Lecture_5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36

1 Structural Geology: Deformation and Mountain Building
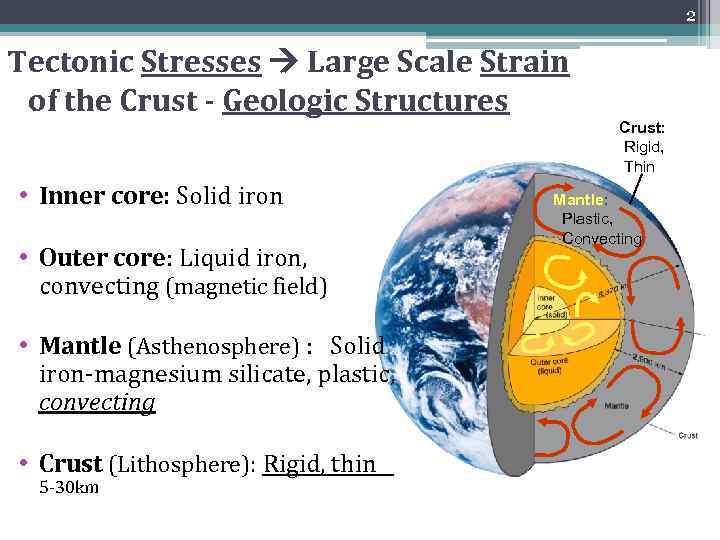
2 Tectonic Stresses Large Scale Strain of the Crust - Geologic Structures Crust: Rigid, Thin • Inner core: Solid iron • Outer core: Liquid iron, convecting (magnetic field) • Mantle (Asthenosphere) : Solid iron-magnesium silicate, plastic, convecting • Crust (Lithosphere): Rigid, thin 5 -30 km Mantle: Plastic, Convecting

3 Tectonics and Structural Geology Tectonic Stresses resulting from Internal Energy (heat driving convection) Strains (deforms) the Mantle and Crust Bends Rocks ductile strain (Folds) • Breaks Rock • brittle strain (Joints) • Moves large blocks • Faults Releases energy Earthquakes
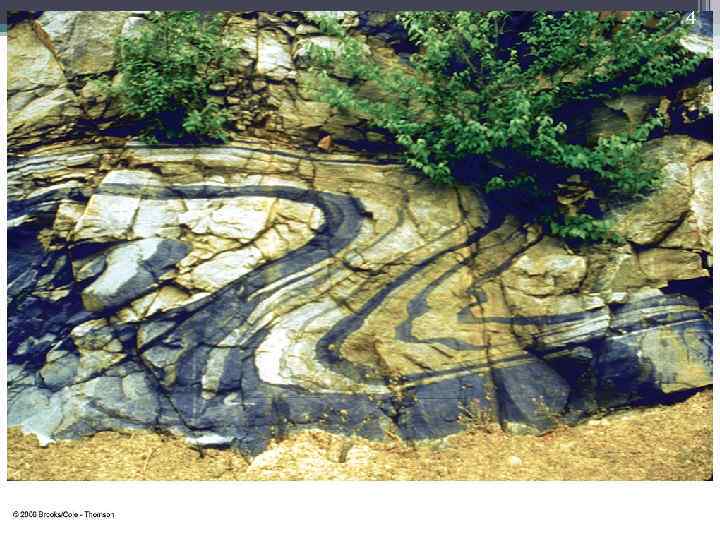

