1 Computer Security Concepts The CIA Triad DAD



















41176-lecture2_foundations.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 1 Computer Security Concepts
1 Computer Security Concepts
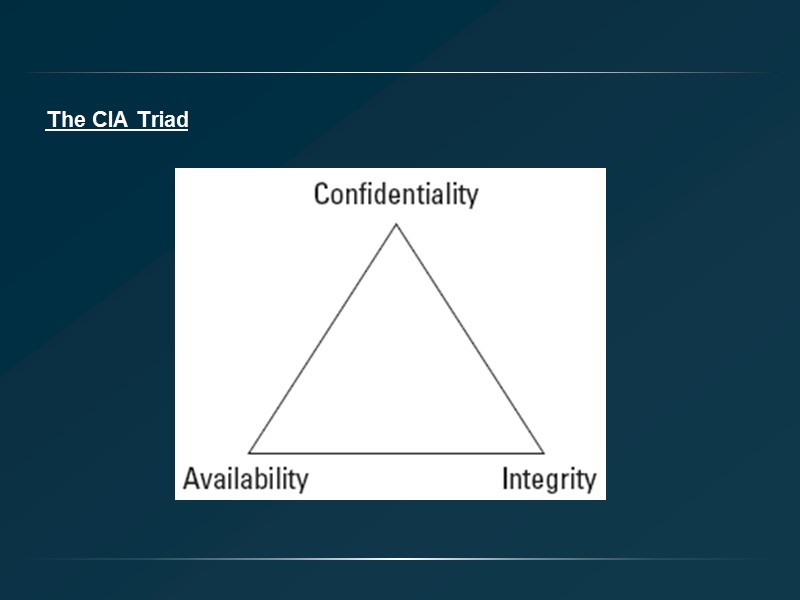
 The CIA Triad
The CIA Triad
 DAD triad Disclosure: Attempts to defeat confidentiality Alteration: Attempts to defeat integrity Destruction: Attempts to defeat availability
DAD triad Disclosure: Attempts to defeat confidentiality Alteration: Attempts to defeat integrity Destruction: Attempts to defeat availability
 Security threats to your computer can be classified in three groups: Hackers, who try to break into your computer without your knowledge or permission. Malware (malicious software), which comes in many forms: viruses, worms, Trojan horses, scripts, rootkits, adware, and spyware. User error, which includes ignorance, laziness, and gullibility.
Security threats to your computer can be classified in three groups: Hackers, who try to break into your computer without your knowledge or permission. Malware (malicious software), which comes in many forms: viruses, worms, Trojan horses, scripts, rootkits, adware, and spyware. User error, which includes ignorance, laziness, and gullibility.
 Identification, Authentication, and Authorization Allow users to identify themselves to the protected resource Provide a means for the resource to objectively confirm the identity of the user Provide the administrator of the resource with mechanisms to specify which users might access the resource and the actions those users might perform
Identification, Authentication, and Authorization Allow users to identify themselves to the protected resource Provide a means for the resource to objectively confirm the identity of the user Provide the administrator of the resource with mechanisms to specify which users might access the resource and the actions those users might perform
 Other popular multifactor authentication techniques include these combinations: A password and a biometric measurement (something the user knows and something the user is) A physical key and a password another example of something the user has and something the user knows) An access card and a biometric measurement (something the user has and something the user is)
Other popular multifactor authentication techniques include these combinations: A password and a biometric measurement (something the user knows and something the user is) A physical key and a password another example of something the user has and something the user knows) An access card and a biometric measurement (something the user has and something the user is)
 Passwords Use passwords whenever possible. Never use a blank password. Change all default passwords immediately. Use strong passwords (passphrases).
Passwords Use passwords whenever possible. Never use a blank password. Change all default passwords immediately. Use strong passwords (passphrases).
