2 At the end of this session, students




![5 Terminology [1-7] The description of the following terms helps the user to understand 5 Terminology [1-7] The description of the following terms helps the user to understand](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_5.jpg)
![6 Terminology [2-7] Operating System (OS) Is collective software that integrates various software programs 6 Terminology [2-7] Operating System (OS) Is collective software that integrates various software programs](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_6.jpg)
![7 Terminology [3-7] Workstation Is a type of computer used for professional tasks that 7 Terminology [3-7] Workstation Is a type of computer used for professional tasks that](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_7.jpg)
![9 Terminology [5-7] The table lists the units of measurement of computer data Computer 9 Terminology [5-7] The table lists the units of measurement of computer data Computer](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_9.jpg)
![10 Terminology [6-7] Units of Speed – kHz, MHz, GHz All electronic components work 10 Terminology [6-7] Units of Speed – kHz, MHz, GHz All electronic components work](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_10.jpg)
![11 Terminology [7-7] Desktop Is the first screen users view after the computer is 11 Terminology [7-7] Desktop Is the first screen users view after the computer is](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_11.jpg)
![13 First Generation [1-2] 1944: IBM developed the first electro-mechanical computer Named it IBM 13 First Generation [1-2] 1944: IBM developed the first electro-mechanical computer Named it IBM](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_13.jpg)
![14 First Generation [2-2] ENIAC was improved further to develop advanced computers based on 14 First Generation [2-2] ENIAC was improved further to develop advanced computers based on](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_14.jpg)
![15 Second Generation [1-2] Was built using transistors instead of vacuum tubes A transistor 15 Second Generation [1-2] Was built using transistors instead of vacuum tubes A transistor](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_15.jpg)
![16 Second Generation [2-2] These computers used symbol-based or assembly language Symbolic languages allowed 16 Second Generation [2-2] These computers used symbol-based or assembly language Symbolic languages allowed](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_16.jpg)
![18 Fourth Generation [1-2] Used microprocessor that includes thousands of integrated circuits on to 18 Fourth Generation [1-2] Used microprocessor that includes thousands of integrated circuits on to](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_18.jpg)
![19 Fourth Generation [2-2] The main characteristics that separated microprocessors from the computers of 19 Fourth Generation [2-2] The main characteristics that separated microprocessors from the computers of](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_19.jpg)
![21 Hardware Components [1-10] Motherboard Is a large rectangular board inside the computer’s cabinet 21 Hardware Components [1-10] Motherboard Is a large rectangular board inside the computer’s cabinet](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_21.jpg)
![22 Hardware Components [2-10] Central Processing Unit (CPU) Is the heart of the computer 22 Hardware Components [2-10] Central Processing Unit (CPU) Is the heart of the computer](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_22.jpg)
![23 Hardware Components [3-10] Input Devices Accepts data from the user and transmits it 23 Hardware Components [3-10] Input Devices Accepts data from the user and transmits it](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_23.jpg)
![24 Hardware Components [4-10] Output Devices Accepts processed data from the computer and present 24 Hardware Components [4-10] Output Devices Accepts processed data from the computer and present](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_24.jpg)
![25 Hardware Components [5-10] Storage Devices Are also called as memory devices Is used 25 Hardware Components [5-10] Storage Devices Are also called as memory devices Is used](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_25.jpg)
![26 Hardware Components [6-10] The table lists some of the commonly used primary storage 26 Hardware Components [6-10] The table lists some of the commonly used primary storage](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_26.jpg)
![27 Hardware Components [7-10] ROM can be further classified as follows: Programmable ROM (PROM) 27 Hardware Components [7-10] ROM can be further classified as follows: Programmable ROM (PROM)](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_27.jpg)
![28 Hardware Components [8-10] The table lists some of the commonly used secondary storage 28 Hardware Components [8-10] The table lists some of the commonly used secondary storage](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_28.jpg)
![29 Hardware Components [9-10] The table lists some of the commonly used secondary storage 29 Hardware Components [9-10] The table lists some of the commonly used secondary storage](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_29.jpg)
![30 Hardware Components [10-10] USB Drives and External Hard Disks Is a type of 30 Hardware Components [10-10] USB Drives and External Hard Disks Is a type of](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_30.jpg)
![31 Software Components [1-3] Software is a program that contains lines of codes or 31 Software Components [1-3] Software is a program that contains lines of codes or](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_31.jpg)