4

5 Folds and Faults (Palmdale, Ca)

6 Kaynasli, Turkey
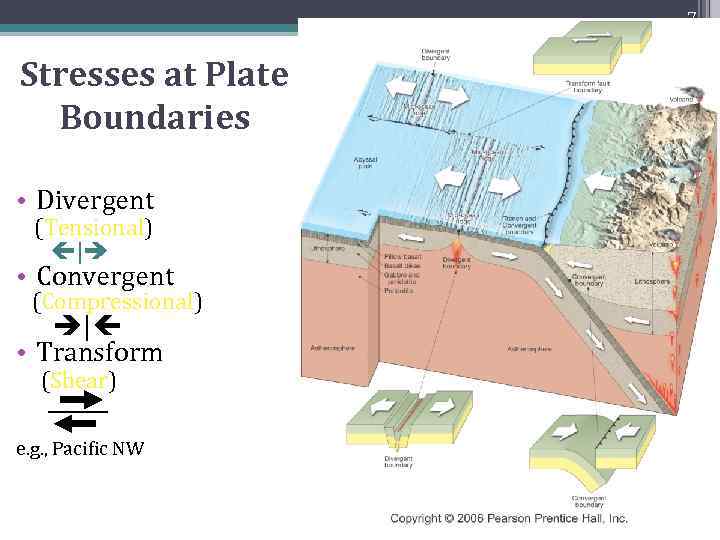
7 Stresses at Plate Boundaries • Divergent (Tensional) | • Convergent (Compressional) | • Transform (Shear) e. g. , Pacific NW
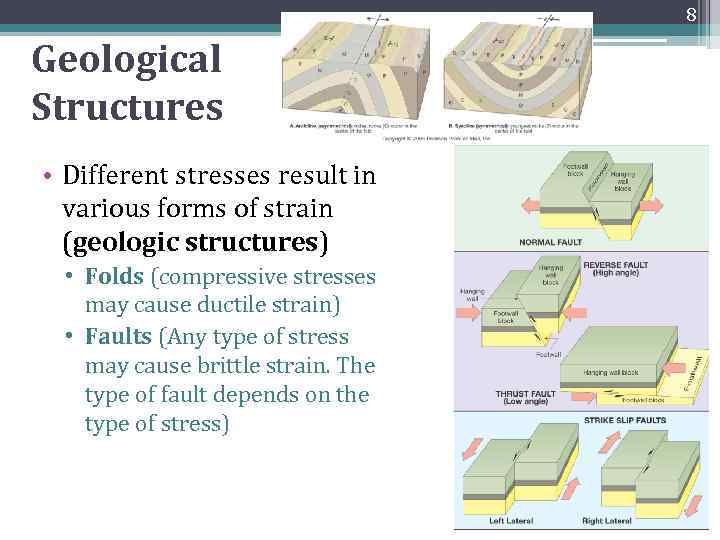
8 Geological Structures • Different stresses result in various forms of strain (geologic structures) • Folds (compressive stresses may cause ductile strain) • Faults (Any type of stress may cause brittle strain. The type of fault depends on the type of stress)