 Passwords Create strong passwords by following these guidelines: at least 8 digits long no repeating digits combination of numbers and letters mix of upper- and lower-case letters special characters (!, @, #, &, %, etc.) within the password, not just at the beginning or end Don’t use dictionary words (including foreign or archaic languages), your account name, proper names, zip codes, or room numbers. Don’t use “password” as your password. Frjyopwec, F5y_
Passwords Create strong passwords by following these guidelines: at least 8 digits long no repeating digits combination of numbers and letters mix of upper- and lower-case letters special characters (!, @, #, &, %, etc.) within the password, not just at the beginning or end Don’t use dictionary words (including foreign or archaic languages), your account name, proper names, zip codes, or room numbers. Don’t use “password” as your password. Frjyopwec, F5y_
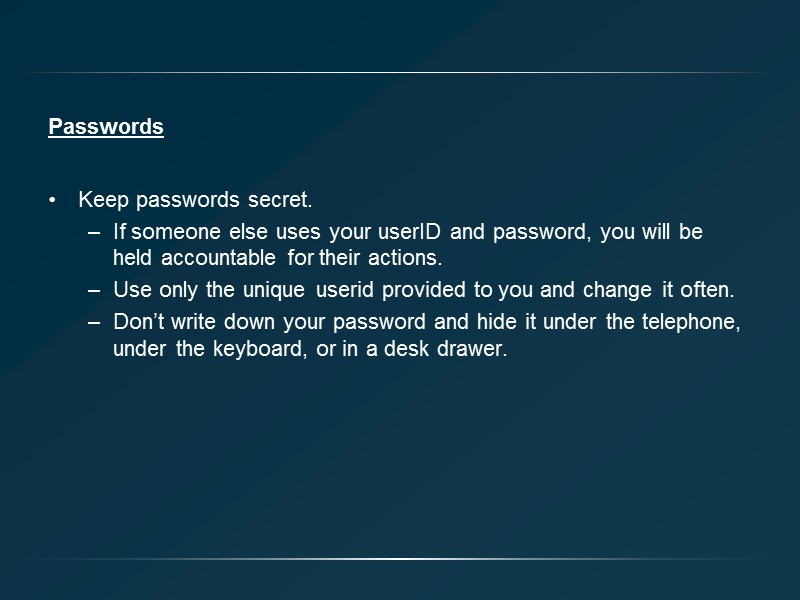
 Passwords Keep passwords secret. If someone else uses your userID and password, you will be held accountable for their actions. Use only the unique userid provided to you and change it often. Don’t write down your password and hide it under the telephone, under the keyboard, or in a desk drawer.
Passwords Keep passwords secret. If someone else uses your userID and password, you will be held accountable for their actions. Use only the unique userid provided to you and change it often. Don’t write down your password and hide it under the telephone, under the keyboard, or in a desk drawer.
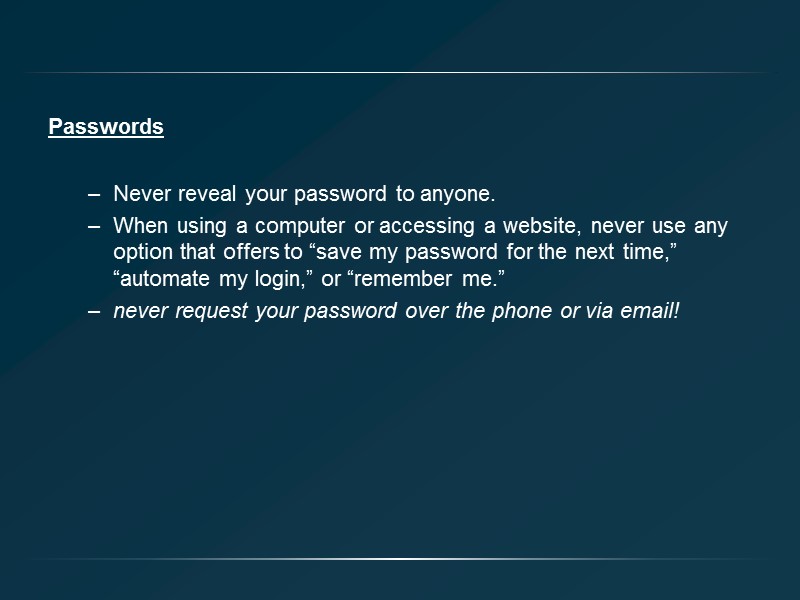
 Passwords Never reveal your password to anyone. When using a computer or accessing a website, never use any option that offers to “save my password for the next time,” “automate my login,” or “remember me.” never request your password over the phone or via email!