![32 Software Components [2-3] System Software Is a set of low-level programs that controls 32 Software Components [2-3] System Software Is a set of low-level programs that controls](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_32.jpg)
![33 Software Components [3-3] Application Software Is designed to enable users to perform a 33 Software Components [3-3] Application Software Is designed to enable users to perform a](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_33.jpg)





office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42

 2 At the end of this session, students will be able to: Define a computer Define basic computer terms Identify the different types of computers Identify the different parts of a computer Describe the working of a computer Objectives Computer Basics / Session 1
2 At the end of this session, students will be able to: Define a computer Define basic computer terms Identify the different types of computers Identify the different parts of a computer Describe the working of a computer Objectives Computer Basics / Session 1
 3 Introduction to Computers A computer: Is an electronic machine Allow users to store information Enables to carry out different operations to process that information Computer Basics / Session 1
3 Introduction to Computers A computer: Is an electronic machine Allow users to store information Enables to carry out different operations to process that information Computer Basics / Session 1
 4 Uses of Computers A computer allow users to store information in various formats and process it to perform different actions: Process complex data Access information remotely Watch movies for entertainment The different tasks that are executed by an user using a computer are: Store, format, and print text files Write, test, and execute different types of software Maintain records of financial statements Present information in a visually appealing manner Access various kinds of information and resources from all over the world Exchange electronic mails with contacts Watch movies, listen to music, and play games Computer Basics / Session 1
4 Uses of Computers A computer allow users to store information in various formats and process it to perform different actions: Process complex data Access information remotely Watch movies for entertainment The different tasks that are executed by an user using a computer are: Store, format, and print text files Write, test, and execute different types of software Maintain records of financial statements Present information in a visually appealing manner Access various kinds of information and resources from all over the world Exchange electronic mails with contacts Watch movies, listen to music, and play games Computer Basics / Session 1
![>5 Terminology [1-7] The description of the following terms helps the user to understand >5 Terminology [1-7] The description of the following terms helps the user to understand](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_5.jpg) 5 Terminology [1-7] The description of the following terms helps the user to understand the working of the computer in detail Hardware Are physical components of a computer Includes all the mechanical, electronic and magnetic parts of a computer Software Is a program that enables the computer to operate Is a set of codes or rules in electronic form Instructs the computer about actions to be taken Referred as a program or an application Example - Internet Explorer is a software for accessing the Internet Computer Basics / Session 1
5 Terminology [1-7] The description of the following terms helps the user to understand the working of the computer in detail Hardware Are physical components of a computer Includes all the mechanical, electronic and magnetic parts of a computer Software Is a program that enables the computer to operate Is a set of codes or rules in electronic form Instructs the computer about actions to be taken Referred as a program or an application Example - Internet Explorer is a software for accessing the Internet Computer Basics / Session 1
![>6 Terminology [2-7] Operating System (OS) Is collective software that integrates various software programs >6 Terminology [2-7] Operating System (OS) Is collective software that integrates various software programs](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_6.jpg) 6 Terminology [2-7] Operating System (OS) Is collective software that integrates various software programs Acts as an interface between the user and the computer Manages interaction between software and hardware resources Example - Microsoft Windows is an operating system Data Is a distinct piece of information present in a form suitable for computer processing Is different from programs Can exist in various formats, such as electronic format or number or text on a paper Example - Numbers entered by the user are data for the calculator program Computer Basics / Session 1
6 Terminology [2-7] Operating System (OS) Is collective software that integrates various software programs Acts as an interface between the user and the computer Manages interaction between software and hardware resources Example - Microsoft Windows is an operating system Data Is a distinct piece of information present in a form suitable for computer processing Is different from programs Can exist in various formats, such as electronic format or number or text on a paper Example - Numbers entered by the user are data for the calculator program Computer Basics / Session 1