9 Geological Structures • Fault: a discontinuity surface across which there has been shear displacement • Hangingwall: the wall and body of rock above an inclined fault • Footwall: the wall and body of rock beneath an inclined fault
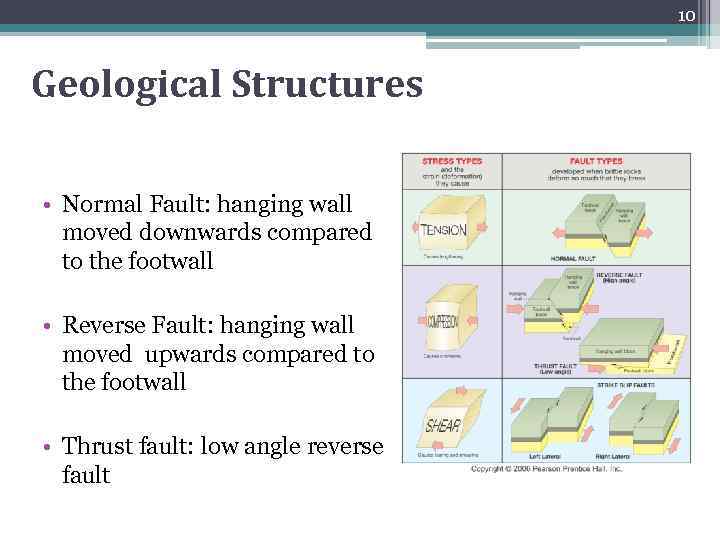
10 Geological Structures • Normal Fault: hanging wall moved downwards compared to the footwall • Reverse Fault: hanging wall moved upwards compared to the footwall • Thrust fault: low angle reverse fault
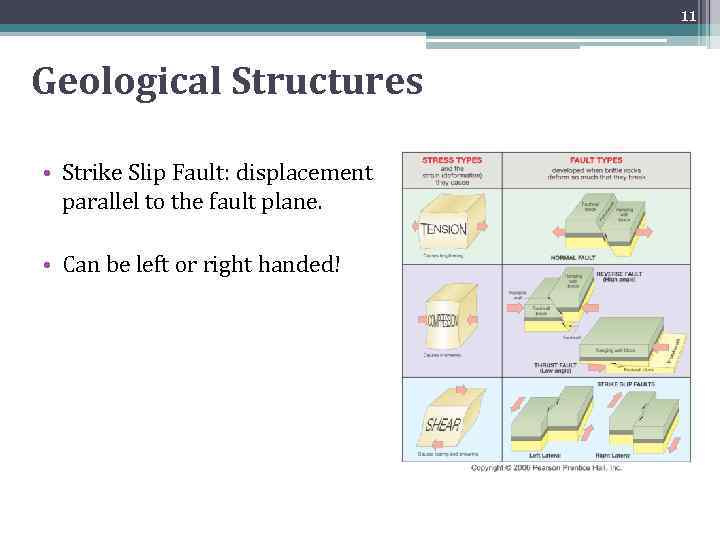
11 Geological Structures • Strike Slip Fault: displacement parallel to the fault plane. • Can be left or right handed!
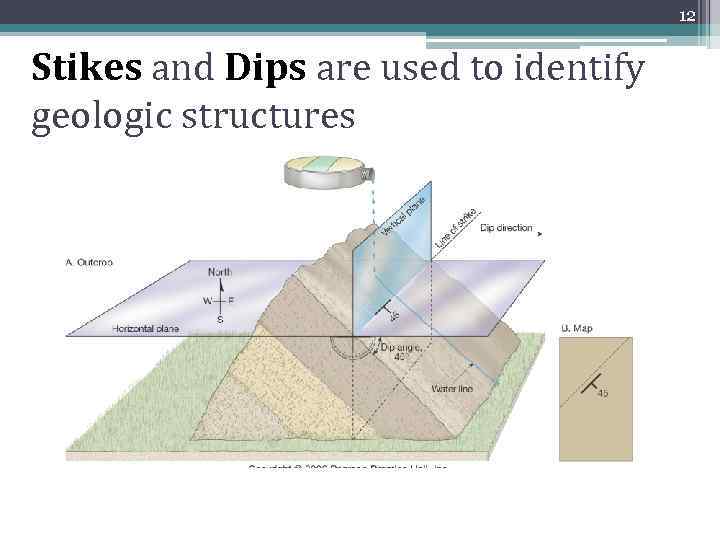