Passwords Never reveal your password to anyone. When using a computer or accessing a website, never use any option that offers to “save my password for the next time,” “automate my login,” or “remember me.” never request your password over the phone or via email!
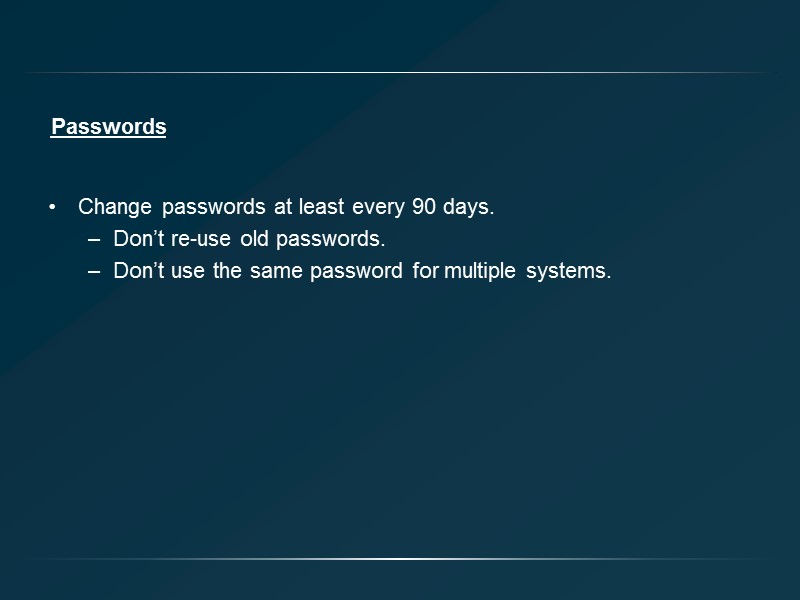
 Passwords Change passwords at least every 90 days. Don’t re-use old passwords. Don’t use the same password for multiple systems.
Passwords Change passwords at least every 90 days. Don’t re-use old passwords. Don’t use the same password for multiple systems.
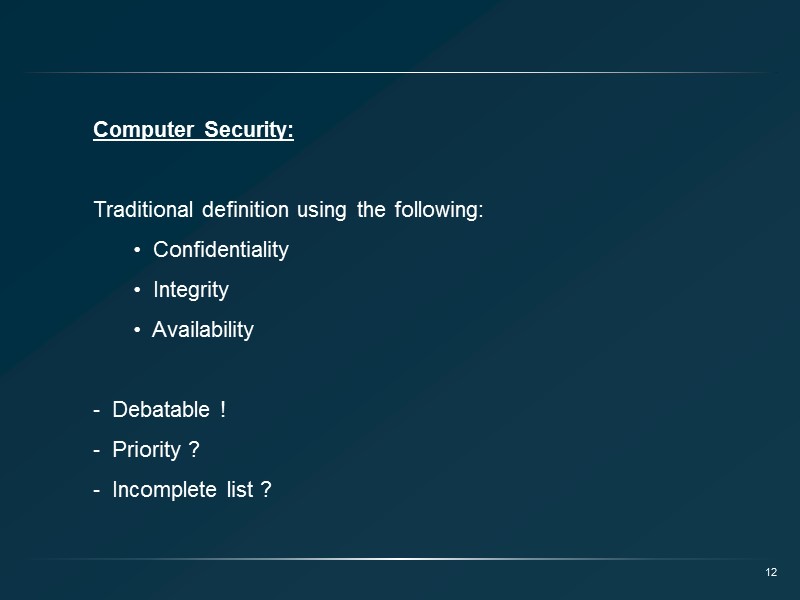
 Computer Security: Traditional definition using the following: Confidentiality Integrity Availability Debatable ! Priority ? Incomplete list ? 12
Computer Security: Traditional definition using the following: Confidentiality Integrity Availability Debatable ! Priority ? Incomplete list ? 12
 Confidentiality (Privacy, Secrecy): The prevention of unauthorised users reading sensitive information Privacy – protection of personal data Secrecy – protection of data of an organization Hide document’s content ? Hide document’s existence ? (Unlinkability and Anonymity) 13
Confidentiality (Privacy, Secrecy): The prevention of unauthorised users reading sensitive information Privacy – protection of personal data Secrecy – protection of data of an organization Hide document’s content ? Hide document’s existence ? (Unlinkability and Anonymity) 13
 Confidentiality Access control mechanisms: Prevent unauthorized individuals from accessing the system. File system security controls: Prevent individuals authorized to use a system from exceeding their authority and reading confidential information they shouldn’t be able to access. Cryptography: Can be used to encrypt the contents of sensitive files and protect them from prying eyes, even when access control and file system security mechanisms fail.