![>7 Terminology [3-7] Workstation Is a type of computer used for professional tasks that >7 Terminology [3-7] Workstation Is a type of computer used for professional tasks that](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_7.jpg) 7 Terminology [3-7] Workstation Is a type of computer used for professional tasks that require high performance Have the capacity to store and process large quantities of data Have more powerful resources than regular desktop computers Linked together to form a network of computers known as local area network Booting Is a process by which the operating system loads and starts when the computer is turned on Computer Basics / Session 1
7 Terminology [3-7] Workstation Is a type of computer used for professional tasks that require high performance Have the capacity to store and process large quantities of data Have more powerful resources than regular desktop computers Linked together to form a network of computers known as local area network Booting Is a process by which the operating system loads and starts when the computer is turned on Computer Basics / Session 1
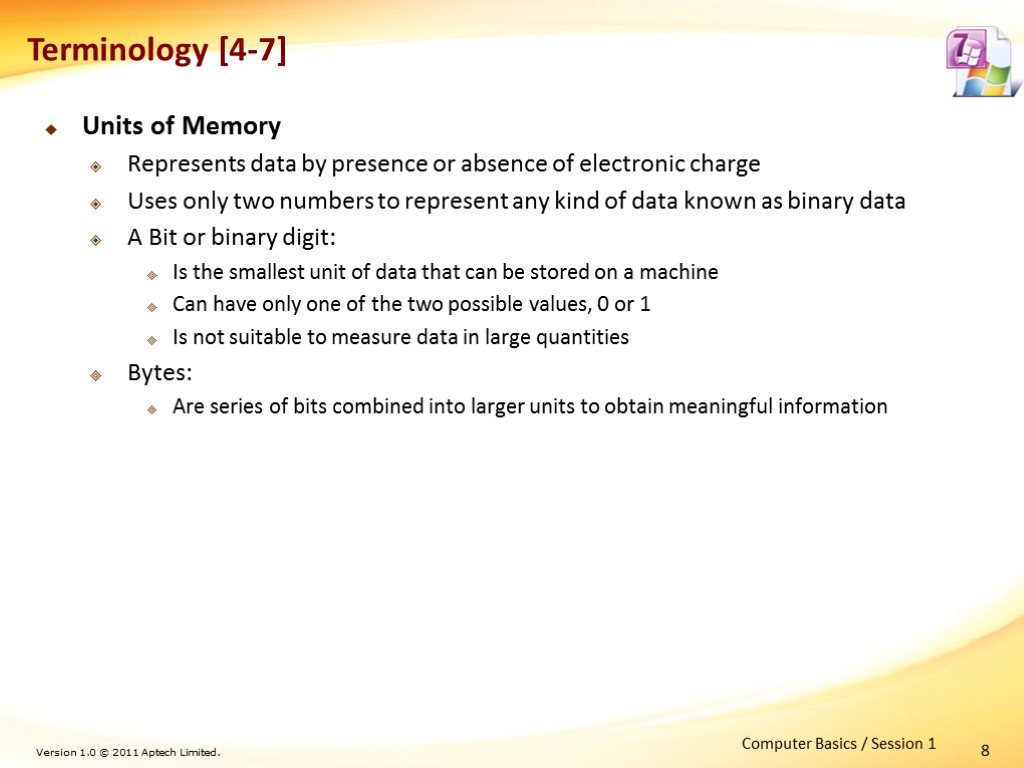
 Units of Memory Represents data by presence or absence of electronic charge Uses only two numbers to represent any kind of data known as binary data A Bit or binary digit: Is the smallest unit of data that can be stored on a machine Can have only one of the two possible values, 0 or 1 Is not suitable to measure data in large quantities Bytes: Are series of bits combined into larger units to obtain meaningful information 8 Terminology [4-7] Computer Basics / Session 1
Units of Memory Represents data by presence or absence of electronic charge Uses only two numbers to represent any kind of data known as binary data A Bit or binary digit: Is the smallest unit of data that can be stored on a machine Can have only one of the two possible values, 0 or 1 Is not suitable to measure data in large quantities Bytes: Are series of bits combined into larger units to obtain meaningful information 8 Terminology [4-7] Computer Basics / Session 1
![>9 Terminology [5-7] The table lists the units of measurement of computer data Computer >9 Terminology [5-7] The table lists the units of measurement of computer data Computer](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_9.jpg) 9 Terminology [5-7] The table lists the units of measurement of computer data Computer Basics / Session 1
9 Terminology [5-7] The table lists the units of measurement of computer data Computer Basics / Session 1
![>10 Terminology [6-7] Units of Speed – kHz, MHz, GHz All electronic components work >10 Terminology [6-7] Units of Speed – kHz, MHz, GHz All electronic components work](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_10.jpg) 10 Terminology [6-7] Units of Speed – kHz, MHz, GHz All electronic components work on a clock signal The number of oscillations per second determines the speed of the device The table lists the different units of speed Computer Basics / Session 1
10 Terminology [6-7] Units of Speed – kHz, MHz, GHz All electronic components work on a clock signal The number of oscillations per second determines the speed of the device The table lists the different units of speed Computer Basics / Session 1
![>11 Terminology [7-7] Desktop Is the first screen users view after the computer is >11 Terminology [7-7] Desktop Is the first screen users view after the computer is](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_11.jpg) 11 Terminology [7-7] Desktop Is the first screen users view after the computer is switched on and the boot up process is completed Soft Copy Is the electronic version of data that users can view on a computer screen and is not in printed form on a paper Hard Copy Is the printed, non-electronic version of the soft copy Is also known as a printout Computer Basics / Session 1
11 Terminology [7-7] Desktop Is the first screen users view after the computer is switched on and the boot up process is completed Soft Copy Is the electronic version of data that users can view on a computer screen and is not in printed form on a paper Hard Copy Is the printed, non-electronic version of the soft copy Is also known as a printout Computer Basics / Session 1
 12 Generations of Computers Major milestones achieved in the history of computer development are regarded as computer generations With each new generation, computers have become smaller in size, more powerful, and less expensive Each generation of computers are characterized by a major technological advancement that changed the way how computers operate Computer Basics / Session 1
12 Generations of Computers Major milestones achieved in the history of computer development are regarded as computer generations With each new generation, computers have become smaller in size, more powerful, and less expensive Each generation of computers are characterized by a major technological advancement that changed the way how computers operate Computer Basics / Session 1
![>13 First Generation [1-2] 1944: IBM developed the first electro-mechanical computer Named it IBM >13 First Generation [1-2] 1944: IBM developed the first electro-mechanical computer Named it IBM](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_13.jpg) 13 First Generation [1-2] 1944: IBM developed the first electro-mechanical computer Named it IBM Automatic Science Controlled Computer (ASCC) or Mark I Made from hundreds of thousands of mechanical components Was huge, slow, and very expensive machine 1946: Presper Eckert and John Mauchly developed Electronic Numerical Integrator And Computer (ENIAC) Was the first general purpose electronic computer that could be programmed to execute different computing tasks Was thousand times faster than electro-mechanical computers developed earlier Used vacuum tubes for circuits and magnetic drums Computer Basics / Session 1