12 Stikes and Dips are used to identify geologic structures
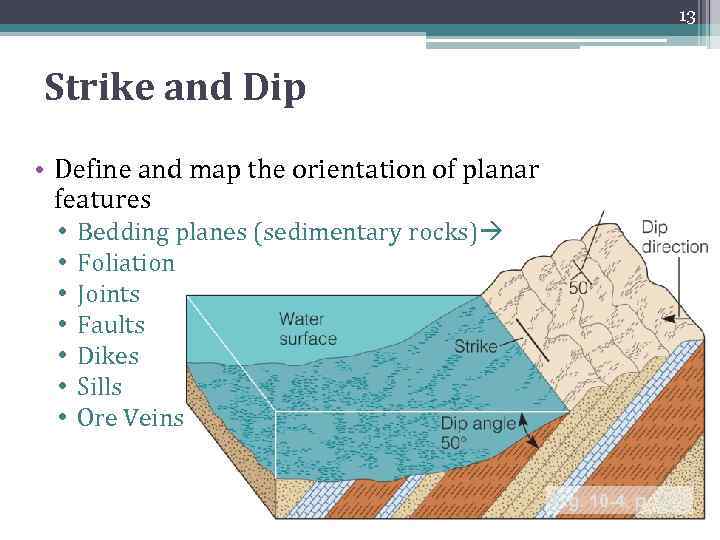
13 Strike and Dip • Define and map the orientation of planar features • • Bedding planes (sedimentary rocks) Foliation Joints Faults Dikes Sills Ore Veins Fig. 10 -4, p. 221
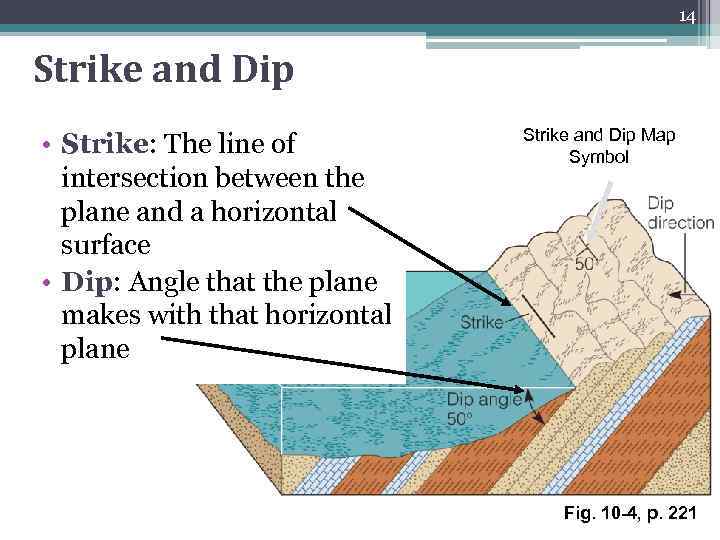
14 Strike and Dip • Strike: The line of intersection between the plane and a horizontal surface • Dip: Angle that the plane makes with that horizontal plane Strike and Dip Map Symbol Fig. 10 -4, p. 221
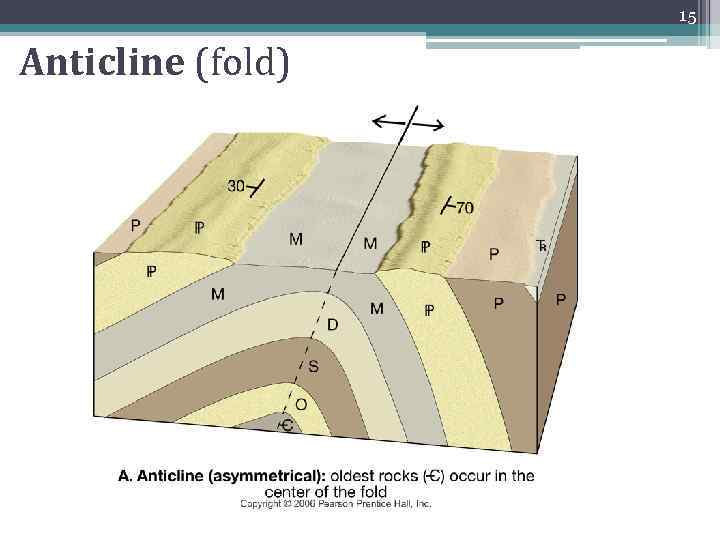
15 Anticline (fold)
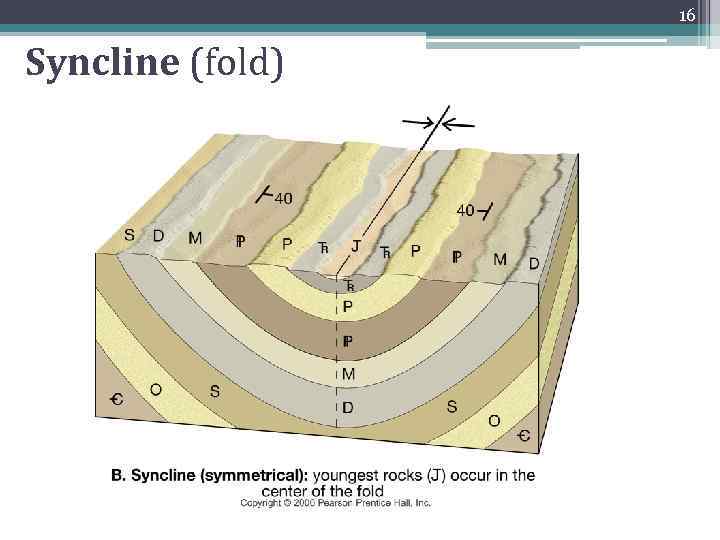
16 Syncline (fold)
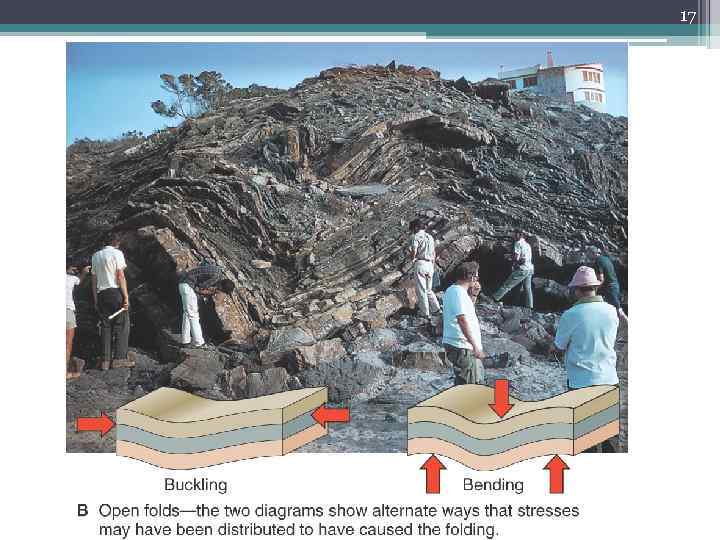

