Congressional review – allows Congress to overrule regulations for federal agencies n Confirmation of presidential appointees n Impeachment American Government: Roots and Reform, 2014 Election Update , 12 e O'Connor | Sabato | Yanus Copyright © 2016, 2014, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
 How Members of Congress Make Decisions 1. Political Parties 2. Constituents 3. Colleagues and Caucuses 1. Logrolling – supporting another members legislation in exchange for future support 4. Interest Groups, Lobbyists, and Political Action Committees 5. Staff and Support Agencies American Government: Roots and Reform, 2014 Election Update , 12 e O'Connor | Sabato | Yanus Copyright © 2016, 2014, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved 6. 5
How Members of Congress Make Decisions 1. Political Parties 2. Constituents 3. Colleagues and Caucuses 1. Logrolling – supporting another members legislation in exchange for future support 4. Interest Groups, Lobbyists, and Political Action Committees 5. Staff and Support Agencies American Government: Roots and Reform, 2014 Election Update , 12 e O'Connor | Sabato | Yanus Copyright © 2016, 2014, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved 6. 5
 Interest Groups, Lobbyists and Political Action Committees 1. Research and Data 1. Provide information to justify members' positions on legislation 2. Persuade constituents to contact or pressure members 2. Fundraising 1. PACS American Government: Roots and Reform, 2014 Election Update , 12 e O'Connor | Sabato | Yanus Copyright © 2016, 2014, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved 6. 5
Interest Groups, Lobbyists and Political Action Committees 1. Research and Data 1. Provide information to justify members' positions on legislation 2. Persuade constituents to contact or pressure members 2. Fundraising 1. PACS American Government: Roots and Reform, 2014 Election Update , 12 e O'Connor | Sabato | Yanus Copyright © 2016, 2014, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved 6. 5
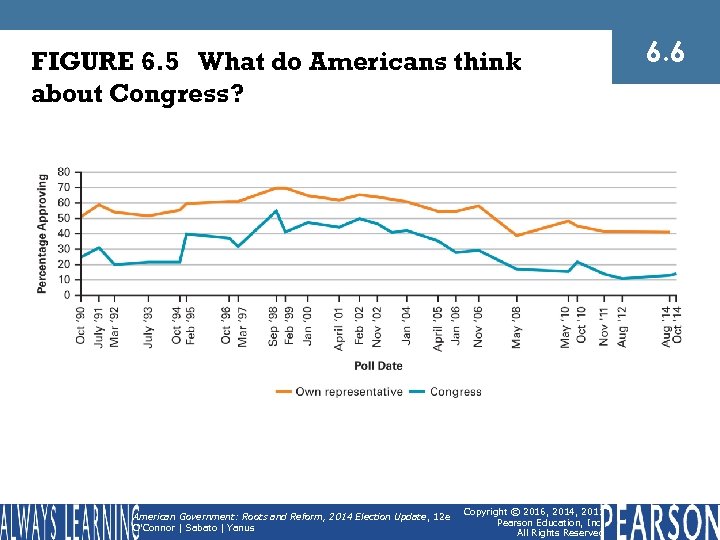 FIGURE 6. 5 What do Americans think about Congress? American Government: Roots and Reform, 2014 Election Update , 12 e O'Connor | Sabato | Yanus Copyright © 2016, 2014, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved 6. 6
FIGURE 6. 5 What do Americans think about Congress? American Government: Roots and Reform, 2014 Election Update , 12 e O'Connor | Sabato | Yanus Copyright © 2016, 2014, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved 6. 6