13 First Generation [1-2] 1944: IBM developed the first electro-mechanical computer Named it IBM Automatic Science Controlled Computer (ASCC) or Mark I Made from hundreds of thousands of mechanical components Was huge, slow, and very expensive machine 1946: Presper Eckert and John Mauchly developed Electronic Numerical Integrator And Computer (ENIAC) Was the first general purpose electronic computer that could be programmed to execute different computing tasks Was thousand times faster than electro-mechanical computers developed earlier Used vacuum tubes for circuits and magnetic drums Computer Basics / Session 1
![>14 First Generation [2-2] ENIAC was improved further to develop advanced computers based on >14 First Generation [2-2] ENIAC was improved further to develop advanced computers based on](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_14.jpg) 14 First Generation [2-2] ENIAC was improved further to develop advanced computers based on vacuum tubes, such as Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic Computer (EDVAC) and Universal Automatic Computer I (UNIVAC I) EDVAC was based on the concept of Turing Machine, a hypothetical machine that could store program and data UNIVAC I was built in 1951 and was the first commercial computer developed in the United States of America (USA) Computers of the first generation used machine language to perform operations Machine language consisted of only binary 1s and 0s which: Was very difficult for programmers to work Could not be easily debugged Executed only one job at a time Executing a large program involving multiple routines was tedious and time-consuming Computer Basics / Session 1
14 First Generation [2-2] ENIAC was improved further to develop advanced computers based on vacuum tubes, such as Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic Computer (EDVAC) and Universal Automatic Computer I (UNIVAC I) EDVAC was based on the concept of Turing Machine, a hypothetical machine that could store program and data UNIVAC I was built in 1951 and was the first commercial computer developed in the United States of America (USA) Computers of the first generation used machine language to perform operations Machine language consisted of only binary 1s and 0s which: Was very difficult for programmers to work Could not be easily debugged Executed only one job at a time Executing a large program involving multiple routines was tedious and time-consuming Computer Basics / Session 1
![>15 Second Generation [1-2] Was built using transistors instead of vacuum tubes A transistor >15 Second Generation [1-2] Was built using transistors instead of vacuum tubes A transistor](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_15.jpg) 15 Second Generation [1-2] Was built using transistors instead of vacuum tubes A transistor is an electronic device made of semi-conductor material Advantages of transistors are as follows: Faster Smaller Energy-efficient Reliable Cheaper than vacuum tubes Generates virtually no heat in comparison to vacuum tubes Second generation of computers used punch cards for individual input and tapes for batch input and printouts for output Memory used in these computers was based on memory core technology Computer Basics / Session 1
15 Second Generation [1-2] Was built using transistors instead of vacuum tubes A transistor is an electronic device made of semi-conductor material Advantages of transistors are as follows: Faster Smaller Energy-efficient Reliable Cheaper than vacuum tubes Generates virtually no heat in comparison to vacuum tubes Second generation of computers used punch cards for individual input and tapes for batch input and printouts for output Memory used in these computers was based on memory core technology Computer Basics / Session 1
![>16 Second Generation [2-2] These computers used symbol-based or assembly language Symbolic languages allowed >16 Second Generation [2-2] These computers used symbol-based or assembly language Symbolic languages allowed](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_16.jpg) 16 Second Generation [2-2] These computers used symbol-based or assembly language Symbolic languages allowed programmers to specify instructions in words Higher-level languages, such as COBOL and FORTRAN were also developed during the second generation Computer Basics / Session 1
16 Second Generation [2-2] These computers used symbol-based or assembly language Symbolic languages allowed programmers to specify instructions in words Higher-level languages, such as COBOL and FORTRAN were also developed during the second generation Computer Basics / Session 1
 17 Third Generation Were based on semiconductor technology Used small chips of semiconducting material Were cheaper, smaller in size, and operated at much faster speeds The use of Integrated Circuits (ICs) mounted on tiny chips led to the shrinking of space Enabled commercial production of personal computers at a large scale Introduced the concept of an operating system Computer Basics / Session 1
17 Third Generation Were based on semiconductor technology Used small chips of semiconducting material Were cheaper, smaller in size, and operated at much faster speeds The use of Integrated Circuits (ICs) mounted on tiny chips led to the shrinking of space Enabled commercial production of personal computers at a large scale Introduced the concept of an operating system Computer Basics / Session 1
![>18 Fourth Generation [1-2] Used microprocessor that includes thousands of integrated circuits on to >18 Fourth Generation [1-2] Used microprocessor that includes thousands of integrated circuits on to](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_18.jpg) 18 Fourth Generation [1-2] Used microprocessor that includes thousands of integrated circuits on to a single semiconductor chip Microprocessor: Was first used in electronic calculators and later lead to development of modern Personal Computers (PCs) Acts as Central Processing Unit (CPU) for most electronic devices Resulted in shrinking of the size of computers Can perform all the tasks of a full-scale computer Computer Basics / Session 1