17
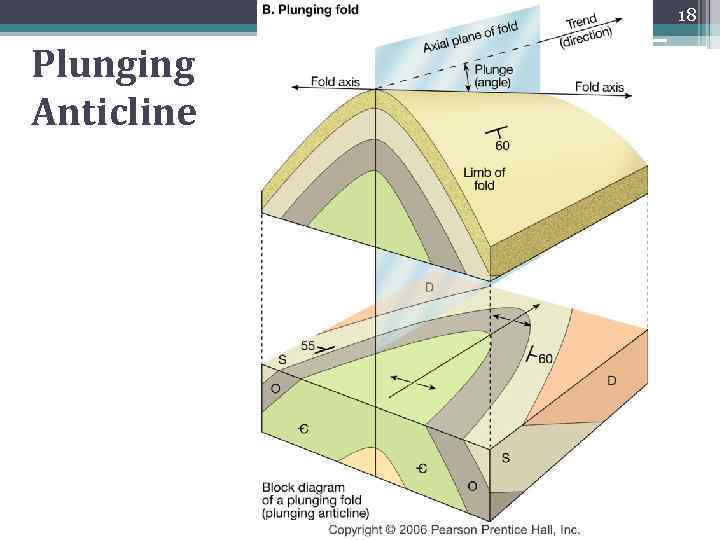
18 Plunging Anticline
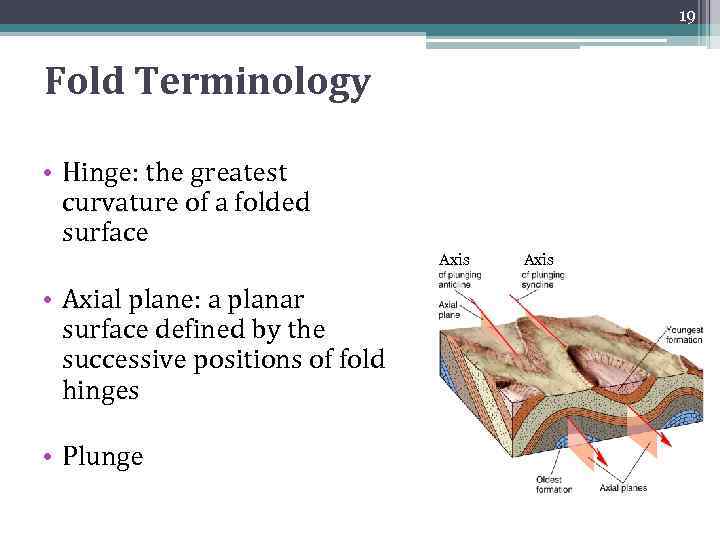
19 Fold Terminology • Hinge: the greatest curvature of a folded surface Axis • Axial plane: a planar surface defined by the successive positions of fold hinges • Plunge Axis