Confidentiality Access control mechanisms: Prevent unauthorized individuals from accessing the system. File system security controls: Prevent individuals authorized to use a system from exceeding their authority and reading confidential information they shouldn’t be able to access. Cryptography: Can be used to encrypt the contents of sensitive files and protect them from prying eyes, even when access control and file system security mechanisms fail.
 Integrity Informally -Making sure everything is as it is supposed to be. Formally -Integrity deals with the prevention of unauthorised writing. Data Integrity “The state that exists when computerised data is the same as that in the source documents and has not been exposed to accidental or malicious alteration or destruction.” 15
Integrity Informally -Making sure everything is as it is supposed to be. Formally -Integrity deals with the prevention of unauthorised writing. Data Integrity “The state that exists when computerised data is the same as that in the source documents and has not been exposed to accidental or malicious alteration or destruction.” 15
 Availability “The property of being accessible and useable upon demand by an authorised entity.” We want to prevent denial of service Denial of service “The prevention of authorised access to resources or the delaying of time-critical operations.” 16
Availability “The property of being accessible and useable upon demand by an authorised entity.” We want to prevent denial of service Denial of service “The prevention of authorised access to resources or the delaying of time-critical operations.” 16
 Accountability Users should be held responsible for their actions Thus system has to identify and authenticate users Audit trail has to be kept “Audit information must be selectively kept and protected so that actions affecting security can be traced to the responsible party” 17
Accountability Users should be held responsible for their actions Thus system has to identify and authenticate users Audit trail has to be kept “Audit information must be selectively kept and protected so that actions affecting security can be traced to the responsible party” 17