18 Fourth Generation [1-2] Used microprocessor that includes thousands of integrated circuits on to a single semiconductor chip Microprocessor: Was first used in electronic calculators and later lead to development of modern Personal Computers (PCs) Acts as Central Processing Unit (CPU) for most electronic devices Resulted in shrinking of the size of computers Can perform all the tasks of a full-scale computer Computer Basics / Session 1
![>19 Fourth Generation [2-2] The main characteristics that separated microprocessors from the computers of >19 Fourth Generation [2-2] The main characteristics that separated microprocessors from the computers of](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_19.jpg) 19 Fourth Generation [2-2] The main characteristics that separated microprocessors from the computers of earlier generations are as follows: Instruction Set - Microprocessors used assembly language for programming Instructions Per Second - The performance of a microprocessor was measured in terms of how many instructions it could execute per second Clock Speed - Defines the frequency (number of clock cycles per second) of the signal at which the microprocessor operates Fourth generation of computers is also characterized by use of Graphical User Interface (GUI) and mouse Computer Basics / Session 1
19 Fourth Generation [2-2] The main characteristics that separated microprocessors from the computers of earlier generations are as follows: Instruction Set - Microprocessors used assembly language for programming Instructions Per Second - The performance of a microprocessor was measured in terms of how many instructions it could execute per second Clock Speed - Defines the frequency (number of clock cycles per second) of the signal at which the microprocessor operates Fourth generation of computers is also characterized by use of Graphical User Interface (GUI) and mouse Computer Basics / Session 1
 20 Basic Computer Components Following components work in conjunction to perform the tasks specified by the user: Hardware components Motherboard Central Processing Unit (CPU) Input Devices Output Devices Storage Devices Software components System Software Application Software Computer Basics / Session 1
20 Basic Computer Components Following components work in conjunction to perform the tasks specified by the user: Hardware components Motherboard Central Processing Unit (CPU) Input Devices Output Devices Storage Devices Software components System Software Application Software Computer Basics / Session 1
![>21 Hardware Components [1-10] Motherboard Is a large rectangular board inside the computer’s cabinet >21 Hardware Components [1-10] Motherboard Is a large rectangular board inside the computer’s cabinet](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_21.jpg) 21 Hardware Components [1-10] Motherboard Is a large rectangular board inside the computer’s cabinet with integrated circuitry that connects several hardware components Provides connectors to connect other peripheral components Computer Basics / Session 1 Sample Motherboard
21 Hardware Components [1-10] Motherboard Is a large rectangular board inside the computer’s cabinet with integrated circuitry that connects several hardware components Provides connectors to connect other peripheral components Computer Basics / Session 1 Sample Motherboard
![>22 Hardware Components [2-10] Central Processing Unit (CPU) Is the heart of the computer >22 Hardware Components [2-10] Central Processing Unit (CPU) Is the heart of the computer](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_22.jpg) 22 Hardware Components [2-10] Central Processing Unit (CPU) Is the heart of the computer Performs various arithmetic and logical operations Controls all the tasks a computer performs Consists of following functional components: Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU) – performs all the computations for arithmetic and logical operations Control Unit (CU) – provides control signals to supervise the operations of the CPU Set of registers – Contains temporary data generated during computations Buses – are communication pathways that carry data between different functional units Computer Basics / Session 1
22 Hardware Components [2-10] Central Processing Unit (CPU) Is the heart of the computer Performs various arithmetic and logical operations Controls all the tasks a computer performs Consists of following functional components: Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU) – performs all the computations for arithmetic and logical operations Control Unit (CU) – provides control signals to supervise the operations of the CPU Set of registers – Contains temporary data generated during computations Buses – are communication pathways that carry data between different functional units Computer Basics / Session 1
![>23 Hardware Components [3-10] Input Devices Accepts data from the user and transmits it >23 Hardware Components [3-10] Input Devices Accepts data from the user and transmits it](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_23.jpg) 23 Hardware Components [3-10] Input Devices Accepts data from the user and transmits it to the CPU in electronic form for processing The table lists some of the commonly used input devices Computer Basics / Session 1
23 Hardware Components [3-10] Input Devices Accepts data from the user and transmits it to the CPU in electronic form for processing The table lists some of the commonly used input devices Computer Basics / Session 1