20 Plunging Anticline, Colorado

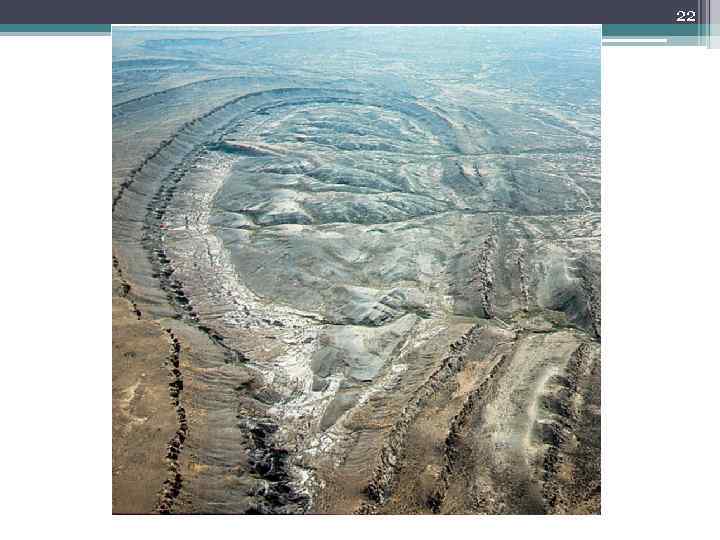
21 Domes and Basins

22
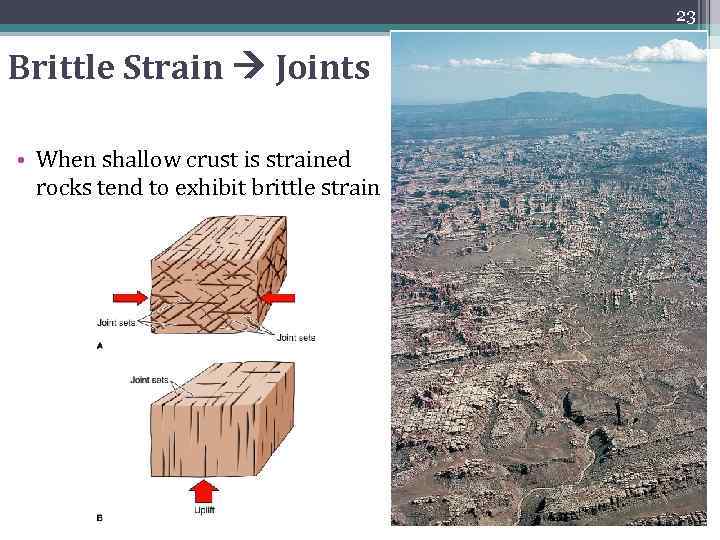
23 Brittle Strain Joints • When shallow crust is strained rocks tend to exhibit brittle strain

24 Sheet Joints
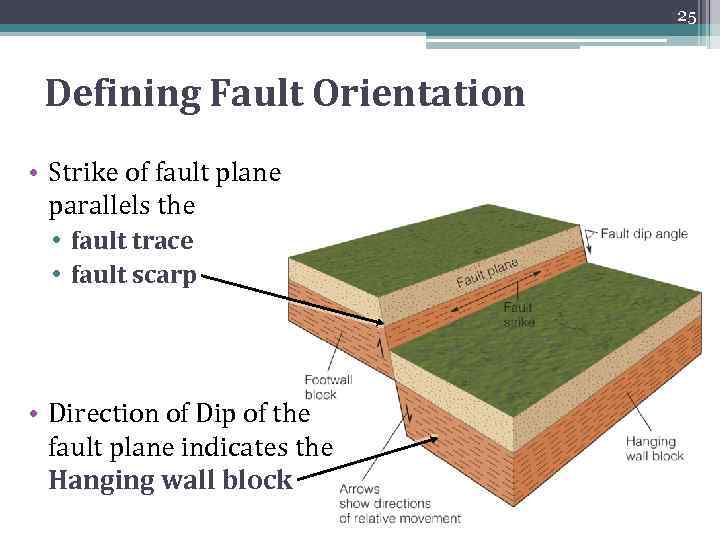
25 Defining Fault Orientation • Strike of fault plane parallels the • fault trace • fault scarp • Direction of Dip of the fault plane indicates the Hanging wall block
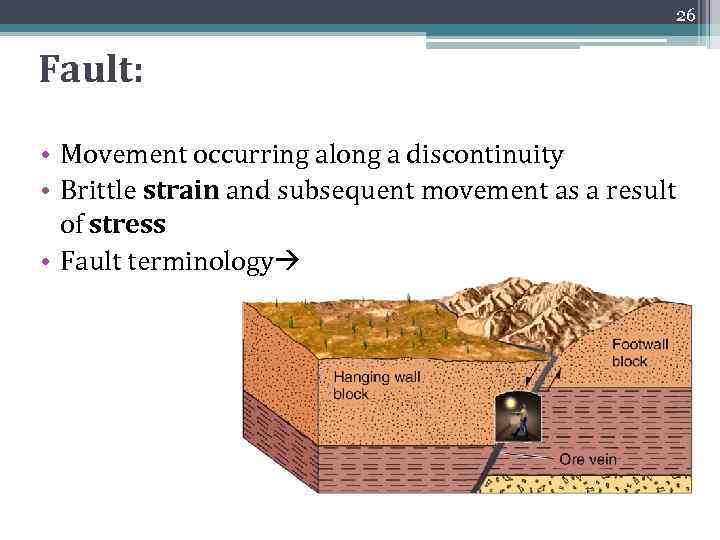
26 Fault: • Movement occurring along a discontinuity • Brittle strain and subsequent movement as a result of stress • Fault terminology
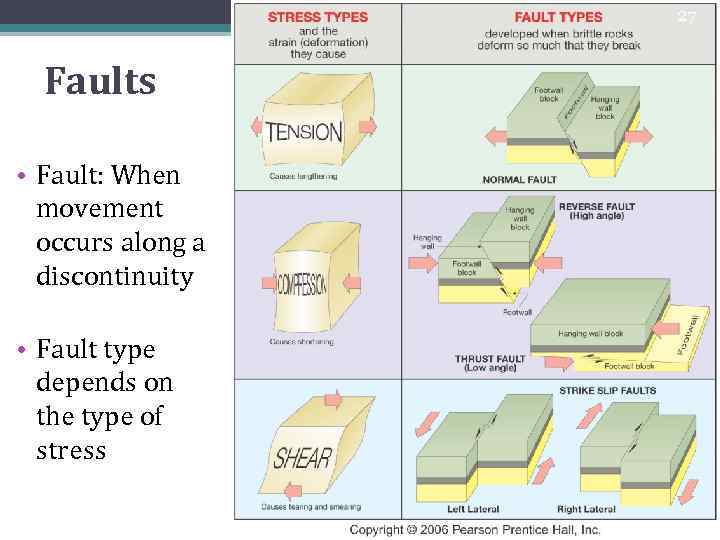
27 Faults • Fault: When movement occurs along a discontinuity • Fault type depends on the type of stress