 18 Reliability Reliability - (accidental) failures Safety - impact of system failures on their environment Security is an aspect of reliability and vice versa! Dependability “The property of a computer system such that reliance can justifiably be placed in the service it delivers”
18 Reliability Reliability - (accidental) failures Safety - impact of system failures on their environment Security is an aspect of reliability and vice versa! Dependability “The property of a computer system such that reliance can justifiably be placed in the service it delivers”
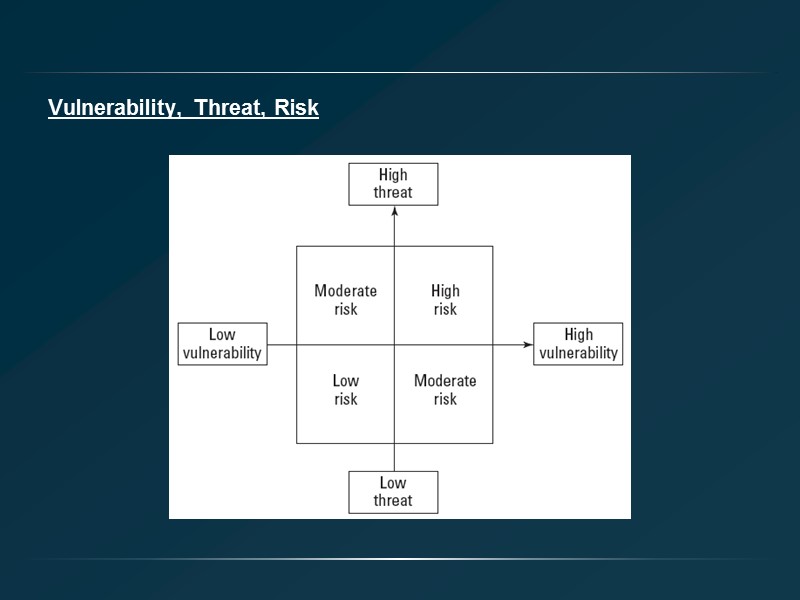
 Vulnerability, Threat, Risk
Vulnerability, Threat, Risk
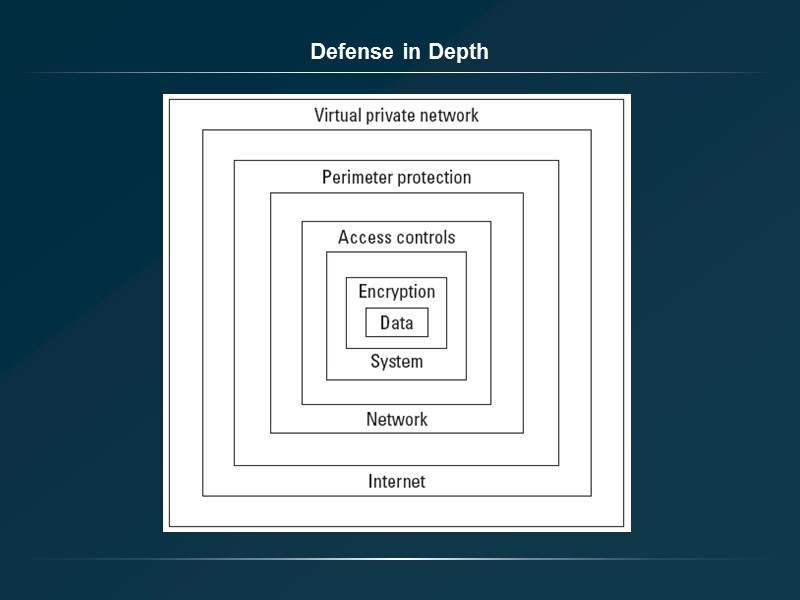
 Security Principles Defense in depth Least privilege Separation of privileges Security through obscurity (the inadvisability thereof)
Security Principles Defense in depth Least privilege Separation of privileges Security through obscurity (the inadvisability thereof)
 Defense in Depth
Defense in Depth
 Least Privilege
Least Privilege
 Separation of Privileges
Separation of Privileges
 Security through Obscurity
Security through Obscurity
 Security: Security is about the protection of assets Knowledge of assets and their value is vital Protection measures: Prevention – sometimes the only feasible measure Detection Reaction 25
Security: Security is about the protection of assets Knowledge of assets and their value is vital Protection measures: Prevention – sometimes the only feasible measure Detection Reaction 25
 26 Data vs. Information Security is about controlling access to information and resources This can be difficult, thus controlling access to data is more viable Data – represents information Information – (subjective) interpretation of data - Problem of inference
26 Data vs. Information Security is about controlling access to information and resources This can be difficult, thus controlling access to data is more viable Data – represents information Information – (subjective) interpretation of data - Problem of inference
 End 27
End 27