![>24 Hardware Components [4-10] Output Devices Accepts processed data from the computer and present >24 Hardware Components [4-10] Output Devices Accepts processed data from the computer and present](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_24.jpg) 24 Hardware Components [4-10] Output Devices Accepts processed data from the computer and present it to the user in a legible format The table lists some of the commonly used output devices Computer Basics / Session 1
24 Hardware Components [4-10] Output Devices Accepts processed data from the computer and present it to the user in a legible format The table lists some of the commonly used output devices Computer Basics / Session 1
![>25 Hardware Components [5-10] Storage Devices Are also called as memory devices Is used >25 Hardware Components [5-10] Storage Devices Are also called as memory devices Is used](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_25.jpg) 25 Hardware Components [5-10] Storage Devices Are also called as memory devices Is used to record digital data from the computer in different formats Can be classified as Primary storage devices and Secondary storage devices Primary Storage Devices Is located within the computer cabinet Is used to store data for direct access by the CPU Computer Basics / Session 1
25 Hardware Components [5-10] Storage Devices Are also called as memory devices Is used to record digital data from the computer in different formats Can be classified as Primary storage devices and Secondary storage devices Primary Storage Devices Is located within the computer cabinet Is used to store data for direct access by the CPU Computer Basics / Session 1
![>26 Hardware Components [6-10] The table lists some of the commonly used primary storage >26 Hardware Components [6-10] The table lists some of the commonly used primary storage](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_26.jpg) 26 Hardware Components [6-10] The table lists some of the commonly used primary storage devices Computer Basics / Session 1
26 Hardware Components [6-10] The table lists some of the commonly used primary storage devices Computer Basics / Session 1
![>27 Hardware Components [7-10] ROM can be further classified as follows: Programmable ROM (PROM) >27 Hardware Components [7-10] ROM can be further classified as follows: Programmable ROM (PROM)](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_27.jpg) 27 Hardware Components [7-10] ROM can be further classified as follows: Programmable ROM (PROM) - Non-volatile memory similar to ROM except that content is written after manufacturing the device Erasable Programmable ROM (EPROM) - Non-volatile memory similar to PROM except that its contents can be erased Electronically Erasable PROM (EEPROM) - Non-volatile memory which can be erased and re-written several times Secondary Storage Devices Is used to permanently store the data for a long time Is not directly accessed by the CPU Acts as an external storage device Computer Basics / Session 1
27 Hardware Components [7-10] ROM can be further classified as follows: Programmable ROM (PROM) - Non-volatile memory similar to ROM except that content is written after manufacturing the device Erasable Programmable ROM (EPROM) - Non-volatile memory similar to PROM except that its contents can be erased Electronically Erasable PROM (EEPROM) - Non-volatile memory which can be erased and re-written several times Secondary Storage Devices Is used to permanently store the data for a long time Is not directly accessed by the CPU Acts as an external storage device Computer Basics / Session 1
![>28 Hardware Components [8-10] The table lists some of the commonly used secondary storage >28 Hardware Components [8-10] The table lists some of the commonly used secondary storage](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_28.jpg) 28 Hardware Components [8-10] The table lists some of the commonly used secondary storage devices Computer Basics / Session 1
28 Hardware Components [8-10] The table lists some of the commonly used secondary storage devices Computer Basics / Session 1
![>29 Hardware Components [9-10] The table lists some of the commonly used secondary storage >29 Hardware Components [9-10] The table lists some of the commonly used secondary storage](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_29.jpg) 29 Hardware Components [9-10] The table lists some of the commonly used secondary storage devices Computer Basics / Session 1
29 Hardware Components [9-10] The table lists some of the commonly used secondary storage devices Computer Basics / Session 1
![>30 Hardware Components [10-10] USB Drives and External Hard Disks Is a type of >30 Hardware Components [10-10] USB Drives and External Hard Disks Is a type of](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_30.jpg) 30 Hardware Components [10-10] USB Drives and External Hard Disks Is a type of Flash Memory Is non-volatile memory that can be erased and reprogrammed Can store large amounts of data in very small sized memory chips USB Drives: Also called as pen drives Are based on Universal Serial Bus (USB) technology External hard disk: Is largest capacity hard drive connected externally to the computer by using a USB cable Is compatible with all operating systems Computer Basics / Session 1
30 Hardware Components [10-10] USB Drives and External Hard Disks Is a type of Flash Memory Is non-volatile memory that can be erased and reprogrammed Can store large amounts of data in very small sized memory chips USB Drives: Also called as pen drives Are based on Universal Serial Bus (USB) technology External hard disk: Is largest capacity hard drive connected externally to the computer by using a USB cable Is compatible with all operating systems Computer Basics / Session 1