28 Normal Faults
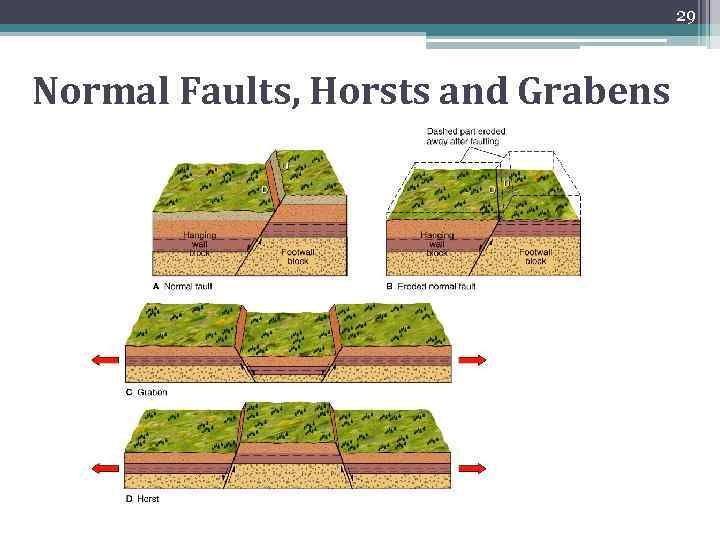
29 Normal Faults, Horsts and Grabens
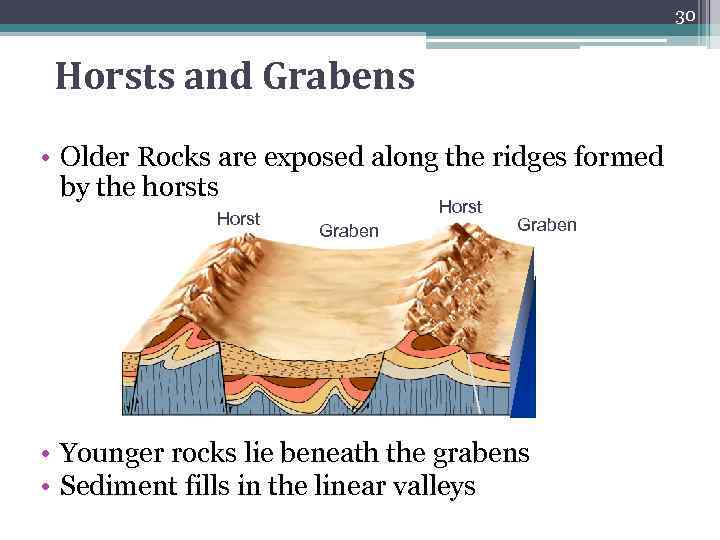
30 Horsts and Grabens • Older Rocks are exposed along the ridges formed by the horsts Horst Graben • Younger rocks lie beneath the grabens • Sediment fills in the linear valleys
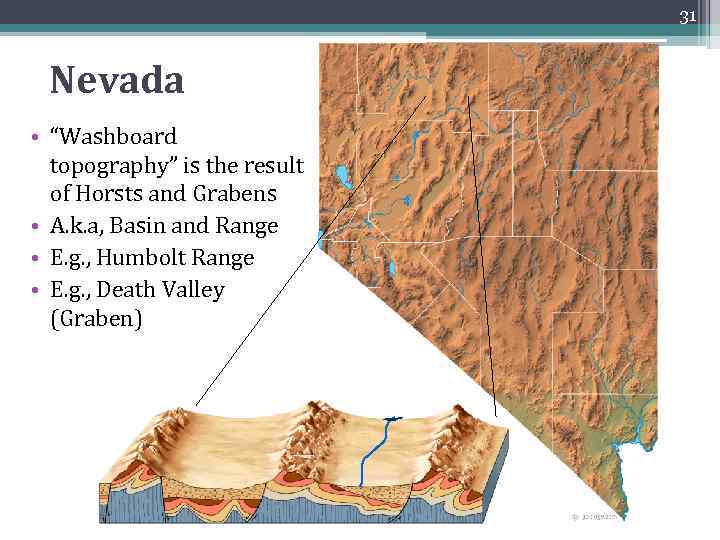
31 Nevada • “Washboard topography” is the result of Horsts and Grabens • A. k. a, Basin and Range • E. g. , Humbolt Range • E. g. , Death Valley (Graben)

32 Horst and Graben, Nevada Horst Graben Humboldt Range, Northern Nevada

33 Horst and Graben, Nevada Horst Graben Humboldt Range, Northern Nevada
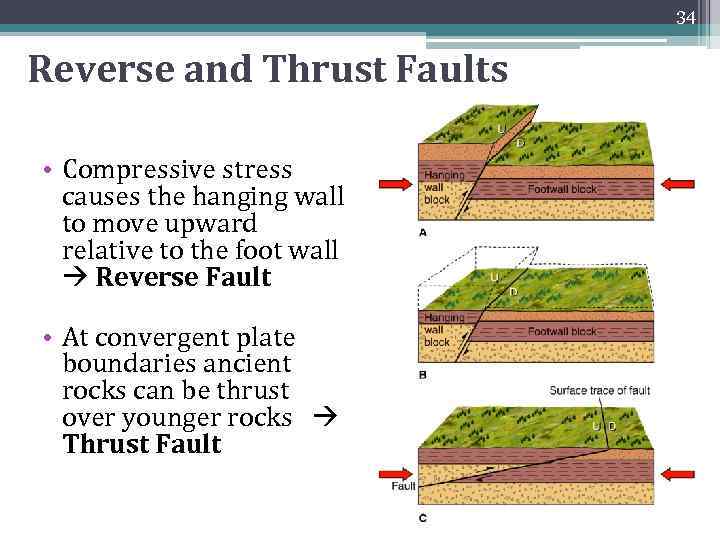
34 Reverse and Thrust Faults • Compressive stress causes the hanging wall to move upward relative to the foot wall Reverse Fault • At convergent plate boundaries ancient rocks can be thrust over younger rocks Thrust Fault

35 Thrust Fault: Glacier NP, Montana Old Younger
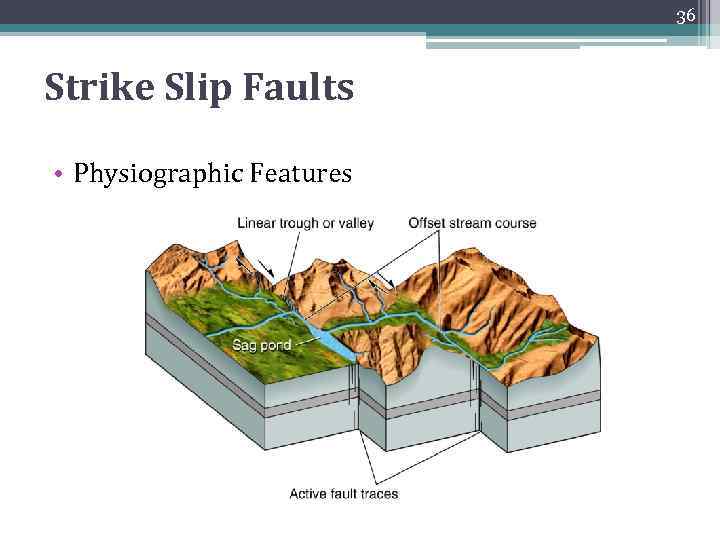
36 Strike Slip Faults • Physiographic Features
Lecture_5.ppt