![>31 Software Components [1-3] Software is a program that contains lines of codes or >31 Software Components [1-3] Software is a program that contains lines of codes or](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_31.jpg) 31 Software Components [1-3] Software is a program that contains lines of codes or instructions Computer software can be categorized in to the following two categories: System Software Application Software The figure displays the organization of a computer Computer Basics / Session 1 Organization of a Computer
31 Software Components [1-3] Software is a program that contains lines of codes or instructions Computer software can be categorized in to the following two categories: System Software Application Software The figure displays the organization of a computer Computer Basics / Session 1 Organization of a Computer
![>32 Software Components [2-3] System Software Is a set of low-level programs that controls >32 Software Components [2-3] System Software Is a set of low-level programs that controls](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_32.jpg) 32 Software Components [2-3] System Software Is a set of low-level programs that controls the computer hardware Is a collective term which refers to the Operating System (OS) Are of following types: Operating System (OS): Is a collection of several small programs that co-ordinate to manage the interaction between user and the computer hardware Is required to be installed before user can install any other program Microsoft Windows, Linux and Apple Macintosh are examples of operating systems Firmware: Is a small software used to operate a specific electronic device Device drivers are an example of firmware Computer Basics / Session 1
32 Software Components [2-3] System Software Is a set of low-level programs that controls the computer hardware Is a collective term which refers to the Operating System (OS) Are of following types: Operating System (OS): Is a collection of several small programs that co-ordinate to manage the interaction between user and the computer hardware Is required to be installed before user can install any other program Microsoft Windows, Linux and Apple Macintosh are examples of operating systems Firmware: Is a small software used to operate a specific electronic device Device drivers are an example of firmware Computer Basics / Session 1
![>33 Software Components [3-3] Application Software Is designed to enable users to perform a >33 Software Components [3-3] Application Software Is designed to enable users to perform a](https://present5.com/customparser/199318844_438261830 --- office_2010-_basics_of_computer.ppt/slide_33.jpg) 33 Software Components [3-3] Application Software Is designed to enable users to perform a specific task on their computer The table lists some of the common types of application software Computer Basics / Session 1
33 Software Components [3-3] Application Software Is designed to enable users to perform a specific task on their computer The table lists some of the common types of application software Computer Basics / Session 1
 Computers can be classified based on size and power Computers can be broadly categorized into following three types: Mainframe Computers – are large-sized, very powerful computers that can be shared by hundreds of users Mini Computers - are also used for multi-processing Personal Computers - are also known as microcomputers and are small sized and inexpensive. The two types of commonly used personal computers are : Desktop computer Laptop computer 34 Computer Basics / Session 1 Types of Computers
Computers can be classified based on size and power Computers can be broadly categorized into following three types: Mainframe Computers – are large-sized, very powerful computers that can be shared by hundreds of users Mini Computers - are also used for multi-processing Personal Computers - are also known as microcomputers and are small sized and inexpensive. The two types of commonly used personal computers are : Desktop computer Laptop computer 34 Computer Basics / Session 1 Types of Computers
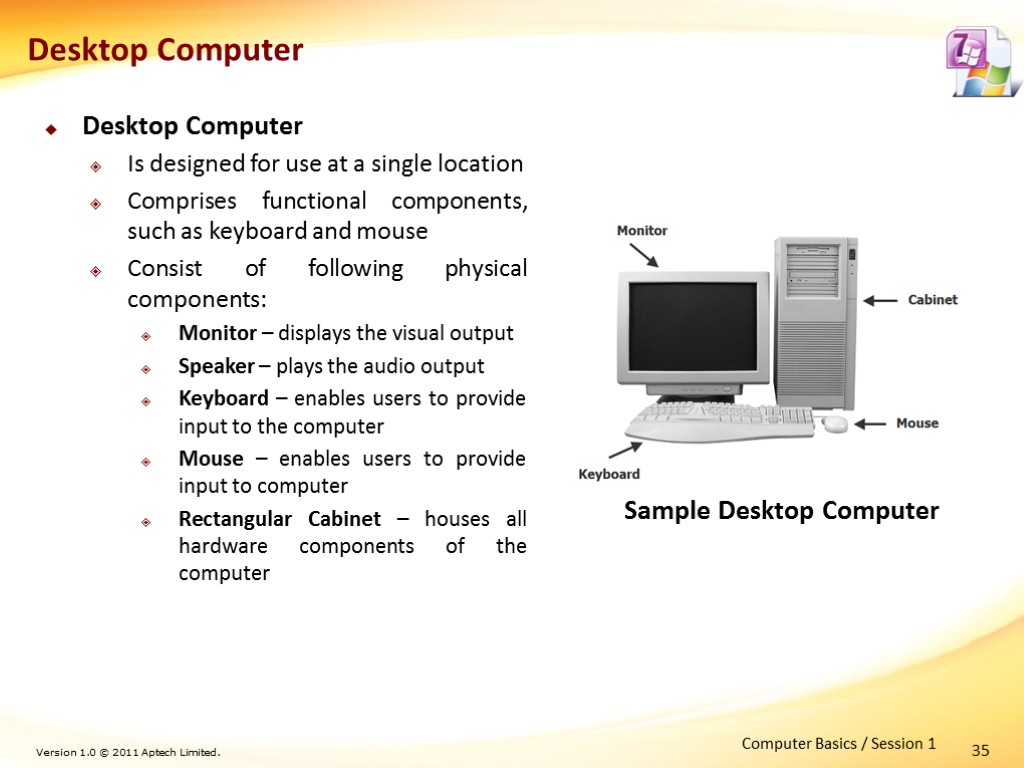
 Desktop Computer Is designed for use at a single location Comprises functional components, such as keyboard and mouse Consist of following physical components: Monitor – displays the visual output Speaker – plays the audio output Keyboard – enables users to provide input to the computer Mouse – enables users to provide input to computer Rectangular Cabinet – houses all hardware components of the computer 35 Computer Basics / Session 1 Sample Desktop Computer Desktop Computer
Desktop Computer Is designed for use at a single location Comprises functional components, such as keyboard and mouse Consist of following physical components: Monitor – displays the visual output Speaker – plays the audio output Keyboard – enables users to provide input to the computer Mouse – enables users to provide input to computer Rectangular Cabinet – houses all hardware components of the computer 35 Computer Basics / Session 1 Sample Desktop Computer Desktop Computer
 Laptop Computer Is a portable computer which integrates a display, keyboard, track pad, and a rechargeable battery Is designed for use on the move Are also known as Notebook Computers or simply Notebooks 36 Computer Basics / Session 1 Sample Laptop Computer Laptop Computer
Laptop Computer Is a portable computer which integrates a display, keyboard, track pad, and a rechargeable battery Is designed for use on the move Are also known as Notebook Computers or simply Notebooks 36 Computer Basics / Session 1 Sample Laptop Computer Laptop Computer
 During the booting process of the computer, the main memory (RAM) is divided into three major sections: Operating System Space – stores the operating system Application Space – stores the different application programs User Data Space – stores all the user related information A computer performs following processing functions in order to generate output depending on the provided input: Accepting the input Processing the input Presenting the output Storing the output 37 Computer Basics / Session 1 How Does a Computer Work [1-2]
During the booting process of the computer, the main memory (RAM) is divided into three major sections: Operating System Space – stores the operating system Application Space – stores the different application programs User Data Space – stores all the user related information A computer performs following processing functions in order to generate output depending on the provided input: Accepting the input Processing the input Presenting the output Storing the output 37 Computer Basics / Session 1 How Does a Computer Work [1-2]
 Consider an example, where a student wants to write some text and get it printed. The text processing application and the OS work in conjunction to execute actions required to complete this task: Accepting the input Processing the input Displaying the output 38 Computer Basics / Session 1 How Does a Computer Work [2-2]
Consider an example, where a student wants to write some text and get it printed. The text processing application and the OS work in conjunction to execute actions required to complete this task: Accepting the input Processing the input Displaying the output 38 Computer Basics / Session 1 How Does a Computer Work [2-2]
 39 User uses the text processing program and types the content that is to be printed The keystrokes from the keyboard are collected by the OS and stored in the memory area of text processing application Simultaneously, the OS also sends instructions to the video card which controls the monitor and displays the typed characters on the screen Computer Basics / Session 1 Accepting Input
39 User uses the text processing program and types the content that is to be printed The keystrokes from the keyboard are collected by the OS and stored in the memory area of text processing application Simultaneously, the OS also sends instructions to the video card which controls the monitor and displays the typed characters on the screen Computer Basics / Session 1 Accepting Input
 40 When the user performs various functions on the text processing application, appropriate commands are sent to the OS The OS sends the instructions for execution on CPU Simultaneously, if some notifications are to be displayed on the screen, appropriate commands are sent to the video card for display Computer Basics / Session 1 Processing the Input
40 When the user performs various functions on the text processing application, appropriate commands are sent to the OS The OS sends the instructions for execution on CPU Simultaneously, if some notifications are to be displayed on the screen, appropriate commands are sent to the video card for display Computer Basics / Session 1 Processing the Input
 41 Users give the print command to the text processing application The text processing application sends this command to the OS The OS collects the data to be printed from the text processing application The OS sends the data to printer’s device driver The device driver sends appropriate commands to the printer The printer prints the data on a sheet of paper Computer Basics / Session 1 Displaying the Output
41 Users give the print command to the text processing application The text processing application sends this command to the OS The OS collects the data to be printed from the text processing application The OS sends the data to printer’s device driver The device driver sends appropriate commands to the printer The printer prints the data on a sheet of paper Computer Basics / Session 1 Displaying the Output
 42 A computer can be used to perform a wide variety of tasks including creating visually stunning/appealing presentations, managing budgets and communicating with people in different parts of the world from the comfort of one’s home. Hardware components of a computer include Motherboard, CPU and various input, output, and storage devices. Application software is a high-level software that allows the user to specify actions to the computer. System software enables the application software to command and control the underlying computer hardware. Application software can be of several types including word processing, spreadsheet, database, and multimedia software. Mainframe computers are powerful computers that are shared between hundreds of users. Mini computers are smaller and less powerful than mainframe computers. Personal computers (also called as micro computers) are small-sized, inexpensive computers designed for a single user. Computer Basics / Session 1 Summary
42 A computer can be used to perform a wide variety of tasks including creating visually stunning/appealing presentations, managing budgets and communicating with people in different parts of the world from the comfort of one’s home. Hardware components of a computer include Motherboard, CPU and various input, output, and storage devices. Application software is a high-level software that allows the user to specify actions to the computer. System software enables the application software to command and control the underlying computer hardware. Application software can be of several types including word processing, spreadsheet, database, and multimedia software. Mainframe computers are powerful computers that are shared between hundreds of users. Mini computers are smaller and less powerful than mainframe computers. Personal computers (also called as micro computers) are small-sized, inexpensive computers designed for a single user. Computer Basics / Session 1 Summary

